Computer Networking A Top-Down Approach 总结
引言
在这篇文章中,我主要对 Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (6th Edition) 一书进行总结。
Computer Networks and the Internet
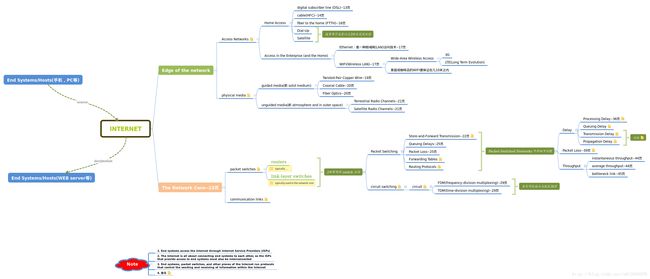
对于第一次接触网络的人来说,会感觉到第一章的内容又杂又多,而且对于某些概念来说,很不容易理解,幸亏作者将文章写得通俗易懂,并搭配很多有助于理解的插图,以及例举出生动的现实生活中的例子去理解一些复杂的概念,相信我你一定会爱上这本书的!
这章中以一个 overview 的形式去讲述网络,这就会导致涉及很多的概念,比如构成网络所需要的软件与硬件,网络的发展历史等,但是概念并不会很深入,因此这章我并不准备去用文字做总结,而是用 Xmind 画了一张图,把这章的重要概念穿插起来,具体的细节我会标明页数参考书即可。
由于上面只是我导出的图片,大家会看不到要相应的备注,为了方便大家阅读并根据自己的意愿去修改总结的内容,我已经把源文件上传到 github,以供大家参考。
思维导图源文件
Application Layer
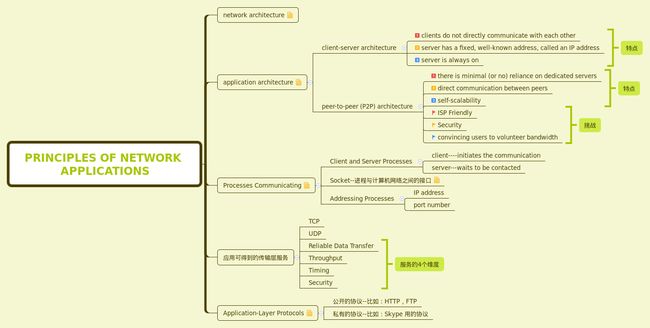
Overview
这章是关于整体的概述,大致内容如下图:
思维导图源文件
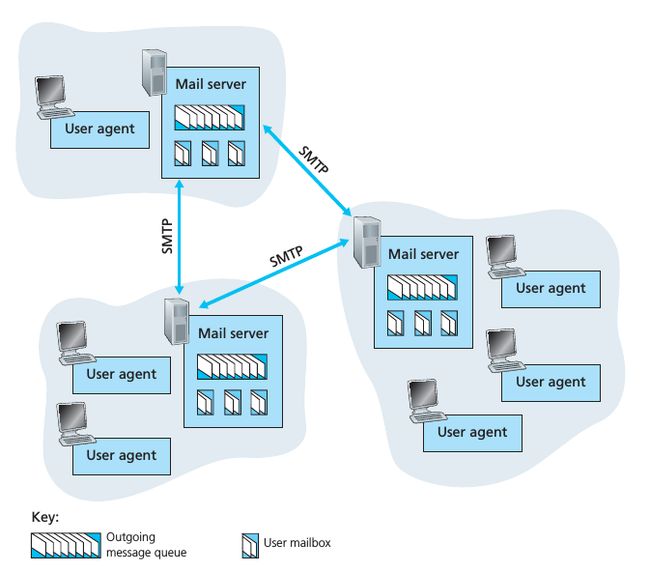
网络中的电子邮件
在这个小节中,作者主要介绍了 Email 中应用广泛的几个协议。下图中是 Internet 邮件系统的大致结构。
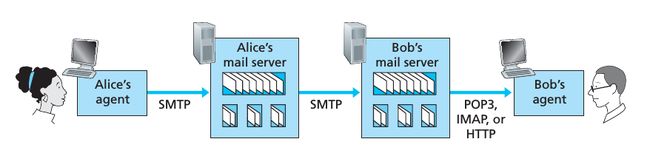
下图是 Alice 和 Bob 之间是如何发送邮件的,它主要分为以下6个步骤:
- Alice 运行起它的 user agent,比如 Foxmail,然后用它写一封邮件给 Bob,完成以后命令 Foxmail 把这封邮件发送出去
- Alice 的 Foxmail 把邮件发送到她的 Mail server,放到消息队列中
- Alice 的 mail server 中运行的 SMTP 客户端看到消息队列中的消息后,它打开了一个 TCP connection 到 Bob 的 mail server 中运行的 SMTP 服务端
- 在一些 initial SMTP handshaking 后,SMTP 客户端发送 Alice 的信息到 TCP connection 中
- 当 Bob 的 mail server 中运行的 SMTP 服务端收到消息后,把消息放入到 Bob 的 mailbox 中
- 等 Bob 方便的时候,他用自己 PC 上的 user agent 从 server 中读取邮件
我们可以看到上面的过程中涉及到几个重要的协议,它们分别是 SMTP,POP3,IMAP,和HTTP. 我觉得协议本身并没有什么可说的,大家可以去官方看看这些协议都是怎么定义的,都实现什么样的命令,如何交互的。下面我主要来说一下几个协议之间的区别,这样大家在选择的时候就不会感到困惑。
对于 SMTP 来说,有一点大家应该知道:在用 SMTP 发送邮件的时候,正常情况它不会用中间的 mail server,即使发送者和接收者2人的 mail server 分别在世界的2端。如果 Bob 的 mail server 挂掉了,信息依然会保存在 Alice 的 server 中,隔一段时间过后,它会继续尝试发送给 Bob 的 server,消息始终不会放到一些中间的 mail server 上。
下面我介绍一下 POP3 和 IMAP 协议之间的区别。当一个基于 POP3 协议的 TCP connection 建立之后,POP3 会进行以下个阶段:
- authorization : user agent 发送用户名和密码到 server 进行授权
- transaction : user agent 获取邮件信息
- update: 这个阶段发生在客户端发布 quit 命令之后
在第2个阶段中,POP3 有2个模式可以配置,它们分别是 download and keep 和 download and delete. 如果你只用一个客户端去读取邮件,那么你可以选择 download and delete 模式,它在 update 阶段的时候会把你的邮件从 mail server 中删除,这样你可以节省 mail server 的空间。但是,如果你有1多个客户端想读取邮件,你就应该用 download and keep 模式,它在 update 阶段过后并不会从 mail server 上删除掉你的邮件。
想像一下这样一种场景,你从 mail server 上获取到相应的邮件信息之后,你会归纳整理一下,比如创建几个文件夹,把不同的要邮件放到不同的文件夹中,如果你用 POP3 协议,你的做法会只保留在你当前的机器上,如你换个机器从 mail server 上下载邮件,你的先前的归类并不会在这个机器上看到,而 IMAP 协议就可以解决这个问题。
