java网络编程之Netty实战心跳检测(八)
Netty实战心跳检测
1 概念理解
我们使用Socket通信一般经常会处理多个服务器之间的心跳检测,一般来讲我们去维护服务器集群,肯定要有一台或(几台)服务器主机(Master),然后还应该有N台(Slave),那么我们的主机肯定要时时刻刻知道自己下面的从服务器的各方面情况。然后进行实时监控的功能。这个在分布式架构里叫做心跳检测或者说心跳监控。最佳处理方案我还是觉得是使用一些通信框架进行实现,我们的Netty就可以去做这样一件事。

废话不多说直接上案例。
2 案例
在编写案例之前先说一下要加入jar包, 1、netty 2、log4j 3、jboss-marshalling jboss-marshalling-serial 4、sigar(这个jar包是用来获得电脑cpu信息、内存信息等)不理解的可去官网查看使用教程,在讲完案例后我附上sigar一些例子。
jar包我已上传github:https://github.com/hfbin/Thread_Socket/tree/master/Socket/heartBeat/jar%E5%8C%85
还是老规矩从实体类入手。
2.1 实体类
public class RequestInfo implements Serializable {
//1
private String ip ;
//2
private HashMap cpuPercMap ;
//3
private HashMap memoryMap;
public String getIp() {
return ip;
}
public void setIp(String ip) {
this.ip = ip;
}
public HashMap getCpuPercMap() {
return cpuPercMap;
}
public void setCpuPercMap(HashMap cpuPercMap) {
this.cpuPercMap = cpuPercMap;
}
public HashMap getMemoryMap() {
return memoryMap;
}
public void setMemoryMap(HashMap memoryMap) {
this.memoryMap = memoryMap;
}
} 这个实体类主要用来封装了客户端的1、ip地址 2、cpu信息 3、内存信息。
2.2 Jboss Marshalling 编解码工具类
public final class MarshallingCodeCFactory {
/**
* 创建Jboss Marshalling解码器MarshallingDecoder
* @return MarshallingDecoder
*/
public static MarshallingDecoder buildMarshallingDecoder() {
//1
final MarshallerFactory marshallerFactory = Marshalling.getProvidedMarshallerFactory("serial");
//2
final MarshallingConfiguration configuration = new MarshallingConfiguration();
configuration.setVersion(5);
//3
UnmarshallerProvider provider = new DefaultUnmarshallerProvider(marshallerFactory, configuration);
//4
MarshallingDecoder decoder = new MarshallingDecoder(provider, 1024 * 1024 * 1);
return decoder;
}
/**
* 创建Jboss Marshalling编码器MarshallingEncoder
* @return MarshallingEncoder
*/
public static MarshallingEncoder buildMarshallingEncoder() {
final MarshallerFactory marshallerFactory = Marshalling.getProvidedMarshallerFactory("serial");
final MarshallingConfiguration configuration = new MarshallingConfiguration();
configuration.setVersion(5);
MarshallerProvider provider = new DefaultMarshallerProvider(marshallerFactory, configuration);
//5
MarshallingEncoder encoder = new MarshallingEncoder(provider);
return encoder;
}
}1、首先通过Marshalling工具类的精通方法获取Marshalling实例对象 参数serial标识创建的是java序列化工厂对象。
2、创建了MarshallingConfiguration对象,配置了版本号为5
3、根据marshallerFactory和configuration创建provider
4、构建Netty的MarshallingDecoder对象,俩个参数分别为provider和单个消息序列化后的最大长度
5、构建Netty的MarshallingEncoder对象,MarshallingEncoder用于实现序列化接口的POJO对象序列化为二进制数组
个人感觉不难都是一些固定的写法,记住每一步要做什么就好,建议你去看一些我编解码技术的这篇文章
2.3 服务端
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
EventLoopGroup pGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup cGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(pGroup, cGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024)
//1
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel sc) throws Exception {
//2
sc.pipeline().addLast(MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingDecoder());
//3
sc.pipeline().addLast(MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingEncoder());
sc.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHeartBeatHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture cf = b.bind(8765).sync();
cf.channel().closeFuture().sync();
pGroup.shutdownGracefully();
cGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
} 1、设置日志(这里需要自己导入log4j.jar) 当然你也可以不设置打印日记
2、这是我们写的Jboss Marshalling工具类的解码器MarshallingDecoder
3、这是我们写的Jboss Marshalling工具类的编码器MarshallingEncoder
其他不懂的去看我Netty的第一篇文章
服务端业务逻辑
public class ServerHeartBeatHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
/** key:ip value:auth */
private static HashMap AUTH_IP_MAP = new HashMap();
private static final String SUCCESS_KEY = "auth_success_key";
static {
AUTH_IP_MAP.put("169.254.165.147", "1234");
}
//认证
private boolean auth(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg){
//System.out.println(msg);
//分割
String [] ret = ((String) msg).split(",");
//在AUTH_IP_MAP中获取values
String auth = AUTH_IP_MAP.get(ret[0]);
if(auth != null && auth.equals(ret[1])){
ctx.writeAndFlush(SUCCESS_KEY);
return true;
} else {
//链接失败,关闭客户端的链接
ctx.writeAndFlush("auth failure !").addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
return false;
}
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
if(msg instanceof String){
auth(ctx, msg);
} else if (msg instanceof RequestInfo) {
//将数据放到RequestInfo中
RequestInfo info = (RequestInfo) msg;
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("当前主机ip为: " + info.getIp());
System.out.println("当前主机cpu情况: ");
HashMap cpu = info.getCpuPercMap();
System.out.println("总使用率: " + cpu.get("combined"));
System.out.println("用户使用率: " + cpu.get("user"));
System.out.println("系统使用率: " + cpu.get("sys"));
System.out.println("等待率: " + cpu.get("wait"));
System.out.println("空闲率: " + cpu.get("idle"));
System.out.println("当前主机memory情况: ");
HashMap memory = info.getMemoryMap();
System.out.println("内存总量: " + memory.get("total"));
System.out.println("当前内存使用量: " + memory.get("used"));
System.out.println("当前内存剩余量: " + memory.get("free"));
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------");
//返回一条状态给客户端
ctx.writeAndFlush("info received!");
} else {
ctx.writeAndFlush("connect failure!").addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
}
} 服务端业务逻辑,主要是获取客户端的信息,但是获取客户端信息必须要经过验证后客户端才能连上服务端,向服务端推送客户端机子的各种信息。为了操作方便,这里采用了一个静态模块用来保存客户端机ip、key(我放在Map中ip为Map中的key,key为Map中的value),注意为了安全起见key建议使用加密后的key,比如用MD5加密,还有这里不建议使用静态模块保存客户端机ip、key,你可以保存到数据库,或者写一个配置文件,我这里为了方便才放在静态模块中的。
由于没什么难的地方我不一一说明了,要说的我都注释在代码中了
这里我要说一下instanceof运算符:
instanceof 运算符是用来在运行时指出对象是否是特定类的一个实例。instanceof通过返回一个布尔值来指出,这个对象是否是这个特定类或者是它的子类的一个实例。
客户端
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel sc) throws Exception {
//1
sc.pipeline().addLast(MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingDecoder());
//2
sc.pipeline().addLast(MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingEncoder());
sc.pipeline().addLast(new ClienHeartBeattHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture cf = b.connect("127.0.0.1", 8765).sync();
cf.channel().closeFuture().sync();
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
} 1、这是我们写的Jboss Marshalling工具类的解码器MarshallingDecoder
2、这是我们写的Jboss Marshalling工具类的编码器MarshallingEncoder
其他不懂的去看我Netty的第一篇文章
客户端业务逻辑
public class ClienHeartBeattHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
//线程池
private ScheduledExecutorService scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
//异步
private ScheduledFuture heartBeat;
//主动向服务器发送认证信息
private InetAddress addr ;
private static final String SUCCESS_KEY = "auth_success_key";
//客户端启动时这个方法自动启动,不懂的可以去官网看看Netty Handler的生命周期
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
//得到本机ip
addr = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
String ip = addr.getHostAddress();
System.out.println("ip = "+ip);
String key = "1234";
//证书
String auth = ip + "," + key;
ctx.writeAndFlush(auth);
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
try {
if(msg instanceof String){
String ret = (String)msg;
if(SUCCESS_KEY.equals(ret)){
// 握手成功,主动发送心跳消息
//1、要执行的任务 传入ctx 是为了能在这个类里面直接可以往服务端发数据
//2、初始化等待时间
//3、多少秒执行一次
//4、
this.heartBeat = this.scheduler.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new HeartBeatTask(ctx), 0, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println(msg);
}
else {
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
} finally {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
}
//内部类
private class HeartBeatTask implements Runnable {
private final ChannelHandlerContext ctx;
public HeartBeatTask(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
this.ctx = ctx;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
RequestInfo info = new RequestInfo();
//ip
info.setIp(addr.getHostAddress());
Sigar sigar = new Sigar();
//cpu
CpuPerc cpuPerc = sigar.getCpuPerc();
HashMap cpuPercMap = new HashMap();
cpuPercMap.put("combined", cpuPerc.getCombined());
cpuPercMap.put("user", cpuPerc.getUser());
cpuPercMap.put("sys", cpuPerc.getSys());
cpuPercMap.put("wait", cpuPerc.getWait());
cpuPercMap.put("idle", cpuPerc.getIdle());
// memory
Mem mem = sigar.getMem();
HashMap memoryMap = new HashMap();
memoryMap.put("total", mem.getTotal() / 1024L);
memoryMap.put("used", mem.getUsed() / 1024L);
memoryMap.put("free", mem.getFree() / 1024L);
info.setCpuPercMap(cpuPercMap);
info.setMemoryMap(memoryMap);
ctx.writeAndFlush(info);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
} 这个也不难,认真读大家都能读懂。难理解的我都在代码中注释了。这里使用线程池执行定时任务每隔两秒就往服务端发送当前机子的cpu等各种信息。
好!到这目前所有代码都编写完了来测试一下效果。
服务端启动打印如图:
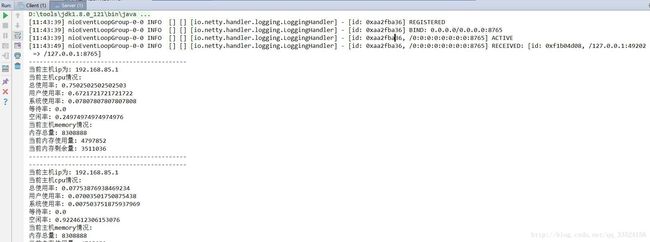
客户端启动打印如图:

这里只截取部分,由于两秒执行一次,打印比较多,自己可以下载代码自己测试效果怎样。
客户端启动后服务端的打印:
这里只截取部分,由于两秒执行一次,打印比较多,自己可以下载代码自己测试效果怎样。
源代码:https://github.com/hfbin/Thread_Socket/tree/master/Socket/heartBeat