网上书城项目
网上书城项目
- 前言
- 思维导图内容分析
- 1、项目背景/价值
- 2、项目角色
- 3、项目需求分析
- 4、项目功能划分
- 5、项目数据库表设计
- 工具类介绍
- 总结
前言
今天为大家分析的知识点是博主最近在做的网上书城项目,整个项目流程以及编码的思路也会分享到,使用到的主要技术是Easyui+自定义Mvc的内容!
思维导图内容分析
1、项目背景/价值
项目背景和价值是首先必须分析的,背景和价值通俗一点来说就是,你为什么要做这个项目,做这个项目有什么价值!
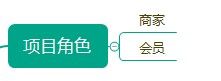
2、项目角色
3、项目需求分析

需求分析分为前端和后台两个部分,可根据项目角色的需求进行需求的划分!
4、项目功能划分
随着需求的进一步分析,我们可以根据需求来进行功能的一个划分,当然也是分为前端和后台两个部分:
后台部分:

后台的话是根据项目的角色进行划分的,
即商家能实现哪些操作,用户能实现哪些操作
5、项目数据库表设计
根据功能的分析与详细划分,总共需要以下七张表才能完成该项目:
1、t_easyui_user 用户表
| 字段名 | 数据类型 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| id | bigint | 用户ID:标识列 |
| name | varchar | 用户名 |
| pwd | varchar | 密码 |
| type | int | 类型 |
2、t_easyui_book 书籍表
| 字段名 | 数据类型 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| id | bigint | ID:标识列 |
| name | varchar | 书籍名称 |
| pinyin | varchar | 拼音 |
| cid | bigint | 书籍类别 |
| author | varchar | 作者 |
| price | float | 价格 |
| image | varchar | 图片路径 |
| publishing | varchar | 出版社 |
| description | varchar | 描述 |
| state | int | 书籍状态(1 未上架 2 已上架 3 已下架 默认值1 ) |
| deployTime | datetime | 上架时间 |
| sales | int | 销量 |
3、t_easyui_permission 权限表
| 字段名 | 数据类型 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| id | bigint | 权限ID |
| name | varchar | 权限名字 |
| description | varchar | 权限描述 |
| url | varchar | 菜单路径 |
| pid | bigint | 父权限 |
| ismenu | int | 是否为菜单 1、菜单 2、按钮 |
| displayno | bigint | 展现顺序 |
4、t_easyui_role_permission 角色权限中间表
| 字段名 | 数据类型 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| rid | bigint | 用户角色 |
| pid | bigint | 用户权限 |
这张表是用来将用户表和权限表进行关联的
5、t_easyui_category 书籍类别表
| 字段名 | 数据类型 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| id | bigint | ID |
| name | varchar | 类型名称 |
6、t_easyui_order 订单表
| 字段名 | 数据类型 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| id | bigint | 订单ID:非标识列,为简化开发 |
| uid | bigint | "用户ID:外键 |
| orderTime | datetime | 下单日期时间:默认为系统当前时间 |
| consignee | varchar | 收货人 |
| phone | varchar | 收货人电话 |
| postalcode | varchar | 收货人邮编 |
| address | varchar | 收货人地址 |
| sendType | int | 发货方式:1 平邮 2 快递 |
| sendTime | datetime | 发货时间 |
| orderPrice | float | 订单总价 |
| orderState | int | 订单状态:1 未发货 2 已发货 3 已签收 4 已撤单 默认值1 |
注:未发货的订单可进行点击取消,即做一个删除操作,还要删除订单项表的记录
7、t_easyui_orderitem 订单项表
| 字段名 | 数据类型 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| id | bigint | N 订单项ID:标识列 |
| oid | bigint | N 订单ID:外键 |
| bid | int | N 书籍ID:外键 |
| quantity | int | N 数量 |
以上这些就是该项目中需要用到的表格~
工具类介绍
当然博主做的这个项目,也会用到很多工具类,接下来由此介绍一波:
BaseDao类:
package com.wangqiuping.util;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 小汪同学 2020/6/29 22:37:15
* 做通用的增删改 分页 的父类
*/
public class BaseDao<T> {
// 查询
public List<T> executeQuery(String sql, PageBean pageBean,Class clz)throws Exception{
List<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
Connection con = DBAccess.getConnection();
PreparedStatement pst=null;
ResultSet rs = null;
if (pageBean!=null && pageBean.isPagination()){
// 获取符合条件的总记录数用于后续分页
String countSql = getCountSql(sql);
pst = con.prepareStatement(countSql);
rs = pst.executeQuery();
if(rs.next()){
pageBean.setTotal(rs.getObject(1).toString());
}
// 查询出页面要展示的结果
String pageSql = getPageSql(sql,pageBean.getStartIndex(),pageBean.getRows());
pst = con.prepareStatement(pageSql);
rs = pst.executeQuery();
}else{
// 不分页
pst = con.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = pst.executeQuery();
}
T t;
while (rs.next()){
