【一】用JavaSE编写简单的贪吃蛇游戏
【时间有限,只花了一晚上写,可能有很多bug,希望各位能理解!】
一 项目简述
本项目主要实现了一个简单的贪吃蛇游戏,目前只实现了“吃豆长大、得分”、“碰壁死亡”、“头撞尾死亡”这些功能,是一个最基本版本的贪吃蛇。该"贪吃蛇"游戏编写很简单,因此对于刚学java的新手能够起到很好的学习作用,并且我本次编写的图形设计主要利用Java.awt里最简单基本的类、方法和事件,对于新手掌握gui能够起到很好的促进作用,同时希望我的这篇博客能够帮助新手更好的理解利用面向对象的方式来编程解决问题。
二 设计前的思考
"贪吃蛇"这个游戏的玩法相信不需要我多言(先是一条小蛇,然后通过吃豆进行成长,如果碰壁或者头尾相连则游戏结束),那么很明显我们至少得有三个类:一个Background类、一个Snake类、一个Bean类。
我们对目前确定的三个基本类进行思考:
- Background类:"贪吃蛇"这个游戏需要提前对位置进行判定,才能准确的吃到豆子,那么我们是不是应该画些网格来辅助游戏者进行位置的判定呢?
- Snake类:因为蛇就像是一条链子一样,由很多小节组成,因此我们是否应该再去增加一个类用来表示每个小节呢?然后蛇的熟悉需要哪些呢?每一小节的属性需要哪些呢?
- Bean类:因为豆子的出现不能是有一定规律的,因此我们是不是应该用随机数来表示豆子每次的出现呢?
三 具体编写
通过上诉的思考,我们能够确定我们大概需要除了上诉三个类还需要一个类用来表示"蛇的每一小节"(我们用Rou来表示),首先,我们进行背景的编写(即Background)。
3.1 Background的基础网格建立
- 首先,我们定义一个类,取名为Background,因为整个背景是一个Frame,且我们需要在Frame上进行绘制网格等操作,因此我们首先让Background继承Frame类。
- 然后,我们因为我们需要对网格进行划分,因此我们需要定义该类的一些属性,包括网格的纵线、横线的数量以及网格的间距,这时我们对继承的Frame类里的paint进行重写从而绘制出网格。
- 这时通过对main方法的编写我们已经能够显示出窗体以及网格了,但是目前这是个不能关闭的程序,因此我们通过加入侦听器接口,然后再重写WindowAdapter()方法实现对窗口的关闭退出功能。
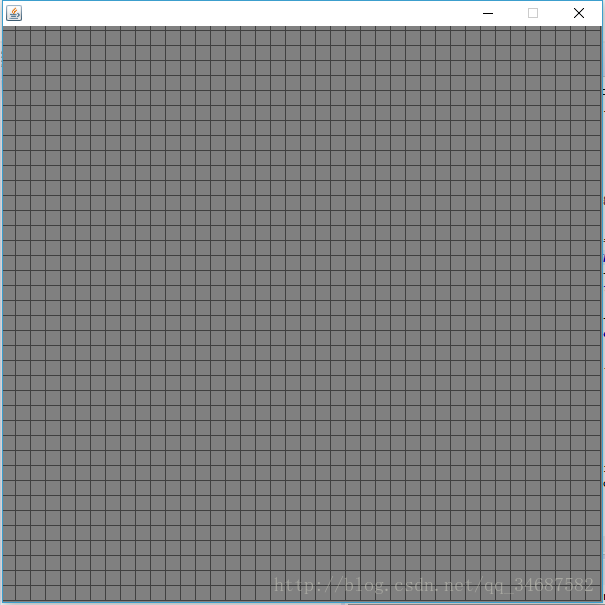
通过上诉步骤我们Background的基本内容已经搭建成功了,代码和实际效果图如下:
public class Background extends Frame{
public static final int Line_x = 40;
public static final int Line_y = 40;
public static final int Dt = 15;
public void Backgroundset() {
this.setSize(Line_x*Dt+5,Line_y*Dt+5);
this.setResizable(false);
this.setBackground(Color.gray);
this.setVisible(true);
this.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
public void paint(Graphics g) {
Color c = g.getColor();
g.setColor(Color.GRAY);
g.fillRect(5, 5, Line_x*Dt,Line_y*Dt);
g.setColor(Color.DARK_GRAY);
for(int i=0;i<=Line_y;i++) {
g.drawLine(i*Dt, 0, i*Dt,Line_y*Dt);
}
for(int i=0;i<=Line_x;i++) {
g.drawLine(0, i*Dt, Line_x*Dt, i*Dt);
}
g.setColor(c);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Background().Backgroundset();
}
}"Background"初步建立后如下:
3.2 Rou的定义
首先,我们建立一个类用来存放蛇的每一小节,我给它取名为Rou(谐音”肉“),通过分析游戏可以发现,对于每一个Rou都需
要至少四个属性(X坐标、Y坐标、宽度、高度、前进方向),但是为了方便后面的编写我再这里又加入了两个属性(前面的Rou,后
