两个案例带你搞定JBoss Marshalling编解码在Netty中的应用
JBoss Marshalling 是一个 Java 对象序列化包,对 JDK 默认的序列化框架进行了优化,但又保持与 Serializable 接口的兼容,同时增加了一些可调用的参数和附加的属性,这些参数可通过工厂类进行配置。
本章主要内容包括:
- Marshalling环境配置
- 基于Netty和Marshalling的图书订购案例
- 基于Netty和Marshalling的自定义消息案例
两个案例带你搞定JBoss Marshalling编解码在Netty中的应用
- 1. Marshalling环境配置
- 2. 基于Netty和Marshalling的图书订购案例
- 2.1 图书订购消息定义
- 2.2. 服务端开发
- 2.3. 客户端开发
- 2.4. 运行结果
- 3. 基于Netty和Marshalling的自定义消息案例
- 3.1 消息定义
- 3.2. 消息编解码器
- 3.2.1. 编码器
- 3.2.2. 解码器
- 3.3. 服务端代码
- 3.4. 客户端代码
- 3.5. 运行结果
1. Marshalling环境配置
本节主要介绍Marshalling开发环境的配置,本文所用工具版本如下:
- JDK 1.8
- Netty 4.0
- IDEA 2020.1
- Marshalling 2.0.9
关于JDK的安装在这里就不再介绍,自行百度即可,关于Netty的安装,大家可以移步博客阅读。
在本次实践中,我们使用的是基于maven的项目,因此我们只需要在pom.xml文件中添加相应的依赖即可,在这里我们给出Marshalling的依赖。
<!-- jboss-marshalling编解码和序列号架包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jboss.marshalling</groupId>
<artifactId>jboss-marshalling</artifactId>
<version>2.0.9.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jboss.marshalling</groupId>
<artifactId>jboss-marshalling-serial</artifactId>
<version>2.0.9.Final</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2. 基于Netty和Marshalling的图书订购案例
本节我们用一个图书订购的案例来介绍一下Marshalling编解码在Netty中的应用,我们首先给出需要编解码消息的定义,然后分服务端和客户端分别介绍实现代码。
2.1 图书订购消息定义
首先给出客户端发出的订购消息,消息定义如下所示:
| 字段名称 | 字段类型 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| subReqID | 整型 | 订购编号 |
| userName | 字符串 | 用户名 |
| productName | 字符串 | 订购的产品名称 |
| productNumber | 字符串 | 订购者电话号码 |
| address | 字符串 | 订购者的家庭住址 |
服务端接收到客户端的订购消息之后,对订单进行验证,如果符合条件则返回订购成功的消息给客户端,具体消息定义如下:
| 字段名称 | 字段类型 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| subReqID | 整型 | 订购编号 |
| respCode | 整型 | 订购结果:0表示成功 |
| desc | 字符串 | 可选的详细描述信息 |
下面给出两个消息的具体代码:
package netty.codec.pojo;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* created by LMR on 2020/5/20
*/
public class SubscribeReq implements Serializable {
/**
* 默认的序列号ID
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private int subReqID;
private String userName;
private String productName;
private String phoneNumber;
private String address;
public final int getSubReqID() {
return subReqID;
}
public final void setSubReqID(int subReqID) {
this.subReqID = subReqID;
}
/**中间的get和set方法省略
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SubscribeReq [subReqID=" + subReqID + ", userName=" + userName
+ ", productName=" + productName + ", phoneNumber="
+ phoneNumber + ", address=" + address + "]";
}
}
package netty.codec.pojo;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class SubscribeResp implements Serializable {
/**
* 默认序列ID
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private int subReqID;
private int respCode;
private String desc;
public final int getSubReqID() {
return subReqID;
}
public final void setSubReqID(int subReqID) {
this.subReqID = subReqID;
}
/**
* 中间的get和set方法省略*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SubscribeResp [subReqID=" + subReqID + ", respCode=" + respCode
+ ", desc=" + desc + "]";
}
}
2.2. 服务端开发
package netty.codec.marshalling;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
/**
* created by LMR on 2020/5/20
*/
public class SubReqServer {
public void bind(int port) throws Exception {
// 配置服务端的NIO线程组
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 100)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
//添加Marshalling解码器
ch.pipeline().addLast(
MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingDecoder());
//添加Marshalling编码器
ch.pipeline().addLast(
MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new SubReqServerHandler());
}
});
// 绑定端口,同步等待成功
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();
// 等待服务端监听端口关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
// 优雅退出,释放线程池资源
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int port = 8080;
new SubReqServer().bind(port);
}
}
在initChannel方法中,在ChannelPipeline中添加Marshalling编解码器,Marshalling编解码器是通过自定义的MarshallingCodeCFactory工厂类来创建。下面来看看MarshallingCodeCFactory工具类是如何实现的。
package netty.codec.marshalling;
import io.netty.handler.codec.marshalling.DefaultMarshallerProvider;
import io.netty.handler.codec.marshalling.DefaultUnmarshallerProvider;
import io.netty.handler.codec.marshalling.MarshallerProvider;
import io.netty.handler.codec.marshalling.MarshallingDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.marshalling.MarshallingEncoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.marshalling.UnmarshallerProvider;
import org.jboss.marshalling.MarshallerFactory;
import org.jboss.marshalling.Marshalling;
import org.jboss.marshalling.MarshallingConfiguration;
/**
* created by LMR on 2020/5/20
*/
public final class MarshallingCodeCFactory {
//创建Jboss Marshalling解码器MarshallingDecoder
public static MarshallingDecoder buildMarshallingDecoder() {
final MarshallerFactory marshallerFactory = Marshalling.getProvidedMarshallerFactory("serial");
final MarshallingConfiguration configuration = new MarshallingConfiguration();
configuration.setVersion(5);
UnmarshallerProvider provider = new DefaultUnmarshallerProvider(marshallerFactory, configuration);
MarshallingDecoder decoder = new MarshallingDecoder(provider, 1024);
return decoder;
}
//创建Jboss Marshalling编码器MarshallingEncoder
public static MarshallingEncoder buildMarshallingEncoder() {
final MarshallerFactory marshallerFactory = Marshalling.getProvidedMarshallerFactory("serial");
final MarshallingConfiguration configuration = new MarshallingConfiguration();
configuration.setVersion(5);
MarshallerProvider provider = new DefaultMarshallerProvider(marshallerFactory, configuration);
MarshallingEncoder encoder = new MarshallingEncoder(provider);
return encoder;
}
}
MarshallingCodeCFactory 工程类中首先通过Marshalling工具类的getProvidedMarshallerFactory静态方法获取MarshallerFactory 实例,参数为“serial”表示创建的是Java序列化工厂对象。然后创建MarshallingConfiguration 对象。然后针对解码和编码分别创建DefaultMarshallerProvider和DefaultUnmarshallerProvider对象,最后利用该对象分别创建MarshallingEncoder 和MarshallingDecoder 用于编码和解码。
服务端在接收到订购消息之后会进行一系列的处理,下面我们来介绍服务端的处理类SubReqServerHandler。
package netty.codec.marshalling;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import netty.codec.pojo.SubscribeReq;
import netty.codec.pojo.SubscribeResp;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
/**
* created by LMR on 2020/5/20
*/
public class SubReqServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
SubscribeReq req = (SubscribeReq) msg;
if ("LMRZero".equalsIgnoreCase(req.getUserName())) {
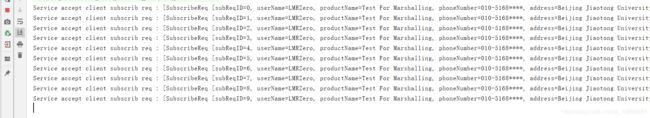
System.out.println("Service accept client subscrib req : [" + req.toString() + "]");
ctx.writeAndFlush(resp(req.getSubReqID()));
}
}
//根据订单ID创建订购成功的返回消息
private SubscribeResp resp(int subReqID) {
SubscribeResp resp = new SubscribeResp();
resp.setSubReqID(subReqID);
resp.setRespCode(0);
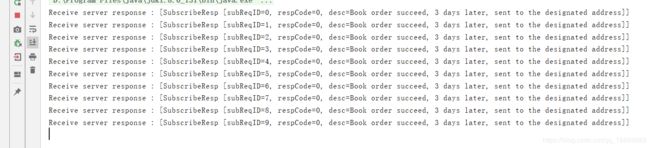
