Python的charts和Jupyter的使用 使数据可视化 对58同城的爬取
尝试学习了将爬取的数据进行清洗,更新数据库后。进行可视化。记录一部分
主要是对两个库的使用
使用pip进行安装
jupyter安装后再cmd下输入 jupyter notebook
确实好用方便
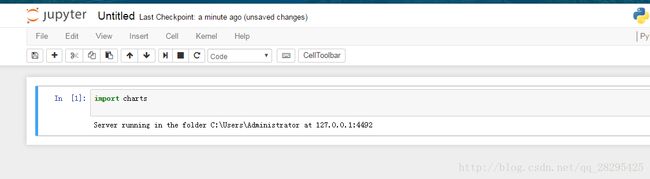
在jupyter中编写
有个库是string中的。是标点符号的库。
punctuation
if not in punctuation
可以做数据的清洗过滤。如果不是标点符号
清洗数据后,更新
update方法
db.collection.update()
接收两个参数
1. 更新哪个文件
2. 怎么改。
如下图:
清洗后
可视化
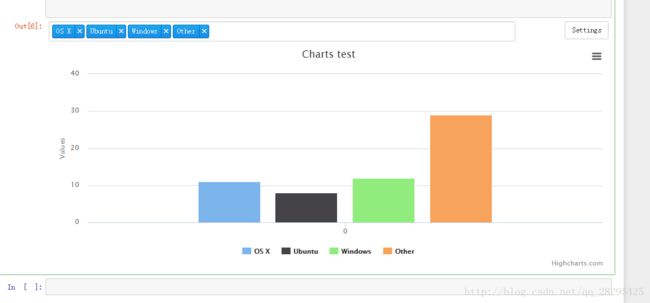
Charts
例子:
import charts
#数据
series =[
{
'name':'OS X',
'data':[11],
'type':'column'
},
{'name':'Ubuntu',
'data':[8],
'type':'column'
},
{'name':'Windows',
'data':[12],
'type':'column'
},
{'name':'Other',
'data':[29],
'type':'column'
}
]
#使用charts绘画
charts.plot(series,show='inline',options=dict(title=dict(text='Charts test')))
运行后:好方便!
我也百度看的别人的博客
http://www.cnblogs.com/pangduzi/p/5889896.html
这个就写的很详细。我也记录下,方便以后使用。
我也爬取了一会58二手数据。。。但是没让电脑跑那么久。
看到这位大佬也爬取了
http://www.cnblogs.com/pangduzi/p/5889952.html
学习了。
对这几天学习的爬取做下总结:
更加熟练的使用BeautifulSoup了。结合谷歌浏览器的复制来获取其分析路径。
然后用其的select方法来获取。
还有对其网页进行分析。
使用多进程快些。多核的话多进程比多线程更快些。
记录下当时的笔记:
对58同城的二手市场爬取
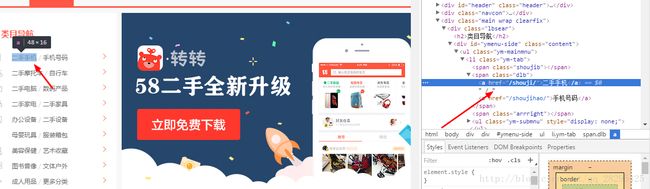
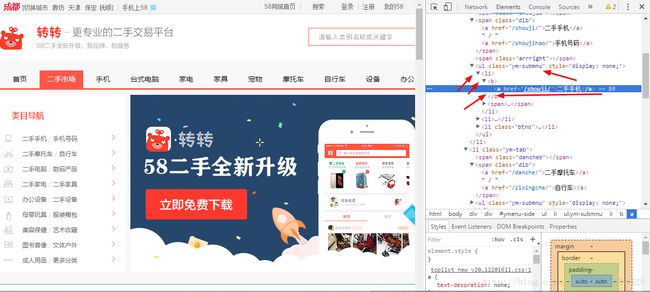
先进入二手市场首页,然后获取所有二手分类
Ul下的li下的b的a
ul.ym-submnu > li > b > a但是返回的只是后面的,并不是完整的url,那么拼接
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
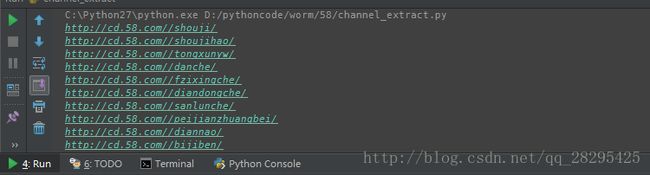
#二手首页,然后获取每个二手分类的url
start_url = 'http://cd.58.com/sale.shtml'
def get_channel_urls(url):
wb_data = requests.get(start_url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(wb_data.content)
links = soup.select('ul.ym-submnu > li > b > a')
for link in links:
page_url = 'http://cd.58.com/'+link.get('href')
print(page_url)
get_channel_urls(start_url)
然后获取每个分类也后的每个商品的url,并存入mongoDB
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import time
import pymongo
#将爬取的url放入数据库,先建立数据库
client = pymongo.MongoClient('localhost',27017)
ceshi = client['ceshi']
url_list = ceshi['url_list']
#第一个爬虫,抓起列表中的url
#每一个二手分类频道里的每个商品获取其url
def get_links_from(channel,pages,who_sells=0):
#http://cd.58.com/diannao/pn2
#页面变的就是pn ,who_sells是分类个人还是商家 默认0也就是个人
list_view = '{}{}/pn{}'.format(channel,str(who_sells),str(pages))
wb_data = requests.get(list_view)
time.sleep(1)
soup = BeautifulSoup(wb_data.content)
for link in soup.select('td.t a.t'):
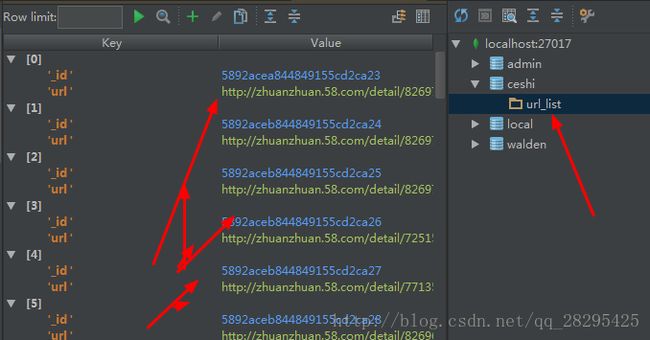
item_link =link.get('href').split('?')[0]
url_list.insert({'url':item_link})
print(item_link)
get_links_from('http://cd.58.com//danche/',2)
但是输入过大的页面有可能就没有了
那么做个判断。
比较有与没有的差别
在于是否有商品,用的是td
就在for前面加个判断
if soup.find('td','t'):
for link in soup.select('td.t a.t'):
item_link =link.get('href').split('?')[0]
url_list.insert({'url':item_link})
print(item_link)
else:
pass
然后第二个爬取,爬取每个商品的详细信息
有可能之前爬取的url突然删除了或者已经交易出去了。
返回的是404页面。那么做个判断
404在 script标签中有404就是灰跳转到404
#爬取商品的详细信息
def get_item_info(url):
wb_data = requests.get(url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(wb_data.content)
#有可能之前爬取的url突然删除了或者已经交易出去了。
no_longer_exist = '404' in soup.find('script',type="text/javascript").get('src').split('/')
if no_longer_exist:
pass
else:
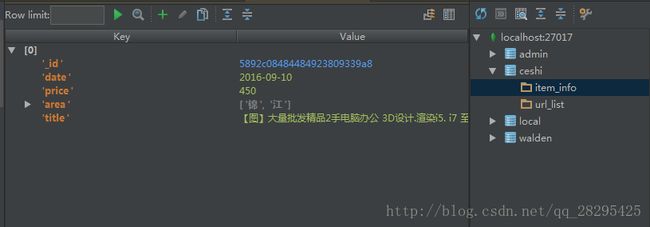
title = soup.title.text
price = soup.select('span.price.c_f50')[0].text
date = soup.select('.time')[0].text
#有的有可能会没有所有在后面做了个if else的判断
##content > div.person_add_top.no_ident_top > div.per_ad_left > div.col_sub.sumary > ul > li:nth-child(3) > div.su_con > span
area = list(soup.select('#content > div.person_add_top.no_ident_top > div.per_ad_left > div.col_sub.sumary > ul > li:nth-of-type(3) > div.su_con > span > a:nth-of-type(1)')[0].text) if soup.find('span','c_25d') else None
item_info.insert({'title':title,'price':price,'date':date,'area':area})
print(area)
get_item_info('http://cd.58.com/diannao/23276725917860x.shtml')
设置代理的话
先有代理ip和端口
然后proxies={‘http’:那个代理}
Request.get(url,headers=headers,proxies=proxies)
对于类似二手交易网站的爬取。
先爬取频道,分析其url。
先进入一个频道,然后分析其商品和需要的数据。使用beautifulsoup来解析,使用谷歌的复制方便些,也可以自己分析其结构。
然后可以进入这个商品的详细信息分析。
使用MongoDB实在是有够方便。。。。
一个爬虫:爬取所有频道url
一个爬取把放入的频道url进行商品的爬取。
还可以写个每个商品的详细信息爬取。
使用多进程要快与多进程5-7倍。单核的电脑不要使用多进程。
可以写个监视py 也就是简单来说每隔一定时间查询数据库中的数据量。
就是多写,多分析。多使用一些python方便的库~