Pytorch打卡第2天:张量、计算图、线性回归、逻辑回归
一、张量的操作
拼接
- torch.cat(): 将张量按维度dim进行拼接
- torch.stack():在新建的维度dim上进行拼接
t = torch.ones((2, 3))
t_0 = torch.cat([t, t], dim=0)
t_1 = torch.stack([t, t], dim=0)
print(t_0)
print(t_0.shape)
print(t_1)
print(t_1.shape)
切分
- torch.chunk(input, chunks, dim): 将张量按维度dim进行平均切分
t = torch.ones((2, 7))
print(t)
list_of_tensor = torch.chunk(t, dim=1, chunks=3)
print(list_of_tensor)
- torch.split(): 将张量按维度dim进行切分
t = torch.ones((2, 7))
print(t)
list_of_tensor_2 = torch.split(t, 3, dim=1)
print(list_of_tensor_2)
list_of_tensor_3 = torch.split(t, [2, 2, 3], dim=1)
print(list_of_tensor_3)
索引
- torch.index_select(): 在维度dim上,按index索引数据
t = torch.randint(0, 9, (3, 3))
print(t)
# index_select
idx=torch.tensor([0,2],dtype=torch.long)
t_index_select=torch.index_select(t,index=idx,dim=0)
print(t_index_select)
- torch.masked_select(): 按mask中的True进行索引, 返回一维张量。
t = torch.randint(0, 9, (3, 3))
print(t)
# masked_select
mask = t.ge(5)
print(mask)
t_masked_select = torch.masked_select(t, mask)
print(t_masked_select)
变换
- torch.reshape: 变换张量形状
notice: 注意事项:当张量在内存中是连续时,新张 量与input共享数据内存
# torch.reshape
t = torch.randperm(8)
print(t)
t_reshape = torch.reshape(t, (2, 4)) # -1代表不关心
print(t_reshape)
- torch.transpose(): 交换张量的两个维度
# torch.transpose
t = torch.rand((2, 3, 4))
print(t)
t_transpose = torch.transpose(t, dim0=1, dim1=2)
print(t_transpose)
-
torch.t(): 2维张量转置,对矩阵而言,等价于 torch.transpose(input, 0, 1)
-
torch.squeeze(): 压缩长度为1的维度(轴)
# torch.squeeze
t=torch.rand((1,2,3,1))
t1=torch.squeeze(t)
print(t1.shape)
t2=torch.squeeze(t,dim=2)
print(t2.shape)
- torch.unsqueeze(): 依据dim扩展维度
二、张量的数学运算
- torch.add(): 逐元素计算 input+alpha×other
# torch.add
t0=torch.rand((3,3))
t1=torch.ones_like(t0)
print(t0)
print(t1)
t_add=torch.add(t0,10,t1)
print(t_add)
- torch.addcdiv()
- torch.addcmul()
三、线性回归
import torch
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
lr = 0.1
# 创建训练数据
x = torch.rand(20, 1) * 10
# print(x)
y = 2 * x + (5 + torch.randn(20, 1))
# 构建回归参数
w = torch.randn(1, requires_grad=True)
b = torch.randn(1, requires_grad=True)
for iteration in range(300):
# 前向传播
wx = torch.mul(w, x)
y_pred = torch.add(wx, b)
# 计算MSE loss
loss = (0.5 * (y - y_pred) ** 2).mean()
# 后向传播,得到梯度
loss.backward()
# 更新参数
b.data.sub_(lr*b.grad)
w.data.sub_(lr*w.grad)
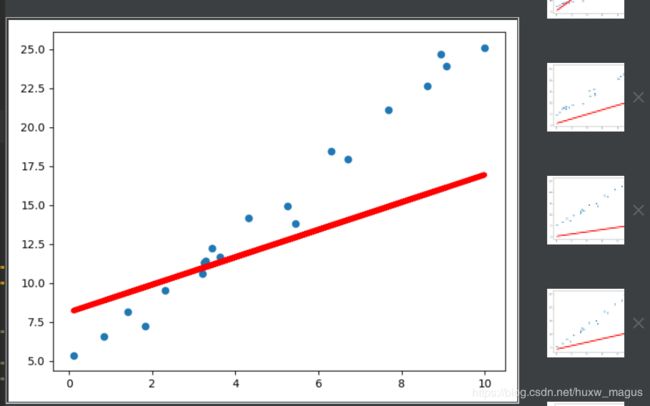
# 绘图
if iteration%100==0:
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(),y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(),y_pred.data.numpy(),'r-',lw=5)
plt.pause(0.5)
if loss.data.numpy()<1:
break
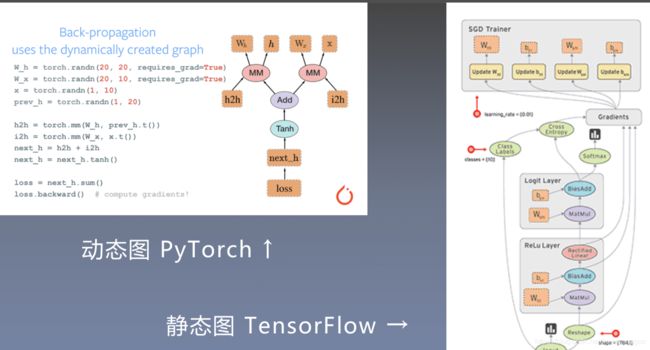
计算图
叶子结点很重要
- retain_grad(): 保留非叶子结点的梯度,防止被释放掉
- is_leaf(): 查看是否为叶子结点,返回:True / False
- grad_fn: 记录创建该张量时所用的方法 (函数)
import torch
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)
x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True)
a = torch.add(w, x)
b = torch.add(w, 1)
y = torch.mul(a, b)
y.backward()
print(w.grad)
# 查看叶子结点
print(a.is_leaf, b.is_leaf, w.is_leaf)
# 查看梯度
print(w.grad, x.grad, a.grad)
# 查看grad_fn
print(w.grad_fn, a.grad_fn)
返回值:
tensor([5.])
