tomcat源码学习
目录
Tomcat 整体概述
收到 request 请求至 sevlet 的处理流程细节
tomcat 包含三种 EndPoint
Poller 循环等待接收 Socket 请求,并送至 SocketProcessor 进行处理
Socket处理器:SocketProcessor
通过 Http11ConnectionHandler 来进一步处理 socket
在 Http11AprProcessor 类中解析 http 请求的头部字段
将对请求信息的处理过度给 CoyoteAdapter 类
Container之旅第一站:StandardEngine
Container之旅第二站:StandardHost
StandardHost 的 PipeLine 中的 Valve 第一站:AccessLogValve
StandardHost 的 PipeLine 中的 Valve 第二站 :ErrorReportValve
StandardHost 的 PipeLine 中的 Valve 第三站:StandardHostValve
Container之旅第三站:StandardContext
StandardContext 的 pipeline 中的 Valve 第一站:NonLoginAuthenticator
StandardContext 的 pipeline 中的 Valve 第二站:StandardContextValve
执行 filterChain 中的 doFilter 方法
执行 MyHttpServlet 中的 service 方法
一些细节
Container中request请求流动图
请求路径映射器 mapper
Tomcat连接器:Coyote框架
Tomcat 整体概述
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-tomcat1/
收到 request 请求至 sevlet 的处理流程细节
tomcat 包含三种 EndPoint
org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.java:
org.apache.tomcat.util.net.JIoEndpoint.java
org.apache.tomcat.util.net.AprEndpoint.java
EndPoint 用于接受客户端 socket 请求(由内部类 Poller 完成),然后对 Socket 进行简单处理(由内部类 SocketProcessor 完成),接着转交给对应的 ProtocolProcessor 进行处理,封装成 request,通过各个Container 后 到达 servlet。下面是关键源码执行流程(以 AprEndpoint 为例,采用 http 协议)
Poller 循环等待接收 Socket 请求,并送至 SocketProcessor 进行处理
AprEndPoint 内部类 Poller 接收到 Socket 请求后, 调用AprEndPoint 的 processSocket 方法,在 processSocket 方法中,首先会从 AprEndPoint 的成员变量 connections 中 获取 socket 包装类 SocketWrapper。确保 SocketWrapper 存在后,再封装进 SocketProcessor 对象 。最后,为了处理性能最大化,会将添加 SocketProcessor 任务至线程池,等待执行。
Socket处理器:SocketProcessor
在 SocketProcessor 中会调用 AprEndPoint 内部接口 Handler 的实现类 Http11ConnectionHandler 来进一步处理 socket 信息。调用截图:
SocketProcessor 类源码:
/**
* This class is the equivalent of the Worker, but will simply use in an
* external Executor thread pool.
*/
protected class SocketProcessor implements Runnable {
private final SocketWrapper socket;
private final SocketStatus status;
public SocketProcessor(SocketWrapper socket,
SocketStatus status) {
this.socket = socket;
if (status == null) {
// Should never happen
throw new NullPointerException();
}
this.status = status;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// Upgraded connections need to allow multiple threads to access the
// connection at the same time to enable blocking IO to be used when
// Servlet 3.1 NIO has been configured
if (socket.isUpgraded() && SocketStatus.OPEN_WRITE == status) {
synchronized (socket.getWriteThreadLock()) {
doRun();
}
} else {
synchronized (socket) {
doRun();
}
}
}
private void doRun() {
// Process the request from this socket
if (socket.getSocket() == null) {
// Closed in another thread
return;
}
System.out.println(this +" CALL "+ handler+" processing");
SocketState state = handler.process(socket, status);
System.out.println(this +" CALL "+ handler+" processing end");
if (state == Handler.SocketState.CLOSED) {
// Close socket and pool
closeSocket(socket.getSocket().longValue());
socket.socket = null;
} else if (state == Handler.SocketState.LONG) {
socket.access();
if (socket.async) {
waitingRequests.add(socket);
}
} else if (state == Handler.SocketState.ASYNC_END) {
socket.access();
SocketProcessor proc = new SocketProcessor(socket,
SocketStatus.OPEN_READ);
getExecutor().execute(proc);
}
}
} 通过 Http11ConnectionHandler 来进一步处理 socket
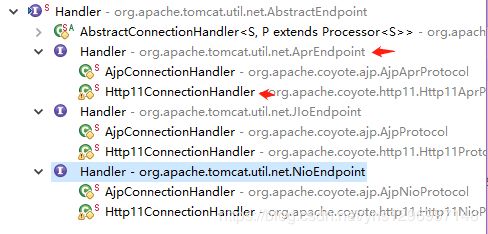
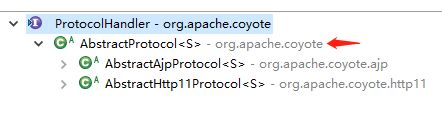
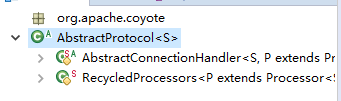
通过 Http11ConnectionHandler 的 process 方法来进一步处理 socket :验证 socket 的状态信息,获取 Http11AprProcessor 处理器来解析 http 请求。Http11ConnectionHandler 的 process 方法来至于 Http11ConnectionHandler 的父类 AbstractConnectionHandler(属于 AbstractProtocol 的内部类,而 AbstractProtocol 实现了 ProtocolHandler 接口)。