面的Rou),并且由于每一个Rou的宽度和高度都是常量,因此我们直接设置高度和宽度不把他们作为变量属性。(其中,对于”前
进方向“我们需要建立枚举类来对它进行管理):
public enum Dir {
U,D,L,R;
}定义了Rou后,然后我们再创建一个"draw"方法用来绘制每个Rou。
public class Rou {
int x;
int y;
int w=Background.Dt;
int h=Background.Dt;
Dir d;
Rou pre=null;
Rou next=null;
public Rou(int x,int y,Dir d,Rou pre,Rou next){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
this.d=d;
this.pre=pre;
this.next=next;
}
void draw(Graphics g) {
Color c = g.getColor();
g.setColor(Color.WHITE);
g.fillRect(Background.Dt* x, Background.Dt*y, w, h);
g.setColor(c);
}
}做完上述步骤后,我们在“Background”类里对“Rou”的“draw”方法进行调用,检测我们是否能够正确的绘制出一个Rou。
Rou r=new Rou(20,20,Dir.L,null,null);
r.draw(g);调用后显示出来结果如下:
3.3 Snake类的编写
首先,Snake这个类是很多Rou的结合,因此对于整条蛇来说,位置、大小、方向等属性已经不需要再去定义了。因此,我们只需要定义蛇的的整体的东西,在这里我定义三个属性(蛇头、蛇尾、蛇Rou的个数),通过这三个量我们能对蛇的宏观进行表示,再由每一个Rou自身的属性值对蛇的微观进行表示,进而表示出了整个蛇。我们再对整个游戏初始的Rou进行设置,从而完成整个Snake的定义
然后,我们开始编写它的方法:
①当我们的小蛇吃到豆子后,会进行增长,这里我设蛇在蛇头的位置进行增长,为什么不选择蛇尾呢,后面我们会提到。因此,我们编写一个“addHead”方法用来处理蛇的增长。
②我们再编写它的绘制方法,一条完整蛇的绘制相当于是将该蛇的每一个“Rou”绘制出来,且当蛇移动时我们可以看成时蛇尾的Rou转移到了蛇头。因此,我们还需要写一个“deleteTail”方法用来删除蛇尾的Rou,这样加一个在蛇头减一个在蛇尾就组成了蛇的运动。
③这时,我们再来编写控制蛇运动的方法,我们通过“方向键”进行操作,因此我们通过编写“keyPressed”方法,通过按键改变蛇头的方向,从而达到控制蛇的效果。
④为了让这个程序不断的绘制刷新画面,我们需要在”Background“类里去建立一个线程用来不断刷新蛇的绘制,从而使蛇运动起来。然后我们还需要在“Background”类里面建立一个“KeyMonitor”进行键盘监听,从而完成对蛇的控制效果。
通过上诉方法的编写我们的小蛇已经可以受我们的控制进行运动了。
public class Snake {
int x=(int) (Math.random()*40);
int y=(int) (Math.random()*40);
public boolean gameOver = false;
Dir enums[] = Dir.values();
Random random = new Random();
Dir d = enums[random.nextInt(enums.length)];
Rou pre=null;
Rou next=null;
Rou rou=new Rou(x,y,d,pre,next);
Rou r=null;
Rou head=null;
Rou tail=null;
int size;
Background bg;
public Snake(Background bg) {
this.head=rou;
this.tail=rou;
this.size=1;
}
public void addHead() {
Rou r=null;
switch(head.d) {
case L:
r = new Rou(head.x - 1, head.y , head.d,null,head);
break;
case D:
r = new Rou(head.x , head.y + 1, head.d,null,head);
break;
case R:
r = new Rou(head.x + 1, head.y , head.d,null,head);
break;
case U:
r = new Rou(head.x , head.y - 1 , head.d,null,head);
break;
}
r.next=head;
size ++;
head.pre=r;
head=r;
}
public void draw(Graphics g) {
move();
for(Rou r = head; r != null; r = r.next) {
r.draw(g);
}
}
private void move() {
addHead();
deleteTail();
}
private void deleteTail() {
tail = tail.pre;
tail.next = null;
size--;
}
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) {
int key = e.getKeyCode();
switch(key) {
case KeyEvent.VK_LEFT :
if(head.d != Dir.R) {
head.d = Dir.L;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.VK_UP :
if(head.d != Dir.D) {
head.d = Dir.U;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.VK_RIGHT :
if(head.d != Dir.L) {
head.d = Dir.R;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.VK_DOWN :
if(head.d != Dir.U) {
head.d = Dir.D;
}
break;
}
}
}3.4 Bean类的编写
首先,像其他类一样我们需要确定它的属性,通过分析我们可以发现豆子只需要位置进行变化,而大小、颜色等都是一个固定的常量。因此,我们首先定义它的位置(即x、y),然后我们再直接给出它的大小,关于x、y的值我们利用"Random"随机函数进行随机给出,使得游戏的挑战性和趣味性更高。
①对Bean进行一系列定义后,我们就可以开始绘制豆子了。像绘制Rou一样,但是这里我们为了让豆子更容易看,且让整个游戏更有意思,我们使豆子的颜色进行红、蓝的变化。,编写完方法后,我们在"Background"中对"draw"方法进行调用。
②这时我们还需要编写一个方法来检测蛇是否吃到豆子,我们通过构建"Rectangle"方法从而对蛇头以及豆子分别建立出两个矩形,当这两个矩形位置相同时,我们认为蛇已经吃到了豆子,这时我们调用"addHead"方法,使蛇的长度增加。
public class Bean {
int x, y;
int w=Background.Dt;
int h=Background.Dt;
private Color color = Color.red;
private static Random r = new Random();
public Bean(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public Bean() {
this(r.nextInt(Background.Line_x - 2) + 2, r.nextInt(Background.Line_y));
}
public Rectangle getRect() {
return new Rectangle(Background.Dt*x,Background.Dt*y, w, h);
}
public void reAppear() {
this.x = r.nextInt(Background.Line_x-2) + 2;
this.y = r.nextInt(Background.Line_y);
}
public void draw(Graphics g) {
Color c = g.getColor();
g.setColor(color);
g.fillOval(Background.Dt*x,Background.Dt*y, w, h);
g.setColor(c);
if(color == Color.red) color = Color.blue;
else color = Color.red;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