IMAP server 不仅可以维护用户的状态信息,同时它也可以允许 user agent 获取信息的部分组件,比如它可以只获取信息的信息头。
DNS — The Internet’s Directory Service
我们可以通过多种方式来识别 Internet 中的某个 host,比如可以通过 hostname 或 IP addresses,对于人类来说 hostname 要相对容易记住,比如:www.baidu.com,但是相信大家很难记住 IP addresses 吧,比如:111.13.100.91,而对于 routers 来说,它更容易处理 fixed-length, hierarchically structured IP addresses,因此我们需要一个服务可以做到 hostnames 与 IP addresses 之间的转换,DNS(domain name system) 的主要任务就是这个。
DNS 是一个应用层的协议,它用 UDP 作为传输层协议,端口号为 53,一些其它的应用层协议(比如:HTTP,SMTP和FTP)通常利用 DNS 去转换用户指定的 hostnames 到对应的 IP addresses. 下面我举个例子,比如一个用户在浏览器中输入 www.baidu.com 之后,按下 enter ,使用 DNS 的过程如下:
- The same user machine runs the client side of the DNS application
- The browser extracts the hostname, www.baidu.com, from the URL and passes the hostname to the client side of the DNS application
- The DNS client sends a query containing the hostname to a DNS server.
- The DNS client eventually receives a reply, which includes the IP address for the hostname
- Once the browser receives the IP address from DNS, it can initiate a TCP connection to the HTTP server process located at port 80 at that IP address
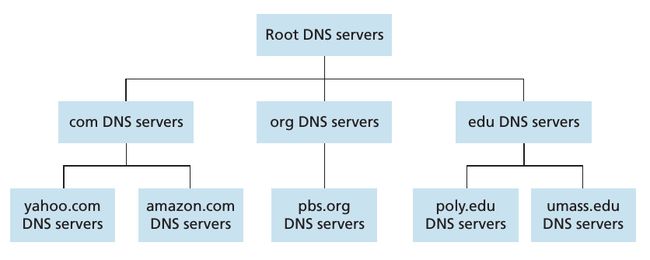
下图是互联网上的 DNS servers 的分层结构图:
除了上图中这3种 DNS server 外,还有一种重要的 DNS server,它就是 local DNS server,严格来讲,它并不属于上图中的任一层级,但是它是整个 DNS 架构中很重要的一部分。一个 host 的 local DNS server 通常都会离它“很近”,比如:For an institutional ISP, the local DNS server may be on the same LAN as the host; for a residential ISP, it is typically separated from the host by no more than a few routers. When a host makes a DNS query, the query is sent to the local DNS server, which acts a proxy, forwarding the query into the DNS server hierarchy.
下图是书中给出的一个例子,cis.poly.edu 这个 host 想要知道 gaia.cs.umass.edu 的 IP 地址,因此它需要寻求 DNS servers 的帮忙,整个过程的步骤如下:
- host 首先发送一个 DNS query message 到它的 local DNS server
- local DNS server 把这个 query message 转发给 root DNS server
- root DNS server 根据 edu 这个后缀,返回一系列负责 edu 的 TLD servers 的 IP 地址给 local DNS server
- local DNS server 再次发送 query message 到其中的1个 IP 地址
- TLD server 根据 umass.edu 返回一个 authoritative DNS server 的 IP 地址
- local DNS server 再次发送 query message 到这个 authoritative DNS server 去获取它想要的 IP 地址
- 最后,authoritative DNS server 返回给它 gaia.cs.umass.edu 的 IP 地址
下图中的整个过程既用了 iterative queries,也用了 recursive queries.
