jQuery源码分析(一)
生成jQuery对象
var global = typeof window !== "undefined" ? window : this;
var factory //line 40 第二个参数
( function( global, factory ) {
"use strict";
if ( typeof module === "object" && typeof module.exports === "object" ) {
// For CommonJS and CommonJS-like environments where a proper `window`
// is present, execute the factory and get jQuery.
// For environments that do not have a `window` with a `document`
// (such as Node.js), expose a factory as module.exports.
// This accentuates the need for the creation of a real `window`.
// e.g. var jQuery = require("jquery")(window);
// See ticket #14549 for more info.
module.exports = global.document ?
factory( global, true ) :
function( w ) {
if ( !w.document ) {
throw new Error( "jQuery requires a window with a document" );
}
return factory( w );
};
} else {
factory( global );
}
// Pass this if window is not defined yet
} )(global, factory);
如果当前容器没用window对象,那么将this作为最父层。factory()函数将会返回jQuery对象。
在CommonJS 或者 CommonJS-like 的环境下 window 对象是没有问题的;如果一个执行环境,它的“window”对象没有“document”的属性,例如Node.js。那么需要暴露一个factory()方法,并将真实的“window”对象传入。var jQuery = require(“jquery”)(window);
通过下面这个代码片段我们可以验证,在nodejs中没有 window对象
router.get('/jquery/window', function(req, res, next) {
console.log("window:" + typeof window);
//window:undefined
res.end();
});
定义公共属性和工具方法
line:48 - line:144
var arr = [];
var document = window.document;
var getProto = Object.getPrototypeOf;
var slice = arr.slice;
var concat = arr.concat;
var push = arr.push;
var indexOf = arr.indexOf;
var class2type = {};
var toString = class2type.toString;
var hasOwn = class2type.hasOwnProperty;
var fnToString = hasOwn.toString;
var ObjectFunctionString = fnToString.call(Object);
var support = {};
通过这种方式避免后面调用过程中一行代码过长
isFunction 判断是否是函数
var isFunction = function isFunction( obj ) {
// Support: Chrome <=57, Firefox <=52
// In some browsers, typeof returns "function" for HTML
// (i.e., `typeof document.createElement( "object" ) === "function"`).
// We don't want to classify *any* DOM node as a function.
return typeof obj === "function" && typeof obj.nodeType !== "number";
};
在部分浏览器中typeof document.createElement( “object” ) === “function”,因此要追加判断。我自己测试了一下,chrome、firefox、IE8+都不存在这种现象。
isWindow 判断对象是否是window对象
var isWindow = function isWindow( obj ) {
// window.window === window;
return obj != null && obj === obj.window;
};
对于上面例子中var isWindow = function isWindow( obj ) {//…};这种写法,做点额外补充。所有的函数都有一个name属性,该属性保存的是该函数名称的字符串。没有名字的函数(匿名函数)依然有name属性,只是属性值为空字符串。参见下面的例子:
var a = function(){}
console.log(a.name);
//IE: ""
//chrome: "a"
var b = function b(){}
console.log(b.name)
//IE: "b"
//chrome: "b"
var c = function cc(){}
console.log(c.name)
//IE: "cc"
//chrome: "cc"
匿名函数的name属性为空字符串,chrome做了额外的事情。
DOMEval 全局作用域内的求值操作
var preservedScriptAttributes = {
type: true,
src: true,
noModule: true
};
function DOMEval( code, doc, node ) {
doc = doc || document;
var i,
script = doc.createElement( "script" );
script.text = code;
if ( node ) {
for ( i in preservedScriptAttributes ) {
if ( node[ i ] ) {
script[ i ] = node[ i ];
}
}
}
doc.head.appendChild( script ).parentNode.removeChild( script );
}
javascript的一大特点就是可以在运行时动态的解释并执行代码。
DOMEval()方法在head部分插入了需要执行的js脚本,该脚本会立即执行,然后从head部分移除掉了,保持页面的整洁,这也是为什么这个方法的名字叫做DOMEval而不是addScript。
这段代码一般用于动态执行从服务器端返回的代码。这种情况一般总是会要求代码在全局作用域内执行。
var url,params;
$.get(url,params,function(code){
//var code="alert(1)";
var script = document.createElement('script');
script.text = code
document.head.appendChild(script).parentNode.removeChild(script)
});
通过这个例子可以看到alert语句被执行了。
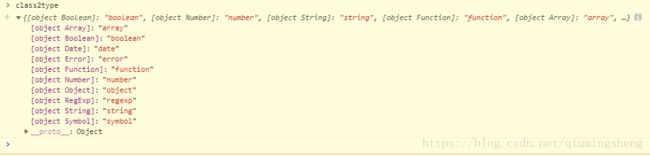
toType 判断对象类型
var class2type = {}; //line:62
function toType( obj ) {
if ( obj == null ) {
return obj + "";
}
// Support: Android <=2.3 only (functionish RegExp)
return typeof obj === "object" || typeof obj === "function" ?
