Apollo基于卷积神经网络分割
该阶段的输入数据来自高精地图ROI过滤器过滤得到的点云数据
该阶段主要分为4个子过程:
- 通道特征提取
- 基于卷积神经网络的障碍物预测
- 障碍物集群
- 后期处理
通道特征提取
给定一个点云框架(cloud_roi),Apollo在地方坐标系中构建俯视图(即投影到X-Y平面)2D网格。基于点的X、Y坐标,相对于LiDAR传感器原点的预定范围内,每个点被量化为2D网格的一个单元。量化后,Apollo计算网格内每个单元格中点的8个统计测量,这将是下一步中传递给(卷积神经网络)CNN的输入通道特征。计算的8个统计测量:
- 单元格中点的最大高度
- 单元格中最高点的强度
- 单元格中点的平均高度
- 单元格中点的平均强度
- 单元格中的点数
- 单元格中心相对于原点的角度
- 单元格中心与原点之间的距离
- 二进制值标示单元格是空还是被占用(单元格内是否有点)
其中单元格中心相对于原点的角度和距离,只和单元格位置有关,其余特征通过对点的特征(点云中的位置x,y,z和强度)进行计算获得。
具体的计算方法如下:
/// file in apollo/modules/perception/obstacle/lidar/segmentation/cnnseg/cnn_segmentation.cc
bool FeatureGenerator::Init(const FeatureParam& feature_param, caffe::Blob* out_blob) {
for (int row = 0; row < height_; ++row) {
for (int col = 0; col < width_; ++col) {
int idx = row * width_ + col;
// * row <-> x, column <-> y
float center_x = Pixel2Pc(row, height_, range_); // 计算映射坐标: center_x
float center_y = Pixel2Pc(col, width_, range_); // 计算映射坐标: center_y
constexpr double K_CV_PI = 3.1415926535897932384626433832795;
direction_data[idx] = static_cast(std::atan2(center_y, center_x) / (2.0 * K_CV_PI)); // 计算方向direction_data(channel 6)
distance_data[idx] = static_cast(std::hypot(center_x, center_y) / 60.0 - 0.5); // 计算距离compute distance_data(channel 7)
}
}
return true;
}
void FeatureGenerator::Generate(const apollo::perception::pcl_util::PointCloudConstPtr& pc_ptr) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < points.size(); ++i) {
// 1. 去除高度在 [-5.0,5.0]之外的点
...
// 2. 去除在x:[-60,60], y:[-60,60]之外的点
...
float pz = points[i].z;
float pi = points[i].intensity / 255.0;
if (max_height_data_[idx] < pz) { //更新单元格中最高的点max_height_data(channel 1)
max_height_data_[idx] = pz;
top_intensity_data_[idx] = pi; // 更新单元格中强度最大的点 top_intensity_data(channel 2)
}
mean_height_data_[idx] += static_cast(pz); //累积单元格高度
mean_intensity_data_[idx] += static_cast(pi); // 累积单元格强度
count_data_[idx] += Dtype(1); //计算单元格中的点数 count_data(channel 5)
}
for (int i = 0; i < siz; ++i) {
constexpr double EPS = 1e-6;
if (count_data_[i] < EPS) {
max_height_data_[i] = Dtype(0);
} else {
mean_height_data_[i] /= count_data_[i]; // 计算单元格平均高度 mean_height_data(channel 3)
mean_intensity_data_[i] /= count_data_[i]; // 计算单元格平均强度mean_intensity_data(channel 5)
nonempty_data_[i] = Dtype(1); // 二进制值标示单元格是空还是被占用nonempty_data(channel 8)
}
}
}
/// file in apollo/modules/perception/obstacle/lidar/segmentation/cnnseg/util.h
inline float Pixel2Pc(int in_pixel, float in_size, float out_range) {
float res = 2.0 * out_range / in_size;
return out_range - (static_cast(in_pixel) + 0.5f) * res;
}
基于卷积神经网络的障碍物预测
通过卷积神经网络预测可以得到关于单元格的12个特征
- channel 0: category_pt 是否是物体预测。Sigmoid激活,并与输入channel 7掩码mask相乘
- channel 1-2: instance_pt 中心偏移预测(包括x方向和y方向的偏移)
- channel 3: confidence_pt 前景物体概率预测。Sigmoid激活
- channel 4-8: classify_pt 物体类别预测。Sigmoid激活(可以对5种物体进行预测,如行人,汽车,自行车等)
- channel 9-10: heading_pt -
- channel 11: height_pt 高度预测。
通过对12个特征进行处理可以得到单元格的4个属性,这4个属性分别用于障碍物集群和后期处理
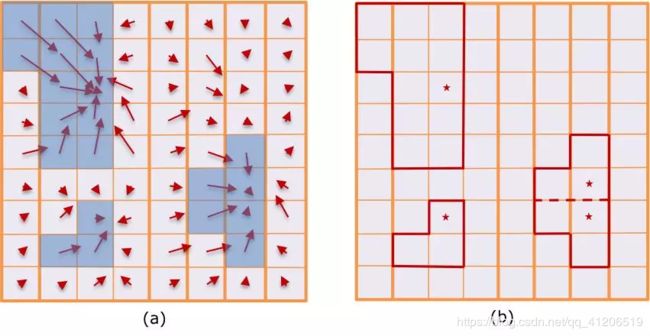
障碍物聚类
为生成障碍物,Apollo基于单元格中心偏移,预测构建有向图,并搜索连接的组件作为候选对象集群。
如下图所示,每个单元格是图的一个节点,并且基于单元格的中心偏移预测构建有向边,其指向对应于另一单元的父节点。
后期处理
聚类后,Apollo获得一组候选对象集,每个候选对象集包括若干单元格。
在后期处理中,Apollo首先对所涉及的单元格的积极性和物体高度值,平均计算每个候选群体的检测置信度分数和物体高度。 然后,Apollo去除相对于预测物体高度太高的点,并收集每个候选集中的有效单元格的点。 最后,Apollo删除具有非常低的可信度分数或小点数的候选聚类,以输出最终的障碍物集。
文中内容来自:
1.阿波罗开发者说
2.Apollo 2.0 框架及源码分析(二)
3.知乎牟家俊