Netty学习之旅------线程模型前置篇Reactor反应堆设计模式实现(基于java.nio)
1、Reactor反应堆设计模式
1.1 单线程模型
单线程模型Reactor(此图来源与网络)
下面以java nio为基础,实现Reactor模型。
Nio服务端代码:
package threadmode.r1;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* Nio服务器,
* 本例主要用来增加对 Ractor 线程模型的理解,不会考虑半包等网络问题
*
* 例子程序的功能:服务器接受客户端的请求数据,然后在后面再追加 (hello,服务器收到了你的信息。)
* @author dingwei2
*
*
*
*
*
*/
public class NioServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//
(new Thread(new Reactor())).start();
}
/**
* Reactor模型,反应堆
* @author dingwei2
*
*/
private static final class Reactor implements Runnable {
// private static final ConcurrentHashMap waitSendData
// = new ConcurrentHashMap();
private static final byte[] b = "hello,服务器收到了你的信息。".getBytes();
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("服务端启动成功,等待客户端接入");
ServerSocketChannel ssc = null;
Selector selector = null;
try {
ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9080));
selector = Selector.open();
ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
Set ops = null;
while(true) {
try {
selector.select(); //如果没有感兴趣的事件到达,阻塞等待
ops = selector.selectedKeys();
} catch(Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
break;
}
//处理相关事件
for (Iterator it = ops.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
SelectionKey key = it.next();
it.remove();
try {
if(key.isAcceptable()) { //客户端建立连接
ServerSocketChannel serverSc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();//这里其实,可以直接使用ssl这个变量
SocketChannel clientChannel = serverSc.accept();
clientChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//向选择器注册读事件,客户端向服务端发送数据准备好后,再处理
clientChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
System.out.println("收到客户端的连接请求。。。");
} else if (key.isWritable()) { //向客户端发送请求
SocketChannel clientChannel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
ByteBuffer buf = (ByteBuffer)key.attachment();
buf.flip();
clientChannel.write(buf);
System.out.println("服务端向客户端发送数据。。。");
//重新注册读事件
clientChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} else if(key.isReadable()) { //处理客户端发送的数据
System.out.println("服务端接收客户端连接请求。。。");
// System.out.println(key);
SocketChannel clientChannel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
// System.out.println("clientChannel.isConnected():" + clientChannel.isConnected());
// System.out.println("clientChannel.isConnectionPending():" +clientChannel.isConnectionPending());
// System.out.println("clientChannel.isOpen():" + clientChannel.isOpen());
// System.out.println("clientChannel.finishConnect():" + clientChannel.finishConnect());
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
System.out.println(buf.capacity());
clientChannel.read(buf);//
buf.put(b);
clientChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE, buf);//注册写事件
}
} catch(Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("客户端主动断开连接。。。。。。。");
ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
Nio客户端代码:
package threadmode.r1;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author dingwei2
*
*/
public class NioClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
SocketChannel clientClient;
Selector selector = null;
try {
clientClient = SocketChannel.open();
clientClient.configureBlocking(false);
selector = Selector.open();
clientClient.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
clientClient.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",9080));
Set ops = null;
while(true) {
try {
selector.select();
ops = selector.selectedKeys();
for (Iterator it = ops.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
SelectionKey key = it.next();
it.remove();
if(key.isConnectable()) {
System.out.println("client connect");
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
// 判断此通道上是否正在进行连接操作。
// 完成套接字通道的连接过程。
if (sc.isConnectionPending()) {
sc.finishConnect();