// 通过反射解决通用查询的问题
// list.add(new Book(rs.getInt("bid"),rs.getString("bname"),rs.getFloat("price")));
// 通过反射来做
t = (T) clz.newInstance();
// 给t中的属性赋值
Field[] fields = clz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field f : fields) {
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(t,rs.getObject(f.getName()));
}
list.add(t);
}
DBAccess.close(con,pst,rs);
return list;
}
// 用原始sql拼装出查询符合条件分页展示的数据的sql
private String getPageSql(String sql, int startIndex, int rows) {
return sql+" limit "+startIndex+","+rows;
}
// 用原始sql拼装出查询符合条件的总记录的sql
private String getCountSql(String sql) {
return " select count(1) from ("+sql+") t";
}
/**
* 通用的增删改操作(hibernate/mybatis的底层)
* @param sql
* @param t book
* @param attrs book实例中的属性
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public int executeUpdate(String sql, T t,String[] attrs)throws Exception{
Connection con = DBAccess.getConnection();
PreparedStatement pst = con.prepareStatement(sql);
// pst.setObject(1, book.getBid());
// pst.setObject(2, book.getBname());
// pst.setObject(3, book.getPrice());
Field f = null;
Field[] fields = t.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (int i = 0; i < attrs.length; i++) {
// 属性数组中的第i个属性对象 下标从0开始
f = t.getClass().getDeclaredField(attrs[i]);
f.setAccessible(true);
// 给第i+1占位符赋值 下表从1开始
pst.setObject(i+1,f.get(t));
}
int num = pst.executeUpdate();
DBAccess.close(con,pst,null);
return num;
}
}
这个类主要放一些通用性的代码,比如经常会使用到的分页,通用的增删改、通用的查询…
BuildTree类:
package com.wangqiuping.util;
import com.javaxl.vo.TreeVo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class BuildTree {
/**
* 默认-1为顶级节点
* @param nodes
* @param <T>
* @return
*/
public static <T> TreeVo<T> build(List<TreeVo<T>> nodes) {
if (nodes == null) {
return null;
}
List<TreeVo<T>> topNodes = new ArrayList<TreeVo<T>>();
for (TreeVo<T> children : nodes) {
String pid = children.getParentId();
if (pid == null || "-1".equals(pid)) {
topNodes.add(children);
continue;
}
for (TreeVo<T> parent : nodes) {
String id = parent.getId();
if (id != null && id.equals(pid)) {
parent.getChildren().add(children);
children.setHasParent(true);
parent.setChildren(true);
continue;
}
}
}
TreeVo<T> root = new TreeVo<T>();
if (topNodes.size() == 1) {
root = topNodes.get(0);
} else {
root.setId("000");
root.setParentId("-1");
root.setHasParent(false);
root.setChildren(true);
root.setChecked(true);
root.setChildren(topNodes);
root.setText("顶级节点");
Map<String, Object> state = new HashMap<>(16);
state.put("opened", true);
root.setState(state);
}
return root;
}
/**
* 指定idparam为顶级节点
* @param nodes
* @param idParam
* @param <T>
* @return
*/
public static <T> List<TreeVo<T>> buildList(List<TreeVo<T>> nodes, String idParam) {
if (nodes == null) {
return null;
}
List<TreeVo<T>> topNodes = new ArrayList<TreeVo<T>>();
for (TreeVo<T> children : nodes) {
String pid = children.getParentId();
if (pid == null || idParam.equals(pid)) {
topNodes.add(children);
continue;
}
for (TreeVo<T> parent : nodes) {
String id = parent.getId();
if (id != null && id.equals(pid)) {
parent.getChildren().add(children);
children.setHasParent(true);
parent.setChildren(true);
continue;
}
}
}
return topNodes;
}
}
这个类呢,主要用来和treevo类搭配使用,将表数据转换为easyui所能识别的treeVo数据,通过BuildTree转化成所需要的格式~
config.properties类:
mysql的配置文件
DateUtil类:
没错,这个类的名称里面就有Date,可想而知,肯定是和Date日期相关的啦~
package com.wangqiuping.util;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 日期处理工具包
