手写mini版Spring IOC容器(一)
通常用Spring,我们都是从DispatchServlet开始的。
这个简易的IOC容器主要目的就是模拟IOC将生成的bean注入到IOC容器中。
代码项目的github地址:https://github.com/harrypitter/CreateSpring.git
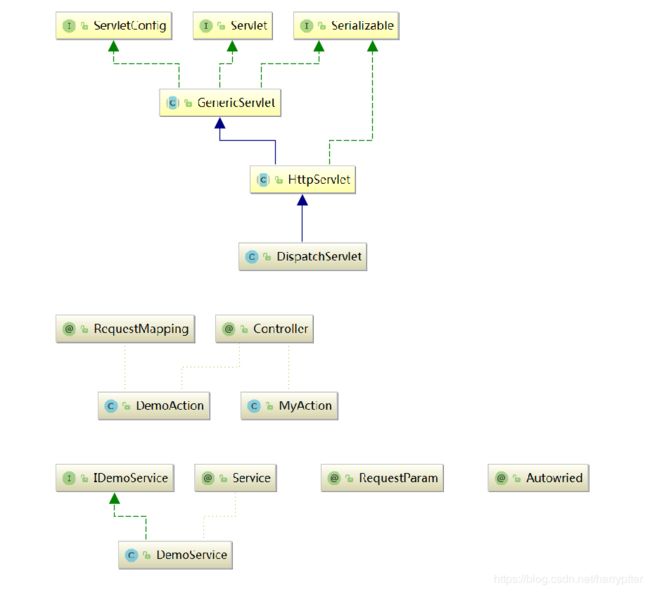
简单类图:
我这边程序中用了jetty runner插件来辅助。
这边需要配置基础的注解:
Autowired:
package com.praticespring.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Autowried {
String value() default "";
}
Controller:
package com.praticespring.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Controller {
String value() default "";
}
RequestMapping:
package com.praticespring.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface RequestMapping {
String value() default "";
}
RequestParam:
package com.praticespring.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface RequestParam {
String value() default "";
}
Serivice:
package com.praticespring.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Service {
String value() default "";
}
这里引入简单的MVC调用的demoService,暂时没写MVC;
接口IDemoService:
package com.praticespring.mvc.service;
public interface IDemoService {
public String get(String name);
}
对应的DemoService:
package com.praticespring.mvc.service;
import com.praticespring.annotation.Service;
@Service
public class DemoService implements IDemoService {
public String get(String name) {
return "My name is " + name;
}
}
DemoAction:
package com.praticespring.mvc.action;
import com.praticespring.annotation.Autowried;
import com.praticespring.annotation.Controller;
import com.praticespring.annotation.RequestMapping;
import com.praticespring.annotation.RequestParam;
import com.praticespring.mvc.service.IDemoService;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class DemoAction {
@Autowried
private IDemoService demoService;
@RequestMapping("/query.json")
public void query(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse resp,
@RequestParam("name") String name){
String result = demoService.get(name);
System.out.println(result);
// try {
// resp.getWriter().write(result);
// } catch (IOException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
}
@RequestMapping("/edit.json")
public void edit(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse resp,Integer id){
}
}
MyAction:
package com.praticespring.mvc.action;
import com.praticespring.annotation.Autowried;
import com.praticespring.annotation.Controller;
import com.praticespring.annotation.RequestMapping;
import com.praticespring.mvc.service.IDemoService;
@Controller
public class MyAction {
@Autowried
IDemoService demoService;
@RequestMapping("/index.html")
public void query(){
}
}
然后写上资源的propoerty文件:
scanPackage=com.praticespring
templateRoot=layouts这边借助了jetty,需要配置相对应的webdefault.xml和web.xml
因为是基础配置,这个就不详细列了,有兴趣的话从上面github地址上下载相关代码看下。
核心的DispatchServlet类:
package com.praticespring.servlet;
import com.praticespring.annotation.Autowried;
import com.praticespring.annotation.Controller;
import com.praticespring.annotation.Service;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class DispatchServlet extends HttpServlet {
private Properties contextConfig = new Properties();
private Map beanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap();
private List classNames = new ArrayList();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req,resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("---------- 调用doPost ----------");
}
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
//开始初始化的进程
//定位
doLoadConfig(config.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation"));