如果整个 DNS 系统能根据相应的主机域名查到对应的 IP 地址,那么在它的数据库中一定会有相应的 DNS 记录,即 resource records (RRs),它提供了 hostname-to-IP address 的映射。每个 RRs 是一个包含下面4个 field 的 four-tuple:
(Name, Value, Type, TTL)
- 如果 Type=A,那么 Name 是一个 hostname,Value 是一个 IP address for the hostname
- 如果 Type=NS,那么 Name 是一个 domain(比如:baidu.com),Value 是一个 authoritative DNS server 的 hostname(比如:dns.baidu.com),这个 server 知道如何获取 IP addresses for hosts in the domain
- 如果 Type=CNAME,那么 Name 是一个 alias hostname,Value 是一个 canonical hostname
- 如果 Type=MX,那么 Name 是一个 alias hostname,Value 是一个 mail server 的 canonical hostname
TTL is the time to live of the resource record; it determines when a resource should be removed from a cache.
下面我来举个例子,来打通整个上面的知识点。假设我在万网买了个域名,diaosi.me,在某个服务器提供商买了个虚拟主机,这个提供商通常给你一个难记的域名(比如:relay1.west-coast.enter-prise.com),让你去做 CNAME 解析,那么这个比较恶心的要域名叫做 canonical hostname,而 diaosi.me 就叫做 alias hostname,那么大家仔细想一下,为什么是 CNAME 解析呢?如果商家要给你1个 IP 地址,让你去做 A 解析不行吗?假设出于什么原因,你当前的主机必须要换个 IP 地址,如果你整个主机上的所有客户全是 A 解析,那么你必须通知他们要重新进行解析,而如果是 CNAME 的解析,你完全不需要通知你的客户们,你只需要把 relay1.west-coast.enter-prise.com 重新用新的 IP 地址进行 A 解析就可以了。
经过我一番苦心经营,我的网站(diao.me)为我挣了一大笔钱,现在我要做更大的生意,我想建一个 authoritative DNS server(假设 IP 地址为:212.212.212.1,主机名为:dns.tuhao.com),然后让其他人在我这里买域名,干掉万网,哈哈。假设,现在有一个土豪在我这买个域名(tuhao.me),在其它地方买了个独立的服务器(假设 IP 地址为:131.278.234.23)。接下来,我需要让我的 TLD 插入2条记录到他们的 DNS server 中,它们分别是:
(tuhao.me, dns.tuhao.com, NS)
(dns.tuhao.com, 212.212.212.1, A)
而这个土豪要做的就是在我的 authoritative DNS server 上插入下面这条记录:
(tuhao.me, 131.278.234.23, A)
这样,当有人访问 tuhao.me 时,通过上图中的那些 DNS query 过程,就可以顺利地找到相应的服务器了,随着我的客户越来越多,我就变得越来越有名了,哈哈。
DNS query 和 reply messages 它们具有相同的格式,书中140页详细介绍了每1个字节所表达的含义,我们可以用 nslookup 程序很容易地发送 query messages 到 DNS server,大家可以动手尝试一下。
Peer-to-Peer 应用
Web, e-mail, 和 DNS 所有这些应用都是基于 client-server 架构的,在这个章节中作者主要介绍了 P2P 架构在 file distribution 中的应用,不同于 CS 架构,在 P2P file distribution 的过程中,每个 peer 可以把它自己收到的文件的任一部分传递给其它的 peers,从而它在这个文件和分发过程中起到了辅助 server 的作用。下面举个具体的例子看看 P2P 架构相比于 CS 架构在 file distribution 应用中有什么优势。
从上图中我们可以看到总共有 N 个 peer 想要下载1个 F bits 的文件,第 i 个 peer 的 access link 上载速度为 ui ,下载速度为 di ,server 的 access link 上载速度为 us ,我们同时也假设所有的瓶颈都在 access link,并且 server 和 client 完全不参与任何其它的网络应用中,现在让我们分别计算一下各个架构的 distribution time(the time it takes to get a copy of the file to all N peers).
对于 client-server 架构来说,由于没有任何的 peers 来辅助 server 分发文件,所以我们有如下2个事实:
- The server must transmit one copy of the file to each of the N peers. Thus the server must transmit NF bits. Since the server’s upload rate is us , the time to distribute the file must be at least NFus
- Let dmin denote the download rate of the peer with the lowest download rate, that is, dmin=min{d1,d2,…,dN} . The peer with the lowest download rate cannot obtain all F bits of the file in less than Fdmin seconds. Thus the minimum distribution time is at least Fdmin
通过上面2个事实,我们可以用下面的式子来表示 distribution time:
由此我们已经得出了时间的下界,习题 P23 让我们描述一种 distribution scheme,从而使下界就是实际所需要的时间,下图是这个题目的答案:
至此,我们已经求出了在 CS 架构中的时间,从这个时间公式可以看出:the distribution time increases linearly with the number of peers N.