* @author 小汪同学 2020/6/29 22:40:11
*
*/
public class DateUtil {
/**
* 日期转字符串
* @param date
* @param format
* @return
*/
public static String formatDate(Date date,String format){
String result="";
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat(format);
if(date!=null){
result=sdf.format(date);
}
return result;
}
/**
* 字符串转日期
* @param str
* @param format
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static Date formatString(String str,String format) throws Exception{
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat(format);
return sdf.parse(str);
}
/**
* 获取当前时间的字符串
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static String getCurrentDateStr()throws Exception{
Date date=new Date();
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddhhmmss");
return sdf.format(date);
}
}
这个类呢,主要包含日期转字符串、字符串转日期
以及获取当前时间的字符串的三个方法,后期在项目中主要是应用到图片的上传,避免图片上传时被覆盖的问题~
MD5加盐加密:
package com.wangqiuping.util;
/**
* 使用MD5算法对字符串进行加密的工具类。
MD5即Message-Digest
* Algorithm5(信息-摘要算法5),是一种用于产生数字签名的单项散列算法, 这个算法是不可逆的,
* 也就是说即使你看到源程序和算法描述,也无法将一个MD5的值变换回原始的字符串
*
*/
public class MD5 {
/*
* 下面这些S11-S44实际上是一个4*4的矩阵,在原始的C实现中是用#define 实现的, 这里把它们实现成为static
* final是表示了只读,切能在同一个进程空间内的多个 Instance间共享
*/
private static final int S11 = 7;
private static final int S12 = 12;
private static final int S13 = 17;
private static final int S14 = 22;
private static final int S21 = 5;
private static final int S22 = 9;
private static final int S23 = 14;
private static final int S24 = 20;
private static final int S31 = 4;
private static final int S32 = 11;
private static final int S33 = 16;
private static final int S34 = 23;
private static final int S41 = 6;
private static final int S42 = 10;
private static final int S43 = 15;
private static final int S44 = 21;
private static final byte[] PADDING = { -128, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 };
/*
* 下面的三个成员是MD5计算过程中用到的3个核心数据,在原始的C实现中 被定义到MD5_CTX结构中
*
*/
private long[] state = new long[4]; // state (ABCD)
private long[] count = new long[2];// number of bits, modulo 2^64(lsbfirst)
private byte[] buffer = new byte[64]; // input buffer
/*
* digest,是最新一次计算结果的2进制内部表示,表示128bit的MD5值.
*/
private byte[] digest = new byte[16];
public MD5() {
md5Init();
}
/*
* getMD5ofStr是类MD5最主要的公共方法,入口参数是你想要进行MD5变换的字符串
* 返回的是变换完的结果,这个结果是从公共成员digestHexStr取得的.
*/
public String getMD5ofStr(String inbuf) {
md5Init();
md5Update(inbuf.getBytes(), inbuf.length());
md5Final();
String digestHexStr = "";
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
digestHexStr += byteHEX(digest[i]);
}
return digestHexStr;
}
/* md5Init是一个初始化函数,初始化核心变量,装入标准的幻数 */
private void md5Init() {
count[0] = 0L;
count[1] = 0L;
// /* Load magic initialization constants.
state[0] = 0x67452301L;
state[1] = 0xefcdab89L;
state[2] = 0x98badcfeL;
state[3] = 0x10325476L;
return;
}
/*
* F, G, H ,I 是4个基本的MD5函数,在原始的MD5的C实现中,由于它们是
* 简单的位运算,可能出于效率的考虑把它们实现成了宏,在java中,我们把它们 实现成了private方法,名字保持了原来C中的。
*/
private long F(long x, long y, long z) {
return (x & y) | ((~x) & z);
}
private long G(long x, long y, long z) {
return (x & z) | (y & (~z));
}
private long H(long x, long y, long z) {
return x ^ y ^ z;
}
private long I(long x, long y, long z) {
return y ^ (x | (~z));
}
/*
* FF,GG,HH和II将调用F,G,H,I进行近一步变换 FF, GG, HH, and II transformations for
* rounds 1, 2, 3, and 4. Rotation is separate from addition to prevent
* recomputation.