resp.setDesc("Book order succeed, 3 days later, sent to the designated address");
return resp;
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();// 发生异常,关闭链路
}
}
SubReqServerHandler 的逻辑十分简单,服务端在接收到订购消息之后,会判断用户名是否是“LMRZero”,如果是,则首先输出接收消息。然后构建订购成功的消息返回给客户端。
2.3. 客户端开发
package netty.codec.marshalling;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
/**
* created by LMR on 2020/5/20
*/
public class SubReqClient {
public void connect(int port, String host) throws Exception {
// 配置客户端NIO线程组
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch)
throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(
MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(
MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new SubReqClientHandler());
}
});
// 发起异步连接操作
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host, port).sync();
// 当代客户端链路关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
// 优雅退出,释放NIO线程组
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int port = 8080;
new SubReqClient().connect(port, "127.0.0.1");
}
}
客户端启动类的代码与服务端基本一致,在这里就不进行介绍,下面看看客户端处理类的实现代码。
package netty.codec.marshalling;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import netty.codec.pojo.SubscribeReq;
/**
* created by LMR on 2020/5/20
*/
public class SubReqClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
/**
* Creates a client-side handler.
*/
public SubReqClientHandler() {
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
ctx.write(subReq(i));
}
ctx.flush();
}
private SubscribeReq subReq(int i) {
SubscribeReq req = new SubscribeReq();
req.setAddress("Beijing Jiaotong University, BeiJing ");
req.setPhoneNumber("010-5168****");
req.setProductName("Test For Marshalling");
req.setSubReqID(i);
req.setUserName("LMRZero");
return req;
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("Receive server response : [" + msg + "]");
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.flush();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
在SubReqClientHandler 类中,为了测试TCP粘包/拆包是否能够被正确处理,本例中连续发送10条订购消息策略。由于我们在ChannelPipeline中添加了编解码器,在这里我们不需要在进行任何设置,Netty会帮我们将订购消息进行编码,将返回的消息进行解码。
2.4. 运行结果
3. 基于Netty和Marshalling的自定义消息案例
3.1 消息定义
相较于第一个案例,本节中的案例更为复杂。在本节中,我们将模拟私有协议传递的消息。
设计的Netty协议消息主要包含两个部分:
- 消息头;
- 消息体;
Netty消息的具体定义如下:
| 变量名称 | 变量类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| header | Header | 消息头定义(自定义) |
| body | Object | 对于请求消息,它是方法的参数;对于响应消息,它是返回值 |
Netty消息头Header定义如下:
| 变量名称 | 变量类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| crcCode | 整型int | 校验码,本例中是固定值 |
| length | 整型int | 整条消息的长度,包括消息头和消息体 |
| type | Byte | 0:业务请求消息;1:业务响应消息;2:业务one way消息(既是请求又是响应);3:握手请求消息;4:握手应答消息;5:心跳请求消息;6:心跳应答消息 |
| attachment | Map |
可选字段,用于扩展 |
消息定义代码如下所示:
package netty.protocol.struct;
/**
* created by LMR on 2020/5/20
*/
public final class NettyMessage {
//消息头
private Header header;
//消息内容
private Object body;
//省略get和set方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return "NettyMessage [header=" + header + "]";
}
}
Header 定义代码如下所示:
package netty.protocol.struct;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* created by LMR on 2020/5/20
*/
public final class Header {
//校验码
private int crcCode = 0xabef0101;
// 消息长度
private int length;
// 消息类型
private byte type;
//附件
private Map<String, Object> attachment = new HashMap<String, Object>();