System.out.println("完成连接!");
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
buffer.put("Hello,Server".getBytes());
buffer.flip();
sc.write(buffer);
}
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} else if(key.isWritable()) {
System.out.println("客户端写");
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
buffer.put("hello server.".getBytes());
buffer.flip();
sc.write(buffer);
} else if(key.isReadable()) {
System.out.println("客户端收到服务器的响应....");
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int count = sc.read(buffer);
if(count > 0 ) {
buffer.flip();
byte[] response = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(response);
System.out.println(new String(response));
}
}
}
} catch(Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
1.2 多线程模型
Reactor多线程模型(多个Nio线程处理网络读写)(此图来源与网络)。
多线程模型,就是1个线程Acceptor接受客户端的连接,然后由一组IO线程(Reactor)来执行网络的读写。下面贴出其实现。
其中NioServer中的Acceptor为接受客户端连接线程。
其中NioReactorThreadGroup为一组IO线程,NioReactorThread为具体IO线程的实现。
package threadmode.r2;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class NioServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
new Thread(new Acceptor()).start();
}
/**
* 连接线程模型,反应堆,转发器 Acceptor
*
* @author dingwei2
*
*/
private static final class Acceptor implements Runnable {
private NioReactorThreadGroup nioReactorThreadGroup;
public Acceptor() {
nioReactorThreadGroup = new NioReactorThreadGroup();
}
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("服务端启动成功,等待客户端接入");
ServerSocketChannel ssc = null;
Selector selector = null;
try {
ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9080));
selector = Selector.open();
ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
Set ops = null;
while (true) {
try {
selector.select(); // 如果没有感兴趣的事件到达,阻塞等待
ops = selector.selectedKeys();
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
break;
}
// 处理相关事件
for (Iterator it = ops.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
SelectionKey key = it.next();
it.remove();
try {
if (key.isAcceptable()) { // 客户端建立连接
System.out.println("收到客户端的连接请求。。。");
ServerSocketChannel serverSc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();// 这里其实,可以直接使用ssl这个变量
SocketChannel clientChannel = serverSc.accept();
clientChannel.configureBlocking(false);
nioReactorThreadGroup.dispatch(clientChannel); // 转发该请求
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("客户端主动断开连接。。。。。。。");
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
package threadmode.r2;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* nio 线程组;简易的NIO线程组
* @author dingwei2
*
*/
public class NioReactorThreadGroup {
private static final AtomicInteger requestCounter = new AtomicInteger(); //请求计数器
private final int nioThreadCount; // 线程池IO线程的数量
private static final int DEFAULT_NIO_THREAD_COUNT;
private NioReactorThread[] nioThreads;
static {
// DEFAULT_NIO_THREAD_COUNT = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() > 1
// ? 2 * (Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() - 1 ) : 2;
DEFAULT_NIO_THREAD_COUNT = 4;
}
public NioReactorThreadGroup() {
this(DEFAULT_NIO_THREAD_COUNT);
}
public NioReactorThreadGroup(int threadCount) {
if(threadCount < 1) {
threadCount = DEFAULT_NIO_THREAD_COUNT;
}
this.nioThreadCount = threadCount;
this.nioThreads = new NioReactorThread[threadCount];
for(int i = 0; i < threadCount; i ++ ) {
this.nioThreads[i] = new NioReactorThread();
this.nioThreads[i].start(); //构造方法中启动线程,由于nioThreads不会对外暴露,故不会引起线程逃逸
}
System.out.println("Nio 线程数量:" + threadCount);
}
public void dispatch(SocketChannel socketChannel) {
if(socketChannel != null ) {
next().register(socketChannel);
}
}
protected NioReactorThread next() {
return this.nioThreads[ requestCounter.getAndIncrement() % nioThreadCount ];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