//加载
doScanner(contextConfig.getProperty("scanPackage"));
//注册
doRegistry();
//自动依赖注入
//在Spring中是通过调用getBean方法才出发依赖注入的
doAutowired();
// DemoAction action = (DemoAction)beanMap.get("demoAction");
// action.query(null,null,"Tom");
//如果是SpringMVC会多设计一个HnandlerMapping
//将@RequestMapping中配置的url和一个Method关联上
//以便于从浏览器获得用户输入的url以后,能够找到具体执行的Method通过反射去调用
initHandlerMapping();
}
private void initHandlerMapping() {
}
private void doAutowired() {
if(beanMap.isEmpty()){ return; }
for (Map.Entry entry : beanMap.entrySet()) {
Field[] fields = entry.getValue().getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields){
if(!field.isAnnotationPresent(Autowried.class)){continue;}
Autowried autowried = field.getAnnotation(Autowried.class);
String beanName = autowried.value().trim();
if("".equals(beanName)){
beanName = field.getType().getName();
}
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
field.set(entry.getValue(),beanMap.get(beanName));
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
private void doRegistry() {
if(classNames.isEmpty()){ return;}
try{
for(String className : classNames){
Class clazz = Class.forName(className);
//在Spring中用的多个子方法来处理的
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Controller.class)){
String beanName = lowerFirstCase(clazz.getSimpleName());
//在Spring中在这个阶段不是不会直接put instance,这里put的是BeanDefinition
beanMap.put(beanName,clazz.newInstance());
}else if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Service.class)){
Service service = clazz.getAnnotation(Service.class);
//默认用类名首字母注入
//如果自己定义了beanName,那么优先使用自己定义的beanName
//如果是一个接口,使用接口的类型去自动注入
//在Spring中同样会分别调用不同的方法 autowriedByName autowritedByType
String beanName = service.value();
if("".equals(beanName.trim())){
beanName = lowerFirstCase(clazz.getSimpleName());
}
Object instance = clazz.newInstance();
beanMap.put(beanName,instance);
Class[] interfaces = clazz.getInterfaces();
for (Class i :interfaces){
beanMap.put(i.getName(),instance);
}
}else{
continue;
}
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void doScanner(String packageName) {
URL url = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("/" + packageName.replaceAll("\\.","/"));
File classDir = new File(url.getFile());
for (File file : classDir.listFiles()){
if(file.isDirectory()){
doScanner(packageName + "." +file.getName());
}else {
classNames.add(packageName + "." + file.getName().replace(".class",""));
}
}
}
private void doLoadConfig(String location) {
InputStream is = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(location.replace("classpath:",""));
try {
contextConfig.load(is);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(null != is){is.close();}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private String lowerFirstCase(String str){
char[] strArray = str.toCharArray();
strArray[0]+= 32;
return strArray.toString();
}
}
这个工程主要目的就是手写这个DispatchServlet类:
IOC的初始过程就是:定位--->加载------>注册------>依赖注入
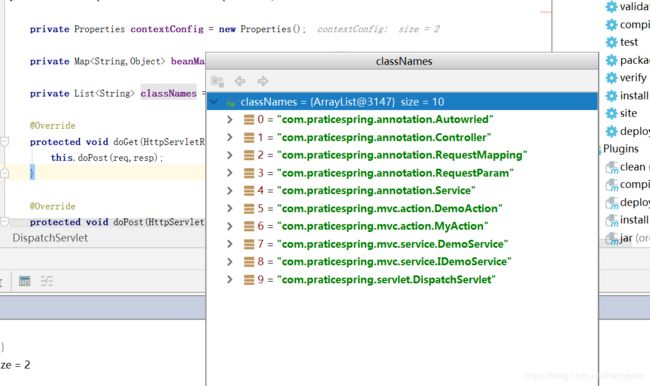
首先通过doLoadConfig()方法,定位application.properties文件里面的内容,然后通过doScanner扫描制定路径下的所有文件内容,再我这个程序里面就是扫描com.praticespring文件夹下的所有文件,然后当时文件的时候就在classNames里面添加对应的.class类文件名。
扫描完之后,进入 doRegistry()方法,这个方法就是将对应的bean方法(上面程序里的逻辑是判断classNames里面的方法,如果是Service方法和Controller方法,就放入beanMap里面)放入指定的IOC容器beanMap里面。
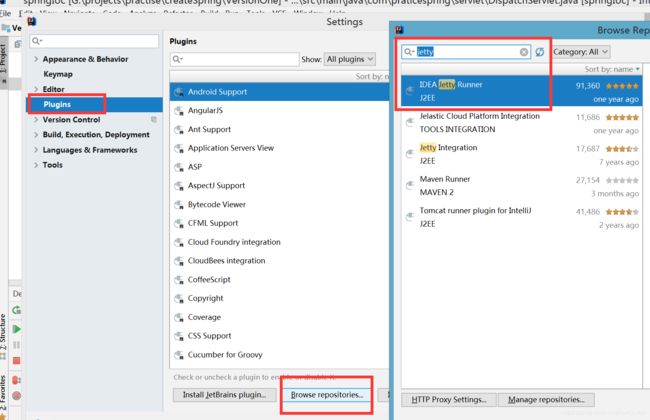
以上就是一件很简单的IOC的逻辑了。之后会写一个更详细的IOC容器。另外,以上的debug借助了jetty Runner ,在IntellJ IDEA的Setting->Plugins->Browse repositories里面搜索jetty runner下载
运行的时候是点击idea右侧Maven projects:
因为主要为了知道IOC的流程,所以用debug模式跑比较好。