建议查看原文:https://www.jianshu.com/p/23c876f8ae39(不定时更新)
源码剖析学习系列:(不断更新)
1、FBKVOController源码剖析与学习
2、MJRefresh源码剖析与学习
3、YYImage源码剖析与学习
MJRefresh是李明杰大神的开源框架,这是一款十分优雅的刷新组件库,这开源组件无论从代码风格,可用性,易读性还是兼容性来讲都十分优秀。本文就最新MJRefresh版本来讲解。耐心看下去,本文和纯解读源码的文章不同。本文码字几天,如果对您有帮助,给个鼓励,谢谢大家!
MJRefresh
一、MJRefreshComponent
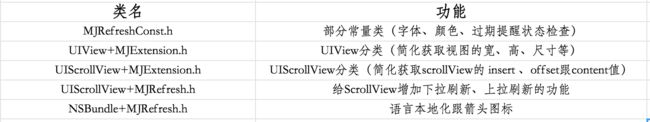
1.导入文件
#import
#import "MJRefreshConst.h"
#import "UIView+MJExtension.h"
#import "UIScrollView+MJExtension.h"
#import "UIScrollView+MJRefresh.h"
#import "NSBundle+MJRefresh.h"
2.状态枚举
/** 刷新控件的状态 */
typedef NS_ENUM(NSInteger, MJRefreshState) {
/** 普通闲置状态 */
MJRefreshStateIdle = 1,
/** 松开就可以进行刷新的状态 */
MJRefreshStatePulling,
/** 正在刷新中的状态 */
MJRefreshStateRefreshing,
/** 即将刷新的状态 */
MJRefreshStateWillRefresh,
/** 所有数据加载完毕,没有更多的数据了 */
MJRefreshStateNoMoreData
};
3、刷新回调
#pragma mark - 刷新回调
/** 正在刷新的回调 */
@property (copy, nonatomic) MJRefreshComponentRefreshingBlock refreshingBlock;
/** 设置回调对象和回调方法 */
- (void)setRefreshingTarget:(id)target refreshingAction:(SEL)action;
/** 回调对象 */
@property (weak, nonatomic) id refreshingTarget;
/** 回调方法 */
@property (assign, nonatomic) SEL refreshingAction;
/** 触发回调(交给子类去调用) */
- (void)executeRefreshingCallback;
4、刷新状态控制
#pragma mark - 刷新状态控制
/** 进入刷新状态 */
- (void)beginRefreshing;
- (void)beginRefreshingWithCompletionBlock:(void (^)(void))completionBlock;
/** 开始刷新后的回调(进入刷新状态后的回调) */
@property (copy, nonatomic) MJRefreshComponentbeginRefreshingCompletionBlock beginRefreshingCompletionBlock;
/** 结束刷新的回调 */
@property (copy, nonatomic) MJRefreshComponentEndRefreshingCompletionBlock endRefreshingCompletionBlock;
/** 结束刷新状态 */
- (void)endRefreshing;
- (void)endRefreshingWithCompletionBlock:(void (^)(void))completionBlock;
/** 是否正在刷新 */
@property (assign, nonatomic, readonly, getter=isRefreshing) BOOL refreshing;
//- (BOOL)isRefreshing;
/** 刷新状态 一般交给子类内部实现 */
@property (assign, nonatomic) MJRefreshState state;
具体方法分析:
#pragma mark 进入刷新状态
- (void)beginRefreshing
{
[UIView animateWithDuration:MJRefreshFastAnimationDuration animations:^{
self.alpha = 1.0;
}];
self.pullingPercent = 1.0;
// 只要正在刷新,就完全显示
if (self.window) {
self.state = MJRefreshStateRefreshing;
} else {
// 预防正在刷新中时,调用本方法使得header inset回置失败
if (self.state != MJRefreshStateRefreshing) {
self.state = MJRefreshStateWillRefresh;
// 刷新(预防从另一个控制器回到这个控制器的情况,回来要重新刷新一下)
[self setNeedsDisplay];
}
}
}
上面做了一个动画效果,多加了一个
willRefresh的状态,我的理解是为了防止self.window为空的时候,突然刷新崩溃(从另一个页面返回的时候),所以需要一个状态来过渡。
设置
state会调用setNeedsLayout方法;如果self.window为空,把状态改成即将刷新,并调用setNeedsDisplay
- 首先
UIView的setNeedsDisplay和setNeedsLayout方法都是异步执行的。而setNeedsDisplay会调用自动调用drawRect方法,这样可以拿到UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext,就可以绘制了,而setNeedsLayout会默认调用layoutSubViews,就可以处理子视图中的一些数据。- 综上所诉,
setNeedsDisplay方便绘图,而layoutSubViews方便出来数据。
//结束刷新
- (void)endRefreshing
{
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
self.state = MJRefreshStateIdle;
});
}
在主线程结束刷新,把刷新状态改为普通闲置状态
5、KVO监听
#pragma mark - KVO监听
