【计算机操作系统】进程调度算法的 C++ 实现(附源码)
文章目录
- 一、实验目的
- 二、实验内容
- 2.1 优先权法和轮转法
- 2.2 算法描述
- 三、流程图
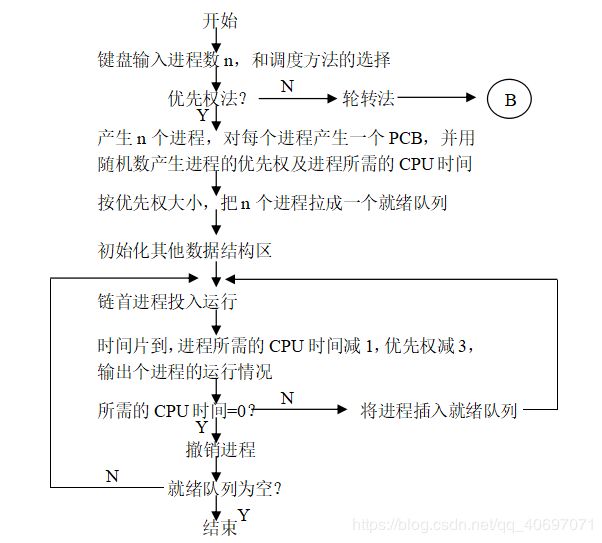
- 3.1 优先权法
- 3.2 轮转法
- 四、实验要求
- 五、设计思想
- 5.1 设计思路
- 5.2 代码解析
- 六、代码实现
- 七、结尾
一、实验目的
多道程序设计中,经常是若干个进程同时处于就绪状态,必须依照某种策略来决定那个进程优先占有处理机。因而引起进程调度。本实验模拟在单处理机情况下的处理机调度问题,加深对进程调度的理解。因为源码中我对一些关键步骤的注释已经比较清晰了,所以在本文中不会再对每一个细节都进行分析,只分析整体的代码结构和所使用到的设计模式。
博客内所有文章均为 原创,所有示意图均为 原创,若转载请附原文链接。
二、实验内容
2.1 优先权法和轮转法
- 简化假设
- 1)进程为计算型的(无I/O)
- 2)进程状态:ready、running、finish
- 3)进程需要的CPU时间以时间片为单位确定
2.2 算法描述
- 1)优先权法——动态优先权
当前运行进程用完时间片后,其优先权减去一个常数。 - 2)轮转法
三、流程图
3.1 优先权法
3.2 轮转法
四、实验要求
1.产生的各种随机数的取值范围加以限制,如所需的CPU时间限制在1~20之间。
2.进程数n不要太大通常取4~8个
3.使用动态数据结构
五、设计思想
5.1 设计思路
在该实验中需要实现两种算法,两种算法的实现思路和流程在流程图中已经详细的给出了,需要注意的是在轮转法中,需要用随机数产生进程所需要的时间片数(而不是固定值1)。
5.2 代码解析
因为两种算法的本质是一样的,因此这里使用了 模板方法设计模式 和 策略模式,其中模板方法设计模式指的是对于优先权法和轮转法设计一个抽象基类,定义该算法的必要功能接口,然后两个算法只需要按照自己的算法来实现该功能就可以了,具体的定义情况如下。
/* 调度算法基类 */
class SchedulingAlgorithm
{
public:
virtual bool initPCB(std::priority_queue<PCB, std::vector<PCB>, std::less<PCB>> * ready_queue, int process_num) = 0;
virtual bool processPCB(PCB & pcb) = 0;
};
/* 优先权法(仅定义类签名,具体代码实现见下文)*/
class DynamicPrioritySchedulingAlgorithm : public SchedulingAlgorithm;
/* 轮转法(仅定义类签名,具体代码实现见下文)*/
class TimeSliceRotationSchedulingAlgorithm : public SchedulingAlgorithm;
DynamicPrioritySchedulingAlgorithm 是动态优先权算法的实现,在该算法实现的 processPCB 方法中定义了每一轮执行完毕后需要对 PCB 所进行的操作,从而实现动态优先权算法。而在 initPCB 方法中会使用随机的方式初始化每一个PCB(随机优先级等)。
class DynamicPrioritySchedulingAlgorithm : public SchedulingAlgorithm
{
public:
bool processPCB(PCB & pcb)
{
pcb.priority -= PRIORITY_DIMINISHING_CONSTANT;
}
bool initPCB(std::priority_queue<PCB, std::vector<PCB>, std::less<PCB>> * ready_queue, int process_num)
{
for (int i = 0; i < process_num; ++i)
{
PCBptr pcb = new PCB();
pcb->pid = i;
pcb->status = Ready;
pcb->time = Util::getRandom(1, 20, i);
pcb->round_trip_time = 1;
pcb->elapsed_time = 0;
// use small intervals to observe changes
pcb->priority = Util::getRandom(1000, 1020, i);
std::cout << "[INFO] init process " << pcb->pid << " with"
<< " status " << pcb->status
<< " need time slices " << pcb->time
<< " priority " << pcb->priority << std::endl;
ready_queue->push(*pcb);
}
std::cout << "[INFO] ready queue init finish." << std::endl;
}
private:
const int PRIORITY_DIMINISHING_CONSTANT = 3;
};
TimeSliceRotationSchedulingAlgorithm 则是时间片轮转法的实现,在该算法中没有对执行完的 PCB 做过多的处理,而主要是在 initPCB 方法中随机产生轮转时间片数量。
class TimeSliceRotationSchedulingAlgorithm : public SchedulingAlgorithm
{
public:
bool processPCB(PCB & pcb)
{
// do nothing
}
bool initPCB(std::priority_queue<PCB, std::vector<PCB>, std::less<PCB>>* ready_queue, int process_num)
{
for (int i = 0; i < process_num; ++i)
{
PCBptr pcb = new PCB();
pcb->pid = i;
pcb->status = Ready;
pcb->time = Util::getRandom(1, 20, i);
pcb->round_trip_time = Util::getRandom(1, 5, i);
pcb->elapsed_time = 0;
pcb->priority = 0;
std::cout << "[INFO] init process " << pcb->pid << " with"
<< " status " << pcb->status
<< " need time slices " << pcb->time
<< " priority " << pcb->priority
<< " round trip time " << pcb->round_trip_time << std::endl;
ready_queue->push(*pcb);
}
std::cout << "[INFO] ready queue init finish." << std::endl;
}
};
最后,在 ProcessScheduling 类中将不同的算法进行聚合和初始化工作(调用不同算法的 initPCB 方法来初始化 PCB ),并能够使外部进行调用,定义共同的逻辑,并通过模板函数的方式传入选择的算法(策略设计模式),从而通过不同的进程调度算法来执行逻辑,这部分的代码就不进行剖析了,直接放在下面的代码实现中。
六、代码实现
#include 七、结尾
如果本文描述的内容或使用的代码存在任何问题,请及时联系我或在本篇文章的下面进行评论,我会本着对每一位学技术同学的负责态度立即修改。在后续还会有三篇计算机操作系统的算法 C++ 复现博文,如果感兴趣可以关注我。