}3.5 其他类的编写
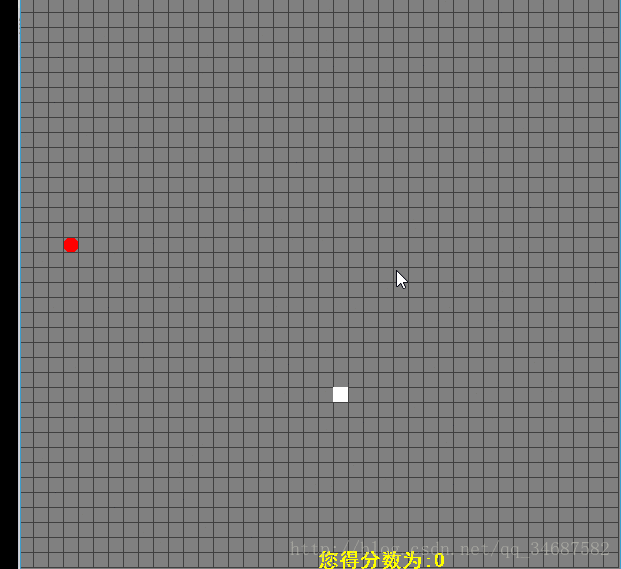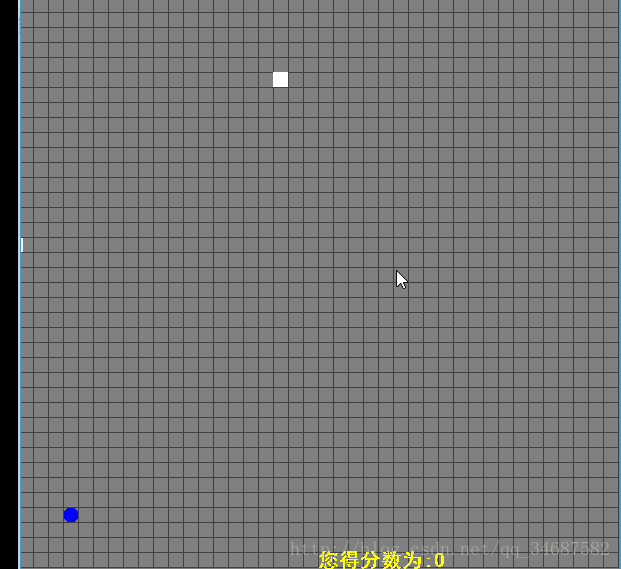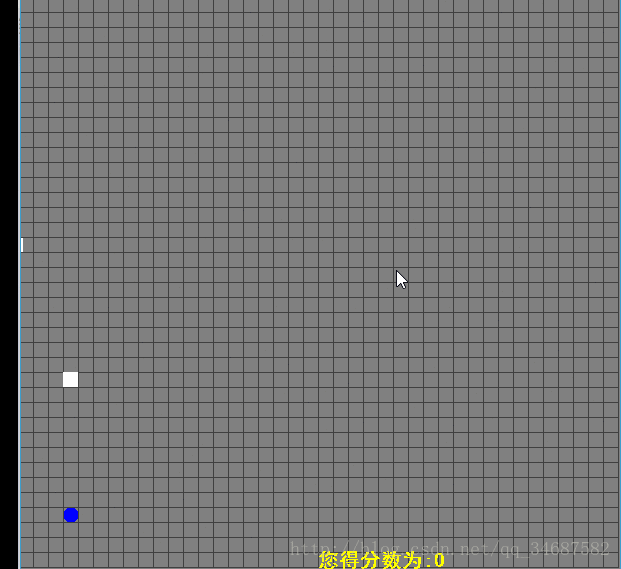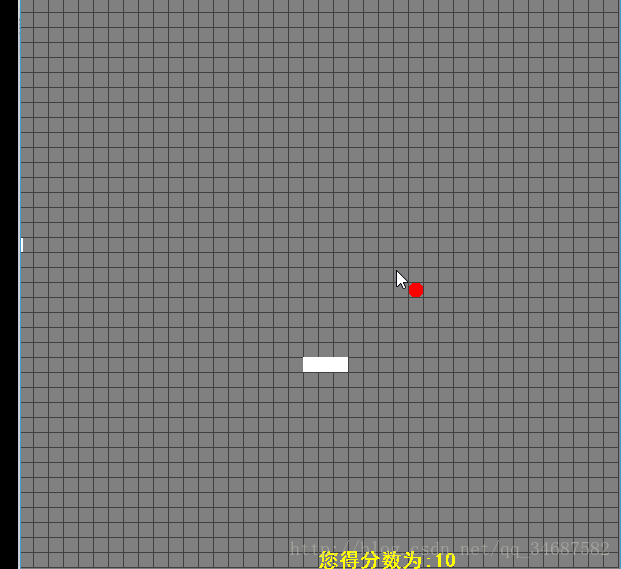
通过上述的操作,我们已经能够控制蛇,且蛇能够吃豆子了,但是这时,还有些小问题,如:一般贪吃蛇在我们碰到墙或者蛇头与蛇身相连时游戏便会结束。因此,我们还需要写些方法来控制游戏的结束、重置等:
①通过编写"checkDead"方法判定蛇是否撞击到墙壁以及判定蛇头与蛇身是否相连来决定游戏是否结束。
②通过编写控制"gameOver"方法来控制游戏结束,通过"reStart"方法来重置游戏,使用户停止游戏后可以通过按键重置游戏(这里我们设置的按键为”7“)。
③为了通过游戏的体验,我们设置了一个"score"属性用来计算玩家的得分,并且通过"drawString"来显示玩家的成绩。
四 最终代码4.1 "Background"类编写
public class Background extends Frame{
Snake s=new Snake(this);
PaintThread paintThread = new PaintThread();
Bean b=new Bean();
Image offScreenImage = null;
private Font fontGameOver = new Font("黑体", Font.BOLD, 70);
private Font Score = new Font("黑体", Font.BOLD, 20);
private boolean gameOver = false;
public static final int Line_x = 40;
public static final int Line_y = 40;
public static final int Dt = 15;
public void Backgroundrun() {
this.setSize(Line_x*Dt+5,Line_y*Dt+5);
this.setResizable(false);
this.setBackground(Color.gray);
this.setVisible(true);
this.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
this.addKeyListener(new KeyMonitor());
new Thread(paintThread).start();
}
public void setGameOver(boolean gameOver) {
this.gameOver = gameOver;
}
public void paint(Graphics g) {
Color c = g.getColor();
g.setColor(Color.GRAY);
g.fillRect(5, 5, Line_x*Dt,Line_y*Dt);
g.setColor(Color.DARK_GRAY);
for(int i=0;i<=Line_y;i++) {
g.drawLine(i*Dt, 0, i*Dt,Line_y*Dt);
}
for(int i=0;i<=Line_x;i++) {
g.drawLine(0, i*Dt, Line_x*Dt, i*Dt);
}
g.setColor(Color.YELLOW);
if(s.gameOver) {
g.setFont(fontGameOver);
g.drawString("游戏结束", 180, 300);
paintThread.setSuspend(true);
}
g.setColor(Color.YELLOW);
g.setFont(Score);
g.drawString("您得分数为:" + s.getScore(), 300, 600);
g.setColor(c);
s.eat(b);
s.draw(g);
b.draw(g);
}
@Override
public void update(Graphics g) {
if(offScreenImage == null) {
offScreenImage = this.createImage(Line_x * Dt, Line_y * Dt);
}
