仓库管理系统报告
一、项目背景
仓库信息管理系统:实现进库出库、展示仓库信息、支持查询功能、数据的长久保存
二、实现环境
1. WSL
2. clang version 10.0.0
Target: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
(c环境都能跑哦~)
三、报告正文
- 实现方法
- 数据使用文件保存
- 采用函数模块化编程思想
- 使用了必要的结构体
- 重要的数据结构
typedef struct{
char name[100];
int count;
}Goods; // 物品结构体,其成员为物品名称和数量。
typedef struct{
Goods goods[50];
int count;
}Store; // 仓库结构体,成员是物品类数组和目前已存进的数目
- 实现过程
- main函数
- 调用
void Init_Store()函数,读取文件数据,初始化全局变量store及其成员 - 使用
switch分支结构,进行每次操作选择
- 调用
- 初始化
- 主控函数
void Init_Store()- 定义文件指针
FILE *fp,只读权限 - 通过
feof(fp)保证文件完成读取,同时更新仓库store内容 - 完成后关闭文件
- 定义文件指针
- 主控函数
- 入库
- 主控函数
int add_to_list(char name[], int count)- 调用函数
int InStore(char name[]),查找该物品是否已经存在 - 若已存在(即返回值不是FALSE),调用函数
int increase_count(char name[], int count, int pos);更新store变量和data.txt数据存储文件 - 若不存在(即返回值为具体下标),调用函数
int add_to_list(char name[], int count);更新store变量和data.txt数据存储文件
- 调用函数
int increase_count(char name[], int count, int pos)- 说明该物品在仓库中已存在,通过下标修改物品数量
int add_to_list(char name[], int count)- 判断仓库是否已满(
store.count > 50 ?) - 判断存储物品的名称是否合法(
strlen(name) > 100 ?) - 若合法,则将物品添加到
store.goods数组末尾;若不合法,则添加失败
- 判断仓库是否已满(
- 主控函数
- 出库
- 主控函数
int delete_goods(char namep[], int count)- 调用函数
int InStore(char name[]),查找仓库中是否有该物品;若不存在则报错 - 获取到物品目前数量,与需取出相比较
- 物品数量不足,取出失败
- 数量恰好,调用函数
int delete_from_list(char name[], int pos) - 数量大于需求,调用函数
int decrease_count(char name[], int count, int pos)
- 取出完成,更新
store变量和data.txt数据存储文件
- 调用函数
int delete_from_list(char name[], int pos)- 判断要删除的位置是否在数组末尾
- 若不是,则删除目前位置内容;并将该位置之后的内容依次向前挪一个单元
- 将数组末尾初始化置为0;
store.count --
int decrease_count(char name[], int count, int pos)- 通过下标修改物品数量
- 主控函数
- 查找
- 遍历仓库
void show_goods() - 查找物品
Goods find_goods(char name[])- 调用函数
int InStore(char name[]) - 若未找到,则返回一个空goods;若找到,则返回变量内容
- 调用函数
- 遍历仓库
- 辅助函数
int InStore(char name[])遍历函数- 查找
store中是否有name - 若有,则返回对应下标;若无,则返回
FALSE
- 查找
void Write_tofile()更新文件函数- 只写方式打开
data.txt - 将
store.goods[]写入,并控制写入格式
- 只写方式打开
- main函数
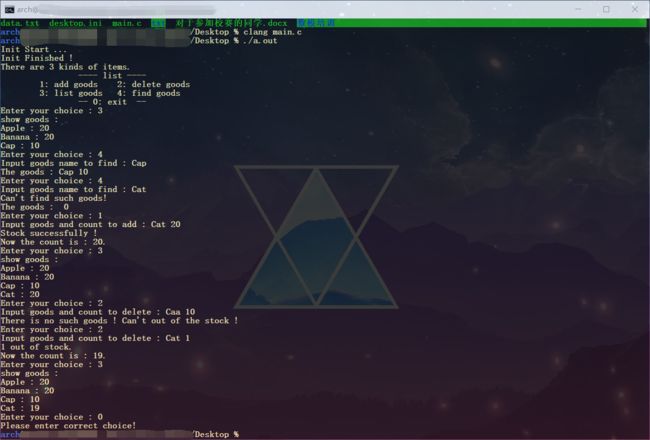
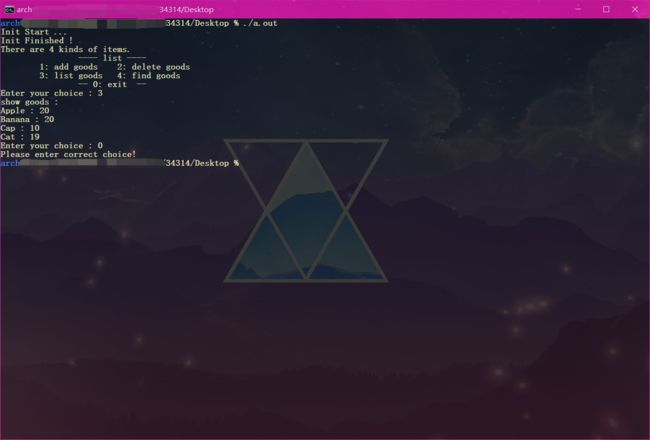
- 测试
- 总结
就简单的写写 ... 题目中也没要求太多 ...