class2type[ toString.call( obj ) ] || "object" :
typeof obj;
}
//line 478
// Populate the class2type map
// 构成对象的键值对
jQuery.each( "Boolean Number String Function Array Date RegExp Object Error Symbol".split( " " ),
function( i, name ) {
class2type[ "[object " + name + "]" ] = name.toLowerCase();
} );
在方法toType中有一个if判断,用来处理obj等于null的情况,下面的例子现实了null对象的强制转换结果:
var a = null;
// null
var b = null + "";
// "null"
typeof a
// object
typeof b
// string
同样的由于undefined==null值为true,所以也会走这个分支。
isArrayLike 判断对象是不是一个类数组结构
//line:482
function isArrayLike(obj) {
// Support: real iOS 8.2 only (not reproducible in simulator)
// `in` check used to prevent JIT error (gh-2145)
// hasOwn isn't used here due to false negatives
// regarding Nodelist length in IE
var length = !!obj && "length" in obj && obj.length,
type = toType(obj);
if (isFunction(obj) || isWindow(obj)) {
return false;
}
return type === "array" || length === 0 ||
typeof length === "number" && length > 0 && (length - 1) in obj;
}
通过这个函数我们能够知道,如果我们希望创建一个类数组的对象,它应该满足以下几个条件:
- 对象不为null或者undefined
- 对象包含length属性
- 对象不是一个函数也不是window对象
- 对象类型为array或者length值为0;如果不满足这两点那么该对象一定要满足length是数值类型,并且length的值大于1,同时(length-1)是该对象的属性之一
根据规则4,我们可以构造如下对象:
var obj = {
0:'name',
1:'age',
length:2
}
isArrayLike(obj);
// true
实际上String对象就是一个典型的类数组对象
Object('str')
//String {"str"}
// 0: "s"
// 1: "t"
// 2: "r"
// length: 3
// __proto__: String
// [[PrimitiveValue]]: "str"
isArrayLike(Object('str'));
// true
jquery 利用正则表达式去除空格
var
// 版本号
version = "3.3.1",
// 定义一个jQuery的本地副本
jQuery = function( selector, context ) {
// The jQuery object is actually just the init constructor 'enhanced'
// Need init if jQuery is called (just allow error to be thrown if not included)
return new jQuery.fn.init( selector, context );
},
// Support: Android <=4.0 only
// Make sure we trim BOM and NBSP
rtrim = /^[\s\uFEFF\xA0]+|[\s\uFEFF\xA0]+$/g;
其中\uFEFF属于BOM标记,用来表示当前文件的字符编码。
BOM(Byte Order Mark),字节顺序标记,出现在文本文件头部,Unicode编码标准中用于标识文件是采用哪种格式的编码。
BOM采用UTF-8编码。几乎所有的文本编辑软件都可以显示并编辑UTF-8编码的文件。但是很遗憾,其中很多软件的表现并不理想。
常见的bug是:
- js文件保存为非utf-8编码时(例如GBK)文件开头会出现乱码
- html文档在浏览器中打开时,顶部会出现一行空白
其中 \xa0 代表非连续空白符。我们通常所用的空格是\x20,是在标准ASCII可见字符 0x20~0x7e 范围内。而 \xa0 属于 latin1 (ISO/IEC_8859-1)中的扩展字符集字符,代表空白符nbsp(non-breaking space)。
rtrim 的正则表达式是一种兼容写法,用于去除字符串首尾的空格。
静态方法
line:297-line:472
expando jquery的唯一标示
// Unique for each copy of jQuery on the page
// jquery的唯一标示。数据缓存,ajax,事件机制都用到了这个。后面集中分析
expando: "jQuery" + (version + Math.random()).replace(/\D/g, ""),