*/
private long FF(long a, long b, long c, long d, long x, long s, long ac) {
a += F(b, c, d) + x + ac;
a = ((int) a << s) | ((int) a >>> (32 - s));
a += b;
return a;
}
private long GG(long a, long b, long c, long d, long x, long s, long ac) {
a += G(b, c, d) + x + ac;
a = ((int) a << s) | ((int) a >>> (32 - s));
a += b;
return a;
}
private long HH(long a, long b, long c, long d, long x, long s, long ac) {
a += H(b, c, d) + x + ac;
a = ((int) a << s) | ((int) a >>> (32 - s));
a += b;
return a;
}
private long II(long a, long b, long c, long d, long x, long s, long ac) {
a += I(b, c, d) + x + ac;
a = ((int) a << s) | ((int) a >>> (32 - s));
a += b;
return a;
}
/*
* md5Update是MD5的主计算过程,inbuf是要变换的字节串,inputlen是长度,这个
* 函数由getMD5ofStr调用,调用之前需要调用md5init,因此把它设计成private的
*/
private void md5Update(byte[] inbuf, int inputLen) {
int i, index, partLen;
byte[] block = new byte[64];
index = (int) (count[0] >>> 3) & 0x3F;
// /* Update number of bits */
if ((count[0] += (inputLen << 3)) < (inputLen << 3))
count[1]++;
count[1] += (inputLen >>> 29);
partLen = 64 - index;
// Transform as many times as possible.
if (inputLen >= partLen) {
md5Memcpy(buffer, inbuf, index, 0, partLen);
md5Transform(buffer);
for (i = partLen; i + 63 < inputLen; i += 64) {
md5Memcpy(block, inbuf, 0, i, 64);
md5Transform(block);
}
index = 0;
} else
i = 0;
// /* Buffer remaining input */
md5Memcpy(buffer, inbuf, index, i, inputLen - i);
}
/*
* md5Final整理和填写输出结果
*/
private void md5Final() {
byte[] bits = new byte[8];
int index, padLen;
// /* Save number of bits */
Encode(bits, count, 8);
// /* Pad out to 56 mod 64.
index = (int) (count[0] >>> 3) & 0x3f;
padLen = (index < 56) ? (56 - index) : (120 - index);
md5Update(PADDING, padLen);
// /* Append length (before padding) */
md5Update(bits, 8);
// /* Store state in digest */
Encode(digest, state, 16);
}
/*
* md5Memcpy是一个内部使用的byte数组的块拷贝函数,从input的inpos开始把len长度的
* 字节拷贝到output的outpos位置开始
*/
private void md5Memcpy(byte[] output, byte[] input, int outpos, int inpos,
int len) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
output[outpos + i] = input[inpos + i];
}
/*
* md5Transform是MD5核心变换程序,有md5Update调用,block是分块的原始字节
*/
private void md5Transform(byte block[]) {
long a = state[0], b = state[1], c = state[2], d = state[3];
long[] x = new long[16];
Decode(x, block, 64);
/* Round 1 */
a = FF(a, b, c, d, x[0], S11, 0xd76aa478L); /* 1 */
d = FF(d, a, b, c, x[1], S12, 0xe8c7b756L); /* 2 */
c = FF(c, d, a, b, x[2], S13, 0x242070dbL); /* 3 */
b = FF(b, c, d, a, x[3], S14, 0xc1bdceeeL); /* 4 */
a = FF(a, b, c, d, x[4], S11, 0xf57c0fafL); /* 5 */
d = FF(d, a, b, c, x[5], S12, 0x4787c62aL); /* 6 */
c = FF(c, d, a, b, x[6], S13, 0xa8304613L); /* 7 */
b = FF(b, c, d, a, x[7], S14, 0xfd469501L); /* 8 */
a = FF(a, b, c, d, x[8], S11, 0x698098d8L); /* 9 */
d = FF(d, a, b, c, x[9], S12, 0x8b44f7afL); /* 10 */
c = FF(c, d, a, b, x[10], S13, 0xffff5bb1L); /* 11 */
b = FF(b, c, d, a, x[11], S14, 0x895cd7beL); /* 12 */
