最值得关注的10个C开源项目之Webbench源码分析
Webbench
Webbench是一个在linux下使用的非常简单的网站压测工具。它使用fork()模拟多个客户端同时访问我们设定的URL,测试网站在压力下工作的性能,最多可以模拟3万个并发连接去测试网站的负载能力。Webbench使用C语言编写, 代码实在太简洁,源码加起来不到600行。整个源码分析主要的分析都被我加在了代码的后面中文注释中,欢迎讨论~
webbench压测的命令:
webbench -c 300 -t 10 url
其中:-c 300 表示并发数(可以了理解成客户端),
-t 10表示时间(秒)
url 想要压测的url
下载链接:http://home.tiscali.cz/~cz210552/webbench.html
整个代码的流程图如下:
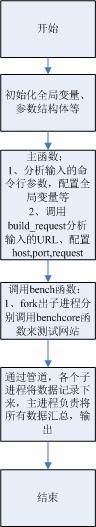
一、首先我们从主函数入手,前面几个都是初始化变量,没什么好说的,出现了一个getopt_long函数,应该有些人没有用过这个函数,我先来分析下这个函数吧~
int getopt_long(int argc, char * const argv[],const char *optstring,const struct option *longopts, int *longindex);
1、前两个参数,就是main函数的argc和argv,这两者直接传入即可,
2、optstring的格式举例说明比较方便,例如:char *optstring = "abcd:";
上面这个optstring在传入之后,getopt函数将依次检查命令行是否指定了 -a, -b, -c及 -d,(这需要多次调用getopt函数,直到其返回-1),当检查到上面某一个参数被指定时,函数会返回被指定的参数名称(即该字母),最后一个参数d后面带有冒号,: 表示参数d是可以指定值的,如 -d 100 或 -d user。
3、longopts指向的是一个由option结构体组成的数组,那个数组的每个元素,指明了一个“长参数”(即形如--name的参数)名称和性质:
struct option {
const char *name;
int has_arg;
int *flag;
int val;
};
name 是参数的名称
has_arg 指明是否带参数值,其数值可选:
no_argument (即 0) 表明这个长参数不带参数(即不带数值,如:--name)
required_argument (即 1) 表明这个长参数必须带参数(即必须带数值,如:--name Bob)
optional_argument(即2)表明这个长参数后面带的参数是可选的,(即--name和--name Bob均可)
flag 当这个指针为空的时候,函数直接将val的数值从getopt_long的返回值返回出去,当它非空时,val的值会被赋到flag指向的整型数中,而函数返回值为0
val 用于指定函数找到该选项时的返回值,或者当flag非空时指定flag指向的数据的值。
static const struct option long_options[]=
{
{"force",no_argument,&force,1},
{"reload",no_argument,&force_reload,1},
{"time",required_argument,NULL,'t'}, //bench的测试时间 默认为30s
{"help",no_argument,NULL,'?'},
{"http09",no_argument,NULL,'9'},
{"http10",no_argument,NULL,'1'},
{"http11",no_argument,NULL,'2'},
{"get",no_argument,&method,METHOD_GET},
{"head",no_argument,&method,METHOD_HEAD},
{"options",no_argument,&method,METHOD_OPTIONS},
{"trace",no_argument,&method,METHOD_TRACE},
{"version",no_argument,NULL,'V'},
{"proxy",required_argument,NULL,'p'},
{"clients",required_argument,NULL,'c'},
{NULL,0,NULL,0}
};例如对于
while ( (opt = getopt_long(argc, argv, optstring, long_options, &option_index)) != -1)
{
printf("opt = %c\n", opt); //被指定的参数名称(即该字母)
printf("optarg = %s\n", optarg); //optarg为参数的指定值
printf("optind = %d\n", optind); //下一个将被处理到的参数在argv中的下标值。
printf("argv[optind - 1] = %s\n", argv[optind - 1]);
printf("option_index = %d\n", option_index); //它指向的变量将记录当前找到参数符合longopts里的第几个元素的描述,即是longopts的下标值。
} 输入命令行test_getopt_long -reqarg 100
输出:
opt = reqarg
optarg = 100
optind = 3
argv[optind - 1] = 100
二、build_request函数
目的是对url进行处理,得到host,proxyport,request
其中request就是之后利用socket与host通信所要发送的报文。
void build_request(const char *url)
{
char tmp[10];
int i;
bzero(host,MAXHOSTNAMELEN); //置host字符串前MAXHOSTNAMELEN个字节为零且包括‘\0’。
bzero(request,REQUEST_SIZE);
if(force_reload && proxyhost!=NULL && http10<1) http10=1;
if(method==METHOD_HEAD && http10<1) http10=1;
if(method==METHOD_OPTIONS && http10<2) http10=2;
if(method==METHOD_TRACE && http10<2) http10=2;
switch(method)
{
default:
case METHOD_GET: strcpy(request,"GET");break;
case METHOD_HEAD: strcpy(request,"HEAD");break;
case METHOD_OPTIONS: strcpy(request,"OPTIONS");break;
case METHOD_TRACE: strcpy(request,"TRACE");break;
}
strcat(request," ");
if(NULL==strstr(url,"://"))
{
fprintf(stderr, "\n%s: is not a valid URL.\n",url);
exit(2);
}
if(strlen(url)>1500)
{
fprintf(stderr,"URL is too long.\n");
exit(2);