Graphics gOff = offScreenImage.getGraphics();
paint(gOff);
g.drawImage(offScreenImage, 0, 0, null);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Background().Backgroundrun();
}
private class PaintThread implements Runnable {
private boolean running = true;
private boolean suspend = false;
private String control = "";
public void run() {
while(running) {
synchronized (control) {
if(suspend ) {
try {
control.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else {
repaint();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public void setSuspend(boolean suspend) {
if (!suspend) {
synchronized (control) {
control.notifyAll();
}
}
this.suspend = suspend;
}
public void reStart() {
s = new Snake(Background.this);
s.gameOver=false;
b.reAppear();
repaint();
running=true;
setSuspend(false);
}
}
private class KeyMonitor extends KeyAdapter {
@Override
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) {
int key = e.getKeyCode();
if(key == KeyEvent.VK_7) {
paintThread.reStart();
}
s.keyPressed(e);
}
}
}4.2 "Snake"类编写
public class Snake {
int x=(int) (Math.random()*40);
int y=(int) (Math.random()*40);
public boolean gameOver = false;
private int score = 0;
Dir enums[] = Dir.values();
Random random = new Random();
Dir d = enums[random.nextInt(enums.length)];
Rou pre=null;
Rou next=null;
Rou rou=new Rou(x,y,d,pre,next);
Rou r=null;
Rou head=null;
Rou tail=null;
int size;
Background bg;
public Snake(Background bg) {
this.head=rou;
this.tail=rou;
this.size=1;
}
public int getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(int score) {
this.score = score;
}
public void addHead() {
Rou r=null;
switch(head.d) {
case L:
r = new Rou(head.x - 1, head.y , head.d,null,head);
break;
case D:
r = new Rou(head.x , head.y + 1, head.d,null,head);
break;
case R:
r = new Rou(head.x + 1, head.y , head.d,null,head);
break;
case U:
r = new Rou(head.x , head.y - 1 , head.d,null,head);
break;
}
r.next=head;
size ++;
head.pre=r;
head=r;
}
public void draw(Graphics g) {
