Spring Data JPA 实战
课程介绍
《Spring Data JPA 实战》内容是基于作者学习和工作中实践的总结和升华,有一句经典的话:“现在的开发人员是站在巨人的肩上,弯道超车”。因现在框架越来越优秀,减少了很多问题和工作量,如果还没有学习 Spring Data JPA 建议赶快了解一下。随着 Java 技术和微服务技术逐渐的广泛的应用,Spring Cloud、Spring Boot 逐渐统一 Java 的框架江湖。市场上的 ORM 框架也逐渐被人重视起来,而 Spring Data 逐渐走入 Java 开发者的视野,被越来越多的架构师作为 ORM 的技术选型方向。
本课的内容分为基础、进阶和深入,对 Spring Data JPA 的使用、手册、实战、源码分析等进行全面的讲解。基础部分内容包括了:整体认识 JPA,从 JPA 基础查询方法出发、定义查询方法(Defining Query Methods)、注解式查询方法,并一步一步进阶之深入部分:@Entity 实例里面常用注解详解、JpaRepository 详解、QueryByExampleExecutor 和 JpaSpecificationExecutor 复杂使用案例和语法、JPA 的 MVC 扩展 Rest 支持、DataSource 源码分析(内存数据库、多数据源)、乐观锁等。
所选的技术版本都是基于 Spring Boot 2.0 来讲解的,选择学习本课程内容,你已经在大多数开发人员领先一步。
作者介绍
张振华,曾经先后在驴妈妈、携程、要买车公司担任过 Java 高级工程师、架构师、开发主管、技术经理等职务。在电商公司工作期间,负责过 PC 站和后端服务的平台架构的实现和升级。目前在做一些 Java 架构工作。前后从业十几年没有离开 Java 开发,2015年出版《Java 并发编程从入门到精通》图书,2018年出版《Spring Data JPA 从入门到精通》一书。
课程内容
第01课:整体认识 JPA
为什么要重新学习“Spring Data JPA”?俗话说的好:“未来已经来临,只是尚未流行”,纵观市场上的 ORM 框架,MyBatis 以灵活著称,但是要维护复杂的配置,并且不是 Spring 官方的天然全家桶,还得做额外的配置工作,如果资深的架构师还得做很多封装;Hibernate 以 HQL 和关系映射著称,但是就是使用起来不是特别灵活;那么 Spring Data JPA 来了,感觉要夺取 ORM 的 JPA 霸主地位了,底层以 Hibernate 为封装,对外提供了超级灵活的使用接口,又非常符合面向对象和 Rest 的风格,感觉是架构师和开发者的福音,并且 Spring Data JPA 与 Spring Boot 配合起来使用具有天然的优势,你会发现越来越多的公司的招聘要用会有传统的 SSH、Spring、MyBatis 要求,逐步的变为 Spring Boot、Spring Cloud、Spring Data 等 Spring 全家桶的要求,而很多新生代的架构师基于其生态的考虑,正在逐步推动者 Spring Data JPA 的更多的使用场景。
本章我们从整体到局部,先来整体认识一下 Spring Data JPA。
市场上 ORM 框架比对
- MyBatis:MyBatis 本是 Apache 的一个开源项目 iBatis,2010 年这个项目由 Apache Software Foundation 迁移到了 Google Code,并且改名为 MyBatis,其着力于 POJO 与 SQL 之间的映射关系,可以进行更为细致的 SQL,使用起来十分灵活、上手简单、容易掌握,所以深受开发者的喜欢,目前市场占有率最高,比较适合互联应用公司的 API 场景;缺点就是工作量比较大,需要各种配置文件的配置和 SQL 语句。
- Hibernate:Hibernate 是一个开放源代码的对象关系映射框架,它对 JDBC 进行了非常轻量级的对象封装,使得 Java 程序员可以随心所欲的使用对象编程思维来操纵数据库,并且对象有自己的生命周期,着力点对象与对象之间关系,有自己的 HQL 查询语言,所以数据库移植性很好。Hibernate 是完备的 ORM 框架,是符合 JPA 规范的,有自己的缓存机制,上手来说比较难,比较适合企业级的应用系统开发。
- Spring Data JPA:可以理解为 JPA 规范的再次封装抽象,底层还是使用了 Hibernate 的 JPA 技术实现,引用 JPQL(Java Persistence Query Language)查询语言,属于 Spring 的整个生态体系的一部分。由于 Spring Boot 和 Spring Cloud 在市场上的流行,Spring Data JPA 也逐渐进入大家的视野,他们有机的整体,使用起来比较方便,加快了开发的效率,使开发者不需要关系和配置更多的东西,完全可以沉浸在 Spring 的完整生态标准的实现下,上手简单、开发效率高,又对对象的支持比较好,又有很大的灵活性,市场的认可度越来越高。
- OpenJPA :是 Apache 组织提供的开源项目,它实现了 EJB 3.0 中的 JPA 标准,为开发者提供功能强大、使用简单的持久化数据管理框架,但功能、性能、普及性等方面更加需要加大力度,所以用的人不人不是特别多。
- QueryDSL:QueryDSL 可以在任何支持的 ORM 框架或者 SQL 平台上以一种通用的 API 方式来构建查询,目前 QueryDSL 支持的平台包括 JPA、JDO、SQL、Java Collections、RDF、Lucene、Hibernate Search,同时 Spring Data JPA 也对 QueryDSL 做了很好的支持。
JPA 的介绍以及哪些开源实现
JPA(Java Persistence API)中文名 Java 持久层 API,是 JDK 5.0 注解或 XML 描述对象-关系表的映射关系,并将运行期的实体对象持久化到数据库中。
Sun 引入新的 JPA ORM 规范出于两个原因:其一,简化现有 Java EE 和 Java SE 应用开发工作;其二,Sun 希望整合 ORM 技术,实现天下归一。
JPA 包括以下三方面的内容
- 一套 API 标准,在 javax.persistence 的包下面,用来操作实体对象,执行 CRUD 操作,框架在后台替代我们完成所有的事情,开发者从繁琐的 JDBC 和 SQL 代码中解脱出来。
- 面向对象的查询语言:Java Persistence Query Language(JPQL),这是持久化操作中很重要的一个方面,通过面向对象而非面向数据库的查询语言查询数据,避免程序的 SQL 语句紧密耦合。
- ORM(Object/Relational Metadata)元数据的映射,JPA 支持 XML 和 JDK 5.0 注解两种元数据的形式,元数据描述对象和表之间的映射关系,框架据此将实体对象持久化到数据库表中。
JPA 的开源实现
JPA 的宗旨是为 POJO 提供持久化标准规范,由此可见,经过这几年的实践探索,能够脱离容器独立运行,方便开发和测试的理念已经深入人心了。Hibernate 3.2+、TopLink 10.1.3 以及 OpenJPA、QueryDSL 都提供了 JPA 的实现,以及最后的 Spring 的整合 Spring Data JPA。目前互联网公司和传统公司大量使用了 JPA 的开发标准规范。
![]()
了解 Spring Data
Spring Data 介绍
Spring Data 项目是从 2010 年开发发展起来的,从创立之初 Spring Data 就想提供一个大家熟悉的、一致的、基于 Spring 的数据访问编程模型,同时仍然保留底层数据存储的特殊特性。它可以轻松地让开发者使用数据访问技术包括:关系数据库、非关系数据库(NoSQL)和基于云的数据服务。
Spring Data Common 是 Spring Data 所有模块的公用部分,该项目提供跨 Spring 数据项目的共享基础设施,它包含了技术中立的库接口以及一个坚持 Java 类的元数据模型。
Spring Data 不仅对传统的数据库访问技术:JDBC、Hibernate、JDO、TopLick、JPA、MyBatis 做了很好的支持和扩展、抽象、提供方便的 API,还对 NoSQL 等非关系数据做了很好的支持:MongoDB 、Redis、Apache Solr 等。
Spring Data 的子项目有哪些
主要项目(Main Modules):
- Spring Data Commons
- Spring Data Gemfire
- Spring Data JPA
- Spring Data KeyValue
- Spring Data LDAP
- Spring Data MongoDB
- Spring Data REST
- Spring Data Redis
- Spring Data for Apache Cassandra
- Spring Data for Apache Solr
社区支持的项目(Community Modules):
- Spring Data Aerospike
- Spring Data Couchbase
- Spring Data DynamoDB
- Spring Data Elasticsearch
- Spring Data Hazelcast
- Spring Data Jest
- Spring Data Neo4j
- Spring Data Vault
其他(Related Modules):
- Spring Data JDBC Extensions
- Spring for Apache Hadoop
- Spring Content
当然了还有许多开源社区做出的许多贡献如 MyBatis 等。
市面上主要的如图所示:
![]()
Spring Data 操作的主要特性
Spring Data 项目旨在为大家提供一种通用的编码模式,数据访问对象实现了对物理数据层的抽象,为编写查询方法提供了方便。通过对象映射,实现域对象和持续化存储之间的转换,而模板提供的是对底层存储实体的访问实现,操作上主要有如下特征:
- 提供模板操作,如 Spring Data Redis 和 Spring Data Riak;
- 强大的 Repository 和定制的数据储存对象的抽象映射;
- 对数据访问对象的支持(Auting 等)。
![]()
Spring Data JPA 的主要类及结构图
我们需要掌握和使用到的类
七个大 Repository 接口:
- Repository(org.springframework.data.repository);
- CrudRepository(org.springframework.data.repository);
- PagingAndSortingRepository(org.springframework.data.repository);
- JpaRepository(org.springframework.data.jpa.repository);
- QueryByExampleExecutor(org.springframework.data.repository.query);
- JpaSpecificationExecutor(org.springframework.data.jpa.repository);
- QueryDslPredicateExecutor(org.springframework.data.querydsl)。
两大 Repository 实现类:
- SimpleJpaRepository(org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.support);
- QueryDslJpaRepository(org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.support)。
类的结构关系图如图所示
![]()
基本上面都是我们要关心的类和接口,先做到大体心中有个数,后面章节会一一做讲解。
需要了解到的类,真正的 JPA 的底层封装类
- EntityManager(javax.persistence);
- EntityManagerImpl(org.hibernate.jpa.internal)。
MySQL 的快速开始实例
以 Spring Boot 2.0 和 Spring JDBC 为技术场景,选用 MySQL 来做一个实例。
环境要求:
- JDK 1.8
- Maven 3.0+
- IntelliJ IDEA
第一步:创建数据库并建立 user 表
(1)创建一个数据的新用户并附上权限
mysql> create database db_example;mysql> create user 'springuser'@'localhost' identified by 'ThePassword';mysql> grant all on db_example.* to 'springuser'@'localhost'; (2)创建一个表
CREATE TABLE `user` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL, `email` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`))第二步:利用 Intellij IDEA 创建 Example1
![]()
![]()
上面的信息是 maven 的 pom 里面所需要的都可以修改。
![]()
选择 JPA 和 MySQL 和 Web 一路单击 Next 按钮,然后完成得到一个工程,完成后如下结构:
![]()
第三步:创建或者修改 application.properties 文件
在工程的 sources 下面的 src/main/resources/application.properties 内容如下:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_examplespring.datasource.username=springuserspring.datasource.password=ThePassword第四步:创建一个 @Entity
src/main/java/example/example1/User.java:
package com.example.example1;import javax.persistence.Entity;import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;import javax.persistence.GenerationType;import javax.persistence.Id;@Entity public class User { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.AUTO) private Long id; private String name; private String email; public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getEmail() { return email; } public void setEmail(String email) { this.email = email; }}第五步:创建一个 Repository
src/main/java/example/example1/UserRepository.java:
package com.example.example1;import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;public interface UserRepository extends CrudRepository {} 第六步:创建一个 controller
package com.example.example1;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;@Controller@RequestMapping(path = "/demo")public class UserController { @Autowired private UserRepository userRepository; @GetMapping(path = "/add") public void addNewUser(@RequestParam String name, @RequestParam String email) { User n = new User(); n.setName(name); n.setEmail(email); userRepository.save(n); } @GetMapping(path = "/all") @ResponseBody public Iterable getAllUsers() { return userRepository.findAll(); }} 第七步:直接运行 Example1Application 的 main() 函数即可
打开 Example1Application 内容如下:
package com.example.example1;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;@SpringBootApplicationpublic class Example1Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Example1Application.class, args); }}访问的 URL 如下:
$ curl 'localhost:8080/demo/[email protected]'$ curl 'localhost:8080/demo/all'这时候已经可以看到效果了。
也可以在2018.05月左右购买《Spring Data JPA 入门到精通》一书,进行整体的学习。
第02课:JPA 基础查询方法 JpaRepository 详解
本篇内容我们一起学习 Spring Data Common 里面的公用基本方法,本章不仅介绍用法,还会介绍一个更好的学习过程。
Spring Data Common 的 Repository
Repository 位于 Spring Data Common 的 lib 里面,是 Spring Data 里面做数据库操作的最底层的抽象接口,最顶级的父类,源码里面其实什么方法都没有,仅仅起到一个标识作用。管理域类以及域类的 ID 类型作为类型参数,此接口主要作为标记接口来捕获要使用的类型,并帮助用户发现扩展此接口的接口。Spring 底层做动态代理的时候发现只要是它的子类或者实现类,都代表储存库操作。
Repository 的源码如下:
package org.springframework.data.repository;import org.springframework.stereotype.Indexed;@Indexedpublic interface Repository {} 有了这个类,我们就能顺腾摸瓜,找到好多 Spring Data JPA 自己提供的基本接口和操作类,及其实现方法,这个接口定义了所有 Repostory 操作的实体和 ID 的泛型参数。当不是继承任何就可,只要继承这个接口,就可以使用 Spring JPA 里面提供的很多约定的方法查询和注解查询,后面章节会详细介绍。
Repository 的类层次关系(Diagms/Hierarchy/Structure)
我们来根据 Repository 这个基类,顺腾摸瓜看看 Spring Data JPA 里面都有些什么?同时将介绍学习的方法,这样不管碰到学习任何一个框架时,方法都雷同,逐步从入门到精通,提高学习效率。
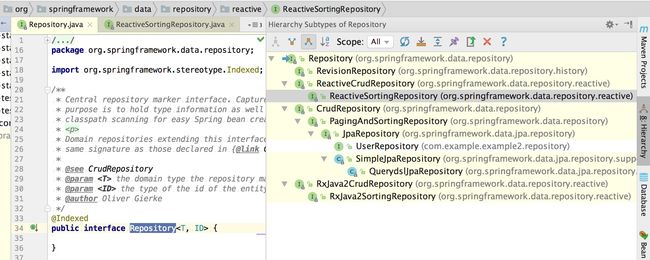
(1)我们用工具 Intellij Idea,打开类 Repository.class,然后单击 Navigate → Type Hierchy,会得到如下视图:
通过该层次结构视图,就会明白基类 Repository 的用意,需要对工程里面的所有 Repository 了如执掌,项目里面有哪些,Spring 的项目里面有哪些一目了然。我们通过上面的类的结构图,可以看得出来 Repository 可以分为三个部分:
- 即本篇要介绍的正常的 JpaRepository 这条线的操作。
- ReactiveRepository 这条线响应式编程,主要支持目前的 NoSQL 方面的操作,因为 NoSQL 大部分的操作都是分布式的,所以足可以看的出来 Spring Data 的野心,想提供关于所有 Data 方面的操,目前主要有 Cassandra、MongoDB 的实现,与 JPA 属于平级项目。
- RxJava2CrudRepository 这条线是为了支持 RxJava 2 做的标准的响应式编程的接口。
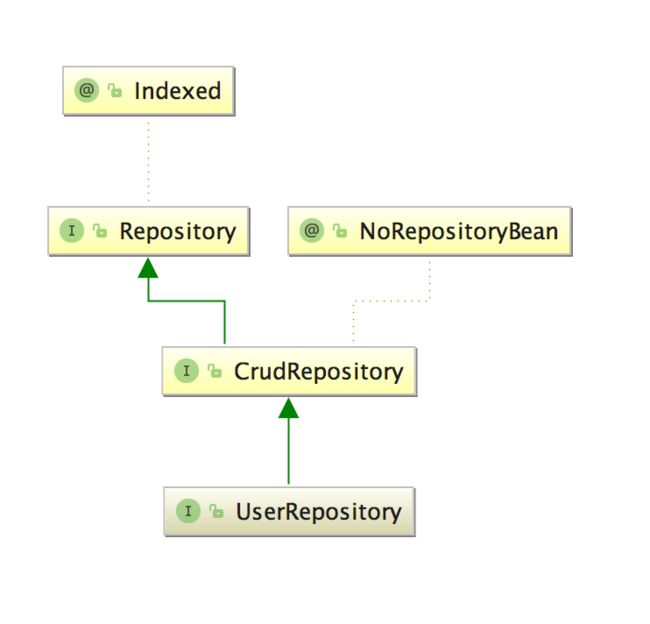
(2)通过 Intellij Idea,打开类上面 Example 1 里面的 UserRepository.java,单击鼠标右键 show diagrams 用图表的方式查看类的关系层次,打开如下图所示:
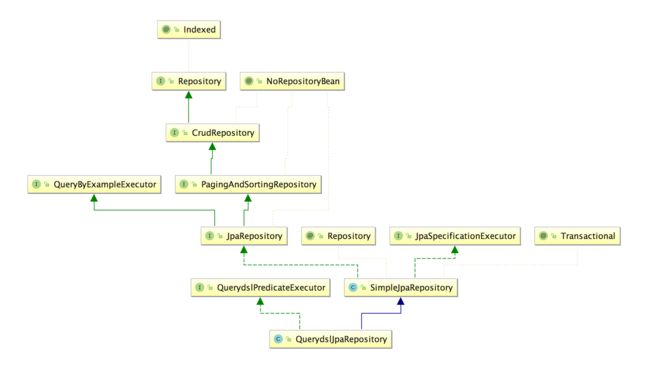
(3)通过 Intellij Idea,打开类 QueryDslJpaRepository,单击鼠标右键 show diagrams 用图表的方式查看类的关系层次,打开如下图所示:
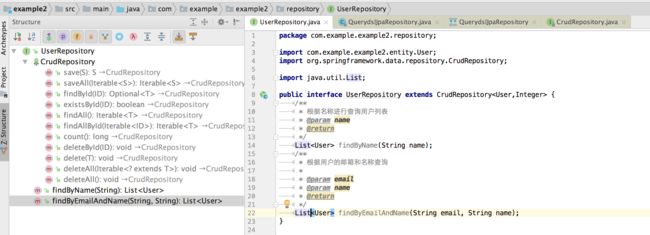
(4)通过 Intellij Idea,打开类上面的 Example 1 里面的 UserRepository.java,单击 Navigate | File Structure 命令,可以查看此类的结构及有哪些方法,以此类推到其他类上,打开如下图所示:
以上三种视图是开发过程中会经常用到的视图,而通过上面的图就可以知道如果要学习 JPA 或者是 Solr 等其他 Spring Data 实现的时候需要掌握哪些东西,本篇内容以 JPA 为主线来讲解。
我们来看一个 Repository 的实例:
package com.example.example2.repository;import com.example.example2.entity.User;import org.springframework.data.repository.Repository;import java.util.List;public interface UserRepository extends Repository { /** * 根据名称进行查询用户列表 * @param name * @return */ List findByName(String name); /** * 根据用户的邮箱和名称查询 * * @param email * @param name * @return */ List findByEmailAndName(String email, String name);} CrudRepository 方法详解
通过上面类关系图可以看到 CrudRepository 提供了公共的通用的 CRUD 方法。
CrudRepository interface 内容
package org.springframework.data.repository;import java.util.Optional;@NoRepositoryBeanpublic interface CrudRepository extends Repository { S save(S entity);(1) Iterable saveAll(Iterable entities);(2) Optional findById(ID id);(3) boolean existsById(ID id);(4) Iterable findAll();(5) Iterable findAllById(Iterable ids);(6) long count();(7) void deleteById(ID id);(8) void delete(T entity);(9) void deleteAll(Iterable entities);(10) void deleteAll();(11)} - 保存实体方法。
原理:我们通过刚才的类关系查看其实现类,SimpleJpaRepository 里面的实现方法如下:
@Transactional public S save(S entity) { if (entityInformation.isNew(entity)) { em.persist(entity); return entity; } else { return em.merge(entity); } }我们发现他是先出查一下传进去的实体是不是存在,然后判断是新增还是更新,是不是存在根据两种机制,一种是根据主键来判断,还有一种是根据 Version 来判断,后面介绍 Version 的时候详解,所以如果去看 JPA 的控制台打印出来的 SQL 最少会有两条,一条是查询,一条是 Insert 或者 Update。
- 批量保存,原理和上面的那一条相同,我们去看实现的话,就是 for 循环调用上面的 save 方法。
- 根据主键查询实体,返回 JDK 1.8 的 Optional,这可以避免 null exception。
- 根据主键判断实体是否存在。
- 查询实体的所有列表。
- 根据主键列表查询实体列表。
- 查询总数。
- 根据主键删除,查看源码会发现,其是先查询出来再进行删除。
- 根据 entity 进行删除。
- 批量删除。
- 删除所有,原理:通过刚才的类关系查看其的实现类,SimpleJpaRepository 里面的 delete 实现方法如下,都是调用 delete 进行删除。
@Transactional public void deleteById(ID id) { Assert.notNull(id, ID_MUST_NOT_BE_NULL); delete(findById(id).orElseThrow(() -> new EmptyResultDataAccessException( String.format("No %s entity with id %s exists!", entityInformation.getJavaType(), id), 1))); } @Transactional public void delete(T entity) { Assert.notNull(entity, "The entity must not be null!"); em.remove(em.contains(entity) ? entity : em.merge(entity)); } @Transactional public void deleteAll(Iterable entities) { Assert.notNull(entities, "The given Iterable of entities not be null!"); for (T entity : entities) { delete(entity); } }我们发现关于 Update、Delete、Save 等操作 JPA 自己也会先查询一下,再去做保存操作,不存在抛出异常。特别强调了一下 Delete 和 Save 方法,是因为看到实际工作中,有同事会画蛇添足,自己在做 Save 的时候先去 Find 一下,其实是没有必要的,Spring JPA 底层都考虑到了。所以这里其实是想告诉大家,当我们用任何第三方方法的时候最好先查一下其源码和逻辑或者 API 再写出优雅的代码。
CrudRepository Interface 的使用案例
使用也很简单,只需要自己的 Repository 继承 CrudRepository 即可。第01课的案例修改如下:UserCrudRepository 继承 CrudRepository:
package com.example.example2.repository;import com.example.example2.entity.User;import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;import java.util.List;public interface UserCrudRepository extends CrudRepository {} 第01课的案例 UserController,修改如下:
package com.example.example2;import com.example.example2.entity.User;import com.example.example2.repository.UserRepository;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;import java.util.Optional;@Controller@RequestMapping(path = "/demo")public class UserController { @Autowired private UserCrudRepository userRepository; @GetMapping(path = "/add") public void addNewUser(@RequestParam String name, @RequestParam String email) { User n = new User(); n.setName(name); n.setEmail(email); userRepository.save(n); } @GetMapping(path = "/all") @ResponseBody public Iterable getAllUsers() { return userRepository.findAll(); } @GetMapping(path = "/info") @ResponseBody public Optional findOne(@RequestParam Integer id) { return userRepository.findById(id); } @GetMapping(path = "/delete") public void delete(@RequestParam Integer id) { userRepository.deleteById(id); }} 然后启动运行就可以直接看效果了。
PagingAndSortingRepository 方法详解
通过类的关系图,我们可以看到 PagingAndSortingRepository 继承 CrudRepository 所有他的基本方法,它都有增加了分页和排序等对查询结果进行限制的一些基本的、常用的、通用的一些分页方法。
PagingAndSortingRepository interface 内容
一样,我们也来查看一下 PagingAndSortingRepository 的源码看看提供了哪些方法。
package org.springframework.data.repository;import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort;@NoRepositoryBeanpublic interface PagingAndSortingRepository extends CrudRepository { Iterable findAll(Sort sort); (1) Page findAll(Pageable pageable); (2)} - 根据排序取所有的对象的集合。
- 根据分页和排序进行查询,并用 Page 对象封装。Pageable 对象包含分页和 Sort 对象。
PagingAndSortingRepository 和 CrudRepository 都是 Spring Data Common 的标准接口,如果我们采用 JPA 那它对应的实现类就是 Spring Data JPA 的 Model 里面的 SimpleJpaRepository。如果是其他 NoSQL 实现 MongoDB,那它的实现就在 Spring Data MongoDB 的 Model 里面。
来看一下 Page 查询的实现内容如下:
public Page findAll(Pageable pageable) { if (isUnpaged(pageable)) { return new PageImpl(findAll()); } return findAll((Specification) null, pageable); } 看源码发现这些查询都会用到后面章节要讲的 Specification 查询方法。
PagingAndSortingRepository 使用案例
也是只需要继承 PagingAndSortingRepository 的接口即可,其他不要做任何改动,UserPagingAndSortingRepository 修改如下:
package com.example.example2.repository;import com.example.example2.entity.User;import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;import org.springframework.data.repository.PagingAndSortingRepository;public interface UserPagingAndSortingRepository extends PagingAndSortingRepository { Page findByName(String name, Pageable pageable) throws Exception;} UserController 修改如下:
@Controller@RequestMapping(path = "/demo")public class UserController { /** * 验证排序和分页查询方法,Pageable的默认实现类:PageRequest * @return */ @GetMapping(path = "/page") @ResponseBody public Page getAllUserByPage() { return userPagingAndSortingRepository.findAll( new PageRequest(1, 20,new Sort(new Sort.Order(Sort.Direction.ASC,"name")))); } /** * 排序查询方法,使用Sort对象 * @return */ @GetMapping(path = "/sort") @ResponseBody public Iterable getAllUsersWithSort() { return userPagingAndSortingRepository.findAll(new Sort(new Sort.Order(Sort.Direction.ASC,"name"))); }} JpaRepository 方法详解
JpaRepository 到这里可以进入到分水岭了,上面的那些都是 Spring Data 为了兼容 NoSQL 而进行的一些抽象封装,而从 JpaRepository 开始是对关系型数据库进行抽象封装,从类图可以看得出来它继承 PagingAndSortingRepository 类,也就继承了其所有方法,并且其实现类也是 SimpleJpaRepository。从类图上还可以看出 JpaRepository 继承和拥有了 QueryByExampleExecutor 的相关方法,而 QueryByExampleExecutor 的详细用法会在后面的章节中详细介绍,先来看一下 JpaRepository 有哪些方法:
package org.springframework.data.jpa.repository;import java.util.List;import javax.persistence.EntityManager;import org.springframework.data.domain.Example;import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort;import org.springframework.data.repository.NoRepositoryBean;import org.springframework.data.repository.PagingAndSortingRepository;import org.springframework.data.repository.query.QueryByExampleExecutor;/** * JPA specific extension of {@link org.springframework.data.repository.Repository}. * * @author Oliver Gierke * @author Christoph Strobl * @author Mark Paluch */@NoRepositoryBeanpublic interface JpaRepository extends PagingAndSortingRepository, QueryByExampleExecutor { /* * (non-Javadoc) * @see org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository#findAll() */ List findAll(); /* * (non-Javadoc) * @see org.springframework.data.repository.PagingAndSortingRepository#findAll(org.springframework.data.domain.Sort) */ List findAll(Sort sort); List findAllById(Iterable ids); List saveAll(Iterable entities); void flush(); S saveAndFlush(S entity); void deleteInBatch(Iterable entities); void deleteAllInBatch(); T getOne(ID id); List findAll(Example example); List findAll(Example example, Sort sort);} 通过源码和 CrudRepository 相比较其支持了 Query By Example、批量删除、提高删除效率、手动刷新数据库的更改方法,将默认实现的查询结果变成了 List。
JpaRepository 使用方法也一样,只需要继承它即可,如下面的例子:
package com.example.example2.repository;import com.example.example2.entity.User;import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;public interface UserJpaRepository extends JpaRepository {} Repository 的实现类 SimpleJpaRepository
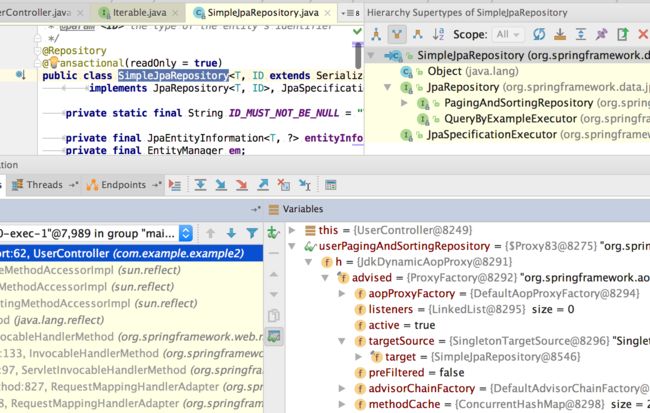
SimpleJpaRepository 是 JPA 整个关联数据库的所有 Repository 的接口实现类,如果想进行扩展,可以继承此类,如 QueryDsl 的扩展,还有默认的处理机制。如果将此类里面的实现方法看透了,基本上 JPA 的 API 就能掌握大部分,同时也是 Spring JPA 的动态代理的实现类,包括我们后面讲的 Query Method。
我们可以通过 Debug 试图看一下动态代理过程,如图:
SimpleJpaRepository 的部分源码如下:
@Repository@Transactional(readOnly = true)public class SimpleJpaRepository implements JpaRepository, JpaSpecificationExecutor { private static final String ID_MUST_NOT_BE_NULL = "The given id must not be null!"; private final JpaEntityInformation entityInformation; private final EntityManager em; private final PersistenceProvider provider; private @Nullable CrudMethodMetadata metadata; ...... @Transactional public void deleteAllInBatch() { em.createQuery(getDeleteAllQueryString()).executeUpdate(); } ...... 可以看出 SimpleJpaRepository 的实现机制还挺清晰的,通过 EntityManger 进行实体的操作,JpaEntityInforMation 里面存着实体的相关信息,还有 crud 方法的元数据等等,后面章节还会经常提到此类,慢慢介绍。
第03课:定义查询方法(Defining Query Methods)
第04课:注解式查询方法
第05课:@Entity 实例里面常用注解详解
第06课:JpaRepository 扩展之 QueryByExampleExecutor
第07课:JpaRepository 扩展之 JpaSpecificationExecutor
第08课:JpaRepository 扩展之自定义 Repository
第09课:Auditing 与 @Version
第10课:对 MVCWeb 的支持分页和排序的支持
第11课:Spring Data JPA 的配置之 SpringBoot 2.0 加载详解
第12课:DataSource 的配置与事务详解、多数据源
第13课:Spring Data JPA 之 QueryDSL 支持
阅读全文: http://gitbook.cn/gitchat/column/5ab9bfd5c864031e9f8301bd