现在,让我们分析一下在 P2P 架构中所需要的 distribution time,由于每个 peer 会辅助 server 分发文件,distribution time 取决于 how each peer distributes portions of the file to the other peers,尽管如此,我们也可以得出一个关于 minimal distribution time 的表达式。通过以下3个事实:
- At the beginning of the distribution, only the server has the file. To get this file into the community of peers, the server must send each bit of the file at least once into its access link. Thus, the minimum distribution time is at least Fus . Unlike the client-server scheme, a bit sent once by the server may not have to be sent by the server again, as the peers may redistribute the bit among themselves
- As with the client-server architecture, the peer with the lowest download rate cannot obtain all F bits of the file in less than Fdmin seconds. Thus the minimum distribution time is at least Fdmin
- Finally, observe that the total upload capacity of the system as a whole is equal to the upload rate of the server plus the upload rates of each of the individual peers, that is, utotal=us+u1+…+uN . The system must deliver (upload) F bits to each of the N peers, thus delivering a total of NF bits. This cannot be done at a rate faster than utotal . Thus, the minimum distribution time is also at least NFus+u1+…+uN
通过上面3个事实,我们可以用下面的式子来表示 distribution time:
由此我们已经得出了时间的下界,习题 P24 让我们描述一种 distribution scheme,从而使下界就是实际所需要的时间。
接下面我来总结一下 BitTorrent 协议的内容,下面是作者给出的关于 torrent 的定义:
the collection of all peers participating in the distribution of a particular
file is called a torrent
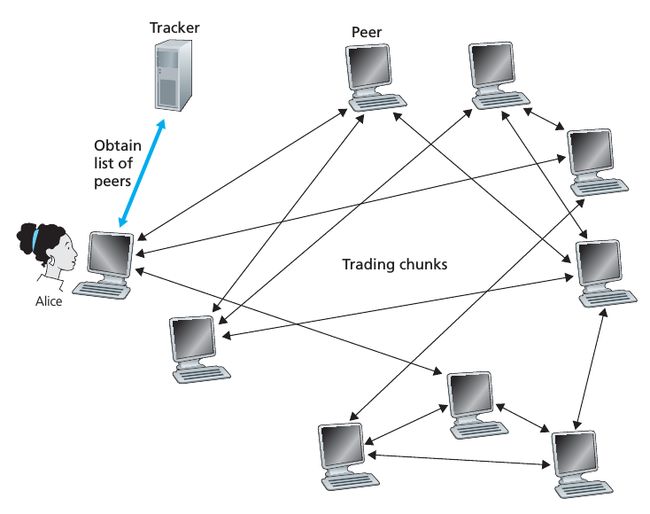
每一个 torrent 都是一个基础性的节点叫做 tracker,当一个 peer 加入 torrent,它去 tracker 那“登记自己”,然后定期地通知 tracker 我仍然在 torrent 中,因此,tracker 保持追踪每一个在 torrent 中的 peers.
在上图中,当 Alice 加入 torrent 时,tracker 会随机地从 torrent 中的 peers 中,选出一个子集,假设这个子集有50个 peers,然后 tracker 会把这50个 peers 的IP地址发送给 Alice,然后 Alice 尝试同时与这50个 peers 建立TCP连接,我们管成功与 Alice 建立TCP连接的这些 peers 叫做 neighboring peers. 那么对于上图来说,Alice 只有3个 neighboring peers,定期地,Alice 会问这些 neighboring peers 它们目前都有哪些 chunks,由于目前 Alice 只有3个 neighboring peers,所以 Alice 会从她的 neighboring peers 中得到这3个 chunks 列表,这些列表记录着每个 neighboring peers 都拥有哪些 chunks,有了这些信息之后,Alice 就会向它的这些 neighboring peers 要她目前还没有的 chunks.
Alice 自己有一些 chunks,同时也知道她的 neighboring peers 都有哪些 chunks,那么现在就会出现2个重要的问题。
- 她首先请求哪个 chunks?
- 当她的这些 neighboring peers 向她请求 chunks 时,她应该先响应哪个邻居呢?
那么对于第1个问题来说,Alice 用一个叫做 rarest first 的技术,The idea is to determine, from among the chunks she does not have, the chunks that are the rarest among her neighbors (that is, the chunks that have the fewest repeated copies among her neighbors) and then request those rarest chunks first.
那么对于第2个问题来说,Alice 会给一个优先权到 supplying her data at the highest rate 的邻居,也就是 Alice 会不断地度量她收到 bits 的速率,然后找出4个 feeding her bits at the highest rate 的 peers,然后她会响应这4个 peers. 每隔10秒,she recalculates the rates and possibly modifies the set of four peers. 在 BitTorrent 术语中,说这4个 peers be unchoked. 同样重要地是,每隔30秒,她会从它的这些 neighboring peers 中随机挑选出一个 peer(假设叫做 Bob),响应这个 peer,那么这个被选种的 peer 被说成 optimistically unchoked,因为 Alice 响应 Bob,即把 Bob 需要的 chunks 发送给他,那么 Alice 很有可能成为 Bob’s top four uploaders,在这种情况下,当 Bob recalculates the rates 的时候,Bob 将开始发送 chunks 给 Alice. 如果 Bob 发送给 Alice 的速率足够高,那么当 Alice recalculates the rates 的时候,Bob 就会变成 Alice’s top four uploaders.
