Redis的RESP协议详解
一、什么是RESP
Redis是Redis序列化协议,Redis客户端RESP协议与Redis服务器通信。Redis协议在以下几点之间做出了折衷:
- 简单的实现
- 快速地被计算机解析
- 简单得可以能被人工解析
二、RESP协议描述
RESP协议在Redis 1.2中引入,但在Redis 2.0中成为与Redis服务器通信的标准方式。这个通信方式就是Redis客户端实现的协议。RESP实际上是一个序列化协议,它支持以下数据类型:简单字符串、错误、整数、大容量字符串和数组。
1、RESP在Redis中用作请求-响应协议的方式如下:
- 客户端将命令以批量字符串的RESP数组的形式发送到Redis服务器,如下:
SET mykey myvalue
*3
$3
SET
$5
mykey
$7
myvalue
*3:SET mykey myvalue 这数组的长度
$3:表示下面的字符长度是3,这里是SET长度是
$5:表示下面的字符的长度是5,这里是mykey的长度
$7:表示下面的字符的长度是7,这里是myvalue的长度- 服务器根据命令实现使用其中一种RESP类型进行响应
2、在RESP中,某些数据的类型取决于第一个字节:
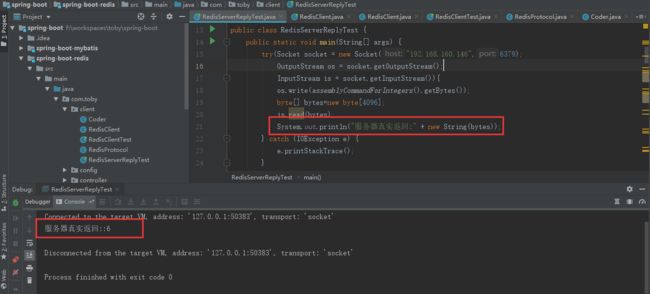
- For Simple Strings the first byte of the reply is "+" 简单字符串回复的第一个字节将是“+”
比如:向服务器发送"set toby xu"命令,实际上服务器的返回是:"+OK\r\n"
- For Errors the first byte of the reply is "-" 错误消息,回复的第一个字节将是“-”
比如:向服务器发送"add toby xu"命令,实际上服务器的返回是:"-ERR unknown command `add`, with args beginning with: `toby`, `xu`,\r\n"
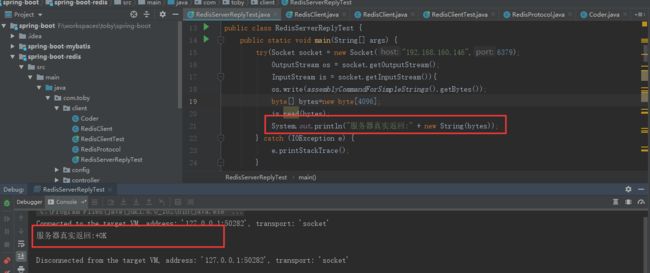
- For Integers the first byte of the reply is ":" 整型数字,回复的第一个字节将是“:”
比如:向服务器发送"incr count"命令,实际上服务器的返回是:":6\r\n"
- For Bulk Strings the first byte of the reply is "$" 批量回复,回复的第一个字节将是“$”
比如:向服务器发送"get toby"命令,实际上服务器的返回是:"$2\r\nxu\r\n"
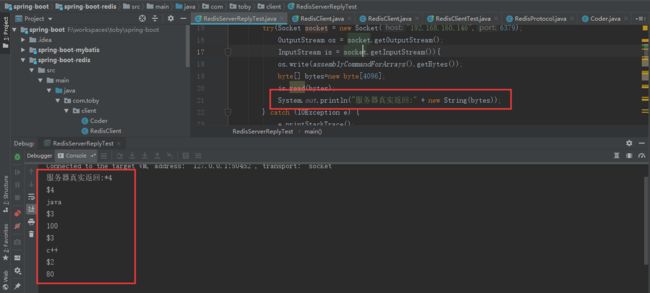
- For Arrays the first byte of the reply is "*" 数组回复的第一个字节将是“*”
比如:向服务器发送"hgetall toby_h"命令,实际上服务器的返回是:"*4\r\n$4\r\njava\r\n$3\r\n100\r\n$3\r\nc++\r\n$2\r\n80\r\n"
示例RedisServerReplyTest代码如下:
/**
* @desc: 测试服务器返回
* @author: toby
* @date: 2019/12/5 23:07
*/
public class RedisServerReplyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(Socket socket = new Socket("192.168.160.146",6379);
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream()){
os.write(assemblyCommandForArrays().getBytes());
byte[] bytes=new byte[4096];
is.read(bytes);
System.out.println("服务器真实返回:" + new String(bytes));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* For Simple Strings the first byte of the reply is "+"
* @return
*/
private static String assemblyCommandForSimpleStrings() {
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
sb.append("*3").append("\r\n");
sb.append("$").append("set".length()).append("\r\n");
sb.append("set").append("\r\n");
sb.append("$").append("toby".length()).append("\r\n");
sb.append("toby").append("\r\n");
sb.append("$").append("xu".length()).append("\r\n");
sb.append("xu").append("\r\n");
return sb.toString();
}
/**
* For Errors the first byte of the reply is "-"
* @return
*/
private static String assemblyCommandForErrors() {
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
sb.append("*3").append("\r\n");
sb.append("$").append("set".length()).append("\r\n");
sb.append("add").append("\r\n");
sb.append("$").append("toby".length()).append("\r\n");
sb.append("toby").append("\r\n");
sb.append("$").append("xu".length()).append("\r\n");
sb.append("xu").append("\r\n");
return sb.toString();
}
/**
* For Integers the first byte of the reply is ":"
* @return
*/
private static String assemblyCommandForIntegers() {
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
sb.append("*2").append("\r\n");
sb.append("$").append("incr".length()).append("\r\n");
sb.append("incr").append("\r\n");
sb.append("$").append("count".length()).append("\r\n");
sb.append("count").append("\r\n");
return sb.toString();
}
/**
* For Bulk Strings the first byte of the reply is "$"
* @return
*/
private static String assemblyCommandForBulkStrings() {
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
sb.append("*2").append("\r\n");
sb.append("$").append("get".length()).append("\r\n");
sb.append("get").append("\r\n");
sb.append("$").append("toby".length()).append("\r\n");
sb.append("toby").append("\r\n");
return sb.toString();
}
/**
* For Arrays the first byte of the reply is "*"
* @return
*/
private static String assemblyCommandForArrays() {
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