isReady 文档是否加载完毕
line 3878 列出了jquery DOM加载的相关方法,这里暂不做讨论
// Assume jQuery is ready without the ready module
isReady: true,
error 调用原生的Error类
error: function (msg) {
throw new Error(msg);
},
noop
指向一个什么都不做的函数,我们经常可以看到某个组件的默认回调被设为$.noop
noop: function () {},
isPlainObject 判断是否为纯粹对象
var getProto = Object.getPrototypeOf;
var class2type = {};
var toString = class2type.toString;
var hasOwn = class2type.hasOwnProperty;
var fnToString = hasOwn.toString;
var ObjectFunctionString = fnToString.call( Object );
// "function Object() { [native code] }"
isPlainObject: function (obj) {
var proto, Ctor;
// Detect obvious negatives
// Use toString instead of jQuery.type to catch host objects
// 使用 toString 而不是jQuery.type来捕获宿主对象,这是因为type也是调用了toString方法,参见jQuery.type()
//jQuery.type = toType; //line 10291 toType方法前面已经介绍过
if (!obj || toString.call(obj) !== "[object Object]") {
return false;
}
//获取对象的原型
proto = getProto(obj);
// Objects with no prototype (e.g., `Object.create( null )`) are plain
// 如果一个对象是通过Object.create( null )来创建的话,那么它的原型为空,相比于用{}来创建的对象,它的开销也就更小。
// 所以如果我们需要一个 json对象仅用来存储参数,可以使用这个方法
if (!proto) {
return true;
}
// Objects with prototype are plain iff they were constructed by a global Object function
// 如果一个对象是是由全局的Object函数来创建的,那么它是纯粹对象
Ctor = hasOwn.call(proto, "constructor") && proto.constructor;
return typeof Ctor === "function" && fnToString.call(Ctor) === ObjectFunctionString;
},
简单来说,一个对象只有通过{}直接创建、 new Object() 或者通过 Object.create(null) 方式创建那么它才是一个纯粹的对象。
isEmptyObject 是否是空对象
isEmptyObject: function (obj) {
/* eslint-disable no-unused-vars */
// See https://github.com/eslint/eslint/issues/6125
var name;
for (name in obj) {
return false;
}
return true;
},
只要对象包含至少一个属性那么就返回false,即不是空对象。
globalEval 全局作用域内的求值操作
参见DOMEval
// Evaluates a script in a global context
globalEval: function (code) {
DOMEval(code);
},
each 遍历方法
首先我们看一下我们是如何使用$.each接口的:
// 回调函数中第一个参数是当前元素在数组中的索引,第二个参数是遍历到的当前元素
$.each(arrObj,function(i,item){
if(//condition){
// 通过return false 可以跳出当前循环
// return false;
}
// TODO: 业务逻辑
});
each: function (obj, callback) {
var length, i = 0;
if (isArrayLike(obj)) {
length = obj.length;
for (; i < length; i++) {
if (callback.call(obj[i], i, obj[i]) === false) {
break;
}
}
} else {
for (i in obj) {
if (callback.call(obj[i], i, obj[i]) === false) {
break;
}
}
}
return obj;
},
通过源码,我们可以清晰的看到对于类数组对象$.each直接遍历数组里面的每个元素,而其他对象则是遍历属性,如果回调函数返回false则跳出循环。
trim 过滤空格
// Support: Android <=4.0 only
trim: function (text) {
return text == null ?
