系列文章:
- Java集合系列01之概览
- Java集合系列02之ArrayList源码分析
- Java集合系列03之LinkedList源码分析
- Java集合系列04之fail-fast机制分析
- Java集合系列05之Vector&Stack源码分析及List总结
- Java集合系列06之Map接口概览
- Java集合系列07之HashMap源码分析
- Java集合系列08之WeakHashMap源码分析
- Java集合系列09之TreeMap源码分析
- Java集合系列10之Hashtable源码分析
前言
本文开始分析LinkedList。ArrayList和LinkedList都实现了List接口,但内部数据结构有所区别,LinkedList内部是基于链表实现的,所以其插入和删除操作效率较高,但是随机访问效率就相对较低。其定义如下:
public class LinkedList
extends AbstractSequentialList
implements List, Deque, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
可以看到LinkedList继承AbstractSequentialList,实现了List,Deque,Cloneable,java.io.Serializable四个接口。
AbstractSequenceList实现了大部分List接口的方法,Deque接口定义了双端队列的操作。
本文源码分析基于jdk 1.8.0_121
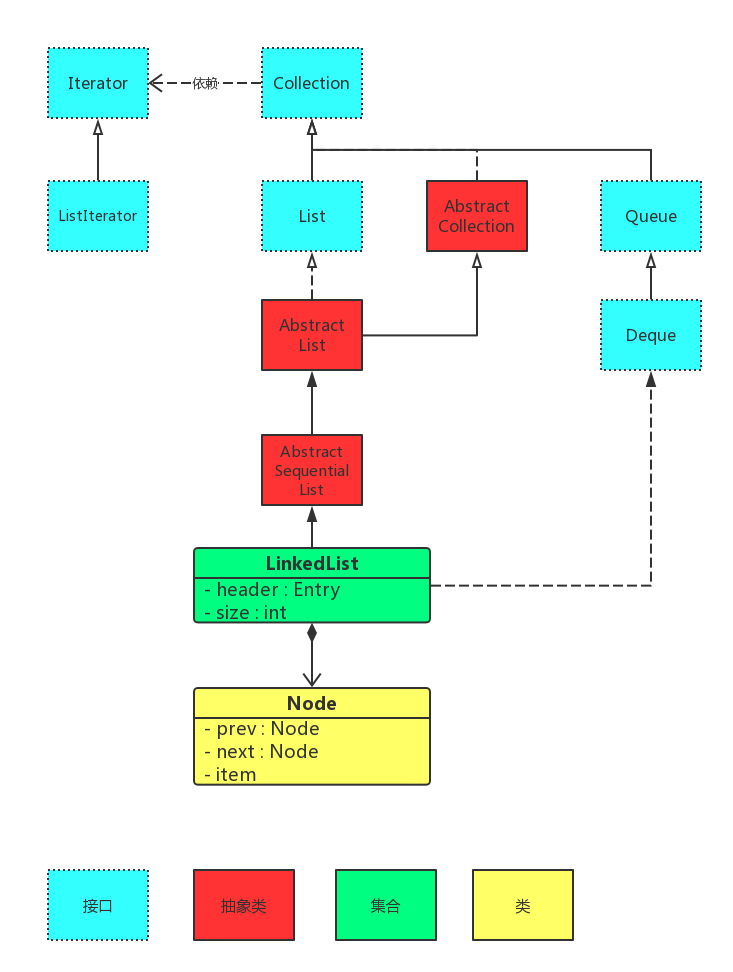
继承关系
LinkedList继承关系
java.lang.Object
|___ java.util.AbstractCollection
|___ java.util.AbstractList
|___ java.util.AbstractSequentialList
|___ java.util.LinkedList
所有已实现的接口:
Serializable, Cloneable, Iterable, Collection, Deque, List, Queue
关系图
LinkedList的本质是双向链表,
LinkedList中
first,last,size等成员比较重要,
first是链表的头指针,
last是尾指针,
size是双向链表中节点的个数,链表的节点对应
Node类数据结构如下:
private static class Node {
E item; // 节点值
Node next; // 指向下一个节点
Node prev; // 指向上一个节点
Node(Node prev, E element, Node next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
AbstractSequenceList
AbstractSequentialList 继承自 AbstractList,是 LinkedList 的父类,提供了List接口大部分实现。
AbstractSequentialList 实现了“随机访问”方法get(int index)、set(int index, E element)、add(int index, E element)、remove(int index)。
要实现一个列表,我们只需要扩展此类,并提供 listIterator 和 size 方法的实现即可。对于不可修改的列表,我们只需要实现列表迭代器的 hasNext、next、hasPrevious、previous、index 方法即可。
API
boolean add(E e)
void add(int index, E element)
boolean addAll(Collection c)
boolean addAll(int index, Collection c)
void addFirst(E e)
void addLast(E e)
void clear()
Object clone()
boolean contains(Object o)
Iterator descendingIterator()
E element()
E get(int index)
E getFirst()
E getLast()
int indexOf(Object o)
int lastIndexOf(Object o)
ListIterator listIterator(int index)
boolean offer(E e)
boolean offerFirst(E e)
boolean offerLast(E e)
E peek()
E peekFirst()
E peekLast()
E poll()
E pollFirst()
E pollLast()
E pop()
void push(E e)
E remove()
E remove(int index)
boolean remove(Object o)
E removeFirst()
boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o)
E removeLast()
boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o)
E set(int index, E element)
int size()
T[] toArray(T[] a)
Object[] toArray()
源码分析
首先我们知道LinkedList是一个双向链表,但是同时也实现了List接口,因此也可以根据索引值(index)来获取,更改,删除节点等。那么是如何把链表和索引值联系的呢?LinkedList是通过一个计数索引值来实现的,当我们调用get(int index)时,我们会把index和链表长度的1/2比较,如果index值小·,则从链表头向后遍历;反之;如果index值大,则从链表尾遍历。其余方法原理类似。
成员对象
transient int size = 0; // 节点个数
transient Node first; // 表头
transient Node last; // 表尾
构造函数
// 默认构造函数
public LinkedList() {
}
// 创建包含集合c的LinkedList
public LinkedList(Collection c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
增加元素
// 添加元素,添加到last节点后
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
// 新建一个节点newNode,让其prev属性为当前last节点,last属性为null
// 如果当前last节点为null,则令first节点为newNode
// 如果当前last节点不为null,则让其next属性为newNode
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node l = last;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
// 先检查index,如果index值正好为size,那么添加到last节点后
// 否则,添加到index位置处,node(index)获取当前index处节点
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
// 先获取当前index处节点的前一个节点pred
// 再新建节点newNode,如果pred节点为null,则令first为newNode
// 否则pred的next节点为newNode,同时改变size和修改计数值
void linkBefore(E e, Node succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node pred = succ.prev;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
// 添加集合c到LinkedList中
public boolean addAll(Collection c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
// 在index处添加所有集合c中所有节点
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Node pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
// 添加元素到头节点位置
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
// 把元素e设置为第一个节点