sb.append("*2").append("\r\n");
sb.append("$").append("hgetall".length()).append("\r\n");
sb.append("hgetall").append("\r\n");
sb.append("$").append("toby_h".length()).append("\r\n");
sb.append("toby_h").append("\r\n");
return sb.toString();
}
}三、自定义简单的Redis Client
我们现在了解了Redis的RESP协议,并且知道网络层上Redis在TCP端口6379上监听到来的连接,客户端连接到来时,Redis服务器为此创建一个TCP连接。在客户端与服务器端之间传输的每个Redis命令或者数据都以\r\n结尾,那么接下来我们自定义一个简单的Client。
(1)编解码器Coder:
/**
* @desc: 编解码器
* @author: toby
* @date: 2019/12/6 19:33
*/
public class Coder {
public static byte[] encode(final String str) {
try {
if (str == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("value sent to redis cannot be null");
}
return str.getBytes(RedisProtocol.CHARSET);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static String decode(final byte[] data) {
try {
return new String(data, RedisProtocol.CHARSET);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}(2)Redis协议RedisProtocol:
/**
* @desc: Redis协议
* @author: toby
* @date: 2019/12/6 19:33
*/
public class RedisProtocol {
public static final String CHARSET = "UTF-8";
public static final byte DOLLAR_BYTE = '$';
public static final byte ASTERISK_BYTE = '*';
public static final byte PLUS_BYTE = '+';
public static final byte MINUS_BYTE = '-';
public static final byte COLON_BYTE = ':';
public static final byte CR_BYTE = '\r';
public static final byte LF_BYTE = '\n';
/**
* *3
* $3
* SET
* $4
* toby
* $2
* xu
* @param os
* @param command
* @param args
*/
public static void sendCommand(final OutputStream os, final Command command, final byte[]... args) {
try {
os.write(ASTERISK_BYTE);
os.write(Coder.encode(String.valueOf(args.length + 1)));
os.write(CR_BYTE);
os.write(LF_BYTE);
os.write(DOLLAR_BYTE);
os.write(Coder.encode(String.valueOf(command.name().length())));
os.write(CR_BYTE);
os.write(LF_BYTE);
os.write(Coder.encode(command.name()));
os.write(CR_BYTE);
os.write(LF_BYTE);
for (final byte[] arg : args) {
os.write(DOLLAR_BYTE);
os.write(Coder.encode(String.valueOf(arg.length)));
os.write(CR_BYTE);
os.write(LF_BYTE);
os.write(arg);
os.write(CR_BYTE);
os.write(LF_BYTE);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public enum Command{
SET, GET
}
}(3)自定义Client RedisClient:
/**
* @desc: 自定义Client
* @author: toby
* @date: 2019/12/6 19:31
*/
public class RedisClient {
private String host;
private int port;
public RedisClient(String host,int port){
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
}
public String set(String key,String value){
try (Socket socket = new Socket(this.host,this.port);
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream()){
RedisProtocol.sendCommand(os,RedisProtocol.Command.SET,Coder.encode(key),Coder.encode(value));
return getReply(is);
}catch (Exception e) {
return e.getMessage();
}
}
public String get(String key){
try (Socket socket = new Socket(this.host,this.port);
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream()){
RedisProtocol.sendCommand(os,RedisProtocol.Command.GET,Coder.encode(key));
return getReply(is);
}catch (Exception e) {
return e.getMessage();
}
}
private String getReply(InputStream is){
try {
byte[] bytes = new byte[4096];
is.read(bytes);
return Coder.decode(bytes);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}(4)Redis Client 测试 RedisClientTest:
/**
* @desc: Redis Client 测试
* @author: toby
* @date: 2019/12/6 19:35
*/
public class RedisClientTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
RedisClient client = new RedisClient("192.168.160.146",6379);
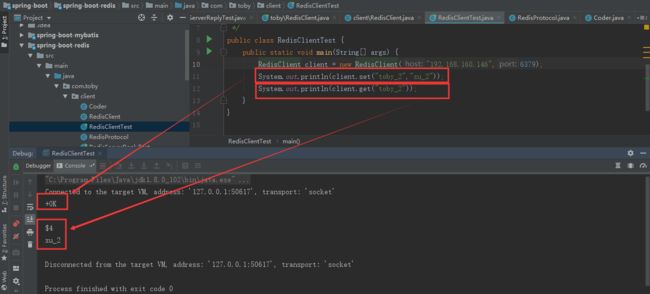
System.out.println(client.set("toby_2","xu_2"));
System.out.println(client.get("toby_2"));
}
}运行结果如下:
至此自定义的简单的Redis Client完成!!!!!!
四、总结
通过本章的学习,了解了什么是Redis的RESP协议?Redis协议几个特点:简单的实现;快速地被计算机解析;简单得可以能被人工解析。有了协议,我们就可以通过自定义的Client想Redis服务端发起请求,从而进行操作Redis。对后面理解Redis客户端Jedis的实现原理有很大的帮助。