"" :
(text + "").replace(rtrim, "");
},
关于中间用到的正则表达式,前面已经详细阐述过了。这里面有一个小技巧,即通过(text + "")调用toString方法。
merge 合并两个数组内容到第一个数组
将第二个数组对象合并到第一个数组对象上
// Support: Android <=4.0 only, PhantomJS 1 only
// push.apply(_, arraylike) throws on ancient WebKit
merge: function (first, second) {
// 将length转成数值类型
var len = +second.length,
j = 0,
i = first.length;
for (; j < len; j++) {
first[i++] = second[j];
}
first.length = i;
return first;
},
makeArray 将类数组对象转变为真实数组
首先看一下接口的使用效果:
var obj = Object('str');
var objArr = $.makeArray(obj);
// (3) ["s", "t", "r"]
obj instanceof Array
// false
objArr instanceof Array
// true
源码:
// results is for internal usage only
makeArray: function (arr, results) {
var ret = results || [];
if (arr != null) {
if (isArrayLike(Object(arr))) {
jQuery.merge(ret,
typeof arr === "string" ? [arr] : arr
);
} else {
push.call(ret, arr);
}
}
return ret;
},
Object(arr)可以将原始类型转变为对象类型(装箱操作)
Object(true)
//Boolean {true}
inArray 返回数组中指定元素的索引值
$.inArray( value, array [, fromIndex ] )
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| value | 任意类型 用于查找的值。 |
| array | Array类型 指定被查找的数组。 |
| fromIndex | 可选。Number类型 指定从数组的指定索引位置开始查找,默认为 0 |
inArray: function (elem, arr, i) {
return arr == null ? -1 : indexOf.call(arr, elem, i);
},
indexOf可以接收两个参数,第二参数表示指定开始查找的位置,我们一般很少使用第二个参数
var s = 'aabv'
s.indexOf('a')
// 0
s.indexOf('a',1)
// 1
s.indexOf('a',2)
// -1
grep 过滤原始数组
$.grep( array, function [, invert ] )
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| array | Array类型将被过滤的数组。 |
| function | Function类型 指定的过滤函数。grep()方法为function提供了两个参数:其一为当前迭代的数组元素,其二是当前迭代元素在数组中的索引。 |
| invert | 可选。 Boolean类型 默认值为false,指定是否反转过滤结果。如果参数invert为true,则结果数组将包含function返回false的所有元素。 |
grep: function (elems, callback, invert) {
var callbackInverse,
matches = [],
i = 0,
length = elems.length,
// 回调函数的期望结果,有invert默认为false,所以callbackExpect默认为true
// 换言之,grep函数保留满足回调函数的数据
callbackExpect = !invert;
// Go through the array, only saving the items
// that pass the validator function
for (; i < length; i++) {
// callbackInverse 保存回调的非值
callbackInverse = !callback(elems[i], i);
if (callbackInverse !== callbackExpect) {
matches.push(elems[i]);
}
}
return matches;
},
grep函数返回了一个新的数组对象,因此原数组的值不会改变。这里有一个非常巧妙的地方就是设置了callbackExpect变量,这样就避免了设置两个数组分别存储希望保留的数据和希望排除的数据。
var a = [1,0, null,undefined,'true','false',4];
var b = $.grep(a,function(item,i){
return item;
});
console.log(b);
b的输出结果是什么?