package threadmode.r2;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* Nio 线程,专门负责nio read,write
* 本类是实例行代码,不会对nio,断线重连,写半包等场景进行处理,旨在理解 Reactor模型(多线程版本)
* @author dingwei2
*
*/
public class NioReactorThread extends Thread {
private static final byte[] b = "hello,服务器收到了你的信息。".getBytes(); //服务端给客户端的响应
private Selector selector;
private List waitRegisterList = new ArrayList(512);
private ReentrantLock registerLock = new ReentrantLock();
public NioReactorThread() {
try {
this.selector = Selector.open();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* socket channel
* @param socketChannel
*/
public void register(SocketChannel socketChannel) {
if(socketChannel != null ) {
try {
registerLock.lock();
waitRegisterList.add(socketChannel);
} finally {
registerLock.unlock();
}
}
}
//private
public void run() {
while(true) {
Set ops = null;
try {
selector.select(1000);
ops = selector.selectedKeys();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
continue;
}
//处理相关事件
for (Iterator it = ops.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
SelectionKey key = it.next();
it.remove();
try {
if (key.isWritable()) { //向客户端发送请求
SocketChannel clientChannel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
ByteBuffer buf = (ByteBuffer)key.attachment();
buf.flip();
clientChannel.write(buf);
System.out.println("服务端向客户端发送数据。。。");
//重新注册读事件
clientChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} else if(key.isReadable()) { //接受客户端请求
System.out.println("服务端接收客户端连接请求。。。");
SocketChannel clientChannel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
System.out.println(buf.capacity());
clientChannel.read(buf);//
buf.put(b);
clientChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE, buf);//注册写事件
}
} catch(Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("客户端主动断开连接。。。。。。。");
}
}
//注册事件
if(!waitRegisterList.isEmpty()) {
try {
registerLock.lock();
for (Iterator it = waitRegisterList.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
SocketChannel sc = it.next();
try {
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} catch(Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();//ignore
}
it.remove();
}
} finally {
registerLock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
}
NioClient与Reactor,单线程版本一样,在这不重复给出。
上述示例代码中,其实并不是完成按照Reacor设计模式而来的,重头戏请看1.3,主从多线程模型(Reacor)实现
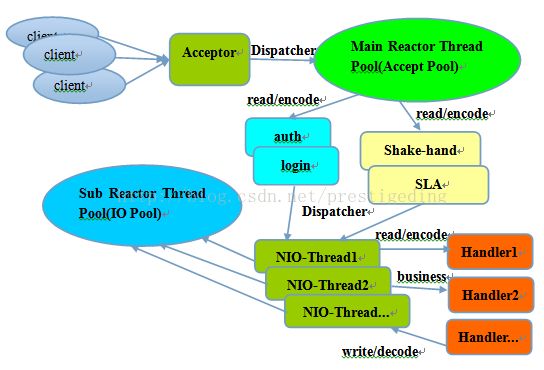
1.3 主从多线程模型(Reactor)
主从多线程模型(此图来源与网络)
重点关注点如下:
- Acceeptor:职责维护java.nio.ServerSocketChannel类,绑定服务端监听端口,然后将该通道注册到MainRector中;
- Main Reactor,监听客户端连接的反应堆,这里使用jdk并发中的Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor线程池来实现,监听客户端的连接事件(OP_ACCEPT)
- Sub Reactor,目前没有使用jdk的并发池,这里用的SubReactorThreadGroup,其实现是数组,当然这里也可以使用jdk线程池,SubReactor的每一个线程都是IO线程,用来处理读,写事件。所有的IO线程公用一个业务线程池(基于juc)实现,用来处理业务逻辑,也就是运行Handel的地方。
Handel:具体业务逻辑实现,本例就是获取客户端的信息后,在请求信息后面追加一段文字,便返回给客户端。相关源码实现:
NioServer(Acceptor)的实现源码:
package persistent.prestige.demo.netty.threadmode.t3;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
* Reactor 主从Reactor模式实现
*
* Acceptor,其实个人认为,这里就是服务端角色
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class NioServer {
private static final int DEFAULT_PORT = 9080;
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new Acceptor()).start();
}
private static class Acceptor implements Runnable {
// main Reactor 线程池,用于处理客户端的连接请求
private static ExecutorService mainReactor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ServerSocketChannel ssc = null;
try {
ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(DEFAULT_PORT));
//转发到 MainReactor反应堆
dispatch(ssc);
System.out.println("服务端成功启动。。。。。。");
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void dispatch(ServerSocketChannel ssc) {
mainReactor.submit(new MainReactor(ssc));
}
}
}
MainReactor 源码如下:
package persistent.prestige.demo.netty.threadmode.t3;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.channels.SelectableChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* 主Reactor,主要用来处理连接请求的反应堆
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class MainReactor implements Runnable {
private Selector selector;
private SubReactorThreadGroup subReactorThreadGroup;
public MainReactor(SelectableChannel channel) {
try {
selector = Selector.open();
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
subReactorThreadGroup = new SubReactorThreadGroup(4);
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("MainReactor is running");
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
while (!Thread.interrupted()) {
Set ops = null;
try {
selector.select(1000);
ops = selector.selectedKeys();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 处理相关事件
for (Iterator it = ops.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
SelectionKey key = it.next();
it.remove();
try {
if (key.isAcceptable()) { // 客户端建立连接
System.out.println("收到客户端的连接请求。。。");
ServerSocketChannel serverSc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();// 这里其实,可以直接使用ssl这个变量
SocketChannel clientChannel = serverSc.accept();
clientChannel.configureBlocking(false);
subReactorThreadGroup.dispatch(clientChannel); // 转发该请求
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("客户端主动断开连接。。。。。。。");
}
}
}
}
}
SubReactor组,IO线程池实现:
package persistent.prestige.demo.netty.threadmode.t3;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* nio 线程组;简易的NIO线程组
* @author dingwei2
*
*/
public class SubReactorThreadGroup {
private static final AtomicInteger requestCounter = new AtomicInteger(); //请求计数器
private final int nioThreadCount; // 线程池IO线程的数量
private static final int DEFAULT_NIO_THREAD_COUNT;
private SubReactorThread[] nioThreads;
private ExecutorService businessExecutePool; //业务线程池
static {
// DEFAULT_NIO_THREAD_COUNT = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() > 1
// ? 2 * (Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() - 1 ) : 2;
DEFAULT_NIO_THREAD_COUNT = 4;
}
public SubReactorThreadGroup() {
this(DEFAULT_NIO_THREAD_COUNT);
}
public SubReactorThreadGroup(int threadCount) {
if(threadCount < 1) {
threadCount = DEFAULT_NIO_THREAD_COUNT;
}
businessExecutePool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threadCount);
this.nioThreadCount = threadCount;
this.nioThreads = new SubReactorThread[threadCount];
for(int i = 0; i < threadCount; i ++ ) {
this.nioThreads[i] = new SubReactorThread(businessExecutePool);
this.nioThreads[i].start(); //构造方法中启动线程,由于nioThreads不会对外暴露,故不会引起线程逃逸
}
System.out.println("Nio 线程数量:" + threadCount);
}
public void dispatch(SocketChannel socketChannel) {
if(socketChannel != null ) {
next().register(new NioTask(socketChannel, SelectionKey.OP_READ));
}
}
protected SubReactorThread next() {
return this.nioThreads[ requestCounter.getAndIncrement() % nioThreadCount ];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
} SubReactor线程实现(IO线程)
package persistent.prestige.demo.netty.threadmode.t3;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* Nio 线程,专门负责nio read,write
* 本类是实例行代码,不会对nio,断线重连,写半包等场景进行处理,旨在理解 Reactor模型(多线程版本)
* @author dingwei2
*
*/
public class SubReactorThread extends Thread {
private Selector selector;
private ExecutorService businessExecutorPool;
private List taskList = new ArrayList(512);
private ReentrantLock taskMainLock = new ReentrantLock();
/**
* 业务线程池
* @param businessExecutorPool
*/
public SubReactorThread(ExecutorService businessExecutorPool) {
try {
this.businessExecutorPool = businessExecutorPool;
this.selector = Selector.open();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* socket channel
*
* @param socketChannel
*/
public void register(NioTask task) {
if (task != null) {
try {