False False True
tensor([5.]) tensor([2.]) None
None <AddBackward0 object at 0x12204aed0>
动态图
Autograd
torch.autograd.backward: 自动求取梯度
-
tensors: 用于求导的张量,如 loss
-
retain_graph : 保存计算图
-
create_graph : 创建导数计算图,用于高阶求导
-
grad_tensors:多梯度权重
-
代码
import torch
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)
x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True)
a = torch.add(w, x)
b = torch.add(w, 1)
y0 = torch.mul(a, b)
y1 = torch.add(a, b)
loss = torch.cat([y0, y1], dim=0)
print(loss)
# 权重的设置
grad_tensors = torch.tensor([1., 1.])
loss.backward(gradient=grad_tensors)
print(w.grad)
- 结果
tensor([6.], grad_fn=<MulBackward0>) tensor([5.], grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
tensor([6., 5.], grad_fn=<CatBackward>)
tensor([7.])
Process finished with exit code 0
torch.autograd.grad: 求取梯度
- outputs: 用于求导的张量,如 loss
- inputs : 需要梯度的张量
- create_graph : 创建导数计算图,用于高阶求导
- retain_graph : 保存计算图
- grad_outputs:多梯度权重
import torch
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = torch.tensor([3.], requires_grad=True)
y = torch.pow(x, 2)
# 一次求导
gard_1 = torch.autograd.grad(y, x, create_graph=True) # res = 6
print(gard_1)
# 二次求导
grad_2 = torch.autograd.grad(gard_1[0], x) # res = 2
print(grad_2)
autograd小贴士:
- 梯度不自动清零,会叠加
- 依赖于叶子结点的结点,requires_grad默认为True
- 叶子结点不可执行in-place(原位’_’)
逻辑回归
机器学习的五大步:
- 数据
- 模型
- 损失函数
- 优化器
- 迭代训练
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
torch.manual_seed(10)
# step1: 生成数据
sample_nums = 100
mean_value = 1.7
bias = 1
n_data = torch.ones(sample_nums, 2) # dim = 100x2
x0 = torch.normal(mean_value * n_data, 1) + bias # 正态分布的随机数
y0 = torch.zeros(sample_nums)
x1 = torch.normal(-mean_value * n_data, 1) + bias
y1 = torch.ones(sample_nums)
train_x = torch.cat((x0, x1), 0)
train_y = torch.cat((y0, y1), 0)
# step2: 模型选择
class LR(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LR, self).__init__()
self.features = nn.Linear(2, 1)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = self.sigmoid(x)
return x
# 实例化
lr_net = LR()
# step3: loss
loss_fn = nn.BCELoss()
# step4: optimizer
lr = 0.01 # learning rate
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(lr_net.parameters(), lr=lr, momentum=0.9)
# 训练
for iteration in range(1000):
# 向前传播
y_pred = lr_net(train_x)
# 计算loss
loss = loss_fn(y_pred.squeeze(), train_y)
# 反向传播
loss.backward()
# 更新参数
optimizer.step()
# 绘图
if iteration % 50 == 0:
# 以0.5进行分类
mask = y_pred.ge(0.5).float().squeeze()
# 计算正确预测的样本数
correct = (mask == train_y).sum()
# 计算准确率
acc = correct.item() / train_y.size(0)
print(acc)
# ...
if acc > 0.999:
break