All other neighboring peers besides these five peers (four “top” peers and one probing peer) are “choked,” that is, they do not receive any chunks from Alice.
把上面的过程总结来说:Every 30 seconds, Alice will randomly choose a new trading partner and initiate trading with that partner. If the two peers are satisfied with the trading, they will put each other in their top four lists and continue trading with each other until one of the peers finds a better partner. 最终效果是上传速率相协调的 peers 趋向于在一起。
Distributed Hash Tables (DHTs)
在 client-server 架构中,我们只需要把所有的 (key, value) pairs 存放在 server 中; 在 P2P 架构中,我们会把 (key, value) pairs 存放在上百万的 peers 中,每个 peer 只有键值对的子集,我们允许任何 peer 用 key 来查询 distributed database,然后 distributed database 会定位到有相应键值对的 peers 并返回 key-value pairs 到查询的 peer,同时任何 peer 将允许插入新的 key-value pairs 到 database,这样的 distributed database 叫做 distributed hash table.
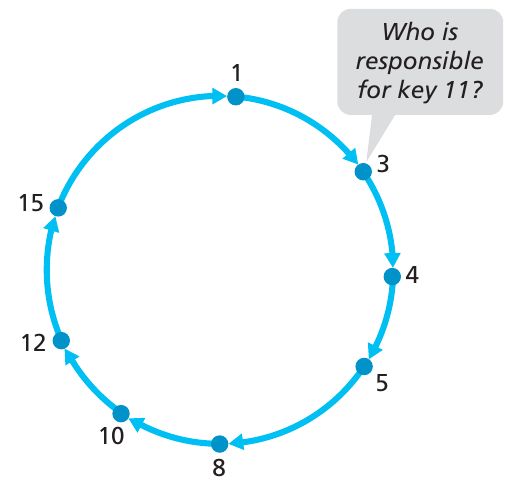
下图就是一个 Circular DHT,下图中总共有8个 peer,每个 peer 都有一个整数的 identifier,比如这个 identifier 的范围为 [0,15] ,同样地,每个 key 也用相应的 hash 函数映射成同样范围的整数,因此一个很自然的方法就是:assign each (key, value) pair to the peer whose identifier is the closest(closest peer as the closest successor of the key) to the key. If the key is exactly equal to one of the peer identifiers, we store the (key, value) pair in that matching peer; and if the key is larger than all the peer identifiers, 我们对其取模, storing the (key, value) pair in the peer with the smallest identifier.
从上图我们也可以看出,每个 peer 都只知道它的直接前驱和后继,比如,peer 5 只知道 peer 4 和 8 的 identifier 和 IP 地址。上图中,当 peer 3问哪个 peer 负责 key 11,然后顺时针地发送这个消息,peer 4 收到消息以后,它知道自己不负责,然后发给了 peer 5,这个消息一直持续发到 peer 12,这时它认为自己负责 key 11,然后发信息告诉 peer 3,是它负责 key 11.
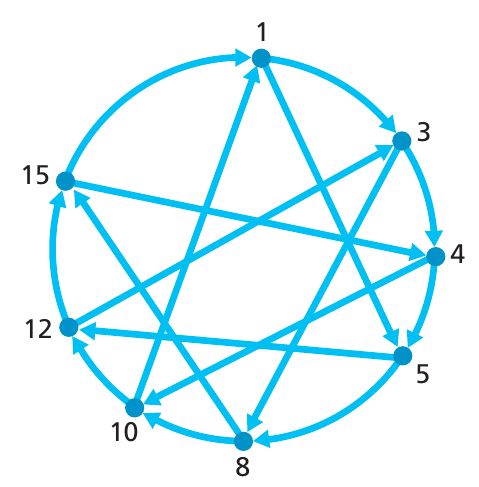
上面的过程存在一个问题,最坏情况下,这个消息将会经过 DHT 中的所有节点,平均来说,也需要 N2 ,N表示节点的个数。Thus, in designing a DHT, there is tradeoff between the number of neighbors each peer has to track and the number of messages that the DHT needs to send to resolve a single query.
上图中,我们为每个 peer 加了 shortcuts,这样上面的整个询问次数就会大大减小,但是这样我们也付出了一定的代价,也就是我们每个 peer 需要 track 更多的 peers.
The Network Layer
Introduction
下面是几个重要的概念:
Forwarding. When a packet arrives at a router’s input link, the router must move the packet to the appropriate output link.
Routing. The network layer must determine the route or path taken by packets as they flow from a sender to a receiver. The algorithms that calculate these paths are referred to as routing algorithms
Forwarding table. Every router has a forwarding table. A router forwards a packet by examining the value of a field in the arriving packet’s header, and then using this header value to index into the router’s forwarding table. The value stored in the forwarding table entry for that header indicates the router’s outgoing link interface to which that packet is to be forwarded.
在这个小节中,作者也介绍了网络层可以提供的服务,比如:Guaranteed delivery,In-order packet delivery 等。但是,我们最亲爱的 Internet’s network layer 只提供了一种服务,叫做 best-effort service,下图是几个 service model 的对比,详情参考书中311页。
Virtual Circuit and Datagram Networks
传输层在2个进程之间可以提供 connectionless service or connection-oriented service,相似地,网络层可以在2个 hosts 之间提供 connectionless service or connection service.