//省略get和set方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Header [crcCode=" + crcCode + ", length=" + length
+ ", type=" + type + ", attachment=" + attachment + "]";
}
}
3.2. 消息编解码器
由于本例中的消息类型比较复杂,我们需要自定义消息的编解码器。本节中将具体介绍编解码器的实现代码。
3.2.1. 编码器
package netty.protocol.codec;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToByteEncoder;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Map;
import netty.protocol.struct.NettyMessage;
/**
* created by LMR on 2020/5/23
*/
public final class NettyMessageEncoder extends
MessageToByteEncoder<NettyMessage> {
MarshallingEncoder marshallingEncoder;
public NettyMessageEncoder() throws IOException {
this.marshallingEncoder = new MarshallingEncoder();
}
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, NettyMessage msg,
ByteBuf sendBuf) throws Exception {
if (msg == null || msg.getHeader() == null)
throw new Exception("The encode message is null");
sendBuf.writeInt((msg.getHeader().getCrcCode()));
sendBuf.writeInt((msg.getHeader().getLength()));
sendBuf.writeByte((msg.getHeader().getType()));
sendBuf.writeInt((msg.getHeader().getAttachment().size()));
String key = null;
byte[] keyArray = null;
Object value = null;
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> param : msg.getHeader().getAttachment().entrySet()) {
//获取key
key = param.getKey();
//将key转化为字节数组
keyArray = key.getBytes("UTF-8");
//标识key的字节数组大小,以便于后续取出key
sendBuf.writeInt(keyArray.length);
//写入key
sendBuf.writeBytes(keyArray);
//获取value
value = param.getValue();
//写入value
marshallingEncoder.encode(value, sendBuf);
}
key = null;
keyArray = null;
value = null;
if (msg.getBody() != null) {
marshallingEncoder.encode(msg.getBody(), sendBuf);
} else
sendBuf.writeInt(0);
//最终更新整条消息的长度
sendBuf.setInt(4, sendBuf.readableBytes() - 8);
}
}
NettyMessageEncoder 类实现了对消息的编码功能。该类继承MessageToByteEncoder,主要实现了其encode方法,可以将一个消息类型的数据NettyMessage转化为字节类型数据ByteBuf 。在具体是实现时,按照头数据(Header)和主体数据(body)的顺序依次编码。对于基本数据类型的数据直接调用ByteBuf的方法将数据转化为字节类型。而Attachment为map类型数据,其中key为String类型,而value为Object类型,都无法直接调用ByteBuf的方法进行编码。字符串数据可以设置标识并且写入字节数组,而Object类型数据则调用MarshallingEncoder的encode方法进行编码,下面来看看该类的具体实现。
package netty.protocol.codec;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.jboss.marshalling.Marshaller;
/**
* created by LMR on 2020/5/23
*/
public class MarshallingEncoder {
private static final byte[] LENGTH_PLACEHOLDER = new byte[4];
Marshaller marshaller;
public MarshallingEncoder() throws IOException {
marshaller = MarshallingCodecFactory.buildMarshalling();
}
protected void encode(Object msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
try {
//获取当前缓冲区指针位置
int lengthPos = out.writerIndex();
//设置临时的占位符,表明当前存储的Object的size
out.writeBytes(LENGTH_PLACEHOLDER);
//利用Marshaller来写msg
ChannelBufferByteOutput output = new ChannelBufferByteOutput(out);
marshaller.start(output);
marshaller.writeObject(msg);
marshaller.finish();
//重新更新当前Object的size
out.setInt(lengthPos, out.writerIndex() - lengthPos - 4);
} finally {
marshaller.close();
}
}
}
MarshallingEncoder 类则是调用Marshaller的方法进行编码,这与第一个例子相同,这里就不再解析。
3.2.2. 解码器
package netty.protocol.codec;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import netty.protocol.struct.Header;
import netty.protocol.struct.NettyMessage;
/**
* created by LMR on 2020/5/23
*/
public class NettyMessageDecoder extends LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder {
MarshallingDecoder marshallingDecoder;