map
$.map( object, callback )
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| object | Array/Object类型 指定的需要处理的数组或对象。 |
| callback | Function类型 指定的处理函数。 |
// arg is for internal usage only
map: function (elems, callback, arg) {
var length, value,
i = 0,
ret = [];
// Go through the array, translating each of the items to their new values
if (isArrayLike(elems)) {
length = elems.length;
for (; i < length; i++) {
value = callback(elems[i], i, arg);
if (value != null) {
ret.push(value);
}
}
// Go through every key on the object,
} else {
for (i in elems) {
value = callback(elems[i], i, arg);
if (value != null) {
ret.push(value);
}
}
}
// Flatten any nested arrays
// 这里需要注意 如果ret是嵌套数组,这里会做扁平化处理,参见下面的示例
return concat.apply([], ret);
},
需要注意的该函数的最后一行,按照我的理解,最后直接return ret就可以了,但是jquery使用apply方法对ret做了扁平化处理。因此当我们使用$.map处理嵌套数组对象时,需要稍微注意一下,考虑下面的这个例子:
var a = [[1,2],[3,4],[5,[6,7]]];
var d = $.map(a,function(item,i){
return item;
});
console.log(d)
// [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, Array(2)]
最终d的值可能并不是我们期望的。
思考 如何将一个多维数组展开成一个一维数组
借助$.map和$.isArray利用递归我们可以将一个多维数组展开成一位数组
function flatten(array){
return $.map(array,function(item){
return $.isArray(item)?flatten(item):item;
});
}
var a = [1,2,3];
var b = [1,[2,3],4];
var c = [1,[2,3],[4,[5,6]]];
console.log(flatten(a));
// [1, 2, 3]
console.log(flatten(b));
// [1, 2, 3, 4]
console.log(flatten(c));
// [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
其他属性
var support = {}; //line:72
jQuery.extend({
// A global GUID counter for objects
// 为对象创建的一个全局GUID 计数器,记录了事件处理器的数量
guid: 1,
// jQuery.support is not used in Core but other projects attach their
// properties to it so it needs to exist.
// jquery 本身没有用到这个变量,用于支持其他组件
support: support
});
jQuery 原型属性及方法
toArray 将jquery对象转换成数组对象
toArray: function () {
return slice.call(this);
},
get 从匹配的元素中获取指定元素或者将所有匹配的元素以数组形式返回
// Get the Nth element in the matched element set OR
// Get the whole matched element set as a clean array
get: function (num) {
// Return all the elements in a clean array
if (num == null) {
return slice.call(this);
}
// Return just the one element from the set
// 如果num为负数,则相当于从后往前取
return num < 0 ? this[num + this.length] : this[num];
},
pushStack
// Take an array of elements and push it onto the stack
// (returning the new matched element set)
pushStack: function (elems) {
// Build a new jQuery matched element set
var ret = jQuery.merge(this.constructor(), elems);
// Add the old object onto the stack (as a reference)
ret.prevObject = this;
// Return the newly-formed element set
return ret;
},
顾名思义,pushStack就是将对象压入栈的意思。jquery在查找元素是,会构造一个堆栈,并且永远会将当前查找到的元素放到栈的顶端。假设我们有如下DOM结构:
<div class="container">
<ul class="list">
<li class="item"><span class="txt">1span>li>
<li class="item"><span class="txt">1span>li>
<li class="item"><span class="txt">1span>li>
<ul>
div>
如果我们使用jquery进行查找
$('.container').find('ul').find('li')
就会形成一个堆栈
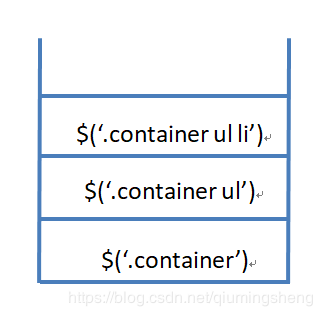
如果想访问上一级元素参见end()方法。
prevObject 用于保存当前元素。jquery中众多的查找方法都是基于pushStack和prevObject
each 遍历元素
这里可以看到原型方法与静态方法的使用区别
// Execute a callback for every element in the matched set.