UI使用qt或者MFC都是不错的选择 ...
或者使用一些宏渲染一下颜色什么的都是可以的 ...
然后也没有进行异常处理 ... 只进行了警告和函数控制 ...
对于程序消耗,struct Store是起控制作用的结构体,完全可以用指针来代替定长数组 ... and so on
就这样吧 ... - 源码
#include
#include
#include
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE -1
typedef struct{
char name[100];
int count;
}Goods;
typedef struct{
Goods goods[50];
int count;
}Store;
Store store;
void Init_Store()
{
printf("Init Start ...\n");
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("data.txt","r");
if(fp == NULL) {
printf("No such file !\n");
exit(0);
}
while(1) {
if(feof(fp)) break;
fscanf(fp, "%s%d", store.goods[store.count].name, &store.goods[store.count].count);
store.count++;
}
fclose(fp);
printf("Init Finished !\n");
printf("There are %d kinds of items.\n", store.count);
}
int InStore(char name[])
{
int i = 0;
for(;i < store.count; ++ i){
if(strcmp(name, store.goods[i].name) == 0)
return i;
}
return FALSE;
}
void Write_tofile()
{
FILE *fp = NULL;
fp = fopen("data.txt","w");
int i = 0;
while(i < store.count) {
fprintf(fp, "%s %d", store.goods[i].name, store.goods[i].count);
if(i != store.count-1) {
fprintf(fp, "\n");
}
i++;
}
fclose(fp);
}
int increase_count(char name[], int count, int pos)
{
store.goods[pos].count += count;
printf("The items already exist and have increased %d.\nNow the count is : %d.\n", count, store.goods[pos].count);
return TRUE;
}
int add_to_list(char name[], int count)
{
if(store.count > 50) {
printf("No more space for this goods ! Can't be stocked !\n");
return FALSE;
}
if(strlen(name) > 100) {
printf("Name's length over 100! Can't be stocked !\n");
return FALSE;
}
strcpy(store.goods[store.count].name, name);
store.goods[store.count].count = count;
printf("Stock successfully !\nNow the count is : %d.\n", store.goods[store.count].count);
store.count ++;
return TRUE;
}
int add_goods(char name[], int count)
{
int instore = InStore(name);
if(instore != FALSE) {
increase_count(name, count, instore);
Write_tofile();
return TRUE;
}
add_to_list(name, count);
Write_tofile();
return 0;
}
int decrease_count(char name[], int count, int pos)
{
store.goods[pos].count -= count;
printf("%d out of stock.\nNow the count is : %d.\n", count, store.goods[pos].count);
return TRUE;
}
int delete_from_list(char name[], int pos)
{
if(pos != store.count-1) {
for(;pos < store.count-1;) {
strcpy(store.goods[pos].name, store.goods[pos+1].name);
store.goods[pos].count = store.goods[pos+1].count;
pos ++;
}
}
store.goods[pos].name[0] = '\0';
store.goods[pos].count = 0;
store.count --;
printf("Out of stock and delete from list.\n");
return TRUE;
}
int delete_goods(char name[], int count)
{
int instore = InStore(name);
if(instore == FALSE) {
printf("There is no such goods ! Can't out of the stock !\n");
return FALSE;
}
int goods_count = store.goods[instore].count;
if(goods_count < count) {
printf("The %s goods isn't enough !\nNow the count is : %d.\n", name, goods_count);
return FALSE;
} else if(goods_count == count) {
delete_from_list(name, instore);
} else if(goods_count > count) {
decrease_count(name, count, instore);
}
Write_tofile();
return TRUE;
}
void show_goods()
{
int i = 0;
printf("show goods : \n");
for(;i < store.count;i ++) {
printf("%s : %d\n",store.goods[i].name, store.goods[i].count);
}
}
Goods find_goods(char name[])
{
int instore = InStore(name);
if(instore == FALSE) {
printf("Can't find such goods!\n");
Goods goods;
goods.count = 0;
goods.name[0] = '\0';
return goods;
}
return store.goods[instore];
}
int main()
{
Init_Store();
printf(" ---- list ---- \n");
printf(" 1: add goods 2: delete goods\n");
printf(" 3: list goods 4: find goods\n");
printf(" -- 0: exit -- \n");
int choice = 1;
while(choice!=0) {
printf("Enter your choice : ");
scanf("%d",&choice);
switch(choice) {
case 1:{
char str[100];
int count;
printf("Input goods and count to add : ");
scanf("%s%d", str, &count);
add_goods(str, count);
break;
}
case 2:{
char str[100];
int count;
printf("Input goods and count to delete : ");
scanf("%s%d", str, &count);
delete_goods(str, count);
break;
}
case 3:{
show_goods();
break;
}
case 4:{
char str[100];
printf("Input goods name to find : ");
scanf("%s",str);
Goods temp = find_goods(str);
printf("The goods : %s %d\n", temp.name, temp.count);
break;
}
default:{
printf("Please enter correct choice!\n");
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}