- (void)addObservers
{
NSKeyValueObservingOptions options = NSKeyValueObservingOptionNew | NSKeyValueObservingOptionOld;
[self.scrollView addObserver:self forKeyPath:MJRefreshKeyPathContentOffset options:options context:nil];
[self.scrollView addObserver:self forKeyPath:MJRefreshKeyPathContentSize options:options context:nil];
self.pan = self.scrollView.panGestureRecognizer;
[self.pan addObserver:self forKeyPath:MJRefreshKeyPathPanState options:options context:nil];
}
- (void)removeObservers
{
[self.superview removeObserver:self forKeyPath:MJRefreshKeyPathContentOffset];
[self.superview removeObserver:self forKeyPath:MJRefreshKeyPathContentSize];
[self.pan removeObserver:self forKeyPath:MJRefreshKeyPathPanState];
self.pan = nil;
}
- (void)observeValueForKeyPath:(NSString *)keyPath ofObject:(id)object change:(NSDictionary *)change context:(void *)context
{
// 遇到这些情况就直接返回
if (!self.userInteractionEnabled) return;
// 这个就算看不见也需要处理
if ([keyPath isEqualToString:MJRefreshKeyPathContentSize]) {
[self scrollViewContentSizeDidChange:change];
}
// 看不见
if (self.hidden) return;
if ([keyPath isEqualToString:MJRefreshKeyPathContentOffset]) {
[self scrollViewContentOffsetDidChange:change];
} else if ([keyPath isEqualToString:MJRefreshKeyPathPanState]) {
[self scrollViewPanStateDidChange:change];
}
}
监听
ContentOffset、ContentSize、手势的State
6、回调
#pragma mark - 内部方法
- (void)executeRefreshingCallback
{
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
if (self.refreshingBlock) {
self.refreshingBlock();
}
if ([self.refreshingTarget respondsToSelector:self.refreshingAction]) {
MJRefreshMsgSend(MJRefreshMsgTarget(self.refreshingTarget), self.refreshingAction, self);
}
if (self.beginRefreshingCompletionBlock) {
self.beginRefreshingCompletionBlock();
}
});
}
MJRefreshMsgSend是时运行时objc_msgSend,第一个参数代表接收者,第二个参数代表选择子(SEL是选择子的类型),后续参数就是消息中的那些参数,其顺序不变。选择子指的就是方法的名字。
二、MJRefreshHeader
1、初始化(构造方法)
#pragma mark - 构造方法
+ (instancetype)headerWithRefreshingBlock:(MJRefreshComponentRefreshingBlock)refreshingBlock
{
MJRefreshHeader *cmp = [[self alloc] init];
cmp.refreshingBlock = refreshingBlock;
return cmp;
}
+ (instancetype)headerWithRefreshingTarget:(id)target refreshingAction:(SEL)action
{
MJRefreshHeader *cmp = [[self alloc] init];
[cmp setRefreshingTarget:target refreshingAction:action];
return cmp;
}
2、覆盖父类方法
- (void)prepare
{
[super prepare];
// 设置key
self.lastUpdatedTimeKey = MJRefreshHeaderLastUpdatedTimeKey;
// 设置高度
self.mj_h = MJRefreshHeaderHeight;
}
- (void)placeSubviews
{
[super placeSubviews];
// 设置y值(当自己(头部)的高度发生改变了,肯定要重新调整Y值,所以放到placeSubviews方法中设置y值)
self.mj_y = - self.mj_h - self.ignoredScrollViewContentInsetTop;
}
prepare设置一下初始化值数据。而placeSubViews更新一下UI。
3、滚动时偏移值变化以及状态的改变
//当scrollView的contentOffset发生改变的时候调用
- (void)scrollViewContentOffsetDidChange:(NSDictionary *)change
{
[super scrollViewContentOffsetDidChange:change];
// 在刷新的refreshing状态
if (self.state == MJRefreshStateRefreshing) {
// 暂时保留
if (self.window == nil) return;
