接下来我们来讨论OOM的问题。
在做美食生活的项目的时候,有个功能是拍照上传图片的功能,没有对图片进行压缩,直接进行了上传,11-21 22:05:28.774: E/dalvikvm-heap(13216): Out of memory on a 10485476-byte allocation.
11-21 22:05:28.784: E/AndroidRuntime(13216): java.lang.OutOfMemoryError
好了,出现了我们的OOM了!
一般造成OOM的最大的原因是Bitmap,Bitmap,Bitmap重要的事情说三遍!
一般的OOM经常出现在加载很多图片或者是加载高清大图的时候!当一个app启动后,虚拟机不停的申请内存资源来装载图片,当超过内存上限时就出现OOM。这个现象如果你在跑monkey进行测试的时候更容易出现!
Android的APP内存组成:
APP内存由 dalvik内存 和 native内存2部分组成,dalvik也就是java堆,创建的对象就是就是在这里分配的,而native是通过c/c++方式申请的内存,Bitmap就是以这种方式分配的。(android3.0以后,系统都默认通过dalvik分配的,native作为堆来管理)。这2部分加起来不能超过android对单个进程,虚拟机的内存限制。
从代码中获取每个手机的内存限制大小:
ActivityManager activityManager = (ActivityManager)context.getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE)
activityManager.getMemoryClass();
而对于head堆的大小限制,可以查看/system/build.prop文件。
dalvik.vm.heapstartsize = 5m
dalvik.vm.heapgrowthlimit = 48m
dalvik.vm.heapsize = 256m
注: heapsize参数表示单个进程heap可用的最大内存,但如果存在以下参数"dalvik.vm.headgrowthlimit =48m"表示单个进程heap内存被限定在48m,即程序运行过程实际只能使用48m内存。
怎么查看APP内存分配情况?
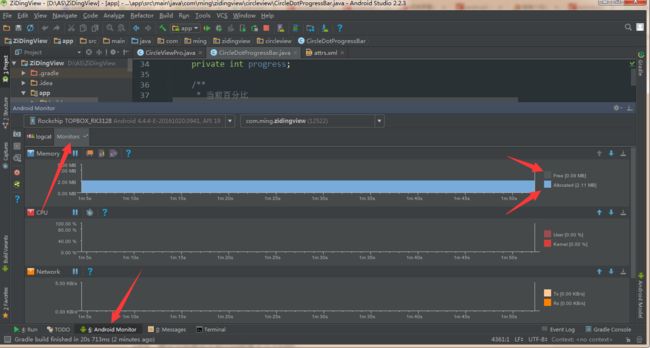
1 在我们的AS中可以通过Monitor监控得到
2 在App里面我们可以通过totalMemory与freeMemory:
Runtime.getRuntime().freeMemory()
RUntime.getRuntime().totalMemory()
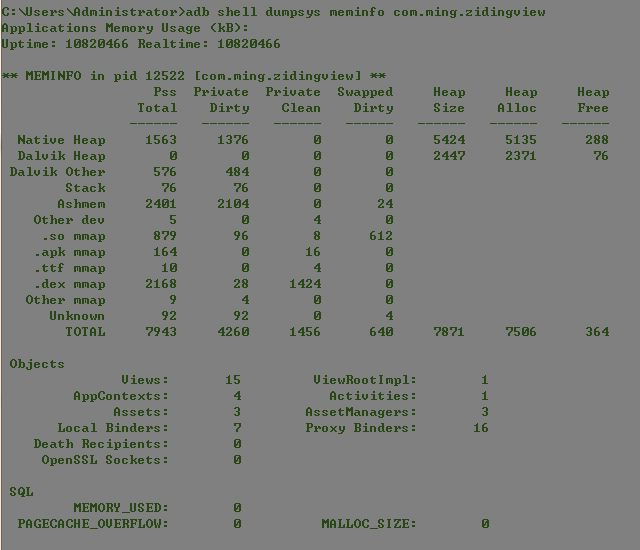
3 adb shell dumpsys meminfo com.android.demo
这个是adb命令了,com.android.demo是包名。不会的可以去看我的另一篇博客:ADB 常用命令及详解
常见避免OOM的几个注意点:
适当调整图像大小 。因为手机屏幕尺寸有限,分配给图像的显示区域有限,尤其对于超大图片,加载自网络或者sd卡,图片文件提及达到几M或者十几个M的:
加载到内存前,先算出该bitmap的大小,然后通过适当调节采样率使得加载的图片刚好,或稍大在手机屏幕上显示就满意了:
BimtapFactory.Option opts = new BitampFactory.Option();
opts.inJustDecodeBounds = true ;
opts.inSampleSize=computeSample(opts, minSideLength, maxNumOfPixels); // Android 提供了一种动态计算的方法 computeSampleSize
opts.inJustDecodeBounds = false ;
try {
return BitmapFactory.decodeFile(imageFile, opts);
} catch (OutOfMemoryError err){
图像缓存
在listview或Gallery等控件中一次性加载大量图片时,只加载屏幕显示的资源,尚未显示的不加载,移出屏幕的资源及时释放,采用强引用+软引用2级缓存,提高加载性能。缓存图像到内存,采用软引用缓存到内存,而不是在每次使用的时候都从新加载到内存。
及时回收图像 。
如果引用了大量的Bitmap对象,而应用又不需要同时显示所有图片。可以将暂时不用到的Bitmap对象及时回收掉。对于一些明确直到图片使用情况的场景可以主动recycle回收
App的启动splash画面上的图片资源,使用完就recycle。对于帧动画,可以加载一张,画一张,释放一张。
不要在循环中创建过多的本地变量 。
慎用static,用static来修饰成员变量时,该变量就属于该类,而不是该类实例,它的生命周期是很长的。如果用它来引用一些内存占用太多的实例,这时候就要谨慎对待了。
重点要来了!!!
对于图App使用图片时避免OOM的几种方式有三四种,我只讲一种:
LruCache + sd的缓存方式 :##
很多图片处理框架和网络请求框架都已经做了三级缓存技术,所以在使用框架加载图片时,利用好他们给的API和方法就行了。
如果就是简单的保存几张图片,简单的缓存,不想引入框架,那么可以看看这个!
/**
* Bitmap缓存,简单缓存的设置类.
* Created by ChangMingShan on 2016/12/26.
*/
