SSD pytorch训练自己的数据集(windows+colab)
目录
- 下载
- 数据集
- 训练代码修改
- config.py
- 新建cancer.py作为数据读入
- __init__文件
- ssd.py
- train.py
- multibox_loss.py
- 验证eval.py代码修改
- 爬坑实录!
- 使用Colab
对于一个小白,想对自己数据的训练实在不容易,花了好几天时间,翻阅了很多资料,在此做个总结。
我的环境是windows+cpu,没有N卡!本文并将讲解用Colab进行训练
默认已配置好Pytorch环境,目录结构如下,便于核对路径问题

下载
1、SSD pytorch代码下载https://github.com/amdegroot/ssd.pytorch
github下载慢的话,可以在码云导入再下载
2、VGG预训练模型下载(https://99baiduyun.com/file/1AVCZSsm52-NA4A_uleXYSQ.html)
数据集
使用LabelImg标注数据集github地址有详细教程不再赘述。
我手上的数据集是cancer医学图像,label是txt格式的,转换的方法可见https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43289424/article/details/106371995
训练代码修改
config.py
因为我的数据集只有一个类别,但还要算上背景,类别+1即共2类
加入以下代码
cancer = {
'num_classes': 2,
'lr_steps': (40000, 50000, 60000),#调整学习率的步数
'max_iter': 60000,#迭代次数,可以先设小测试下能否运行
'feature_maps': [38, 19, 10, 5, 3, 1],
'min_dim': 300,
'steps': [8, 16, 32, 64, 100, 300],
'min_sizes': [30, 60, 111, 162, 213, 264],
'max_sizes': [60, 111, 162, 213, 264, 315],
'aspect_ratios': [[2], [2, 3], [2, 3], [2, 3], [2], [2]],
'variance': [0.1, 0.2],
'clip': True,
'name': 'CANCER',
}
新建cancer.py作为数据读入
对于源代码修改的地方标了######
import os.path as osp
import sys
import torch
import torch.utils.data as data
import cv2
import numpy as np
if sys.version_info[0] == 2:
import xml.etree.cElementTree as ET
else:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
CANCER_CLASSES = ['cancer']#######
CANCER_ROOT = "data/cancer_or_not/"#######
class CANCERAnnotationTransform(object):######
"""Transforms a CANCER annotation into a Tensor of bbox coords and label index
Initilized with a dictionary lookup of classnames to indexes
Arguments:
class_to_ind (dict, optional): dictionary lookup of classnames -> indexes
(default: alphabetic indexing of MASK's 2 classes)
keep_difficult (bool, optional): keep difficult instances or not
(default: False)
height (int): height
width (int): width
"""
def __init__(self, class_to_ind=None, keep_difficult=False):
# self.class_to_ind = class_to_ind or dict(
# zip(CANCER_CLASSES, range(len(CANCER_CLASSES))))
self.class_to_ind = class_to_ind or dict(cancer=0)#####我这里是一个类别就直接创建字典了
self.keep_difficult = keep_difficult
def __call__(self, target, width, height):
"""
Arguments:
target (annotation) : the target annotation to be made usable
will be an ET.Element
Returns:
a list containing lists of bounding boxes [bbox coords, class name]
"""
res = []
for obj in target.iter('object'):
difficult = int(obj.find('difficult').text) == 1
if not self.keep_difficult and difficult:
continue
name = obj.find('name').text.lower().strip()
bbox = obj.find('bndbox')
pts = ['xmin', 'ymin', 'xmax', 'ymax']
bndbox = []
for i, pt in enumerate(pts):
cur_pt = int(bbox.find(pt).text) - 1
# scale height or width
cur_pt = cur_pt / width if i % 2 == 0 else cur_pt / height
bndbox.append(cur_pt)
label_idx = self.class_to_ind[name]
bndbox.append(label_idx)
res += [bndbox] # [xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, label_ind]
# img_id = target.find('filename').text[:-4]
return res # [[xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, label_ind], ... ]
class CANCERDetection(data.Dataset):########
"""VOC Detection Dataset Object
input is image, target is annotation
Arguments:
root (string): filepath to VOCdevkit folder.
image_set (string): imageset to use (eg. 'train', 'val', 'test')
transform (callable, optional): transformation to perform on the
input image
target_transform (callable, optional): transformation to perform on the
target `annotation`
(eg: take in caption string, return tensor of word indices)
dataset_name (string, optional): which dataset to load
(default: 'VOC2007')
"""
#image_sets=[('2007', 'trainval'), ('2012', 'trainval')],
def __init__(self, root,
image_sets='trainval',######
transform=None, target_transform=CANCERAnnotationTransform(),#######
dataset_name='CANCER'):#######
self.root = root
self.image_set = image_sets
self.transform = transform
self.target_transform = target_transform
self.name = dataset_name
self._annopath = osp.join('%s', 'Annotations', '%s.xml')
self._imgpath = osp.join('%s', 'JPEGImages', '%s.jpg')
self.ids = list()
for line in open(CANCER_ROOT+'/ImageSets/Main/'+self.image_set+'.txt'):
self.ids.append((CANCER_ROOT, line.strip()))#######
def __getitem__(self, index):
im, gt, h, w = self.pull_item(index)
return im, gt
def __len__(self):
return len(self.ids)
def pull_item(self, index):
img_id = self.ids[index]
target = ET.parse(self._annopath % img_id).getroot()
img = cv2.imread(self._imgpath % img_id)
height, width, channels = img.shape
if self.target_transform is not None:
target = self.target_transform(target, width, height)
if self.transform is not None:
target = np.array(target)
img, boxes, labels = self.transform(img, target[:, :4], target[:, 4])
# to rgb
img = img[:, :, (2, 1, 0)]
# img = img.transpose(2, 0, 1)
target = np.hstack((boxes, np.expand_dims(labels, axis=1)))
return torch.from_numpy(img).permute(2, 0, 1), target, height, width
# return torch.from_numpy(img), target, height, width
def pull_image(self, index):
'''Returns the original image object at index in PIL form
Note: not using self.__getitem__(), as any transformations passed in
could mess up this functionality.
Argument:
index (int): index of img to show
Return:
PIL img
'''
img_id = self.ids[index]
return cv2.imread(self._imgpath % img_id, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
def pull_anno(self, index):
'''Returns the original annotation of image at index
Note: not using self.__getitem__(), as any transformations passed in
could mess up this functionality.
Argument:
index (int): index of img to get annotation of
Return:
list: [img_id, [(label, bbox coords),...]]
eg: ('001718', [('dog', (96, 13, 438, 332))])
'''
img_id = self.ids[index]
anno = ET.parse(self._annopath % img_id).getroot()
gt = self.target_transform(anno, 1, 1)
return img_id[1], gt
def pull_tensor(self, index):
'''Returns the original image at an index in tensor form
Note: not using self.__getitem__(), as any transformations passed in
could mess up this functionality.
Argument:
index (int): index of img to show
Return:
tensorized version of img, squeezed
'''
return torch.Tensor(self.pull_image(index)).unsqueeze_(0)
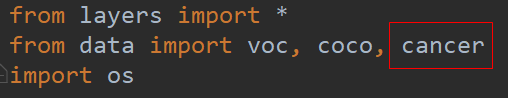
__init__文件
# from .voc0712 import VOCDetection, VOCAnnotationTransform, VOC_CLASSES, VOC_ROOT
from .cancer import CANCERDetection, CANCERAnnotationTransform, CANCER_CLASSES, CANCER_ROOT
# from .coco import COCODetection, COCOAnnotationTransform, COCO_CLASSES, COCO_ROOT, get_label_map
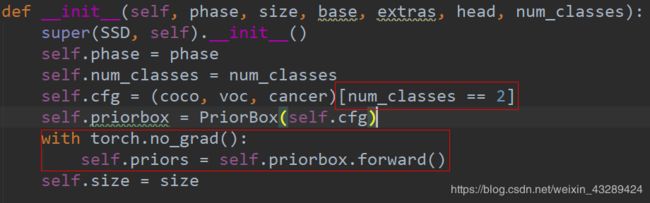
ssd.py
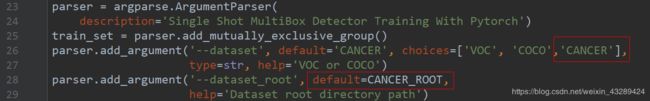
train.py
elif args.dataset == 'CANCER':
# if args.dataset_root == CANCER_ROOT:
# parser.error('Must specify dataset if specifying dataset_root')
cfg = cancer
dataset = CANCERDetection(root=args.dataset_root,
transform=SSDAugmentation(cfg['min_dim'],
MEANS))
报错:StopIteration,将images, targets = next(batch_iterator)改成
try:
images, targets = next(batch_iterator)
except StopIteration:
batch_iterator = iter(data_loader)
images, targets = next(batch_iterator)
报错:IndexError: invalid index of a 0-dim tensor. Use tensor.item() to convert a 0-dim tensor to a Python number,反向传播处将data[0]改成data.item()