move();
for(Rou r = head; r != null; r = r.next) {
r.draw(g);
}
}
private void move() {
addHead();
deleteTail();
checkDead();
}
private void checkDead() {
if(head.x < 2 || head.y < 0 || head.x > Background.Line_x|| head.y > Background.Line_y) {
gameOver=true;
}
for(Rou n = head.next; n != null; n = n.next) {
if(head.x == n.x && head.y == n.y) {
gameOver=true;
}
}
}
private void deleteTail() {
tail = tail.pre;
tail.next = null;
size--;
}
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) {
int key = e.getKeyCode();
switch(key) {
case KeyEvent.VK_LEFT :
if(head.d != Dir.R) {
head.d = Dir.L;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.VK_UP :
if(head.d != Dir.D) {
head.d = Dir.U;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.VK_RIGHT :
if(head.d != Dir.L) {
head.d = Dir.R;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.VK_DOWN :
if(head.d != Dir.U) {
head.d = Dir.D;
}
break;
}
}
public void eat(Bean e) {
if(this.getRect().intersects(e.getRect())) {
e.reAppear();
this.addHead();;
setScore(getScore()+5);
}
}
private Rectangle getRect() {
return new Rectangle(Background.Dt* head.x, Background.Dt* head.y,head.w,head.h);
}
}public class Bean {
int x, y;
int w=Background.Dt;
int h=Background.Dt;
private Color color = Color.red;
private static Random r = new Random();
public Bean(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public Bean() {
this(r.nextInt(Background.Line_x - 2) + 2, r.nextInt(Background.Line_y));
}
public Rectangle getRect() {
return new Rectangle(Background.Dt*x,Background.Dt*y, w, h);
}
public void reAppear() {
this.x = r.nextInt(Background.Line_x-2) + 2;
this.y = r.nextInt(Background.Line_y);
}
public void draw(Graphics g) {
Color c = g.getColor();
g.setColor(color);
g.fillOval(Background.Dt*x,Background.Dt*y, w, h);
g.setColor(c);
if(color == Color.red) color = Color.blue;
else color = Color.red;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
}
public enum Dir {
U,D,L,R;
}4.5 最终效果