public class BitmapMemoryCache {
private static final String TAG = "BitmapMemoryCache";
private static BitmapMemoryCache sInstance = new BitmapMemoryCache();
private LruCache mMemoryCache;
/**
* 单例模式.
*/
public static BitmapMemoryCache getInstance() {
return BitmapMemoryCache.sInstance;
}
private BitmapMemoryCache() {
int maxMemory = (int) (Runtime.getRuntime().maxMemory() / 1024);
int cacheSize = maxMemory / 8;
mMemoryCache = new LruCache(cacheSize) {
@Override
protected int sizeOf(String key, Bitmap bitmap) {
// 重写此方法来衡量每张图片的大小,默认返回图片数量。
return bitmap.getByteCount() / 1024;
}
};
}
public synchronized void addBitmapToMemoryCache(String key, Bitmap bitmap) {
if (mMemoryCache.get(key) == null) {
if (key != null && bitmap != null)
mMemoryCache.put(key, bitmap);
} else
Log.w(TAG, "the res is aready exits");
}
public synchronized Bitmap getBitmapFromMemCache(String key) {
Bitmap bm = mMemoryCache.get(key);
if (key != null) {
return bm;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 移除缓存
*
* @param key
*/
public synchronized void removeImageCache(String key) {
if (key != null) {
if (mMemoryCache != null) {
Bitmap bm = mMemoryCache.remove(key);
if (bm != null)
bm.recycle();
}
}
}
/**
* 移除缓存
*/
public synchronized void clearImageCache() {
if (mMemoryCache != null) {
if (mMemoryCache.size() > 0) {
Log.d("CacheUtils",
"mMemoryCache.size() " + mMemoryCache.size());
mMemoryCache.evictAll();
Log.d("CacheUtils", "mMemoryCache.size()" + mMemoryCache.size());
}
mMemoryCache = null;
}
}
public void clearCache() {
if (mMemoryCache != null) {
if (mMemoryCache.size() > 0) {
Log.d("CacheUtils",
"mMemoryCache.size() " + mMemoryCache.size());
mMemoryCache.evictAll();
Log.d("CacheUtils", "mMemoryCache.size()" + mMemoryCache.size());
}
mMemoryCache = null;
}
}
public Bitmap loadLocal(String path) {/*这是加载本地的图片的步骤*/
Bitmap bitmap=BitmapFactory.decodeFile(path);
addBitmapToMemoryCache(path, bitmap);
return getBitmapFromMemCache(path);
}
/*
将图片进行压缩代码,本次未用到
BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
options.inJustDecodeBounds = false; // 设置了此属性一定要记得将值设置为false
Bitmap bitmap = null;
bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeFile(url, options);
int be = (int) ((options.outHeight > options.outWidth ? options.outHeight / 150
: options.outWidth / 200));
if (be <= 0) // 判断200是否超过原始图片高度
be = 1; // 如果超过,则不进行缩放
options.inSampleSize = be;
options.inPreferredConfig = Bitmap.Config.ARGB_4444;