public NettyMessageDecoder(int maxFrameLength, int lengthFieldOffset, int lengthFieldLength) throws IOException {
super(maxFrameLength, lengthFieldOffset, lengthFieldLength);
marshallingDecoder = new MarshallingDecoder();
}
@Override
protected Object decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in) throws Exception {
ByteBuf frame = (ByteBuf) super.decode(ctx, in);
if (frame == null) {
return null;
}
NettyMessage message = new NettyMessage();
Header header = new Header();
header.setCrcCode(frame.readInt());
header.setLength(frame.readInt());
header.setType(frame.readByte());
//读取附件的个数
int size = frame.readInt();
if (size > 0) {
Map<String, Object> attch = new HashMap<String, Object>(size);
int keySize = 0;
byte[] keyArray = null;
String key = null;
//依次解码每个附件
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
keySize = frame.readInt();
keyArray = new byte[keySize];
frame.readBytes(keyArray);
key = new String(keyArray, "UTF-8");
attch.put(key, marshallingDecoder.decode(frame));
}
keyArray = null;
key = null;
header.setAttachment(attch);
}
//如果有消息体,则解码
if (frame.readableBytes() > 4) {
message.setBody(marshallingDecoder.decode(frame));
}
message.setHeader(header);
return message;
}
}
NettyMessageDecoder 继承了LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder ,该解码器支持自动的TCP粘包和半包处理,只需要给出标识消息长度字段偏移量和消息长度本身的字节数,Netty就能够实现对半包的处理。在具体业务上先调用LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder 的解码方法解决粘包或半包的问题,返回整包数据或者空数据,之后再进行具体的解码方法,其中MarshallingDecoder 实现代码如下:
package netty.protocol.codec;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.StreamCorruptedException;
import org.jboss.marshalling.ByteInput;
import org.jboss.marshalling.Unmarshaller;
/**
* created by LMR on 2020/5/23
*/
public class MarshallingDecoder {
private final Unmarshaller unmarshaller;
public MarshallingDecoder() throws IOException {
unmarshaller = MarshallingCodecFactory.buildUnMarshalling();
}
protected Object decode(ByteBuf in) throws Exception {
//获取消息的size
int objectSize = in.readInt();
//获取当前消息缓冲区的子区域
ByteBuf buf = in.slice(in.readerIndex(), objectSize);
ByteInput input = new ChannelBufferByteInput(buf);
try {
//利用Unmarshaller解码
unmarshaller.start(input);
Object obj = unmarshaller.readObject();
unmarshaller.finish();
in.readerIndex(in.readerIndex() + objectSize);
return obj;
} finally {
unmarshaller.close();
}
}
}
实现过程再代码中有详细注释,就不再解释。
3.3. 服务端代码
package netty.protocol.server;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import java.io.IOException;
import netty.protocol.codec.NettyMessageDecoder;
import netty.protocol.codec.NettyMessageEncoder;
/**
* created by LMR on 2020/5/23
*/
public class NettyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new NettyServer().bind(8080);
}
public void bind(int port) throws Exception {
// 配置服务端的NIO线程组
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 100)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch)
throws IOException {
//自定义消息解码器
ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyMessageDecoder(1024 * 1024, 4, 4));
//自定义消息编码器
ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyMessageEncoder());
//服务端处理类
ch.pipeline().addLast("ServerHandler", new ServerHandler());
}
});
// 绑定端口,同步等待成功
b.bind(port).sync();
System.out.println("Netty server start ok : " + port);
}
}
在initChannel方法中,我们在ChannelPipeline中添加了自定义的解码器和编码器,其中解码器设置的最大消息长度为1024*1024,消息长度标识所在的位置4(字节数组下标为4)和消息长度标识本身的字节长度4(int类型)。下面我们看看具体的服务端处理类ServerHandler的实现代码:
package netty.protocol.server;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import netty.protocol.struct.Header;
import netty.protocol.struct.NettyMessage;
/**
* created by LMR on 2020/5/23
*/
public class ServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
NettyMessage message = (NettyMessage) msg;
// 如果是握手请求消息,处理,(这里仅仅考虑这种情况)
if (message.getHeader() != null && message.getHeader().getType() == (byte) 3) {
NettyMessage loginResp = buildResponse((byte) 0);
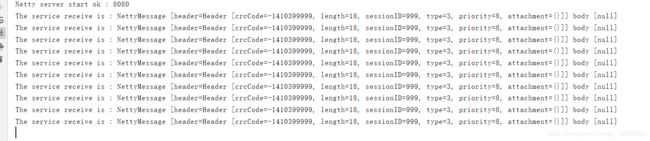
System.out.println("The service receive is : " + message + " body [" + message.getBody() + "]");
ctx.writeAndFlush(loginResp);
}
}
private NettyMessage buildResponse(byte result) {
NettyMessage message = new NettyMessage();
Header header = new Header();
header.setType((byte)4);
message.setHeader(header);
message.setBody(result);
return message;
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();// 发生异常,关闭链路
}
}
3.4. 客户端代码
package netty.protocol.client;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.ReadTimeoutHandler;
import netty.protocol.NettyConstant;
import netty.protocol.codec.NettyMessageDecoder;
import netty.protocol.codec.NettyMessageEncoder;
/**
* created by LMR on 2020/5/23
*/
public class NettyClient {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
public void connect(int port, String host) throws Exception {
// 配置客户端NIO线程组
try {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch)
throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyMessageDecoder(1024 * 1024, 4, 4));
ch.pipeline().addLast("MessageEncoder", new NettyMessageEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast("ClientHandler", new ClientHandler());
}
});
// 发起异步连接操作
ChannelFuture future = b.connect(
new InetSocketAddress(host, port),
new InetSocketAddress(NettyConstant.LOCALIP,
NettyConstant.LOCAL_PORT)).sync();
// 当对应的channel关闭的时候,就会返回对应的channel。
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
//释放资源
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new NettyClient().connect(8080, "127.0.0.1");
}
}
客户端的操作与服务端类似,都需要添加自定义编解码器,然后加入客户端操作实例,下面看看ClientHandler具体实现。
package netty.protocol.client;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import netty.protocol.MessageType;
import netty.protocol.struct.Header;
import netty.protocol.struct.NettyMessage;
/**
* created by LMR on 2020/5/23
*/
public class ClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
ctx.write(buildMessage());
}
ctx.flush();
}
private NettyMessage buildMessage() {
NettyMessage message = new NettyMessage();
Header header = new Header();
header.setType(MessageType.LOGIN_REQ.value());
header.setLength(999);
header.setPriority((byte)8);
header.setSessionID(999l);
message.setHeader(header);
return message;
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
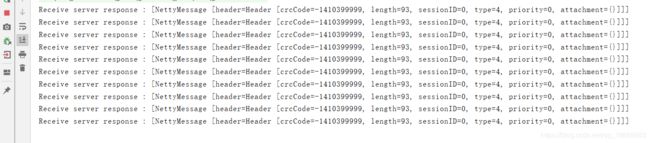
System.out.println("Receive server response : [" + msg + "]");
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.flush();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
channelActive在初始化时执行,便向服务端发送消息,一共发送10条数据,以便于测试粘包,拆包现象是否能够解决。
3.5. 运行结果
参考博客及书籍:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/64dc7ee8c713
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_24871519/article/details/82668828
《Netty 权威指南》
如果喜欢的话希望点赞收藏,关注我,将不间断更新博客。
希望热爱技术的小伙伴私聊,一起学习进步
来自于热爱编程的小白