Http11ConnectionHandler 继承关系图
AbstractProtocol 继承关系图
AbstractProtocol 内部类 AbstractConnectionHandler 示意图
调用 Http11AprProcessor 类的 process 方法示意图
AbstractConnectionHandler 类的 process 方法源码
protected abstract static class AbstractConnectionHandler>
implements AbstractEndpoint.Handler {
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation") // Old HTTP upgrade method has been deprecated
public SocketState process(SocketWrapper wrapper,
SocketStatus status) {
System.out.println(this + "(AbstractProtocol&AbstractConnectionHandler)");
if (wrapper == null) {
// Nothing to do. Socket has been closed.
return SocketState.CLOSED;
}
S socket = wrapper.getSocket();
if (socket == null) {
// Nothing to do. Socket has been closed.
return SocketState.CLOSED;
}
Processor processor = connections.get(socket);
if (status == SocketStatus.DISCONNECT && processor == null) {
// Nothing to do. Endpoint requested a close and there is no
// longer a processor associated with this socket.
return SocketState.CLOSED;
}
wrapper.setAsync(false);
ContainerThreadMarker.markAsContainerThread();
try {
if (processor == null) {
processor = recycledProcessors.poll();
}
if (processor == null) {
processor = createProcessor();
System.out.println("create processor: " + processor);
}
initSsl(wrapper, processor);
SocketState state = SocketState.CLOSED;
do {
if (status == SocketStatus.DISCONNECT &&
!processor.isComet()) {
// Do nothing here, just wait for it to get recycled
// Don't do this for Comet we need to generate an end
// event (see BZ 54022)
} else if (processor.isAsync() || state == SocketState.ASYNC_END) {
state = processor.asyncDispatch(status);
if (state == SocketState.OPEN) {
// release() won't get called so in case this request
// takes a long time to process, remove the socket from
// the waiting requests now else the async timeout will
// fire
getProtocol().endpoint.removeWaitingRequest(wrapper);
// There may be pipe-lined data to read. If the data
// isn't processed now, execution will exit this
// loop and call release() which will recycle the
// processor (and input buffer) deleting any
// pipe-lined data. To avoid this, process it now.
state = processor.process(wrapper);
}
} else if (processor.isComet()) {
state = processor.event(status);
} else if (processor.getUpgradeInbound() != null) {
state = processor.upgradeDispatch();
} else if (processor.isUpgrade()) {
state = processor.upgradeDispatch(status);
} else {
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + processor);
state = processor.process(wrapper);
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + processor + " end");
}
if (state != SocketState.CLOSED && processor.isAsync()) {
state = processor.asyncPostProcess();
}
if (state == SocketState.UPGRADING) {
// Get the HTTP upgrade handler
HttpUpgradeHandler httpUpgradeHandler =
processor.getHttpUpgradeHandler();
// Release the Http11 processor to be re-used
release(wrapper, processor, false, false);
// Create the upgrade processor
processor = createUpgradeProcessor(
wrapper, httpUpgradeHandler);
// Mark the connection as upgraded
wrapper.setUpgraded(true);
// Associate with the processor with the connection
connections.put(socket, processor);
// Initialise the upgrade handler (which may trigger
// some IO using the new protocol which is why the lines
// above are necessary)
// This cast should be safe. If it fails the error
// handling for the surrounding try/catch will deal with
// it.
httpUpgradeHandler.init((WebConnection) processor);
} else if (state == SocketState.UPGRADING_TOMCAT) {
// Get the UpgradeInbound handler
org.apache.coyote.http11.upgrade.UpgradeInbound inbound =
processor.getUpgradeInbound();
// Release the Http11 processor to be re-used
release(wrapper, processor, false, false);
// Create the light-weight upgrade processor
processor = createUpgradeProcessor(wrapper, inbound);
inbound.onUpgradeComplete();
}
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLog().debug("Socket: [" + wrapper +
"], Status in: [" + status +
"], State out: [" + state + "]");
}
} while (state == SocketState.ASYNC_END ||
state == SocketState.UPGRADING ||
state == SocketState.UPGRADING_TOMCAT);
if (state == SocketState.LONG) {
// In the middle of processing a request/response. Keep the
// socket associated with the processor. Exact requirements
// depend on type of long poll
connections.put(socket, processor);
longPoll(wrapper, processor);
} else if (state == SocketState.OPEN) {
// In keep-alive but between requests. OK to recycle
// processor. Continue to poll for the next request.
connections.remove(socket);
release(wrapper, processor, false, true);
} else if (state == SocketState.SENDFILE) {
// Sendfile in progress. If it fails, the socket will be
// closed. If it works, the socket either be added to the
// poller (or equivalent) to await more data or processed
// if there are any pipe-lined requests remaining.
connections.put(socket, processor);
} else if (state == SocketState.UPGRADED) {
// Need to keep the connection associated with the processor
connections.put(socket, processor);
// Don't add sockets back to the poller if this was a
// non-blocking write otherwise the poller may trigger
// multiple read events which may lead to thread starvation
// in the connector. The write() method will add this socket
// to the poller if necessary.
if (status != SocketStatus.OPEN_WRITE) {
longPoll(wrapper, processor);
}
} else {
// Connection closed. OK to recycle the processor. Upgrade
// processors are not recycled.
connections.remove(socket);
if (processor.isUpgrade()) {
processor.getHttpUpgradeHandler().destroy();
} else if (processor instanceof org.apache.coyote.http11.upgrade.UpgradeProcessor) {
// NO-OP
} else {
release(wrapper, processor, true, false);
}
}
return state;
} catch(java.net.SocketException e) {
// SocketExceptions are normal
getLog().debug(sm.getString(
"abstractConnectionHandler.socketexception.debug"), e);
} catch (java.io.IOException e) {
// IOExceptions are normal
getLog().debug(sm.getString(
"abstractConnectionHandler.ioexception.debug"), e);
}
// Future developers: if you discover any other
// rare-but-nonfatal exceptions, catch them here, and log as
// above.
catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
// any other exception or error is odd. Here we log it
// with "ERROR" level, so it will show up even on
// less-than-verbose logs.
getLog().error(
sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.error"), e);
}
// Make sure socket/processor is removed from the list of current
// connections
connections.remove(socket);
// Don't try to add upgrade processors back into the pool
if (!(processor instanceof org.apache.coyote.http11.upgrade.UpgradeProcessor)
&& !processor.isUpgrade()) {
release(wrapper, processor, true, false);
}
return SocketState.CLOSED;
}
} 在 Http11AprProcessor 类中解析 http 请求的头部字段
通过 Http11AprProcessor 类中 process 方法(来自父类 AbstractHttp11Processor)来处理 http 请求,主要是解析头部字段,然后调用 CoyoteAdapter 来进一步处理 request 参数。
AbstractHttp11Processor.java
1:调用 CoyoteAdapter 类的 service 方法。
process方法源码
@Override
public SocketState process(SocketWrapper socketWrapper)
throws IOException {
System.out.println(this);
RequestInfo rp = request.getRequestProcessor();
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_PARSE);
// Setting up the I/O
System.out.println(this + " set up the I/O");
setSocketWrapper(socketWrapper);
getInputBuffer().init(socketWrapper, endpoint);
getOutputBuffer().init(socketWrapper, endpoint);
// Flags
keepAlive = true;
comet = false;
openSocket = false;
sendfileInProgress = false;
readComplete = true;
if (endpoint.getUsePolling()) {
keptAlive = false;
} else {
keptAlive = socketWrapper.isKeptAlive();
}
if (disableKeepAlive()) {
socketWrapper.setKeepAliveLeft(0);
}
while (!getErrorState().isError() && keepAlive && !comet && !isAsync() &&
upgradeInbound == null &&
httpUpgradeHandler == null && !endpoint.isPaused()) {
// Parsing the request header
try {
System.out.println("start Parsing the request header--------------------");
setRequestLineReadTimeout();
if (!getInputBuffer().parseRequestLine(keptAlive)) {
if (handleIncompleteRequestLineRead()) {
break;
}
}
if (endpoint.isPaused()) {
// 503 - Service unavailable
response.setStatus(503);
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, null);
} else {
keptAlive = true;
// Set this every time in case limit has been changed via JMX
request.getMimeHeaders().setLimit(endpoint.getMaxHeaderCount());