// sectionheader停留解决
//刷新的时候:偏移量(self.scrollView.mj_offsetY) = 状态栏 + 导航栏 + header的高度(54+64=118 iphoneX则为54+88=142)
//内边距高度(_scrollViewOriginalInset.top)= 状态栏 + 导航栏 = 64
CGFloat insetT = - self.scrollView.mj_offsetY > _scrollViewOriginalInset.top ? - self.scrollView.mj_offsetY : _scrollViewOriginalInset.top;
insetT = insetT > self.mj_h + _scrollViewOriginalInset.top ? self.mj_h + _scrollViewOriginalInset.top : insetT;
self.scrollView.mj_insetT = insetT;
self.insetTDelta = _scrollViewOriginalInset.top - insetT;
return;
}
// 跳转到下一个控制器时,contentInset可能会变
_scrollViewOriginalInset = self.scrollView.mj_inset;
// 当前的contentOffset
CGFloat offsetY = self.scrollView.mj_offsetY;
// 头部控件刚好出现的offsetY
CGFloat happenOffsetY = - self.scrollViewOriginalInset.top;
// 如果是向上滚动到看不见头部控件,直接返回
// >= -> >
if (offsetY > happenOffsetY) return;
// 普通闲置 即将刷新 的临界点
//个人觉得normal2pullingOffsetY应该是头部完全出来时的Y轴偏移值
CGFloat normal2pullingOffsetY = happenOffsetY - self.mj_h;
CGFloat pullingPercent = (happenOffsetY - offsetY) / self.mj_h;
if (self.scrollView.isDragging) { // 如果正在拖拽
self.pullingPercent = pullingPercent;
if (self.state == MJRefreshStateIdle && offsetY < normal2pullingOffsetY) { //手指拖拽中,状态是默认状态以及下拉距离(偏移值)大于临界点距离
// 转为可以进行刷新状态
self.state = MJRefreshStatePulling;
} else if (self.state == MJRefreshStatePulling && offsetY >= normal2pullingOffsetY) {
//手指拖拽中,状态是默认状态以及下拉距离(偏移值)小于临界点距离,也就是拖得比较下
// 转为普通状态
self.state = MJRefreshStateIdle;
}
} else if (self.state == MJRefreshStatePulling) {// 即将刷新 && 手松开
// 开始刷新
[self beginRefreshing];
} else if (pullingPercent < 1) {
self.pullingPercent = pullingPercent;//手松开后,默认状态时,恢复self.pullingPercent
}
}
状态切换的因素有两个:一个是下拉的距离是否超过临界值,另一个是 手指是否离开屏幕。
手指还贴在屏幕的时候是不能进行刷新的。即使在下拉的距离超过了临界距离(状态栏 + 导航栏 + header高度),如果手指没有离开屏幕,那么也不能马上进行刷新,而是将状态切换为:可以刷新。一旦手指离开了屏幕,马上将状态切换为正在刷新。
普通闲置与即将刷新的分界点,看下图,一目了然
4、改变状态时的相应操作(setter方法)
- (void)setState:(MJRefreshState)state
{
MJRefreshCheckState
//MJRefreshCheckState是宏,其实也就是下面语句,为了检测状态是否相同,相同则return
// MJRefreshState oldState = self.state;
// if (state == oldState) {
// NSLog(@"相同");
// return;
// }
// [super setState:state];
// 根据状态做事情
if (state == MJRefreshStateIdle) {
if (oldState != MJRefreshStateRefreshing) return;
// 保存刷新时间
[[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] setObject:[NSDate date] forKey:self.lastUpdatedTimeKey];
[[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] synchronize];
// 恢复inset和offset
[UIView animateWithDuration:MJRefreshSlowAnimationDuration animations:^{
//此时要加上scrollView刷新时跟普通闲置时的偏移差值(刷新时偏移值为118或者142,self.insetTDelta值为header高度-54),恢复后self.scrollView.mj_insetT = 64(或者88)
self.scrollView.mj_insetT += self.insetTDelta;
// 自动调整透明度
if (self.isAutomaticallyChangeAlpha) self.alpha = 0.0;
} completion:^(BOOL finished) {
self.pullingPercent = 0.0;
if (self.endRefreshingCompletionBlock) {
self.endRefreshingCompletionBlock();
}
}];
} else if (state == MJRefreshStateRefreshing) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
