egg学习(一):使用egg的egg-mongoose搭建本地数据库
搭建一个egg项目:
代码地址:demo
结合node搭建本地服务器的框架有很多,今天选择的是egg这个框架,他是koa框架的封装形式,用起来会比较小白一点。由于本人用的是MongoDB搭建本地的数据库,所以选择了egg的egg-mongoose模块来搭建项目
安装egg的初始化框架
$ npm i egg-init -g
$ egg-init egg-example --type=simple
$ cd egg-example
$ npm i
启动项目
$ npm run dev
$ open localhost:7001
链接到本地的MongoDB:
安装mongoose并引入到项目中
npm install egg-mongoose -S
- 在config文件中找到 config.default.js 文件
// 引入egg-mongoose
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
module.exports = appInfo => {
const config = exports = {};
config.keys = appInfo.name + '_1539588102822_7832'; // 此处的字符是自己设定的cookie加密码
// 添加 view 配置,nunjucks是一个用来在服务器端渲染HTML的插件,用npm 安装即可
exports.view = {
defaultViewEngine: 'nunjucks',
mapping: {
'.tpl': 'nunjucks',
},
};
exports.mongoose = {
url: 'mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/mongoTest',
// 链接到本地的MongoDB,mongoTest是我本地数据库的名字,根据自己数据库名字进行填写即可
options: {},
};
// add your config here
config.middleware = [];
return config;
};
介绍项目目录分配
- controller : 是用来分发路由接口请求的文件夹,指定了不同的路由对应的操作
- middleware : 是用来存放中间件的文件夹
- model : 是用来定义数据库中表单的数据类型的文件夹
- service : 是用来操作数据库的文件存放的地方,他是从controller中细化出来的,主要用来写一些sql语言,保持 Controller 中的逻辑更加简洁。
- view : 是用来存放一些需要服务器渲染的页面的
.html或.tpl文件的地方 - router :是用来分配接口路由的文件
- router.js :为了让router 文件夹中的路由文件看起来整洁有明确的分类,在外层用router.js这样一个文件做一个入口和索引的作用
介绍了以上的文件夹的作用,就可以开始写自己的后台项目了,每个模块对应的命名有一定的要求,比如我现在要创建一个关于学生选修课的接口,我先创建一个学生的数据库表格,我给文件命名为student,那么我就需要在controller,service,model中创建一个student.js,入门级的使用方式可以参照 egg快速入门
第一步:分配路由:(在router.js文件中)
module.exports = app => {
const { router, controller } = app;
router.get('/getStudentList', controller.student.list);
// 1、我定义这个接口是获取表格中所有学生的信息, 这是一个get请求
// 2、对应的是controller下面的student.js文件里面的list方法
router.post('/add', controller.student.add);
// 这是一个post请求,调用的是controller里面的add方法
};
那么我就需要在controller文件夹下面创建一个student.js文件,并在里面创立一个list方法,因为controller对应的是不同路由的操作的文件夹,所以这里当我们接收到对应的路由请求之后,对数据路进行对应的操作
// app/controller/student.js
const Controller = require('egg').Controller;
class UserController extends Controller {
// 这里的 list 就是上面 controller.student.list 里面的 list
async list() {
const ctx = this.ctx;
var aa = await ctx.service.student.list()
// 为了方便文件的管理,当后续controller的方法变多的时候,操作数据库的语言就不适合都挤在一个文件里面,所以egg框架的service文件夹就起到了分配压力的作用,所有具体的sql操作会写在service文件夹中,我也是为了方便操作的复用。
// 此处我们调用的是 service 文件夹里面的student.js 文件里面的 list方法
// 调用玩这个方法后,会返回一个数据库中查找出来的数据,我们用变量 aa 来接收
ctx.body = aa
// 将接收到返回的数据渲染出来,也可以用return的方式放回给前端
}
}
module.exports = UserController;
在上面的操作中我们需要调用service文件夹里面的student.js里面的list方法,那么我们就要在service文件夹里面创建一个student.js文件
// app/service/student.js
const Service = require('egg').Service;
class UserService extends Service {
async list() {
const ctx = this.ctx;
return ctx.model.Student.find({})
// ctx.model.Student.find({"title":"111"}) 表示在数据库中查找title 为111的对应数据
}
}
module.exports = UserService;
现在controller,service里面都有student.js文件了,还有model 里面需要,我们需要在model中规定数据库的数据类型,防止错误格式的储存
// app/model/student.js
module.exports = app => {
const mongoose = app.mongoose;
const Schema = mongoose.Schema;
const UserSchema = new Schema({
studentName: { type: String, required: true },
age: { type: Number},
gender:{type : String, enum:['男','女']},
phone:{
type:String,
validate: {
validator: function(v) {
if(v.length < 8){
return false
}
},
message: '${v} is not a valid phone number!'
