小熊派移植 TencentOS-tiny+EC20+SAL框架对接 TCP/UDP 服务器
1. SAL套接字抽象层
SAL全称Socket Abstract Layer,即套接字抽象层,主要作用是对上层应用提供统一的 socket 编程接口,屏蔽底层网络硬件的差异。
1.1. SAL层向下提供的接口
SAL层向下提供的接口在net/sal_module_wrapper/sal_module_wrapper.h文件中声明,如下:
typedef struct sal_module_st {
int (*init)(void);
int (*get_local_mac)(char *mac);
int (*get_local_ip)(char *ip, char *gw, char *mask);
int (*parse_domain)(const char *host_name, char *host_ip, size_t host_ip_len);
int (*connect)(const char *ip, const char *port, sal_proto_t proto);
int (*send)(int sock, const void *buf, size_t len);
int (*recv_timeout)(int sock, void *buf, size_t len, uint32_t timeout);
int (*recv)(int sock, void *buf, size_t len);
int (*sendto)(int sock, char *ip, char *port, const void *buf, size_t len);
int (*recvfrom)(int sock, void *buf, size_t len);
int (*recvfrom_timeout)(int sock, void *buf, size_t len, uint32_t timeout);
int (*close)(int sock);
} sal_module_t;
这些接口需要用户实现,一般使用AT框架与模组通信实现,也就是常说的通信模组驱动,比如device文件夹下存放的ESP2866、M26、EC20这些驱动:

以本节文章使用的EC20为例,实现接口的代码如下:
sal_module_t sal_module_ec20 = {
.init = ec20_init,
.connect = ec20_connect,
.send = ec20_send,
.recv_timeout = ec20_recv_timeout,
.recv = ec20_recv,
.close = ec20_close,
.parse_domain = ec20_parse_domain,
};
实现之后调用tos_sal_module_register注册到系统中,如下:
if (tos_sal_module_register(&sal_module_ec20) != 0) {
return -1;
}
1.2. SAL层向上提供的API
SAL层提供了以下的API供上层网络应用程序调用:
- 声明:
net/sal_module_wrapper/sal_module_wrapper.h - 实现:
net/sal_module_wrapper/sal_module_wrapper.c
tos_sal_module_register
int tos_sal_module_register(sal_module_t *module);
-
功能描述
注册一个联网模组
-
参数解释
IN/OUT 参数名 描述 [in] module 联网模组句柄 -
返回值
0,返回成功。
-1,返回失败。
tos_sal_module_init
int tos_sal_module_init(void);
-
功能描述
初始化模组
-
参数解释
无
-
返回值
0,返回成功。
-1,返回失败。
tos_sal_module_parse_domain
int tos_sal_module_parse_domain(const char *host_name, char *host_ip);
-
功能描述
域名解析,将一个域名转换为IP地址。
-
参数解释
IN/OUT 参数名 描述 [in] host_name 待解析的域名 [out] host_ip 解析后的IP地址 -
返回值
0,返回成功。
-1,返回失败。
tos_sal_module_connect
int tos_sal_module_connect(const char *ip, const char *port, sal_proto_t proto);
-
功能描述
向远端发起连接
-
参数解释
IN/OUT 参数名 描述 [in] ip IP地址 [in] port 端口 [in] proto TCP/UDP协议 -
返回值
成功,则返回连接的socket id。
失败,返回-1。
tos_sal_module_send
int tos_sal_module_send(int sock, const void *buf, size_t len);
-
功能描述
向远端发送数据(TCP协议栈)
-
参数解释
IN/OUT 参数名 描述 [in] sock socket id(由tos_sal_module_connect获取) [in] buf 发送的数据起始地址 [in] len 发送的数据长度 -
返回值
发送的数据长度。
tos_sal_module_recv
int tos_sal_module_recv(int sock, void *buf, size_t len);
-
功能描述
从远端读取数据(TCP协议栈)
-
参数解释
IN/OUT 参数名 描述 [in] sock socket id(由tos_sal_module_connect获取) [out] buf 接收数据buffer [in] len 接收数据buffer长度 -
返回值
实际接收到的数据长度。
tos_sal_module_recv_timeout
int tos_sal_module_recv_timeout(int sock, void *buf, size_t len, uint32_t timeout);
-
功能描述
从远端接收数据(TCP协议栈)
-
参数解释
IN/OUT 参数名 描述 [in] sock socket id(由tos_sal_module_connect获取) [in] buf 数据起始地址 [in] len 数据长度 [in] timeout 超时参数 -
返回值
实际接收到的数据长度。
tos_sal_module_sendto
int tos_sal_module_sendto(int sock, char *ip, char *port, void *buf, size_t len);
-
功能描述
向远端发送数据(UDP协议栈)
-
参数解释
IN/OUT 参数名 描述 [in] sock socket id(由tos_sal_module_connect获取) [in] ip IP地址 [in] port 端口 [in] buf 待发送数据起始地址 [in] len 待发送数据长度 -
返回值
发送的数据长度。
tos_sal_module_recvfrom
int tos_sal_module_recvfrom(int sock, char *ip, char *port, void *buf, size_t len);
-
功能描述
从远端接收数据(UDP协议栈)
-
参数解释
IN/OUT 参数名 描述 [in] sock socket id(由tos_sal_module_connect获取) [in] ip IP地址 [in] port 端口 [in] buf 接收数据buffer起始地址 [in] len 接收数据buffer长度 -
返回值
实际接收到的数据长度。
tos_sal_module_close
int tos_sal_module_close(int sock);
-
功能描述
关闭与远端的连接
-
参数解释
IN/OUT 参数名 描述 [in] sock socket id(由tos_sal_module_connect获取) -
返回值
0,返回成功。
-1,返回失败。
2. 搭建TCP服务器
服务器使用Python编写,本文中开启两个TCP服务器,一个监听8080端口,另一个接收8001端口:
# tcpserver.py
from socket import *
host = ''
#第一个程序监听8080,第二个程序监听8001端口
port = 8080
# 创建server socket
server_socket = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM)
# 绑定socket监听地址
server_addr = (host,port)
server_socket.bind(server_addr)
# 开始监听,最大允许连接数5
server_socket.listen(5)
# 处理连接请求
try:
while True:
print('waiting for connect...')
#阻塞等待客户端的连接
client_socket, client_addr = server_socket.accept()
# 连接成功后,打印客户端信息
print('a client connnect from:', client_addr)
while(True):
# 向客户端发送数据
client_socket.send('Hello, client!'.encode())
# 接收客户端的数据
data = client_socket.recv(1024)
print('recv data is ', data.decode())
# 接收到quit则关闭socket
if "quit" in data.decode():
break
# 关闭socket
client_socket.close()
server_socket.close()
print("socket closed.")
break
except:
client_socket.close()
server_socket.close()
print("socket closed.")
在服务器上开启第一个监听程序:

在服务器上开启第二个监听程序:
![]()
3. 创建TCP测试工程
在helloworld工程的基础上开始创建TCP测试工程。
3.1. 添加C文件
首先添加串口的HAL驱动,此驱动和具体的硬件平台相关,在platform\hal\st\stm32l4xx\src路径中:
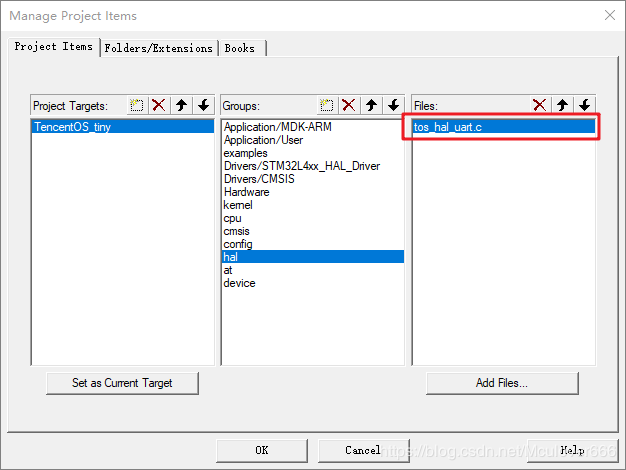
再添加SAL框架的源码,在net\sal_module_wrapper路径中:

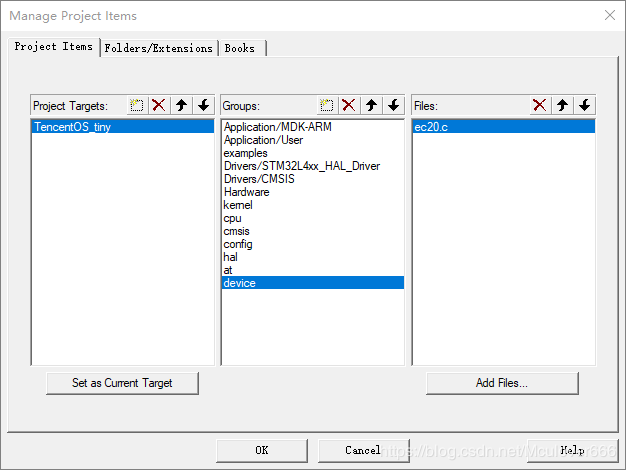
最后添加EC20的设备驱动,在devices\ec20路径中:
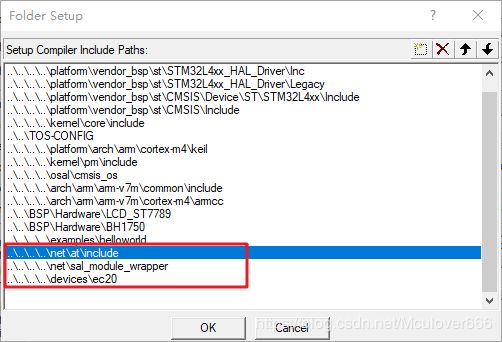
3.2. 添加头文件路径
3.3. 添加demo测试文件
移植helloworld示例程序,添加位于examples\tcp_through_module路径下的示例文件:

示例程序是使用ESP8266的,修改使用EC20:
① 修改头文件:
//#include "esp8266.h"
#include "ec20.h"
//#define USE_ESP8266
#define USE_EC20
② 修改模组初始化
#ifdef USE_EC20
ec20_sal_init(HAL_UART_PORT_0);
#endif
③ 修改ip:
socket_id_0 = tos_sal_module_connect("117.50.111.72", "8080", TOS_SAL_PROTO_TCP);
...
socket_id_1 = tos_sal_module_connect("117.50.111.72", "8001", TOS_SAL_PROTO_TCP);
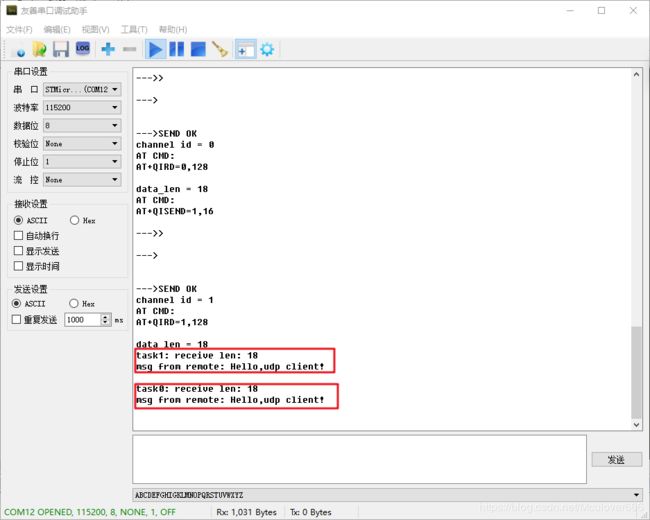
接下来编译、下载、在串口终端查看实验结果:

在第一个服务器可以看到模组发送的小修:

在第二个服务器可以看到模组发送的不同消息:

4. 搭建UDP服务器
# udp-server.py
from socket import *
host = ''
#第一个程序为8001,二个程序为8081
port = 8001
# 创建server socket
server_socket = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_DGRAM)
# 绑定socket监听地址
server_addr = (host,port)
server_socket.bind(server_addr)
print('UDP Server Start...')
# 处理连接请求
while(True):
# 接收客户端的数据
data, addr = server_socket.recvfrom(1024)
print("Receive from %s:%s" % addr % data)
if data == b"quit":
server_socket.sendto(b"Good bye!\n", addr)
continue
server_socket.sendto(b"Hello,udp client!\n", addr)
第一个程序启动后如图:
第二个程序启动后如图:
5. 创建DUP测试工程
同样进行修改。
① 修改头文件:
//#include "esp8266.h"
#include "ec20.h"
...
//#define USE_ESP8266
#define USE_EC20
② 修改初始化:
#ifdef USE_EC20
ec20_sal_init(HAL_UART_PORT_0);
#endif
③ 修改ip和端口:
socket_id_0 = tos_sal_module_connect("117.50.111.72", "8002", TOS_SAL_PROTO_UDP);
...
socket_id_1 = tos_sal_module_connect("117.50.111.72", "8081", TOS_SAL_PROTO_UDP);
在第一个服务器程序可以看到模组发送的数据:

在第二个服务器程序可以看到模组发送的数据:

至此,测试完成。
接收更多精彩文章及资源推送,欢迎订阅我的微信公众号:『mculover666』。
![]()