[UIView animateWithDuration:MJRefreshFastAnimationDuration animations:^{
CGFloat top = self.scrollViewOriginalInset.top + self.mj_h;
// 增加滚动区域top
self.scrollView.mj_insetT = top;
//增加滚动区域top(赋值给scrollView.inset.top)
CGPoint offset = self.scrollView.contentOffset;
offset.y = -top;
[self.scrollView setContentOffset:offset animated:NO];
} completion:^(BOOL finished) {
//执行正在刷新的回调
[self executeRefreshingCallback];
}];
});
}
}
注意
[super setState:state]的位置,等基类的state赋值给oldState,再跟新状态对比,对比完后,再[super setState:state]调用基类,从而赋值基类state
该方法主要要注意状态在普通闲置状态以及刷新状态的scrollView.contentOffset变化
三、MJRefreshStateHeader
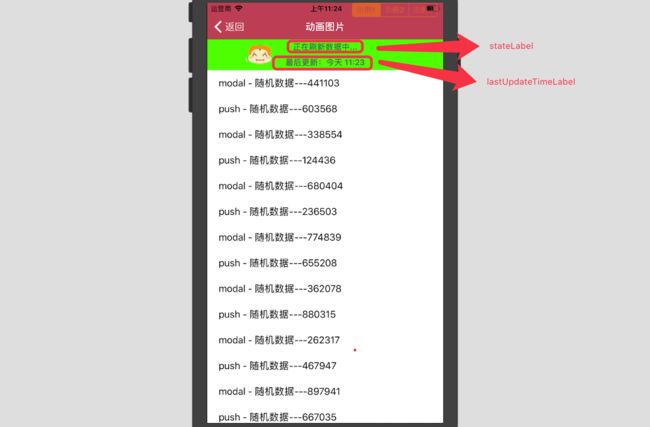
该类是MJRefreshHeader的子类,主要用来设置显示上一次刷新时间的label:lastUpdatedTimeLabel和显示刷新状态的label:stateLabel属性等
1、stateLabel初始化方法
- (void)setTitle:(NSString *)title forState:(MJRefreshState)state
{
if (title == nil) return;
self.stateTitles[@(state)] = title;
self.stateLabel.text = self.stateTitles[@(self.state)];
}
#pragma mark - 覆盖父类的方法
- (void)prepare
{
[super prepare];
// 初始化间距
self.labelLeftInset = MJRefreshLabelLeftInset;
// 初始化文字
[self setTitle:[NSBundle mj_localizedStringForKey:MJRefreshHeaderIdleText] forState:MJRefreshStateIdle];
[self setTitle:[NSBundle mj_localizedStringForKey:MJRefreshHeaderPullingText] forState:MJRefreshStatePulling];
[self setTitle:[NSBundle mj_localizedStringForKey:MJRefreshHeaderRefreshingText] forState:MJRefreshStateRefreshing];
}
prepare初始化方法,实现本地化(不同字体),并根据不同状态赋值给stateLabel
2、lastUpdatedLabel赋值
#pragma mark key的处理
- (void)setLastUpdatedTimeKey:(NSString *)lastUpdatedTimeKey
{
[super setLastUpdatedTimeKey:lastUpdatedTimeKey];
// 如果label隐藏了,就不用再处理
if (self.lastUpdatedTimeLabel.hidden) return;
NSDate *lastUpdatedTime = [[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] objectForKey:lastUpdatedTimeKey];
// 如果有block
//用户定义的时间格式
if (self.lastUpdatedTimeText) {
self.lastUpdatedTimeLabel.text = self.lastUpdatedTimeText(lastUpdatedTime);
return;
}
if (lastUpdatedTime) {
// 1.获得年月日
NSCalendar *calendar = [self currentCalendar];
NSUInteger unitFlags = NSCalendarUnitYear| NSCalendarUnitMonth | NSCalendarUnitDay |NSCalendarUnitHour |NSCalendarUnitMinute;
NSDateComponents *cmp1 = [calendar components:unitFlags fromDate:lastUpdatedTime];
NSDateComponents *cmp2 = [calendar components:unitFlags fromDate:[NSDate date]];
// 2.格式化日期
NSDateFormatter *formatter = [[NSDateFormatter alloc] init];
BOOL isToday = NO;
if ([cmp1 day] == [cmp2 day]) { // 今天
formatter.dateFormat = @" HH:mm"; //返回11:11样式
isToday = YES;
} else if ([cmp1 year] == [cmp2 year]) { // 今年
formatter.dateFormat = @"MM-dd HH:mm"; //返回02-08 11:11样式
} else {
formatter.dateFormat = @"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm"; //返回2018-02-08 11:11样式
}
NSString *time = [formatter stringFromDate:lastUpdatedTime];
// 3.显示日期
//[NSBundle mj_localizedStringForKey:MJRefreshHeaderLastTimeText] 会返回简体(英文、繁体)的 【最后更新:】
//isToday ? [NSBundle mj_localizedStringForKey:MJRefreshHeaderDateTodayText] : @"" 如果上一次刷新也是今天,则返回简体(英文、繁体)的 【今天】,不是则返回空字符串