但是,网络层不像传输层那样,可以同时提供2个服务。在目前所有的 computer network architectures(Internet, ATM, frame relay, and so on) 中,网络层要么提供 host-to-host connectionless service,要么提供 host-to-host connection service,但是不能同时提供2个!我们把只提供 connection service 的计算机网络叫做 virtual-circuit (VC) networks; 把只提供 connectionless service 的计算机网络叫做 datagram networks. 我们的 Internet 是 datagram networks,而 ATM 和 frame relay 是 virtual-circuit networks.
Virtual-Circuit Networks
详情参考书中 314 页
Datagram Networks
In a datagram network, each time an end system wants to send a packet, it stamps the packet with the address of the destination end system and then pops the packet into the network.
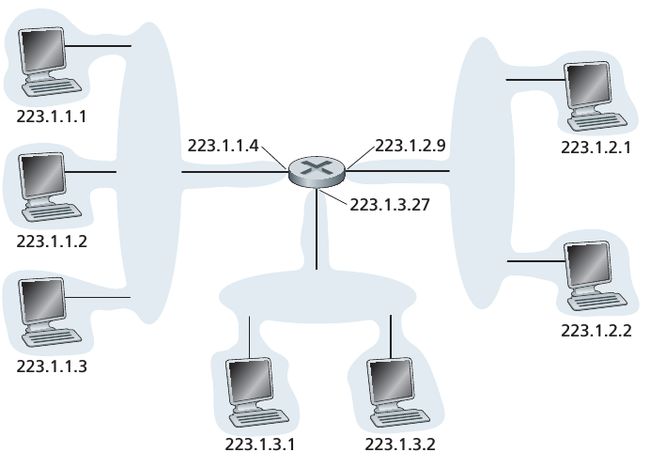
一个从 source 到 destination 的 packet 会经过很多个 routers. 当一个 packet 到达 router 时,router 会用 packet’s destination address 去查它的 forwarding table,从而决定出一个合适的 output link interface. 下面是一个关于查找的例子。
由于 IPV4 的地址长度有32位,我们不可能把所有的这些地址可能性全放在 forwarding table 中,因此我们选择了下图中的方法,也就是根据 IP 地址的前缀来查表,如果存在2个匹配项,则用 longest prefix matching rule.
In a datagram network the forwarding tables are modified by the routing algorithms, which typically update a forwarding table every one-to-five minutes or so. Because forwarding tables in datagram networks can be modified at any time, a series of packets sent from one end system to another may follow different paths through the network and may arrive out of order.
What’s Inside a Router
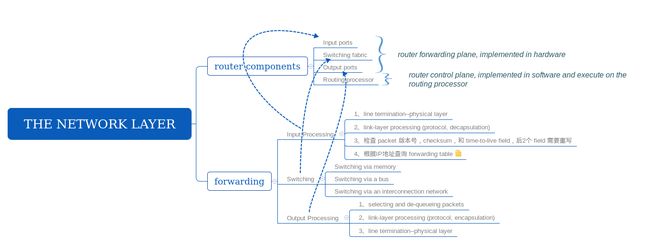
整个章节的思维导图如下:
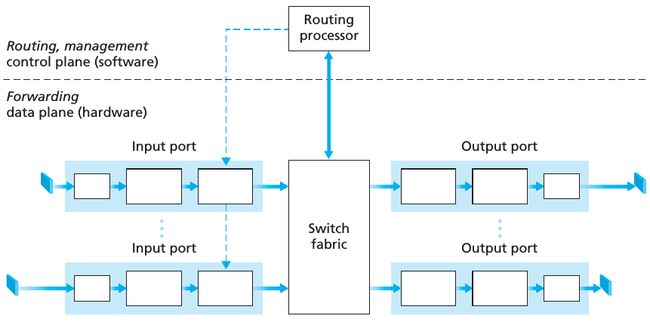
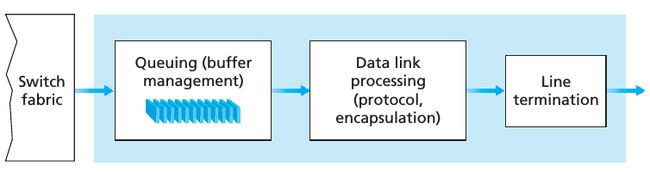
下图是 router 的结构:
从上图可以看到,一个 router 的 input ports, output ports, 和 switching fabric 共同实现了 forwarding function,并且主要都是在硬件上实现的。These forwarding functions are sometimes collectively referred to as the router forwarding plane; These router control plane functions are usually implemented in software and execute on the routing processor (typically a traditional CPU). The network-wide routing control plane is decentralized—with different pieces (e.g., of a routing algorithm) executing at different routers and interacting by sending control messages to each other. Indeed, today’s Internet routers and the routing algorithms we’ll study in Section 4.6 operate in exactly this manner.
