Java Swing 学习笔记
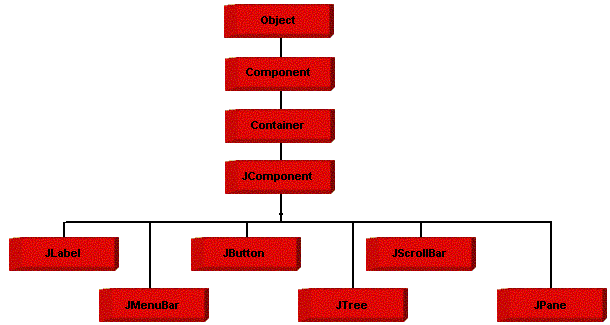
Java Swing class hierarchy
The class JComponent, descended directly from Container, is the root class for most of Swing’s user interface components.
JFrame:
JFrame Features
It’s a window with title, border, (optional) menu bar and user-specified components.
It can be moved, resized, iconified.
It is not a subclass of JComponent.
Delegates responsibility of managing user-specified components to a content pane, an instance of JPanel.
Crating a JFrame Window
Step 1: Construct an object of the JFrame class.
Step 2: Set the size of the Jframe.
Step 3: Set the title of the Jframe to appear in the title bar (title bar will be blank if no title is set).
Step 4: Set the default close operation. When the user clicks the close button, the program stops running.
Step 5: Make the Jframe visible例子:
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class JFrameDemo {
public static void main(String s[]) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("JFrame Source Demo");
// Add a window listner for close button
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
// This is an empty content area in the frame
JLabel jlbempty = new JLabel("");
jlbempty.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(175, 100));
frame.getContentPane().add(jlbempty, BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
} 关于Pack方法:
在 Frame 类中有一个从类 java.awt.Window 继承的方法 pack() 。pack最初在window类中定义的,就是让容器适应内部控件的大小, 比如你在对话框上显示一个图片,就可以让对话框根据当前图片的大小来调整自己的大小。 当然,如果调用了pack()之后又对这个容器强制使用setSize(),那么pack()将失效。
public void pack()
调整此窗口的大小,以适合其子组件的首选大小和布局。如果该窗口和/或其所有者仍不可显示,则两者在计算首选大小之前变得可显示。在计算首选大小之后,将会验证该 Window。
JInternalFrame
A JInternalFrame is confined to a visible area of a container it is placed in. JInternalFrame a top level swing component that has a contentpane.
- It can be iconified — in this case the icon remains in the main application container.
- It can be maximized — Frame consumes the main application
- It can be closed using standard popup window controls
- It can be layered
例子:
package swing;
import javax.swing.JInternalFrame;
import javax.swing.JDesktopPane;
import javax.swing.JMenu;
import javax.swing.JMenuItem;
import javax.swing.JMenuBar;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class JInternalFrameDemo extends JFrame {
JDesktopPane jdpDesktop;
static int openFrameCount = 0;
public JInternalFrameDemo() {
super("JInternalFrame Usage Demo");
// Make the main window positioned as 50 pixels from each edge of the
// screen.
int inset = 50;
Dimension screenSize = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getScreenSize();
setBounds(inset, inset, screenSize.width - inset * 2,
screenSize.height - inset * 2);
// Add a Window Exit Listener
addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
// Create and Set up the GUI.
jdpDesktop = new JDesktopPane();
// A specialized layered pane to be used with JInternalFrames
createFrame(); // Create first window
setContentPane(jdpDesktop);
setJMenuBar(createMenuBar());
// Make dragging faster by setting drag mode to Outline
jdpDesktop.putClientProperty("JDesktopPane.dragMode", "outline");
}
protected JMenuBar createMenuBar() {
JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar();
JMenu menu = new JMenu("Frame");
menu.setMnemonic(KeyEvent.VK_N);
JMenuItem menuItem = new JMenuItem("New IFrame");
menuItem.setMnemonic(KeyEvent.VK_N);
menuItem.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
createFrame();
}
});
menu.add(menuItem);
menuBar.add(menu);
return menuBar;
}
protected void createFrame() {
MyInternalFrame frame = new MyInternalFrame();
frame.setVisible(true);
// Every JInternalFrame must be added to content pane using JDesktopPane
jdpDesktop.add(frame);
try {
frame.setSelected(true);
} catch (java.beans.PropertyVetoException e) {
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
JInternalFrameDemo frame = new JInternalFrameDemo();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
class MyInternalFrame extends JInternalFrame {
static final int xPosition = 30, yPosition = 30;
public MyInternalFrame() {
super("IFrame #" + (++openFrameCount), true, // resizable
true, // closable
true, // maximizable
true);// iconifiable
setSize(300, 300);
// Set the window's location.
setLocation(xPosition * openFrameCount, yPosition
* openFrameCount);
}
}
}