self.lastUpdatedTimeLabel.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@%@%@",
[NSBundle mj_localizedStringForKey:MJRefreshHeaderLastTimeText],
isToday ? [NSBundle mj_localizedStringForKey:MJRefreshHeaderDateTodayText] : @"",
time];
} else {
//没有获得上次更新时间
self.lastUpdatedTimeLabel.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@%@",
[NSBundle mj_localizedStringForKey:MJRefreshHeaderLastTimeText],
[NSBundle mj_localizedStringForKey:MJRefreshHeaderNoneLastDateText]];
}
}
注意一下时间格式,本地化以及不同上次刷新时间的
lastUpdatedTimeLabel显示
上面代码还给用户自定义时间格式,没有才使用默认,默认的格式逻辑显示,我已在上面注释清楚
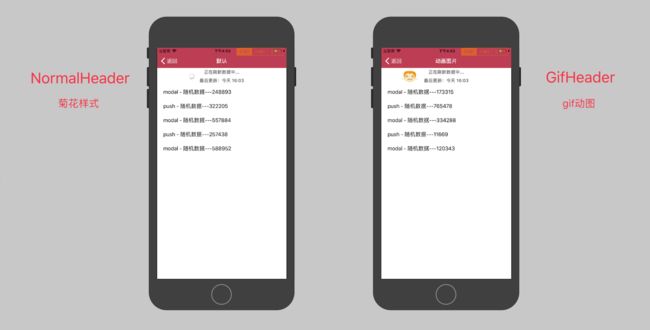
MJRefreshNormalHeader和MJRefreshGifHeader都是MJRefreshStateHeader的子类,前者和后者的布局一样,不同的就是header左边一个是菊花的样式,另外一个是gif,详看下图:
由此看来,这两种形式的
header都有相同的共性,我们在做类似的功能时,如果有几个控件或者几个类共性一样,比如说,一个保险类(InsuranceClass),一个房地产类(RealEstateClass),他们可以有一个基类销售类(SalesClass),SalesClass拥有销售员工、顾客、金额、销售日期等 保险类 和 房地产类 需要的共同属性
四、MJRefreshNormalHeader
1、在
MJRefreshStateHeader上添加了箭头和菊花
2、布局这两种样式
View,且在状态切换时更改样式切换
1、圈圈(菊花)和箭头的布局
- (void)placeSubviews
{
[super placeSubviews];
// 箭头的中心点
CGFloat arrowCenterX = self.mj_w * 0.5;
if (!self.stateLabel.hidden) {
CGFloat stateWidth = self.stateLabel.mj_textWith; //状态label文字的宽度
CGFloat timeWidth = 0.0;
if (!self.lastUpdatedTimeLabel.hidden) {
timeWidth = self.lastUpdatedTimeLabel.mj_textWith; //时间label文字的宽度
}
CGFloat textWidth = MAX(stateWidth, timeWidth); //求出一个最宽的文字宽度
arrowCenterX -= textWidth / 2 + self.labelLeftInset; //箭头(菊花)中心点x还要减去(最宽的文字宽度/2 + 文字距离圈圈、箭头的距离)
}
//中心点y设置为header的高度的一半
CGFloat arrowCenterY = self.mj_h * 0.5;
CGPoint arrowCenter = CGPointMake(arrowCenterX, arrowCenterY);
// 箭头
if (self.arrowView.constraints.count == 0) { //箭头没有其他布局约束
self.arrowView.mj_size = self.arrowView.image.size; //箭头大小跟提供的arrowView图片大小一致
self.arrowView.center = arrowCenter;
}
// 圈圈
if (self.loadingView.constraints.count == 0) { //圈圈(菊花)没有其他布局约束
self.loadingView.center = arrowCenter;
}
self.arrowView.tintColor = self.stateLabel.textColor;
}
上面代码主要实现了圈圈(菊花)和箭头的布局,需要注意的是让箭头菊花紧跟刷新文字或者状态文字居中的逻辑,我已在注释写明
2、不同状态下菊花和箭头的互换
- (void)setState:(MJRefreshState)state
{
MJRefreshCheckState
// 根据状态做事情
if (state == MJRefreshStateIdle) {
if (oldState == MJRefreshStateRefreshing) { //上次状态是正在刷新,准备改变成普通闲置状态
self.arrowView.transform = CGAffineTransformIdentity; //仿射变换初始化
[UIView animateWithDuration:MJRefreshSlowAnimationDuration animations:^{
self.loadingView.alpha = 0.0; //把菊花变成完全透明
} completion:^(BOOL finished) {
// 如果执行完动画发现不是idle状态,就直接返回,进入其他状态
if (self.state != MJRefreshStateIdle) return;
// self.loadingView.backgroundColor = [UIColor greenColor];
self.loadingView.alpha = 1.0; //菊花变成完全显示 (为什么要这样?求大佬告诉)
[self.loadingView stopAnimating]; //菊花停止转动,同时会隐藏菊花(loadingView.hidesWhenStopped = YES;)
self.arrowView.hidden = NO; //箭头显示
}];
} else { //上次状态是拖拽或者普通闲置状态,准备改变成普通闲置状态 --> 把菊花停止转动,菊花隐藏,箭头显示
[self.loadingView stopAnimating];
self.arrowView.hidden = NO;
