还在 if(obj==null)?太low了!
作为一名java开发人员,每个人都会遇到这样的问题:调用一个方法得到了返回值却不能直接将返回值作为参数去调用别的方法。我们首先要判断这个返回值是否为null,只有在非空的前提下才能将其作为其他方法的参数。否则就会出现NPE异常,就是传说中的空指针异常。
举个例子:
if(null == str) { // 空指针判定 return 0;}return str.length();
//采用optionalreturn Optional.ofNullable(str).map(String::length).orElse(0);
//再来个复杂点的public String isCheckUser(User user){ if(null != user){// 获取角色 if(null != user.getRole()){// 获取管理员权限 if(null != user.getRole().getPermission()){ return "获取管理员权限"; } } }else{ return "用户为空"; } }
//使用optional类public String isCheckUser(User user){ return Optional.ofNullable(user) .map(u -> u.getRole) .map(p -> p.getPermission()) .orElse("用户为空");}本文将根据java8新特性Optional类源码来逐步分析以及教会大家如何使用Optional类去优雅的判断是否为null。
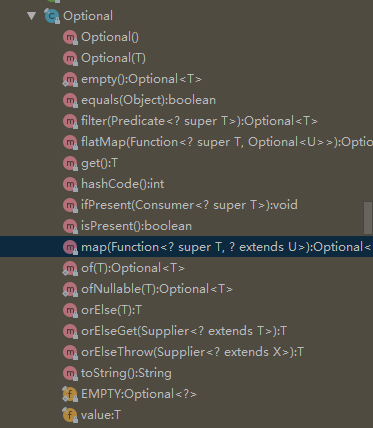
optional类的组成如下图所示:
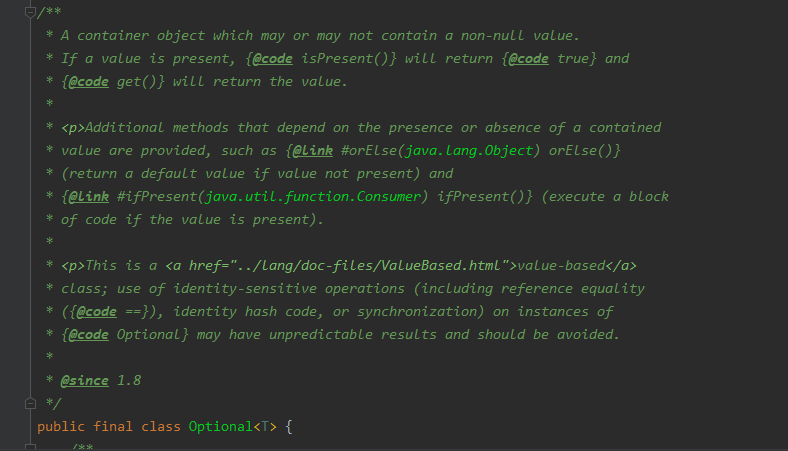
通过类上面的注释我们可知:这是一个可以为null或者不为null的容器对象。如果值存在则isPresent()方法会返回true,调用get()方法会返回该对象。
接下来将会为大家逐个探讨Optional类里面的方法,并举例说明。
of
源码:/** * Returns an {@code Optional} with the specified present non-null value. * * @param the class of the value * @param value the value to be present, which must be non-null * @return an {@code Optional} with the value present * @throws NullPointerException if value is null */ public static Optional of(T value) { return new Optional<>(value); }通过源码注释可知,该方法会返回一个不会null的optional对象,如果value为null的话则会抛出NullPointerException 异常。
实例如下:
//调用工厂方法创建Optional实例 Optional<String> name = Optional.of("javaHuang");//传入参数为null,抛出NullPointerException. Optional<String> nullValue= Optional.of(null);ofNullable
源码:/** * Returns an {@code Optional} describing the specified value, if non-null, * otherwise returns an empty {@code Optional}. * * @param the class of the value * @param value the possibly-null value to describe * @return an {@code Optional} with a present value if the specified value * is non-null, otherwise an empty {@code Optional} */ public static Optional ofNullable(T value) { return value == null ? empty() : of(value); }通过注释可以知道:当value不为null时会返回一个optional对象,如果value为null的时候,则会返回一个空的optional对象。
实例如下:
//返回空的optional对象 Optional emptyValue = Optional.ofNullable(null);or//返回name为“javaHuang”的optional对象 Optional name= Optional.ofNullable("javaHuang");isPresent
源码:/** * Return {@code true} if there is a value present, otherwise {@code false}. * * @return {@code true} if there is a value present, otherwise {@code false} */ public boolean isPresent() { return value != null; }通过注释可以知道:如果值为null返回false,不为null返回true。
实例如下:
if (name.isPresent()) { System.out.println(name.get());//输出javaHuang } emptyValue.isPresent()==falseget
源码:/** * If a value is present in this {@code Optional}, returns the value, * otherwise throws {@code NoSuchElementException}. * * @return the non-null value held by this {@code Optional} * @throws NoSuchElementException if there is no value present * * @see Optional#isPresent() */ public T get() { if (value == null) { throw new NoSuchElementException("No value present"); } return value; }通过注释可以知道:如果value不为null的话,返回一个optional对象,如果value为null的话,抛出NoSuchElementException异常。
实例如下:
try { System.out.println(emptyValue.get()); } catch (NoSuchElementException ex) { System.err.println(ex.getMessage()); }ifPresent
源码:/** * If a value is present, invoke the specified consumer with the value, * otherwise do nothing. * * @param consumer block to be executed if a value is present * @throws NullPointerException if value is present and {@code consumer} is * null */ public void ifPresent(Consumersuper T> consumer) { if (value != null) consumer.accept(value); }通过源码可以知道:如果Optional实例有值则为其调用consumer,否则不做处理
实例如下:
name.ifPresent((value) -> { System.out.println("His name is: " + value); });//打印 His name is javaHuangorElse
源码:/** * Return the value if present, otherwise return {@code other}. * * @param other the value to be returned if there is no value present, may * be null * @return the value, if present, otherwise {@code other} */ public T orElse(T other) { return value != null ? value : other; }通过注释可以知道:如果value不为null的话直接返回value,否则返回传入的other值。
实例如下:
System.out.println(empty.orElse("There is no value present!")); //返回:There is no value present! System.out.println(name.orElse("There is some value!")); //返回:javaHuang
orElseGet
源码:/** * Return the value if present, otherwise invoke {@code other} and return * the result of that invocation. * * @param other a {@code Supplier} whose result is returned if no value * is present * @return the value if present otherwise the result of {@code other.get()} * @throws NullPointerException if value is not present and {@code other} is * null */ public T orElseGet(Supplier extends T> other) { return value != null ? value : other.get(); }通过注释可以知道:orElseGet与orElse方法类似,区别在于得到的默认值。orElse方法将传入的字符串作为默认值,orElseGet方法可以接受Supplier接口的实现用来生成默认值
实例如下:
System.out.println(empty.orElseGet(() -> "Default Value"));System.out.println(name.orElseGet(String::new));orElseThrow
源码:/** * Return the contained value, if present, otherwise throw an exception * to be created by the provided supplier. * * @apiNote A method reference to the exception constructor with an empty * argument list can be used as the supplier. For example, * {@code IllegalStateException::new} * * @param Type of the exception to be thrown * @param exceptionSupplier The supplier which will return the exception to * be thrown * @return the present value * @throws X if there is no value present * @throws NullPointerException if no value is present and * {@code exceptionSupplier} is null */ public T orElseThrow(Supplier exceptionSupplier) throws X { if (value != null) { return value; } else { throw exceptionSupplier.get(); } }通过注释可以得知:如果有值则将其返回,否则抛出supplier接口创建的异常。
实例如下:
try { empty.orElseThrow(IllegalArgumentException::new); } catch (Throwable ex) { System.out.println("error:" + ex.getMessage()); }map
源码:/** * If a value is present, apply the provided mapping function to it, * and if the result is non-null, return an {@code Optional} describing the * result. Otherwise return an empty {@code Optional}. * * @apiNote This method supports post-processing on optional values, without * the need to explicitly check for a return status. For example, the * following code traverses a stream of file names, selects one that has * not yet been processed, and then opens that file, returning an * {@code Optional}: * * {@code * Optional fis = * names.stream().filter(name -> !isProcessedYet(name)) * .findFirst() * .map(name -> new FileInputStream(name)); * } * * Here, {@code findFirst} returns an {@code Optional}, and then * {@code map} returns an {@code Optional} for the desired * file if one exists. * * @param The type of the result of the mapping function * @param mapper a mapping function to apply to the value, if present * @return an {@code Optional} describing the result of applying a mapping * function to the value of this {@code Optional}, if a value is present, * otherwise an empty {@code Optional} * @throws NullPointerException if the mapping function is null */ public Optional map(Functionsuper T, ? extends U> mapper) { Objects.requireNonNull(mapper); if (!isPresent()) return empty(); else { return Optional.ofNullable(mapper.apply(value)); } }
通过代码可以得知:如果有值,则对其执行调用mapping函数得到返回值。如果返回值不为null,则创建包含mapping返回值的Optional作为map方法返回值,否则返回空Optional。
实例如下:
Optional upperName = name.map((value) -> value.toUpperCase()); System.out.println(upperName.orElse("empty"));flatMap
源码:/** * If a value is present, apply the provided {@code Optional}-bearing * mapping function to it, return that result, otherwise return an empty * {@code Optional}. This method is similar to {@link #map(Function)}, * but the provided mapper is one whose result is already an {@code Optional}, * and if invoked, {@code flatMap} does not wrap it with an additional * {@code Optional}. * * @param The type parameter to the {@code Optional} returned by * @param mapper a mapping function to apply to the value, if present * the mapping function * @return the result of applying an {@code Optional}-bearing mapping * function to the value of this {@code Optional}, if a value is present, * otherwise an empty {@code Optional} * @throws NullPointerException if the mapping function is null or returns * a null result */ public Optional flatMap(Functionsuper T, Optional<U>> mapper) { Objects.requireNonNull(mapper); if (!isPresent()) return empty(); else { return Objects.requireNonNull(mapper.apply(value)); } }通过注释可以得知:如果有值,为其执行mapping函数返回Optional类型返回值,否则返回空Optional。
实例如下:
upperName = name.flatMap((value) -> Optional.of(value.toUpperCase()));System.out.println(upperName.get());filter
源码:/** * If a value is present, and the value matches the given predicate, * return an {@code Optional} describing the value, otherwise return an * empty {@code Optional}. * * @param predicate a predicate to apply to the value, if present * @return an {@code Optional} describing the value of this {@code Optional} * if a value is present and the value matches the given predicate, * otherwise an empty {@code Optional} * @throws NullPointerException if the predicate is null */ public Optional filter(Predicatesuper T> predicate) { Objects.requireNonNull(predicate); if (!isPresent()) return this;else return predicate.test(value) ? this : empty(); }通过代码可以得知:如果有值并且满足断言条件返回包含该值的Optional,否则返回空Optional。
实例如下:
List<String> names = Arrays.asList("javaHuang","tony"); for(String s:names) { Optional<String> nameLenLessThan7 = Optional.of(s).filter((value) -> "tony".equals(value)); System.out.println(nameLenLessThan7.orElse("The name is javaHuang")); }扫码关注最新动态,更有价值万元的精品课程免费送哦!