a = FF(a, b, c, d, x[12], S11, 0x6b901122L); /* 13 */
d = FF(d, a, b, c, x[13], S12, 0xfd987193L); /* 14 */
c = FF(c, d, a, b, x[14], S13, 0xa679438eL); /* 15 */
b = FF(b, c, d, a, x[15], S14, 0x49b40821L); /* 16 */
/* Round 2 */
a = GG(a, b, c, d, x[1], S21, 0xf61e2562L); /* 17 */
d = GG(d, a, b, c, x[6], S22, 0xc040b340L); /* 18 */
c = GG(c, d, a, b, x[11], S23, 0x265e5a51L); /* 19 */
b = GG(b, c, d, a, x[0], S24, 0xe9b6c7aaL); /* 20 */
a = GG(a, b, c, d, x[5], S21, 0xd62f105dL); /* 21 */
d = GG(d, a, b, c, x[10], S22, 0x2441453L); /* 22 */
c = GG(c, d, a, b, x[15], S23, 0xd8a1e681L); /* 23 */
b = GG(b, c, d, a, x[4], S24, 0xe7d3fbc8L); /* 24 */
a = GG(a, b, c, d, x[9], S21, 0x21e1cde6L); /* 25 */
d = GG(d, a, b, c, x[14], S22, 0xc33707d6L); /* 26 */
c = GG(c, d, a, b, x[3], S23, 0xf4d50d87L); /* 27 */
b = GG(b, c, d, a, x[8], S24, 0x455a14edL); /* 28 */
a = GG(a, b, c, d, x[13], S21, 0xa9e3e905L); /* 29 */
d = GG(d, a, b, c, x[2], S22, 0xfcefa3f8L); /* 30 */
c = GG(c, d, a, b, x[7], S23, 0x676f02d9L); /* 31 */
b = GG(b, c, d, a, x[12], S24, 0x8d2a4c8aL); /* 32 */
/* Round 3 */
a = HH(a, b, c, d, x[5], S31, 0xfffa3942L); /* 33 */
d = HH(d, a, b, c, x[8], S32, 0x8771f681L); /* 34 */
c = HH(c, d, a, b, x[11], S33, 0x6d9d6122L); /* 35 */
b = HH(b, c, d, a, x[14], S34, 0xfde5380cL); /* 36 */
a = HH(a, b, c, d, x[1], S31, 0xa4beea44L); /* 37 */
d = HH(d, a, b, c, x[4], S32, 0x4bdecfa9L); /* 38 */
c = HH(c, d, a, b, x[7], S33, 0xf6bb4b60L); /* 39 */
b = HH(b, c, d, a, x[10], S34, 0xbebfbc70L); /* 40 */
a = HH(a, b, c, d, x[13], S31, 0x289b7ec6L); /* 41 */
d = HH(d, a, b, c, x[0], S32, 0xeaa127faL); /* 42 */
c = HH(c, d, a, b, x[3], S33, 0xd4ef3085L); /* 43 */
b = HH(b, c, d, a, x[6], S34, 0x4881d05L); /* 44 */
a = HH(a, b, c, d, x[9], S31, 0xd9d4d039L); /* 45 */
d = HH(d, a, b, c, x[12], S32, 0xe6db99e5L); /* 46 */
c = HH(c, d, a, b, x[15], S33, 0x1fa27cf8L); /* 47 */
b = HH(b, c, d, a, x[2], S34, 0xc4ac5665L); /* 48 */
/* Round 4 */
a = II(a, b, c, d, x[0], S41, 0xf4292244L); /* 49 */
d = II(d, a, b, c, x[7], S42, 0x432aff97L); /* 50 */
c = II(c, d, a, b, x[14], S43, 0xab9423a7L); /* 51 */
b = II(b, c, d, a, x[5], S44, 0xfc93a039L); /* 52 */
a = II(a, b, c, d, x[12], S41, 0x655b59c3L); /* 53 */
d = II(d, a, b, c, x[3], S42, 0x8f0ccc92L); /* 54 */
c = II(c, d, a, b, x[10], S43, 0xffeff47dL); /* 55 */
b = II(b, c, d, a, x[1], S44, 0x85845dd1L); /* 56 */
a = II(a, b, c, d, x[8], S41, 0x6fa87e4fL); /* 57 */
d = II(d, a, b, c, x[15], S42, 0xfe2ce6e0L); /* 58 */
c = II(c, d, a, b, x[6], S43, 0xa3014314L); /* 59 */
b = II(b, c, d, a, x[13], S44, 0x4e0811a1L); /* 60 */
a = II(a, b, c, d, x[4], S41, 0xf7537e82L); /* 61 */
d = II(d, a, b, c, x[11], S42, 0xbd3af235L); /* 62 */
c = II(c, d, a, b, x[2], S43, 0x2ad7d2bbL); /* 63 */
b = II(b, c, d, a, x[9], S44, 0xeb86d391L); /* 64 */
state[0] += a;
state[1] += b;
state[2] += c;
state[3] += d;
}
/*