[UIView animateWithDuration:MJRefreshFastAnimationDuration animations:^{
self.arrowView.transform = CGAffineTransformIdentity; //在操作结束之后对箭头设置量进行还原
}];
}
} else if (state == MJRefreshStatePulling) { //拖拽状态:菊花停止转动,箭头显示
[self.loadingView stopAnimating];
self.arrowView.hidden = NO;
[UIView animateWithDuration:MJRefreshFastAnimationDuration animations:^{
self.arrowView.transform = CGAffineTransformMakeRotation(0.000001 - M_PI);//(改变箭头的方向,但是为什么要0.000001 - M_PI?)
}];
} else if (state == MJRefreshStateRefreshing) { //正在刷新状态:菊花完全显示并且开始转动,箭头隐藏
self.loadingView.alpha = 1.0; // 防止refreshing -> idle的动画完毕动作没有被执行
[self.loadingView startAnimating];
self.arrowView.hidden = YES;
}
}
通过不同的状态控制菊花和箭头的隐藏和消失,及他们的动画效果,如箭头的朝上朝下,和菊花的转与不转
四、MJRefreshGifHeader
1、加载不同状态对应的动画图片
2、设置不同状态对应的动画时间
1、懒加载
#pragma mark - 懒加载
//gigView显示gif
- (UIImageView *)gifView
{
if (!_gifView) {
UIImageView *gifView = [[UIImageView alloc] init];
[self addSubview:_gifView = gifView];
}
return _gifView;
}
- (NSMutableDictionary *)stateImages
{
if (!_stateImages) {
self.stateImages = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
}
return _stateImages;
}
- (NSMutableDictionary *)stateDurations
{
if (!_stateDurations) {
self.stateDurations = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
}
return _stateDurations;
}
2、设置不通过状态对应的动画图片以及动画时间
#pragma mark - 公共方法
- (void)setImages:(NSArray *)images duration:(NSTimeInterval)duration forState:(MJRefreshState)state
{
if (images == nil) return;
self.stateImages[@(state)] = images;
self.stateDurations[@(state)] = @(duration);
/* 根据图片设置控件的高度 */
UIImage *image = [images firstObject];
if (image.size.height > self.mj_h) {
self.mj_h = image.size.height;
}
}
- (void)setImages:(NSArray *)images forState:(MJRefreshState)state
{
[self setImages:images duration:images.count * 0.1 forState:state];
}
3、实现图片的切换和gifView布局
#pragma mark - 实现父类的方法
- (void)prepare
{
[super prepare];
// 初始化间距
self.labelLeftInset = 20;
}
//根据拖拽进度设置透明度
- (void)setPullingPercent:(CGFloat)pullingPercent
{
[super setPullingPercent:pullingPercent];
NSArray *images = self.stateImages[@(MJRefreshStateIdle)]; //选择闲置状态下的图片组
if (self.state != MJRefreshStateIdle || images.count == 0) return; //状态不是闲置或者图片为空,则直接返回
// 停止动画
[self.gifView stopAnimating];
// 设置当前需要显示的图片
NSUInteger index = images.count * pullingPercent;
if (index >= images.count) index = images.count - 1;
self.gifView.image = images[index];
}
- (void)placeSubviews
{
[super placeSubviews];
if (self.gifView.constraints.count) return; //gifView没有约束,直接返回
self.gifView.frame = self.bounds;
if (self.stateLabel.hidden && self.lastUpdatedTimeLabel.hidden) { //上次刷新时间和状态文字都隐藏了,图片内容就居ifView中间显示
self.gifView.contentMode = UIViewContentModeCenter;
} else { //图片居gifView右边显示
self.gifView.contentMode = UIViewContentModeRight;
//下面代码同样也是为了让gifView紧挨着文字居中显示。算出最长的文字,通过减去文字的一般宽度,调整gifView的x值,跟NormalHeader的方法一样,详细请看normalHeader
CGFloat stateWidth = self.stateLabel.mj_textWith;
CGFloat timeWidth = 0.0;
