redis+springboot2.0实现数据缓存
1、在pom.xml中引入相关依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commonsgroupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2artifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jsonartifactId>
dependency>
2、配置redisconfig,在实际项目中可以通过配置KeyGenerator来指定缓存信息的key的生成规则
RedisConfig.java
package com.shenju.utils;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.crypto.KeyGenerator;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
/**
*
* @author SJ-001
*
*/
@EnableCaching
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
// 使用Jackson2JsonRedisSerialize 替换默认序列化
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
objectMapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
objectMapper.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(objectMapper);
// 设置value的序列化规则和 key的序列化规则
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
//缓存管理器
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory lettuceConnectionFactory) {
RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfig = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig();
// 设置缓存管理器管理的缓存的默认过期时间
defaultCacheConfig = defaultCacheConfig.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(60))
// 不缓存空值
.disableCachingNullValues();
Set<String> cacheNames = new HashSet<>();
cacheNames.add("my-redis-cache1");
// 对每个缓存空间应用不同的配置
Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> configMap = new HashMap<>();
configMap.put("my-redis-cache1", defaultCacheConfig.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(50)));
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = RedisCacheManager.builder(lettuceConnectionFactory)
.cacheDefaults(defaultCacheConfig)
.initialCacheNames(cacheNames)
.withInitialCacheConfigurations(configMap)
.build();
return cacheManager;
}
}
3、配置文件 application.yml
server:
port: 8889
spring:
#redis配置
redis:
database: 0
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 6379
password:
lettuce:
pool:
# 连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制) 默认 8
max-active: 8
# 连接池最大阻塞等待时间,单位毫秒(使用负值表示没有限制) 默认 -1
max-wait: -1ms
# 连接池中的最小空闲连接
max-idle: 8
# 连接池中的最大空闲连接 默认 8
min-idle: 0
# 连接超时时间
timeout: 2000ms
cache:
type: redis
4 配置启动类-启动缓存
package com.shenju;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching //开启缓存
public class SpringbootRedisApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootRedisApplication.class, args);
}
}
5 缓存注解@Cacheable、@CacheEvict、@CachePut详解
5.1 注解使用的地方
用在方法上表示:该方法的返回值将被缓存起来。
用在类上表示:表示该类的所有方法都支持该注解。
5.2 key的生成策略
key属性是用来指定Spring缓存方法的返回结果时对应的key的。该属性支持SpringEL表达式。当我们没有指定该属性时,Spring将使用默认策略生成key。
自定义策略是指我们可以通过Spring的EL表达式来指定我们的key。这里的EL表达式可以使用方法参数及它们对应的属性。使用方法参数时我们可以直接使用“#参数名”或者“#p参数index”。下面是几个使用参数作为key的示例。
@Cacheable(value="users", key="#id")
public User find(Integer id) {
returnnull;
}
@Cacheable(value="users", key="#p0")
public User find(Integer id) {
returnnull;
}
@Cacheable(value="users", key="#user.id")
public User find(User user) {
returnnull;
}
@Cacheable(value="users", key="#p0.id")
public User find(User user) {
returnnull;
}
5.3 root对象的使用
除了上述使用方法参数作为key之外,Spring还为我们提供了一个root对象可以用来生成key。通过该root对象我们可以获取到以下信息。
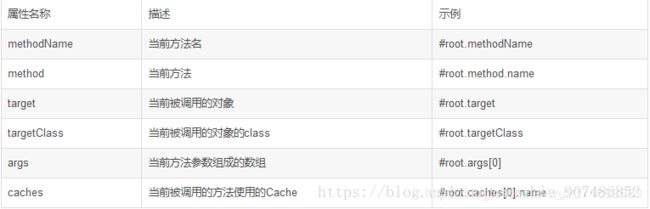
详细使用情况看我下面的案例和注释。
5.4 @CachePut
在支持Spring Cache的环境下,对于使用@Cacheable标注的方法,Spring在每次执行前都会检查Cache中是否存在相同key的缓存元素,如果存在就不再执行该方法,而是直接从缓存中获取结果进行返回,否则才会执行并将返回结果存入指定的缓存中。@CachePut也可以声明一个方法支持缓存功能。与@Cacheable不同的是使用@CachePut标注的方法在执行前不会去检查缓存中是否存在之前执行过的结果,而是每次都会执行该方法,并将执行结果以键值对的形式存入指定的缓存中。 一般使用在保存,更新方法中。
5.5 @CacheEvict
@CacheEvict是用来标注在需要清除缓存元素的方法或类上的。当标记在一个类上时表示其中所有的方法的执行都会触发缓存的清除操作。@CacheEvict可以指定的属性有value、key、condition、allEntries和beforeInvocation。其中value、key和condition的语义与@Cacheable对应的属性类似。即value表示清除操作是发生在哪些Cache上的(对应Cache的名称);key表示需要清除的是哪个key,如未指定则会使用默认策略生成的key;condition表示清除操作发生的条件。下面我们来介绍一下新出现的两个属性allEntries和beforeInvocation。
allEntries属性
allEntries是boolean类型,表示是否需要清除缓存中的所有元素。默认为false,表示不需要。当指定了allEntries为true时,Spring Cache将忽略指定的key。有的时候我们需要Cache一下清除所有的元素,这比一个一个清除元素更有效率。