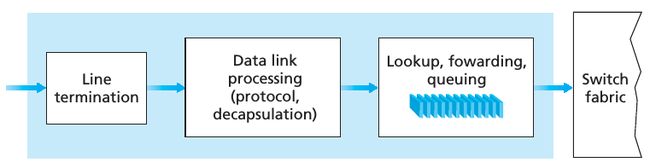
下图是关于 Input port processing:
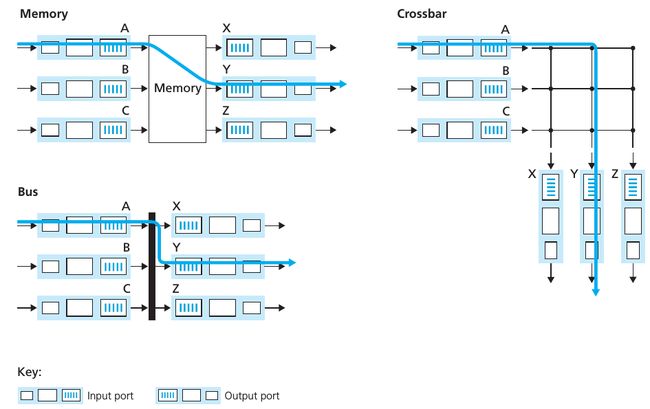
下图是3个 switching techniques,详情参考书中324页:
下图是 Output port processing:
Where Does Queuing Occur
在文章中的上面提到了 Queuing delay 和 packet lost,既然现在已经了解 router 内部的结构,让我们才探寻一下这些 Queuing 和 lost 发生在哪里?
The location and amount of queueing (either at the input port queues or the output port queues) will depend on the traffic load, the relative speed of the switching fabric, and the line speed.
Suppose that the input and output line speeds (transmission rates) all have an identical transmission rate of Rline packets per second, and that there are N input ports and N output ports. Define the switching fabric transfer rate Rswitch as the rate at which packets can be moved from input port to output port.
如果 Rswitch=Rline∗N ,那么 input ports 的 queueing 可以忽略不计。下图就是一个最坏情况发生的例子,所有 N 个 input lines 都收到了 packets,并且它们都被 forwarded 到同一个 output port.
上图中的 N=3 ,所以根据我们的假设, Rswitch 是 Rline 的3倍快。在单位时间内,一个 output port 只能 transmit 一个 packet,但是有3个到达的 packet,因此,随着时间的增长,queued packets can grow large enough to exhaust available memory at the output port, in which case packets are dropped.
由于在 output port 存在 queuing,因此需要一个 packet scheduler 来选择让哪个 packet 先出去。最简单的就是 first-come-first-served (FCFS) scheduling. 复杂的就是 weighted fair queuing (WFQ),which shares the outgoing link fairly among the different end-to-end connections that have packets queued for transmission.
同样地道理,当 output port 的内存耗尽时,a decision must be made to either drop the arriving packet (a policy known as drop-tail) or remove one or more already-queued packets to make room for the newly arrived packet.
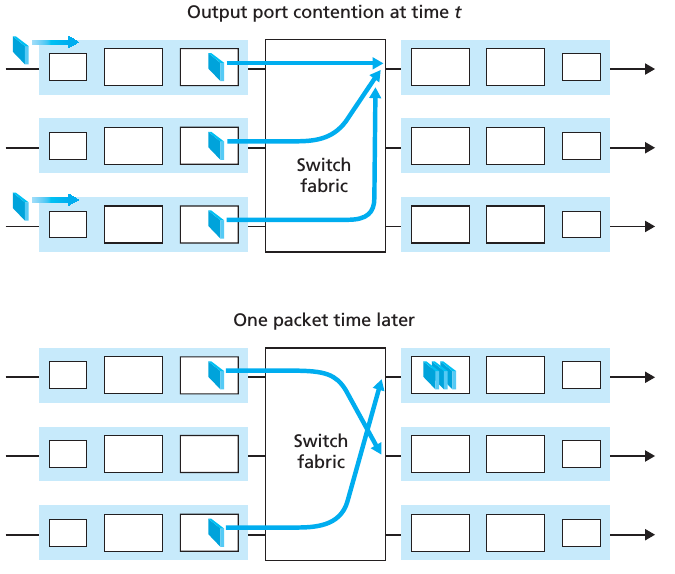
If the switch fabric is not fast enough (relative to the input line speeds) to transfer all arriving packets through the fabric without delay, then packet queuing can also occur at the input ports, as packets must join input port queues to wait their turn to be transferred through the switching fabric to the output port. 在这种情况下,会产生一个问题,叫做 head-of-the-line (HOL) blocking,如下图所示:
上图中用的是 crossbar switching fabric. 其中1和3号 packet 有着同一个目标,由于它们的目标相同,所以只能有1个先过去。在一个单位时间过后,1号 packet 到达了目标,但是不幸的是,虽然4号 packet 的目标与3号不同,但是由于3号在它前面,它也不得不等待,这种情况就叫做 HOL.
Internet Protocol (IP)
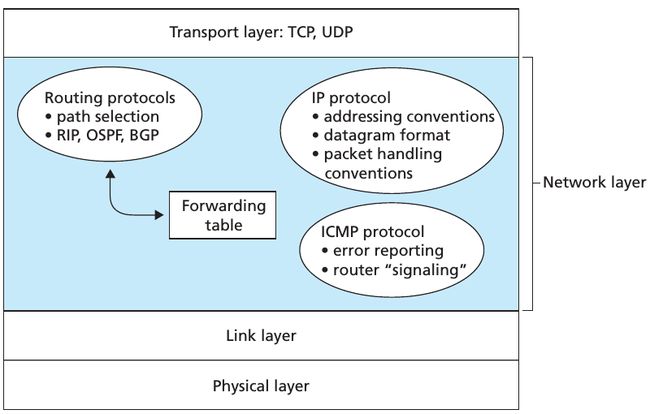
在上面的章节中,我们并没有指定具体的 computer network,在这以后,主要关注 Internet. 这个小节主要关注 how addressing and forwarding are done in the Internet. 下图是几个组成 Internet’s network layer 的重要组件:
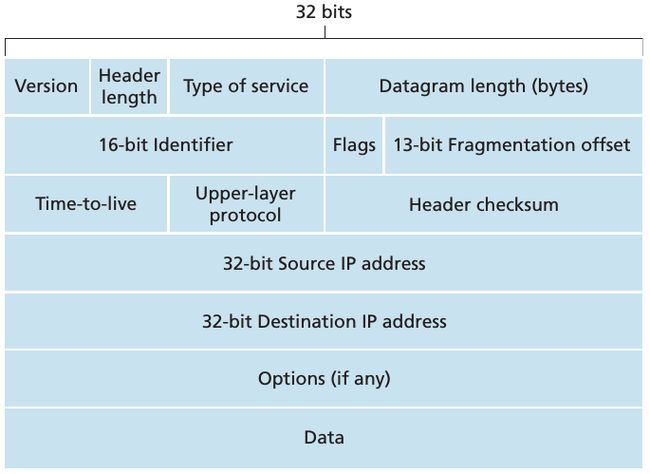
Datagram Format
具体 filed 的含义请参考书中 333 页。
上图中第2行的3个 field 是用作 IP Datagram Fragmentation 目的.下面我来总结一下什么叫做 Datagram Fragmentation.
一个 link-layer frame 可以携带的最大的数据量叫做 maximum transmission unit (MTU). 限制 datagram 的大小这不是问题,what is a problem is that each of the links along the route between sender and destination can use different link-layer protocols, and each of these protocols can have different MTUs.
所以,当一个 oversized IP datagram 到达一个小于它的 MTU 的 outgoing link 时,IPV4 的做法是:fragment the data in the IP datagram into two or more smaller IP datagrams, encapsulate each of these smaller IP datagrams in a separate link-layer frame; and send these frames over the outgoing link. Each of these smaller datagrams is referred to as a fragment.
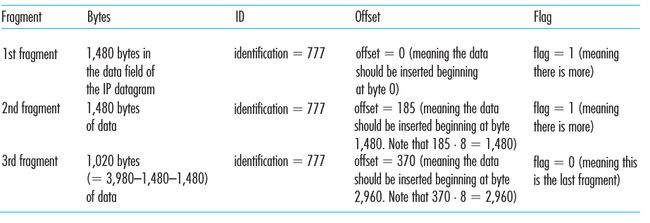
由于坚持使 network core 简单的原则,IPv4 的设计者把 datagram reassembly 的工作放到了 end systems 上,destination host 正是用上面的3个 field 来做这个工作。例子:A datagram of 4,000 bytes (20 bytes of IP
header plus 3,980 bytes of IP payload) arrives at a router and must be forwarded to a link with an MTU of 1,500 bytes,下表就是 IP fragment 的结果:
由于 MTU 为1500 bytes,header 需要20个 bytes,所以每个 fragment(即datagram)中只有1480 bytes 在 data field 中。最初的 identification 为777,所以这3个 fragment 都为777; Offset 没什么可说的,由于它的值 be specified in units of 8-byte chunks; 最后一个 fragment 的 flag 要为0.
At the destination, the payload of the datagram is passed to the transport layer only after the IP layer has fully reconstructed the original IP datagram. If one or more of the fragments does not arrive at the destination, the incomplete datagram is discarded and not passed to the transport layer.
IPv4 Addressing
A host typically has only a single link into the network; when IP in the host wants to send a datagram, it does so over this link. The boundary between the host and the physical link is called an interface.
由于 router 的工作就是从一个 link 接收 datagram,然后转发到其它的 link,所以它通常会有2个或更多个 link. The boundary between the router and any one of its links is also called an interface. A router thus has multiple interfaces, one for each of its links.
Because every host and router is capable of sending and receiving IP datagrams, IP requires each host and router interface to have its own IP address. Thus, an IP address is technically associated with an interface, rather than with the host or router containing that interface.
- subnet
- Classless Interdomain Routing (CIDR—pronounced cider)
- 怎么用前缀各种找地址,子网
- classful addressing
- 组织如何获得一大块地址
- host 如何获得地址
- DHCP
- 家庭网络解决设备多问题
- NAT
- Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
- ping
-
Traceroute
IGMP, 407 页
which is used to manage a host’s joining and leaving of multicast groups - IPv6 Datagram Format
- Transitioning from IPv4 to IPv6
- dual-stack approach
- Tunneling
A Comparison of LS and DV Routing Algorithms