},
}
});
// 以上定义了表数据的类型
return mongoose.model('student', UserSchema,'studentInfo');
// model(参数1,参数2,参数3)参数3是你数据表中需要操作的表的名字,
// 比如我现在要操作的是名字叫mongoTest里面的叫studentInfo的表
}
npm run dev 运行项目~
可以利用 postman 进行请求的模拟:
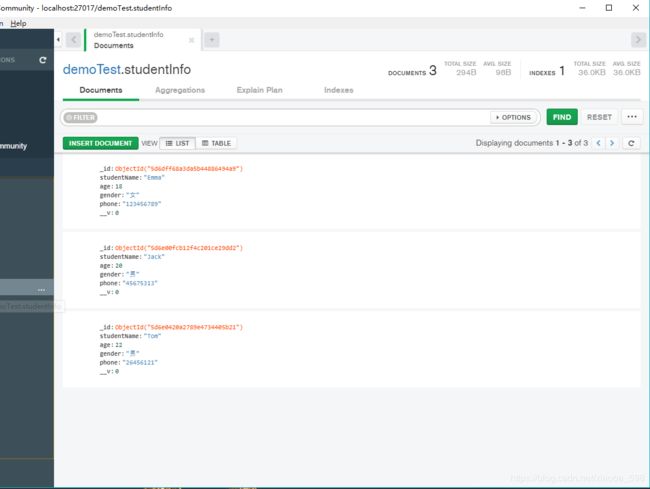
我的数据库表单里面有三条信息:(这是mongodb的一个可视化工具,叫Mongo compass,可以百度一下具体使用方法。

这就是你本地数据库里面获取到的信息,也可以写一个增加数据
这个是查询的功能,我们还会有增删改,其中增删改都会涉及到数据操作是成功还是失败的信息的返回,我们就以增加数据来举例:
还是第一步:分配路由
module.exports = app => {
const { router, controller } = app;
router.get('/getStudentList', app.controller.student.list);
// 添加学生信息
router.post('/add', app.controller.student.add);
// 学生信息更新
router.post('/edit', app.controller.student.edit);
};
然后是去controller的user.js里面添加add方法:
// app/controller/user.js
const Controller = require('egg').Controller;
class UserController extends Controller {
// 这里的 list 就是上面 controller.user.list 里面的 list
async list() {
const ctx = this.ctx;
var aa = await ctx.service.student.list()
// 此处我们将操作数据库,所以调用的是 service 文件夹里面的user.js 文件里面的 list方法
// 调用玩这个方法后,会返回一个数据,我们用 aa 来接收
ctx.body = aa
// 将接收到返回的数据渲染出来
}
// 添加用户
async add() {
const ctx = this.ctx;
const req = ctx.request.body
// 获取请求体的内容
ctx.body = await ctx.service.student.add(req);
}
}
module.exports = UserController;
然后是service文件夹:
// app/service/user.js
const Service = require('egg').Service;
class UserService extends Service {
async list() {
const ctx = this.ctx;
return ctx.model.Student.find({})
// ctx.model.User.find({"title":"111"}) 表示在数据库中查找title 为111的对应数据
}
// 添加用户
async add(req) {
const ctx = this.ctx
return ctx.model.Student.create(req).then(res => {
return { success: true, msg: res, code: 0 };
}).catch(err => {
return { success: false, err };
});
}
}
module.exports = UserService;
发送请求,然后报错,gg
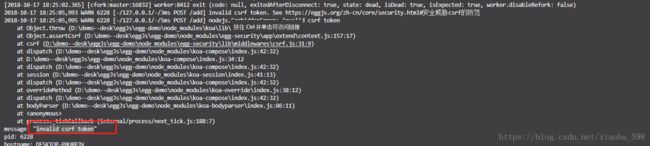
请教了一下同行,说是需要在 config 文件夹的 config.default.js 中加上这个:
const config = exports = {
security: {
csrf: {
enable: false
}
}
};
因为之前在model中已经定义了数据表的数据类型,这里就不需要再定义,直接上postman测试:
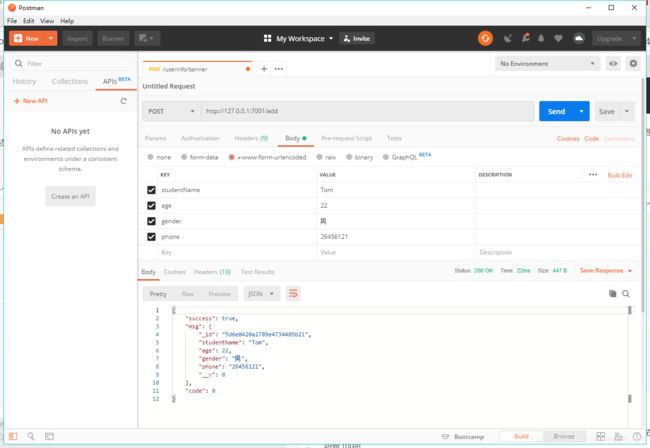
拿到自定义的返回内容,表示插入成功!再打开Mongo compass 查看一下数据表:
如果在真正的项目开发中,需要写的接口特别的多,需要对路由进行分配和归类,我们可以在 app 文件夹下创建一个子文件,叫做 route
此时更改一下router.js文件内容:
'use strict';
/**
* @param {Egg.Application} app - egg application
*/
module.exports = app => {
const { router, controller } = app;
require('./route/student')(app)
// 我将之前所有跟用户信息相关的路由操作都放在一个类别中
};
在route文件夹中创建一个user.js的文件
// app/route/student.js
module.exports = app => {
//
app.router.get('/getStudentList', app.controller.student.list);
// 添加用户信息
app.router.post('/add', app.controller.student.add);
};
运行一次,得到之前同样的效果。这样写在遇到大量接口的时候会更加清晰简洁