}
if(proxyhost==NULL)
if (0!=strncasecmp("http://",url,7))
{
fprintf(stderr,"\nOnly HTTP protocol is directly supported, set --proxy for others.\n");
exit(2);
}
/* protocol/host delimiter */
i=strstr(url,"://")-url+3; //找到url中:'//'的出现的位置
/* printf("%d\n",i); */
if(strchr(url+i,'/')==NULL) { //判断url中除去http://后是否存在'/'
fprintf(stderr,"\nInvalid URL syntax - hostname don't ends with '/'.\n");
exit(2);
}
if(proxyhost==NULL) //if里面都是为了获取端口号 主机名 和 request
{ //比如url="http://localhost:12345/test"; //if运行结束后 proxyport=12345,host=localhost
/* get port from hostname */
if(index(url+i,':')!=NULL &&
index(url+i,':')0)
strcat(request,"User-Agent: WebBench "PROGRAM_VERSION"\r\n");
if(proxyhost==NULL && http10>0)
{
strcat(request,"Host: ");
strcat(request,host);
strcat(request,"\r\n");
}
if(force_reload && proxyhost!=NULL)
{
strcat(request,"Pragma: no-cache\r\n");
}
if(http10>1)
strcat(request,"Connection: close\r\n");
/* add empty line at end */
if(http10>0) strcat(request,"\r\n");
// printf("Req=%s\n",request);
} 三、bench函数
该函数主要采用fork出子进程来测试网站,并且利用主进程来读取所有子进程写入的数据,每个子进程调用benchcore函数来测试存到全局变量speed faulted,
最后主进程汇总各个子线程的数据显示出来~
/* vraci system rc error kod */
static int bench(void)
{
int i,j,k;
pid_t pid=0;
FILE *f;
/* check avaibility of target server */
i=Socket(proxyhost==NULL?host:proxyhost,proxyport); //测试网站是否能连
if(i<0) {
fprintf(stderr,"\nConnect to server failed. Aborting benchmark.\n");
return 1;
}
close(i);
/* create pipe */
if(pipe(mypipe))
{
perror("pipe failed.");
return 3;
}
/* not needed, since we have alarm() in childrens */
/* wait 4 next system clock tick */
/*
cas=time(NULL);
while(time(NULL)==cas)
sched_yield();
*/
/* fork childs */
for(i=0;i
四、benchcore函数
该函数主要采用socket连接、发送request、接收来测试网站,测试结果存在全局变量speed faulted,bytes
定时时间结束则退出函数~
其中关于sigaction函数的使用:
int sigaction(int signo,const struct sigaction *restrict act,struct sigaction *restrict oact);
其中signo的信息可参考:http://blog.csdn.net/liucimin/article/details/40507443
其中结构sigaction定义如下:
struct sigaction{
void (*sa_handler)(int);
sigset_t sa_mask;
int sa_flag;
void (*sa_sigaction)(int,siginfo_t *,void *);
}; sa_handler字段包含一个信号捕捉函数的地址
sa_flag标志。
void benchcore(const char *host,const int port,const char *req)
{
int rlen;
char buf[1500];
int s,i;
struct sigaction sa;
/* setup alarm signal handler */ //设定定时器,该进程benchtime之后结束测试
sa.sa_handler=alarm_handler;
sa.sa_flags=0;
if(sigaction(SIGALRM,&sa,NULL)) //通过信号设置时间结束后全局变量timerexpired的值
exit(3);
alarm(benchtime); //alarm也称为闹钟函数,它可以在进程中设置一个定时器,当定时器指定的时间到时
//,它向进程发送SIGALRM信号。如果忽略或者不捕获此信号
//,则其默认动作是终止调用该alarm函数的进程。
rlen=strlen(req);
nexttry:while(1)
{
if(timerexpired) //到点后结束函数
{
if(failed>0)
{
/* fprintf(stderr,"Correcting failed by signal\n"); */
failed--;
}
return;
}
s=Socket(host,port); //Socket是头文件中自己写的函数,返回socket连接后的结果
if(s<0) { failed++;continue;}
if(rlen!=write(s,req,rlen)) {failed++;close(s);continue;} //往服务器发request
if(http10==0)
if(shutdown(s,1)) { failed++;close(s);continue;}
if(force==0)
{
/* read all available data from socket */
while(1)
{
if(timerexpired) break;
i=read(s,buf,1500); //成功返回读取的字节数,出错返回-1并设置errno,如果在调read之前已到达文件末尾,则这次read返回0
/* fprintf(stderr,"%d\n",i); */
if(i<0) //读取失败 failed++,重新发送request读数据
{
failed++;
close(s);
goto nexttry;
}
else
if(i==0) break;
else
bytes+=i;
}
}
if(close(s)) {failed++;continue;}
speed++;
}
}