each: function (callback) {
return jQuery.each(this, callback);
},
map 对匹配的元素做相应操作
map: function (callback) {
return this.pushStack(jQuery.map(this, function (elem, i) {
return callback.call(elem, i, elem);
}));
},
slice 选取匹配的元素
其表现形式与slice函数相似
slice: function () {
return this.pushStack(slice.apply(this, arguments));
},
eq 选取指定下标的元素
eq: function (i) {
var len = this.length,
j = +i + (i < 0 ? len : 0);
return this.pushStack(j >= 0 && j < len ? [this[j]] : []);
},
first 选取第一个元素
first: function () {
return this.eq(0);
},
last 选取最后一个元素
last: function () {
return this.eq(-1);
},
end
返回链式结构的上一级元素,最顶级是jquery的构造器。参见pushStack函数。
end: function () {
return this.prevObject || this.constructor();
},
其他属性及方法
jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype = {
// The current version of jQuery being used
// 指向版本号
jquery: version,
// 指向jQuery对象
constructor: jQuery,
// The default length of a jQuery object is 0
length: 0,
// For internal use only.
// Behaves like an Array's method, not like a jQuery method.
// 以下三个方法仅供内部调用
push: push,
sort: arr.sort,
splice: arr.splice
};
extend 用于将一个或多个对象的内容合并到目标对象
$.extend( target [, object1 ] [, objectN ] )
指示是否深度合并
$.extend( [deep ], target, object1 [, objectN ] )
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| deep | 可选。 Boolean类型 指示是否深度合并对象,默认为false。如果该值为true,且多个对象的某个同名属性也都是对象,则该"属性对象"的属性也将进行合并。 |
| target | Object类型 目标对象,其他对象的成员属性将被附加到该对象上。 |
| object1 | 可选。 Object类型 第一个被合并的对象。 |
| objectN | 可选。 Object类型 第N个被合并的对象。 |
jQuery.extend = jQuery.fn.extend = function () {
var options, name, src, copy, copyIsArray, clone,
target = arguments[0] || {},
i = 1,
length = arguments.length,
deep = false;
// Handle a deep copy situation
// 选用深拷贝还是浅拷贝,默认浅拷贝
if (typeof target === "boolean") {
deep = target;
// Skip the boolean and the target
// 如果第一个参数是bool型,那么target应为第二个参数
target = arguments[i] || {};
// i++的目的是为了标记剩下对象的参数下标
i++;
}
// Handle case when target is a string or something (possible in deep copy)
// 当target不是对象也是函数时,可能是字符串或其他值类型
if (typeof target !== "object" && !isFunction(target)) {
target = {};
}
// Extend jQuery itself if only one argument is passed
// 当只有一个参数时,意味着向jQuery对象上添加属性或方法
if (i === length) {
target = this;
i--;
}
for (; i < length; i++) {
// Only deal with non-null/undefined values
// 只处理有效的对象
if ((options = arguments[i]) != null) {
// Extend the base object
for (name in options) {
src = target[name];
copy = options[name];
// Prevent never-ending loop
// 防止死循环
if (target === copy) {
continue;
}
// Recurse if we're merging plain objects or arrays
// 调用递归合并纯粹对象或数组
if (deep && copy && (jQuery.isPlainObject(copy) ||
(copyIsArray = Array.isArray(copy)))) {
if (copyIsArray) {
copyIsArray = false;
clone = src && Array.isArray(src) ? src : [];
} else {
clone = src && jQuery.isPlainObject(src) ? src : {};
}
// Never move original objects, clone them
target[name] = jQuery.extend(deep, clone, copy);
// Don't bring in undefined values
// 对于undefined的值忽略
} else if (copy !== undefined) {
target[name] = copy;
}
}
}
}
// Return the modified object
返回已经修改的对象
return target;
};