beforeInvocation属性
清除操作默认是在对应方法成功执行之后触发的,即方法如果因为抛出异常而未能成功返回时也不会触发清除操作。使用beforeInvocation可以改变触发清除操作的时间,当我们指定该属性值为true时,Spring会在调用该方法之前清除缓存中的指定元素。该属性表示的是是否在方法执行前就清空,缺省为 false,如果指定为 true,则在方法还没有执行的时候就清空缓存,缺省情况下,如果方法执行抛出异常,则不会清空缓存。
6. 缓存注解的使用
6.1 user.java
package com.shenju;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class User implements Serializable{
private String name;
private int age;
public User() {
super();
}
public User(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
6.2 controller层
package com.shenju;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private CacheServiceImpl cacheServiceImpl;
/**
* targetClass和methodName的含义和使用
* 存储的key的样子
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(path="/findUserId",method= {RequestMethod.GET})
public int findUserId() {
User user=new User();
user.setName("wuk");
int result=cacheServiceImpl.findUserId(user);
return result;
}
/**
* #p0的使用和unless的使用
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(path="/listUser",method= {RequestMethod.GET})
public List<User> listUser() {
return cacheServiceImpl.listUser(2,3);
}
/**
* condition的使用
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(path="/finUser",method= {RequestMethod.GET})
public User findUser() {
User user=new User();
user.setName("wuk");
user.setAge(24);
user=cacheServiceImpl.findUser(user);
return user;
}
/**
* (1)Cacheable注解:
* Spring在每次执行前都会检查Cache中是否存在相同key的缓存元素,如果存在就不再执行该方法,
* 而是直接从缓存中获取结果进行返回,否则才会执行并将返回结果存入指定的缓存中。
* (2)CachePut注解:
* 与@Cacheable不同的是使用@CachePut标注的方法在执行前不会去检查缓存中是否存在之前执行过的结果,
* 而是每次都会执行该方法,并将执行结果以键值对的形式存入指定的缓存中。
* (3)使用@CachePut时我们可以指定的属性跟@Cacheable是一样的。
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(path="/save",method= {RequestMethod.GET})
public User save() {
User user=new User();
user.setName("zhangsan");
user.setAge(24);
user=cacheServiceImpl.save(user);
return user;
}
/**
* (1)CacheEvict注解是用来标注在需要清除缓存元素的方法或类上的 当标记在一个类上时表示其中所有的方法的执行都会触发缓存的清除操作
* (2)CacheEvict可以指定的属性有value、key、condition、allEntries和beforeInvocation
* (3)value表示清除操作是发生在哪些Cache上的(对应Cache的名称)
* (4)key表示需要清除的是哪个key,如未指定则会使用默认策略生成的key
* (5)condition表示清除操作发生的条件
* (6)allEntries属性 allEntries是boolean类型,表示是否需要清除缓存中的所有元素。默认为false
* (7)beforeInvocation属性 清除操作默认是在对应方法成功执行之后触发的,即方法如果因为抛出异常而未能成功返回时也不会触发清除操作
* 使用beforeInvocation可以改变触发清除操作的时间,当我们指定该属性值为true时,Spring会在调用该方法之前清除缓存中的指定元素。
*/
@RequestMapping(path="/delete",method= {RequestMethod.GET})
public void delete() {
}
}
6.3 服务层
package com.shenju;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class CacheServiceImpl {
/**
* 1 这里面的targetClass=#root.targetClass methodName=#root.methodName
* 2 存储的key为 user::class com.shenju.CacheServiceImpl:findUserId_wuk
*
* @return
*/
@Cacheable(value = "user", key = "targetClass + ':' + methodName + '_' + #p0.name")
public int findUserId(User user) {
System.out.println("执行find方法.....");
return 1;
}
/**
* 1 #p0 表示第一个参数
* 2 存储的key为 user::class com.shenju.CacheServiceImpl:listUser_2
* 3 unless 缓存条件:判断unless,如果返回false,则放入缓存
* 4 #result 表示的是返回结果
*/
@Cacheable(value = "user", key = "targetClass + ':' + methodName + '_' + #p0", unless = "#result.size() <= 0")
public List<User> listUser(int pageNum, int pageSize) {
System.out.println("执行listUser方法。。。。");
List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
users.add(new User("zhengsan", 22));
users.add(new User("lisi", 20));
return users;
}
/**
* 1 存储的key为: user::class com.shenju.CacheServiceImpl:findUser_wuk
* 2 condition 表示的是缓存的条件,只有当为true
*
*/
@Cacheable(value = "user", key = "targetClass + ':' + methodName + '_' + #p0.name", condition="#user.age==25")
public User findUser(User user) {
System.out.println("执行findUser方法。。。。");
user.setName("wukaikai");
return user;
}
@CachePut(value = "user", key = "targetClass + ':' + methodName + '_' + #p0.name")
public User save(User user) {
System.out.println("执行save方法。。。。");
return user;
}
}