options.inPurgeable = true;
options.inInputShareable = true;
options.inJustDecodeBounds = false;
try {
bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeFile(url, options);
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
System.gc();
Log.e(TAG, "OutOfMemoryError");
}
*/
}
我们可以这样定义:map里面的键是用来放图片地址的,既可以是网络上的图片地址,也可以SDcard上的图片地址,
map里面的值里面放的是持有软引用的Bitmap
/**
* Bitmap缓存网络图片或者是本地图片,简单缓存.
* Created by ChangMingShan on 2016/12/26.
*/
public class SaveBitmapMemoryCache {
private Map> imageMap = new HashMap>();
private static final String TAG = "NetBitmapMemoryCache";
public Bitmap loadBitmap(final String imageUrl,final ImageCallBack imageCallBack) {
SoftReference reference = imageMap.get(imageUrl);
if(reference != null) {
if(reference.get() != null) {
return reference.get();
}
}
final Handler handler = new Handler() {
public void handleMessage(final android.os.Message msg) {
//加入到缓存中
Bitmap bitmap = (Bitmap)msg.obj;
imageMap.put(imageUrl, new SoftReference(bitmap));
if(imageCallBack != null) {
imageCallBack.getBitmap(bitmap);
}
}
};
new Thread(){
public void run() {
Message message = handler.obtainMessage();
message.obj = downloadBitmap(imageUrl);
handler.sendMessage(message);
}
}.start();
return null ;
}
// 从网上下载图片
private Bitmap downloadBitmap (String imageUrl) {
Bitmap bitmap = null;
try {
bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(new URL(imageUrl).openStream());
return bitmap ;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/* public static boolean saveUrlAs(String fileUrl, String savePath)/*fileUrl网络资源地址*/
{//这是将图片缓存到本地的代码,此次也未用到,用到改一下就ok
try
{
URL url = new URL(fileUrl);/*将网络资源地址传给,即赋值给url*/
HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection)url.openConnection();
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(connection.getInputStream());
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(savePath));
byte[] buffer = new byte[4096];
int count = 0;
while ((count = in.read(buffer)) > 0)/*将输入流以字节的形式读取并写入buffer中*/
{
out.write(buffer, 0, count);
}
out.close();/*前额安吉的将流关闭*/
in.close();
connection.disconnect();
return true; /*网络资源截取并存储本地成功返回true*/
}
catch (Exception e)
{
return false;
}*/
}
public interface ImageCallBack{
void getBitmap(Bitmap bitmap);
}
}
如果能将Bitmap这个东西解决好,你的OOM基本不怎么会出现了,不建议修改系统或者是dalvike里面的东西。
还有一些OOM情况出现在加载非常多条目信息的listview,gridview等的情况,在这里推荐使用Recyclerview或者在这些adapter的getView函数里有个convertView参数。