前提
这篇文章是《SpringBoot2.x入门》专辑的第3篇文章,使用的SpringBoot版本为2.3.1.RELEASE,JDK版本为1.8。
主要介绍SpringBoot的web模块引入,会相对详细地分析不同的Servlet容器(如Tomcat、Jetty等)的切换,以及该模块提供的SpringMVC相关功能的使用。
依赖引入
笔者新建了一个多模块的Maven项目,这次的示例是子模块ch1-web-module。
SpringBoot的web模块实际上就是spring-boot-starter-web组件(下称web模块),前面的文章介绍过使用BOM全局管理版本,可以在(父)POM文件中添加dependencyManagement元素:
2.3.1.RELEASE
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-dependencies
${spring.boot.version}
import
pom
接来下在(子)POM文件中的dependencies元素引入spring-boot-starter-web的依赖:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
项目的子POM大致如下:
4.0.0
club.throwable
spring-boot-guide
1.0-SNAPSHOT
ch1-web-module
1.0-SNAPSHOT
jar
ch1-web-module
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
ch1-web-module
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
${spring.boot.version}
repackage
spring-boot-starter-web模块中默认使用的Servlet容器是嵌入式(Embedded)Tomcat,配合打包成一个Jar包以便可以直接使用java -jar xxx.jar命令启动。
SpringMVC的常用注解
web模块集成和扩展了SpringMVC的功能,移除但兼容相对臃肿的XML配置,这里简单列举几个常用的Spring或者SpringMVC提供的注解,简单描述各个注解的功能:
组件注解:
@Component:标记一个类为Spring组件,扫描阶段注册到IOC容器。@Repository:标记一个类为Repository(仓库)组件,它的元注解为@Component,一般用于DAO层。@Service:标记一个类为Service(服务)组件,它的元注解为@Component。@Controller:标记一个类为Controller(控制器)组件,它的元注解为@Component,一般控制器是访问的入口,衍生注解@RestController,简单理解为@Controller标记的控制器内所有方法都加上下面提到的@ResponseBody。
参数注解:
@RequestMapping:设置映射参数,包括请求方法、请求的路径、接收或者响应的内容类型等等,衍生注解为GetMapping、PostMapping、PutMapping、DeleteMapping、PatchMapping。@RequestParam:声明一个方法参数绑定到一个请求参数。@RequestBody:声明一个方法参数绑定到请求体,常用于内容类型为application/json的请求体接收。@ResponseBody:声明一个方法返回值绑定到响应体。@PathVariable:声明一个方法参数绑定到一个URI模板变量,用于提取当前请求URI中的部分到方法参数中。
编写控制器和启动类
在项目中编写一个控制器club.throwable.ch1.controller.HelloController如下:
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import java.util.Optional;
@Slf4j
@Controller
@RequestMapping(path = "/ch1")
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping(path = "/hello")
public ResponseEntity hello(@RequestParam(name = "name") String name) {
String value = String.format("[%s] say hello", name);
log.info("调用[/hello]接口,参数:{},响应结果:{}", name, value);
return ResponseEntity.of(Optional.of(value));
}
}
HelloController只提供了一个接收GET请求且请求的路径为/ch1/hello的方法,它接收一个名称为name的参数(参数必传),然后返回简单的文本:${name} say hello。可以使用衍生注解简化如下:
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Optional;
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping(path = "/ch1")
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping(path = "/hello")
public ResponseEntity hello(@RequestParam(name = "name") String name) {
String value = String.format("[%s] say hello", name);
log.info("调用[/hello]接口,参数:{},响应结果:{}", name, value);
return ResponseEntity.of(Optional.of(value));
}
}
接着编写一个启动类club.throwable.ch1.Ch1Application,启动类是SpringBoot应用程序的入口,需要提供一个main方法:
package club.throwable.ch1;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Ch1Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Ch1Application.class, args);
}
}
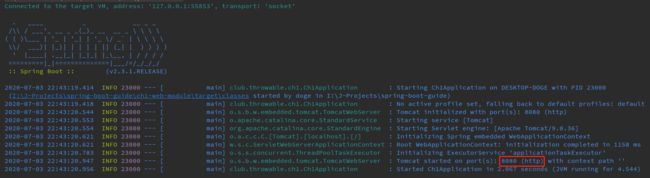
然后以DEBUG模式启动一下:
Tomcat默认的启动端口是8080,启动完毕后见日志如下:
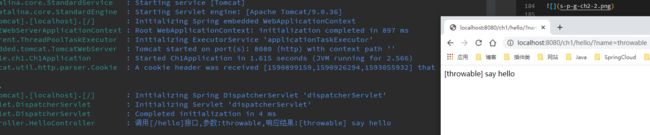
用用浏览器访问http://localhost:8080/ch1/hello?name=thrwoable可见输出如下:
至此,一个简单的基于spring-boot-starter-web开发的web应用已经完成。
切换Servlet容器
有些时候由于项目需要、运维规范或者个人喜好,并不一定强制要求使用Tomcat作为Servlet容器,常见的其他选择有Jetty、Undertow,甚至Netty等。以Jetty和Undertow为例,切换为其他嵌入式Servlet容器需要从spring-boot-starter-web中排除Tomcat的依赖,然后引入对应的Servlet容器封装好的starter。
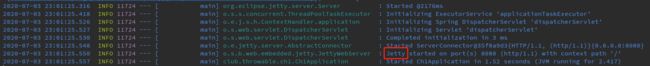
切换为Jetty,修改POM文件中的dependencies元素:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-tomcat
org.springframework.boot
spring‐boot‐starter‐jetty
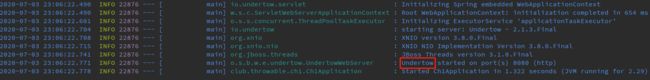
切换为Undertow,修改POM文件中的dependencies元素:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-tomcat
org.springframework.boot
spring‐boot‐starter‐undertow
小结
这篇文章主要分析了如何基于SpringBoot搭建一个入门的web服务,还简单介绍了一些常用的SpringMVC注解的功能,最后讲解如何基于spring-boot-starter-web切换底层的Servlet容器。学会搭建MVC应用后,就可以着手尝试不同的请求方法或者参数,尝试常用注解的功能。
代码仓库
这里给出本文搭建的web模块的SpringBoot应用的仓库地址(持续更新):
- Github:https://github.com/zjcscut/spring-boot-guide/tree/master/ch1-web-module
(本文完 c-2-d e-a-20200703 23:09 PM)
技术公众号《Throwable文摘》(id:throwable-doge),不定期推送笔者原创技术文章(绝不抄袭或者转载):
![]()