OpenCV学习28--在图像中寻找轮廓
查找轮廓
什么是轮廓:一个轮廓是由图像中的一系列点组成的,也就是图像中的一条曲线。在OpenCV中一般用序列来存储轮廓信息。序列中的每个元素是曲线中每个点的位置。
关于序列:序列是内存存储器中可以存储的一种对象,序列是某种结构的链表。
下面是序列结构体:
typedef sturct CvSeq{
int flags;
int header_size;
CvSeq * h_prev;
CvSeq * h_next;
CvSeq * v_prev;
CvSeq * v_next;
int total;
int elem_size;
char *bolck_max;
char * ptr;
int delta_elems;
CvMemStorage * storage;
CvSeqBlock * free_blocks;
CvSeqBlock * first;
}
Freeman编码
在Freeman链码中,多边形被表示成一系列的位移,每一个位移都有8个方向,这8个方向从0到7表示。
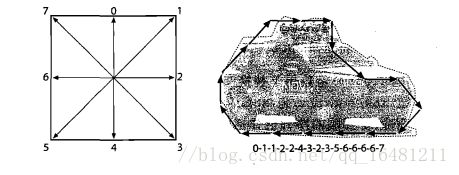
2. 相关API
findContours()函数来寻找图像中物体的轮廓,并结合drawContours()函数将找到的轮廓绘制出。
void cv::findContours ( InputOutputArray image,
OutputArrayOfArrays contours,
OutputArray hierarchy,
int mode,
int method,
Point offset = Point()
)
参数解释:
- image:输入图像,图像必须为8-bit单通道图像,图像中的非零像素将被视为1,0像素是0,加载图像后自动转化为二值化图像。我们同样可以使用cv::compare,cv::inRange,cv::threshold,cv::adaptiveThreshold,cv::Canny等函数来创建二值图像。
- contours 检测到的轮廓,每个轮廓都是以点向量的形式进行存储即使用point类型的vector表示。
- hierarchy 可选的输出向量包括了图像的拓扑信息。
- mode 轮廓检索模式
- method 轮廓近似方法
void cv::drawContours ( InputOutputArray image,
InputArrayOfArrays contours,
int contourIdx,
const Scalar & color,
int thickness = 1,
int lineType = LINE_8,
InputArray hierarchy = noArray(),
int maxLevel = INT_MAX,
Point offset = Point()
)
参数解释:
- image 输入Mat类型图像
- contours 检测到的轮廓数据。
- contourldx 绘制轮廓的只是变量,如果为负值则在轮廓内部绘制。
- line type 线条类型 LINE_4 4-connected line LINE_8 8-connected line LINE_AA antialiased line
- hierarchy 可选层次结构
- maxLevel 用于绘制轮廓的最大等级
- offset 可选轮廓偏置参数,制定偏移量offset=(dx, dy)给出绘制轮廓的偏移量
3. 示例代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main()
{
Mat src,dst,gray_img;
src = imread("1.jpg");
if(src.empty())
{
cout<<"图像加载失败";
waitKey(0);
return -1;
}
else
cout<<"图像加载成功";
namedWindow("1",WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow("1",src);
cvtColor(src,gray_img,CV_BGR2GRAY);
vector>contours;
vectorhierarchy;
gray_img = gray_img > 100;
findContours(gray_img,contours,hierarchy,CV_RETR_CCOMP,CV_CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
//绘制轮廓图
dst = Mat::zeros(src.size(), CV_8UC3);
for (int i = 0; i < hierarchy.size(); i++)
{
Scalar color = Scalar(rand() % 255, rand() % 255, rand() % 255);
drawContours(dst, contours, i, color, CV_FILLED, 8, hierarchy);
}
imshow("轮廓图", dst);
waitKey(0);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}

