Python图像处理(14):神经网络分类器
快乐虾
http://blog.csdn.net/lights_joy/
欢迎转载,但请保留作者信息
在opencv中支持神经网络分类器,本文尝试在python中调用它。
和前面的贝叶斯分类器一样,神经网络也遵循先训练再使用的方式,我们直接在贝叶斯分类器的测试代码上做简单修改,完成两类数据点的分类。
首先也是先创建训练用的数据:
# 训练的点数
train_pts = 30
# 创建测试的数据点,2类
# 以(-1.5, -1.5)为中心
rand1 = np.ones((train_pts,2)) * (-2) + np.random.rand(train_pts, 2)
print('rand1:')
print(rand1)
# 以(1.5, 1.5)为中心
rand2 = np.ones((train_pts,2)) + np.random.rand(train_pts, 2)
print('rand2:')
print(rand2)
# 合并随机点,得到训练数据
train_data = np.vstack((rand1, rand2))
train_data = np.array(train_data, dtype='float32')
train_label = np.vstack( (np.zeros((train_pts,1), dtype='float32'), np.ones((train_pts,1), dtype='float32')))
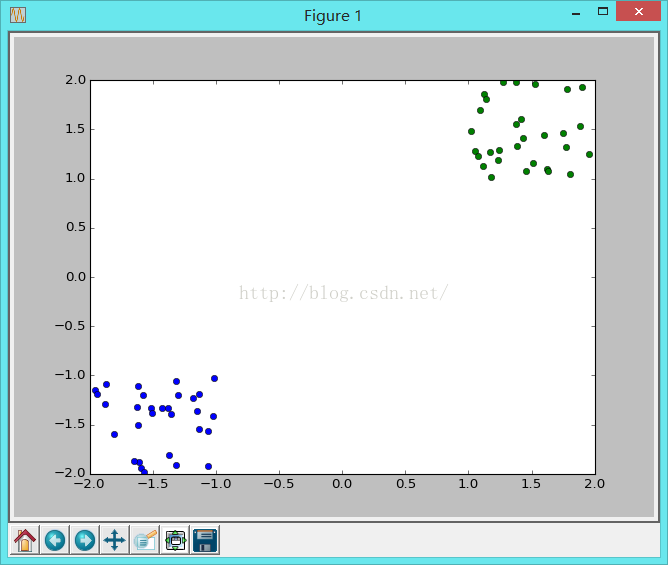
# 显示训练数据
plt.figure(1)
plt.plot(rand1[:,0], rand1[:,1], 'o')
plt.plot(rand2[:,0], rand2[:,1], 'o')
类似这样的数据:
在得到训练数据后,接着创建一个网络并配置训练参数:
# 创建网络
ann = cv2.ml.ANN_MLP_create()
ann.setLayerSizes(np.array([2, 10, 10, 1])) # 必须首先执行此行
ann.setActivationFunction(cv2.ml.ANN_MLP_SIGMOID_SYM)
ann.setTrainMethod(cv2.ml.ANN_MLP_BACKPROP)
ann.setBackpropWeightScale(0.1)
ann.setBackpropMomentumScale(0.1)
由于我们的输入是数据点的坐标值,输出是此数据点所属的类别,因此这个网络的输入层有2个节点,输出则只有一个节点。中间有两个隐层,各有10个节点。
接着我们对此网络进行训练:
# 训练
ret = ann.train(train_data, cv2.ml.ROW_SAMPLE, train_label)
在训练完成后就可以使用测试数据进行预测了:
# 测试数据,20个点[-2,2]
pt = np.array(np.random.rand(20,2) * 4 - 2, dtype='float32')
(ret, res) = ann.predict(pt)
predict通过res返回得到一个20x1的数组,每一行对应一个输入点,由于我们选择sigmoid做为激活函数,因此计算得到的值是一个介于[0,1]之间的浮点数,我们取0.5为阈值进行分类并显示结果:
# 按label进行分类显示
plt.figure(2)
res = np.hstack((res, res))
# 第一类
type_data = pt[res < 0.5]
type_data = np.reshape(type_data, (type_data.shape[0] / 2, 2))
plt.plot(type_data[:,0], type_data[:,1], 'o')
# 第二类
type_data = pt[res >= 0.5]
type_data = np.reshape(type_data, (type_data.shape[0] / 2, 2))
plt.plot(type_data[:,0], type_data[:,1], 'o')
看看最后的结果: