OpenCV学习笔记(十四)圆检测技术
圆检测技术:
圆检测技术目前用处还是特别的广泛的,锅炉、管道等类似的情况,我们不能切开或者打孔去测试流量,温度等参数。这是我们可以在管道上画一个圆,用摄像机去检测圆中心,进而测试出我们需要的信息。
对于一个圆,就需要用三个参数来确定。使用Hough梯度法的依据是圆心一定出现在圆上的每个点的模向量上,圆上点的模向量的交点就是圆心的所在位置。Hough梯度法的第一步就是找到这些圆心,这样三维的累加平面就转化为二维累加平面。第二步就是根据所有候选中心的边缘非零像素对其的支持程度来确定半径。
void HoughCircles(InputArray image, OutputArray circles, int method, double dp, double minDist, double param1=100, doubleparam2=100, int minRadius=0, int maxRadius=0 )
- image – 8-bit, single-channel, grayscale input image.
- circles – Output vector of found circles. Each vector is encoded as a 3-element floating-point vector
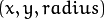 .圆心和圆
.圆心和圆 - method – 目前只有霍夫梯度法可用,HOUGH_GRADIENT。
- dp – 用来检测圆心的累加器图像的分辨率与输入图像之比的导数。. For example, if dp=1 , the accumulator has the same resolution as the input image. If dp=2 , the accumulator has half as big width and height.
- minDist – Minimum distance between the centers of the detected circles. If the parameter is too small, multiple neighbor circles may be falsely detected in addition to a true one. If it is too large, some circles may be missed.
- param1 – First method-specific parameter. In case of HOUGH_GRADIENT , it is the higher threshold of the two passed to the Canny() edge detector (the lower one is twice smaller).
- param2 – Second method-specific parameter. In case of HOUGH_GRADIENT , it is the accumulator threshold for the circle centers at the detection stage. The smaller it is, the more false circles may be detected. Circles, corresponding to the larger accumulator values, will be returned first.
- minRadius – Minimum circle radius.
- maxRadius – Maximum circle radius.
使用此函数,可以很容易的检测出圆的中心,但是它找不到合适的圆半径。我们可以通过minRadius和maxRadius指定最小和最大的圆半径,来辅助检测的效果。或者直接返回0,然后用额外的步骤确定圆的半径。
void circle(Mat& img, Point center, int radius, const Scalar& color, int thickness=1, int lineType=8, int shift=0)
- img – Image where the circle is drawn.
- center – Center of the circle.
- radius – Radius of the circle.
- color – Circle color.
- thickness – Thickness of the circle outline, if positive. Negative thickness means that a filled circle is to be drawn.
- lineType – Type of the circle boundary. See the line() description. Type=8/4/CV_AA
- shift – Number of fractional bits in the coordinates of the center and in the radius value. shift =0
实例程序:
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main(int args,char** argv)
{
Mat srcImage = imread("D:\\5.jpg");
if (!srcImage.data)
return -1;
imshow("srcImage", srcImage);
Mat srcGray;
cvtColor(srcImage, srcGray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
//高斯平滑滤波
GaussianBlur(srcGray, srcGray, Size(9, 9), 2,2);
vector circles;
//Hough圆检测
HoughCircles(srcGray, circles, HOUGH_GRADIENT,1,srcGray.rows/8,200,100,0,0);
//将得到的结果绘图
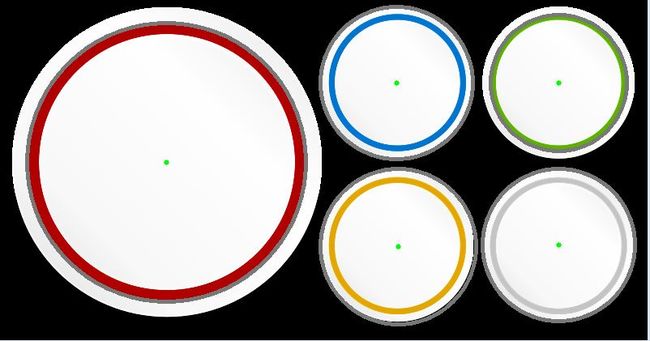
for (size_t i = 0; i < circles.size(); i++)
{
Point center(cvRound(circles[i][0]), cvRound(circles[i][1]));
int radius = cvRound(circles[i][2]);
//检测圆中心
circle(srcImage, center, 3, Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1, 8, 0);
//检测圆轮廓
circle(srcImage, center, radius, Scalar(120, 120, 120), 3, 8, 0);
}
imshow("HoughResult", srcImage);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
} 效果图:
Hough梯度法的缺点:同心圆难以检测;临近圆易出错;Sobel导数会产生噪声。