taskMainLock.lock();
taskList.add(task);
} finally {
taskMainLock.unlock();
}
}
}
// private
public void run() {
while (!Thread.interrupted()) {
Set ops = null;
try {
selector.select(1000);
ops = selector.selectedKeys();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
continue;
}
// 处理相关事件
for (Iterator it = ops.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
SelectionKey key = it.next();
it.remove();
try {
if (key.isWritable()) { // 向客户端发送请求
SocketChannel clientChannel = (SocketChannel) key
.channel();
ByteBuffer buf = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
buf.flip();
clientChannel.write(buf);
System.out.println("服务端向客户端发送数据。。。");
// 重新注册读事件
clientChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} else if (key.isReadable()) { // 接受客户端请求
System.out.println("服务端接收客户端连接请求。。。");
SocketChannel clientChannel = (SocketChannel) key
.channel();
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
System.out.println(buf.capacity());
clientChannel.read(buf);//解析请求完毕
//转发请求到具体的业务线程;当然,这里其实可以向dubbo那样,支持转发策略,如果执行时间短,
//,比如没有数据库操作等,可以在io线程中执行。本实例,转发到业务线程池
dispatch(clientChannel, buf);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("客户端主动断开连接。。。。。。。");
}
}
// 注册事件
if (!taskList.isEmpty()) {
try {
taskMainLock.lock();
for (Iterator it = taskList
.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
NioTask task = it.next();
try {
SocketChannel sc = task.getSc();
if(task.getData() != null) {
sc.register(selector, task.getOp(), task.getData());
} else {
sc.register(selector, task.getOp());
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();// ignore
}
it.remove();
}
} finally {
taskMainLock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 此处的reqBuffer处于可写状态
* @param sc
* @param reqBuffer
*/
private void dispatch(SocketChannel sc, ByteBuffer reqBuffer) {
businessExecutorPool.submit( new Handler(sc, reqBuffer, this) );
}
}
NioTask,NIO相关任务封装类:
package persistent.prestige.demo.netty.threadmode.t3;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
/**
* Nio task
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class NioTask implements Serializable {
private SocketChannel sc;
private int op;
private Object data;
public NioTask(SocketChannel sc, int op) {
this.sc = sc;
this.op = op;
}
public NioTask(SocketChannel sc, int op, Object data) {
this(sc, op);
this.data = data;
}
public SocketChannel getSc() {
return sc;
}
public void setSc(SocketChannel sc) {
this.sc = sc;
}
public int getOp() {
return op;
}
public void setOp(int op) {
this.op = op;
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
业务Handle类实现:
package persistent.prestige.demo.netty.threadmode.t3;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
/**
* 业务线程
* 该handler的功能就是在收到的请求信息,后面加上 hello,服务器收到了你的信息,然后返回给客户端
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class Handler implements Runnable {
private static final byte[] b = "hello,服务器收到了你的信息。".getBytes(); // 服务端给客户端的响应
private SocketChannel sc;
private ByteBuffer reqBuffer;
private SubReactorThread parent;
public Handler(SocketChannel sc, ByteBuffer reqBuffer,
SubReactorThread parent) {
super();
this.sc = sc;
this.reqBuffer = reqBuffer;
this.parent = parent;
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("业务在handler中开始执行。。。");
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//业务处理
reqBuffer.put(b);
parent.register(new NioTask(sc, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE, reqBuffer));
System.out.println("业务在handler中执行结束。。。");
}
}
Nio客户端的实现,与上文一样。
注:本文代码旨在理解Reactor反应堆线程模型,对nio涉及到的断线重连,写半包等未做处理。本文关于Reactor模型的三个图片来源与网络,非原创,如果有侵权,请联系作者,将马上删除,谢谢。
欢迎加笔者微信号(dingwpmz),加群探讨,笔者优质专栏目录:
1、源码分析RocketMQ专栏(40篇+)
2、源码分析Sentinel专栏(12篇+)
3、源码分析Dubbo专栏(28篇+)
4、源码分析Mybatis专栏
5、源码分析Netty专栏(18篇+)
6、源码分析JUC专栏
7、源码分析Elasticjob专栏
8、Elasticsearch专栏
9、源码分析Mycat专栏