* Encode把long数组按顺序拆成byte数组,因为java的long类型是64bit的, 只拆低32bit,以适应原始C实现的用途
*/
private void Encode(byte[] output, long[] input, int len) {
int i, j;
for (i = 0, j = 0; j < len; i++, j += 4) {
output[j] = (byte) (input[i] & 0xffL);
output[j + 1] = (byte) ((input[i] >>> 8) & 0xffL);
output[j + 2] = (byte) ((input[i] >>> 16) & 0xffL);
output[j + 3] = (byte) ((input[i] >>> 24) & 0xffL);
}
}
/*
* Decode把byte数组按顺序合成成long数组,因为java的long类型是64bit的,
* 只合成低32bit,高32bit清零,以适应原始C实现的用途
*/
private void Decode(long[] output, byte[] input, int len) {
int i, j;
for (i = 0, j = 0; j < len; i++, j += 4)
output[i] = b2iu(input[j]) | (b2iu(input[j + 1]) << 8)
| (b2iu(input[j + 2]) << 16) | (b2iu(input[j + 3]) << 24);
return;
}
/*
* b2iu是我写的一个把byte按照不考虑正负号的原则的"升位"程序,因为java没有unsigned运算
*/
private static long b2iu(byte b) {
return b < 0 ? b & 0x7F + 128 : b;
}
/*
* byteHEX(),用来把一个byte类型的数转换成十六进制的ASCII表示,
* 因为java中的byte的toString无法实现这一点,我们又没有C语言中的 sprintf(outbuf,"%02X",ib)
*/
private static String byteHEX(byte ib) {
char[] Digit = { '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'A',
'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F' };
char[] ob = new char[2];
ob[0] = Digit[(ib >>> 4) & 0X0F];
ob[1] = Digit[ib & 0X0F];
String s = new String(ob);
return s;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
String source = "888888";
MD5 md5 = new MD5();
String s1 = md5.getMD5ofStr(source);// length=32
System.out.println(s1);
}
}
主要是有两种加密方式:
1、明文加密
该加密方式可通过MD5在线解密工具进行解密:
MD5在线解密工具

使用这种解密方式的缺点:明文密码加密之后,对应一个密文密码,如果拿到密文密码,可以反推得到密码,在企业中通常不使用~
2、密文加密 (也称加盐加密)
原理:这种方式在加密的过程中加了盐,加盐的过程属于生成随机数的过程,也就是说加盐加密不再是一对一的关系,而是一对多的关系,一个明文密码对应着成千上万种结果,所以难以破解~
EasyuiResult类:
package com.wangqiuping.util;
import lombok.*;
/**
* @author 小汪同学
* 2020-06-29 11:09
*/
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE)
@AllArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE)
@ToString
public class EasyuiResult<T> {
private long total;
private T rows;
private int code;
private String msg;
// 响应成功
public static EasyuiResult SUCCESS = new EasyuiResult(200,"响应成功");
private EasyuiResult(int code, String msg) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
private EasyuiResult(long total, T rows) {
this.total = total;
this.rows = rows;
}
private EasyuiResult(T rows) {
this.rows = rows;
}
// 带分页的
public static <T> EasyuiResult<T> ok(long total, T rows){
return new EasyuiResult<T>(total,rows);
}
// 不带分页的
public static <T> EasyuiResult<T> ok(T rows){
return new EasyuiResult<T>(rows);
}
}
其中以上这个类中的这几行注解做着重解释:
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE)
@AllArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE)
@ToString
@Data 表示实体类中的set/get方法
@NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE) 无参构造器
@AllArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE) 有参构造器
@ToString 表示 ToString方法
总结
由于篇幅原因,就不在这里分享前端设计的页面以及代码啦,下篇博客见,总而言之,想要做好一个项目还是先弄清楚项目背景/价值,然后再做需求分析,然后再根据需求进行功能的划分,接下来就是设计数据库表格以及字段名,最后根据逻辑进行编码就好,内容就到这里啦,拜拜~