if (!self.lastUpdatedTimeLabel.hidden) {
timeWidth = self.lastUpdatedTimeLabel.mj_textWith;
}
CGFloat textWidth = MAX(stateWidth, timeWidth);
self.gifView.mj_w = self.mj_w * 0.5 - textWidth * 0.5 - self.labelLeftInset;
}
}
- (void)setState:(MJRefreshState)state
{
MJRefreshCheckState
// 根据状态做事情
if (state == MJRefreshStatePulling || state == MJRefreshStateRefreshing) { //状态变为拖拽或者正在刷新,获取各自状态该显示的图片组
NSArray *images = self.stateImages[@(state)];
if (images.count == 0) return;
[self.gifView stopAnimating];
if (images.count == 1) { // 单张图片
self.gifView.image = [images lastObject];
} else { // 多张图片
self.gifView.animationImages = images;
self.gifView.animationDuration = [self.stateDurations[@(state)] doubleValue];
[self.gifView startAnimating];
}
} else if (state == MJRefreshStateIdle) {
[self.gifView stopAnimating];
}
}
到此,我对MJRefreshHeader那一块的源码已经读完,剩下MJRefreshFooter,但由于实现逻辑基本一致,故在此不再详说。迟点,发现MJRefreshFooter有其他特殊之处,我会更新此文,谢谢大家!
学习
1、巧用Model
我们可能见到一些开发者会在didSelectRowAtIndexPath协议方法里面这样写
- (void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView didSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
MJExample *exam = self.examples[indexPath.section];
UIViewController *vc = [[exam.vcClass alloc] init];
vc.title = exam.titles[indexPath.row];
[vc setValue:exam.methods[indexPath.row] forKeyPath:@"method"];
[self.navigationController pushViewController:vc animated:YES];
if (indexPath.row == 0) {
UIViewController *test1 = [UIViewController new];
test1.title = @"test1";
[self.navigationController pushViewController:test1 animated:YES];
}else if (indexPath.row == 1) {
UIViewController *test2 = [UIViewController new];
test2.title = @"test2";
[self.navigationController pushViewController:test2 animated:YES];
}else if (indexPath.row == 2) {
UIViewController *test3 = [UIViewController new];
test3.title = @"test3";
[self.navigationController pushViewController:test3 animated:YES];
}else {
;
}
}
这样会造成
didSelectRowAtIndexPath方法过于臃肿,且重复代码过多,太多if else 或者 switch,我们可以用Model很好的解决这个问题,代码如下:
- (NSArray *)examples
{
if (!_examples) {
MJExample *exam0 = [[MJExample alloc] init];
exam0.header = MJExample00;
exam0.vcClass = [MJTableViewController class];
exam0.titles = @[@"默认", @"动画图片", @"隐藏时间", @"隐藏状态和时间", @"自定义文字", @"自定义刷新控件"];
exam0.methods = @[@"example01", @"example02", @"example03", @"example04", @"example05", @"example06"];
MJExample *exam1 = [[MJExample alloc] init];
exam1.header = MJExample10;
exam1.vcClass = [MJTableViewController class];
exam1.titles = @[@"默认", @"动画图片", @"隐藏刷新状态的文字", @"全部加载完毕", @"禁止自动加载", @"自定义文字", @"加载后隐藏", @"自动回弹的上拉01", @"自动回弹的上拉02", @"自定义刷新控件(自动刷新)", @"自定义刷新控件(自动回弹)"];
exam1.methods = @[@"example11", @"example12", @"example13", @"example14", @"example15", @"example16", @"example17", @"example18", @"example19", @"example20", @"example21"];
MJExample *exam2 = [[MJExample alloc] init];
exam2.header = MJExample20;
exam2.vcClass = [MJCollectionViewController class];
exam2.titles = @[@"上下拉刷新"];