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node f = first;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
// 添加元素到尾节点位置
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
设置元素
public E set(int index, E element) {
checkElementIndex(index);
Node x = node(index);
E oldVal = x.item;
x.item = element;
return oldVal;
}
获取元素
// 返回index处节点值
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
// 返回头节点值
public E getFirst() {
final Node f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
// 返回尾节点值
public E getLast() {
final Node l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
删除元素
// 从LinkedList中删除对象o
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
// 删除index处节点
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
// 删除第一个元素
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
// 删除第一个元素
public E removeFirst() {
final Node f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
// 删除最后一个元素
public E removeLast() {
final Node l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
toArray
// 返回LinkedList的Object[]数组
public Object[] toArray() {
Object[] result = new Object[size];
int i = 0;
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
result[i++] = x.item;
return result;
}
// 返回T类型的数组
public T[] toArray(T[] a) {
// 若数组a的大小小于LinkedList的元素个数
// 则新建一个T[]数组,T[]的大小为LinkedList大小,并将该T[]赋值给a。
if (a.length < size)
a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance(
a.getClass().getComponentType(), size);
int i = 0;
Object[] result = a;
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
result[i++] = x.item;
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
}
克隆函数
// 克隆函数
public Object clone() {
LinkedList clone = superClone();
// 重新初始化
clone.first = clone.last = null;
clone.size = 0;
clone.modCount = 0;
// 添加所有节点数值
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
clone.add(x.item);
return clone;
}
// 调用父clone函数
private LinkedList superClone() {
try {
return (LinkedList) super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}
其余函数
// 将e添加到链表末尾
public boolean offer(E e) {
return add(e);
}
// 将e添加到链表头节点处
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
addFirst(e);
return true;
}
// 将e添加到链表末尾
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
// 返回头节点,头节点为null则返回null
public E peekFirst() {
final Node f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
// 返回尾节点,尾节点为null则返回null
public E peekLast() {
final Node l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : l.item;
}
// 返回头节点并删除
// 头节点为null则返回null
public E pollFirst() {
final Node f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
// 返回尾节点并删除
// 尾节点为null则返回null
public E pollLast() {
final Node l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l);
}
// 将e插入到双向链表头节点
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
// 删除并返回第一个节点
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
小结
-
LinkedList是通过双向链表实现的,内部有节点的数据结构 -
LinkedList实现了Deque,而Deque接口定义了在队列两端访问元素的方法,有增加,删除,获取第一个元素等方法。 -
LinkedList可以作为FIFO先进先出的队列,下列方法等效
| 队列方法 | 等效方法 |
|---|---|
| add(e) | addLast(e) |
| offer(e) | offerLast(e) |
| remove() | removeFirst() |
| poll() | pollFirst() |
| element() | getFirst() |
| peek() | peekFirst() |
-
LinkedList可以作为LIFO后进先出的栈,下列方法等效
| 栈方法 | 等效方法 |
|---|---|
| push(e) | addFirst(e) |
| pop() | removeFirst() |
| peek() | peekFirst() |
遍历方式
迭代器遍历
Iterator iter = list.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
iter.next();
}
随机访问
for (int i=0; iforeach循环
for (Integer integ:list) {
;
}
pollFirst
while(list.pollFirst() != null)
;
pollLast
while(list.pollLast() != null)
;
removeFirst
try {
while(list.removeFirst() != null)
;
} catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
...
}
##
removeLast
try {
while(list.removeLast() != null)
;
} catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
...
}
通过随机访问的方式遍历LinkedList时,效率很低,因此需要尽量避免这种方式。
参考内容
- Java 集合系列05之 LinkedList详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
- LinkedList 的实现原理