报错xavier_uniform已经被弃用,使用xavier_uniform_代替

multibox_loss.py
报错:IndexError: The shape of the mask [32, 2990] at index 0 does not match the shape of the indexed tensor [95680, 1] at index 0类似的,解决方法:在这里加上

这样仍然会报错AttributeError: ‘Tensor’ object has no attribute ‘bool’
注意要使用torch1.3版本以上
报错:UserWarning: size_average and reduce args will be deprecated, please use reduction=‘sum’ instead. warnings.warn(warning.format(ret)),将loss_c = F.cross_entropy(conf_p, targets_weighted, size_average=False)改成
loss_c = F.cross_entropy(conf_p, targets_weighted, reduction=‘sum’)
验证eval.py代码修改
爬坑实录!
RuntimeError: Error(s) in loading state_dict for SSD:
size mismatch for conf.0.weight: copying a param with shape torch.Size([804, 512, 3, 3]) from checkpoint, the shape in current model is torch.Size([20, 512, 3, 3]).
在config文件中修改了,还是不管用,没搞懂这份代码怎么调用类别的,无奈之下!直接把build_ssd中的类别修改成数字
在train.py文件下

eval.py文件下

AttributeError: ‘Tensor’ object has no attribute 'bool’
这个问题解决只需使用torch1.3版本以上即可!
Legacy autograd function with non-static forward method is deprecated and will be removed in 1.3.
调用eval.py报错!调用torch1.2版本即可!
真的牛批!总而言之!训练用torch1.3以上,验证用torch
1.2版本
使用Colab
把代码文件上传至Google的云盘,直接传输大量文件会卡死,所以先压缩

在Colab中,先加载进云盘
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount('/content/drive')
进入云盘把压缩文件加载进来
%cd /content/drive/My Drive
!mv ssd_pytorch_cancer.zip /content
解压
%cd /content
!unzip ssd_pytorch_cancer.zip
!mv ssd_pytorch_cancer /content/drive/My\ Drive
运行训练代码
import os
os.chdir("/content/drive/My Drive/ssd_pytorch_cancer")
!python train.py --learning-rate 1e-5
参考https://www.cnblogs.com/xiximayou/p/12546556.html