exam2.methods = @[@"example21"];
MJExample *exam3 = [[MJExample alloc] init];
exam3.header = MJExample30;
exam3.vcClass = [MJWebViewViewController class];
exam3.titles = @[@"下拉刷新"];
exam3.methods = @[@"example31"];
self.examples = @[exam0, exam1, exam2, exam3];
}
return _examples;
}
- (void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView didSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
MJExample *exam = self.examples[indexPath.section];
UIViewController *vc = [[exam.vcClass alloc] init];
vc.title = exam.titles[indexPath.row];
[vc setValue:exam.methods[indexPath.row] forKeyPath:@"method"];
[self.navigationController pushViewController:vc animated:YES];
}
2、跳转巧用
ViewController.h
- (IBAction)tappdeBtn:(id)sender {
UIViewController *vc = [[BViewController alloc] init];
vc.title = @"example01";
[vc setValue:@"example01" forKeyPath:@"method"];
[self.navigationController pushViewController:vc animated:YES];
}
上面是跳转方法,请留意
[vc setValue:@"example01" forKeyPath:@"method"];这句代码,下面会详解
BViewController.h
#import "BViewController.h"
#import "UIViewController+Example.h"
#define MJPerformSelectorLeakWarning(Stuff) \
do { \
_Pragma("clang diagnostic push") \
_Pragma("clang diagnostic ignored \"-Warc-performSelector-leaks\"") \
Stuff; \
_Pragma("clang diagnostic pop") \
} while (0)
@implementation BViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
MJPerformSelectorLeakWarning(
[self performSelector:NSSelectorFromString(self.method) withObject:nil];
);
}
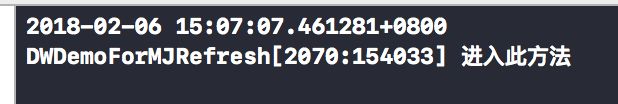
- (void)example01
{
NSLog(@"进入此方法");
}
结果:
1、由上可以看到
[self performSelector:NSSelectorFromString(self.method) withObject:nil];没有指明方法名,仍可以调用- (void)example01(),这是运用了runtime的黑魔法,定义了UIViewController+Example分类方法,runtime的使用可以看我之前的文章-->iOS进阶之runtime作用
2、
MJPerformSelectorLeakWarning( );如果selector是在运行时才确定的,performSelector时,若先把selector保存起来,等到某事件发生后再调用,相当于在动态绑定之上再使用动态绑定,不过这是编译器不知道要执行的selector是什么,因为这必须到了运行时才能确定,使用这种特性的代价是,如果在ARC下编译代码,编译器会发生警告,可用#pragma clang diagnostic ignored "-Warc-performSelector-leaks"忽略警告
#import
@interface UIViewController (Example)
@property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *method;
@end
----------------------------
#import "UIViewController+Example.h"
#import
@implementation UIViewController (Example)
static char MethodKey;
- (void)setMethod:(NSString *)method
{
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, &MethodKey, method, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC);
}
- (NSString *)method
{
return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, &MethodKey);
}
这是runtime中为分类添加属性的经典用法,把上面跳转方法中的
[vc setValue:@"example01" forKeyPath:@"method"];赋值的example01利用runtime关联,这样分类中的method属性值就为example01
解析一下 static char
比如有这样一个函数
exp()
{
char a[] = "Hello!" ;
static char b[] = "Hello!" ;
}
当调用这个函数完后,a[]就不存在了,而b[]依然存在,并且值为hello;
参考:
performSelector系列方法编译器警告-Warc-performSelector-leaks
#pragma clang diagnostic ignored 用法
UIView常用的setNeedsDisplay和setNeedsLayout