request.getCookies().setLimit(getMaxCookieCount());
// Currently only NIO will ever return false here
if (!getInputBuffer().parseHeaders()) {
// We've read part of the request, don't recycle it
// instead associate it with the socket
openSocket = true;
readComplete = false;
break;
}
if (!disableUploadTimeout) {
setSocketTimeout(connectionUploadTimeout);
}
}
System.out.println("Parsing the request header END--------------------");
} catch (IOException e) {
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLog().debug(
sm.getString("http11processor.header.parse"), e);
}
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_NOW, e);
break;
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
UserDataHelper.Mode logMode = userDataHelper.getNextMode();
if (logMode != null) {
String message = sm.getString(
"http11processor.header.parse");
switch (logMode) {
case INFO_THEN_DEBUG:
message += sm.getString(
"http11processor.fallToDebug");
//$FALL-THROUGH$
case INFO:
getLog().info(message, t);
break;
case DEBUG:
getLog().debug(message, t);
}
}
// 400 - Bad Request
response.setStatus(400);
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, t);
getAdapter().log(request, response, 0);
}
if (!getErrorState().isError()) {
// Setting up filters, and parse some request headers
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_PREPARE);
try {
prepareRequest();
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLog().debug(sm.getString(
"http11processor.request.prepare"), t);
}
// 500 - Internal Server Error
response.setStatus(500);
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, t);
getAdapter().log(request, response, 0);
}
}
if (maxKeepAliveRequests == 1) {
keepAlive = false;
} else if (maxKeepAliveRequests > 0 &&
socketWrapper.decrementKeepAlive() <= 0) {
keepAlive = false;
}
// Process the request in the adapter
if (!getErrorState().isError()) {
try {
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_SERVICE);
System.out.println(this + "(AbstractHttp11Processor) CALL " + adapter);
adapter.service(request, response);
System.out.println(this + "(AbstractHttp11Processor) CALL " + adapter + " END");
// Handle when the response was committed before a serious
// error occurred. Throwing a ServletException should both
// set the status to 500 and set the errorException.
// If we fail here, then the response is likely already
// committed, so we can't try and set headers.
if(keepAlive && !getErrorState().isError() && (
response.getErrorException() != null ||
(!isAsync() &&
statusDropsConnection(response.getStatus())))) {
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, null);
}
setCometTimeouts(socketWrapper);
} catch (InterruptedIOException e) {
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_NOW, e);
} catch (HeadersTooLargeException e) {
getLog().error(sm.getString("http11processor.request.process"), e);
// The response should not have been committed but check it
// anyway to be safe
if (response.isCommitted()) {
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_NOW, e);
} else {
response.reset();
response.setStatus(500);
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, e);
response.setHeader("Connection", "close"); // TODO: Remove
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
getLog().error(sm.getString("http11processor.request.process"), t);
// 500 - Internal Server Error
response.setStatus(500);
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, t);
getAdapter().log(request, response, 0);
}
}
// Finish the handling of the request
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDINPUT);
if (!isAsync() && !comet) {
if (getErrorState().isError()) {
// If we know we are closing the connection, don't drain
// input. This way uploading a 100GB file doesn't tie up the
// thread if the servlet has rejected it.
getInputBuffer().setSwallowInput(false);
} else {
// Need to check this again here in case the response was
// committed before the error that requires the connection
// to be closed occurred.
checkExpectationAndResponseStatus();
}
endRequest();
}
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDOUTPUT);
// If there was an error, make sure the request is counted as
// and error, and update the statistics counter
if (getErrorState().isError()) {
response.setStatus(500);
}
request.updateCounters();
if (!isAsync() && !comet || getErrorState().isError()) {
if (getErrorState().isIoAllowed()) {
getInputBuffer().nextRequest();
getOutputBuffer().nextRequest();
}
}
if (!disableUploadTimeout) {
if(endpoint.getSoTimeout() > 0) {
setSocketTimeout(endpoint.getSoTimeout());
} else {
setSocketTimeout(0);
}
}
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_KEEPALIVE);
if (breakKeepAliveLoop(socketWrapper)) {
break;
}
}
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDED);
if (getErrorState().isError() || endpoint.isPaused()) {
return SocketState.CLOSED;
} else if (isAsync() || comet) {
return SocketState.LONG;
} else if (isUpgrade()) {
return SocketState.UPGRADING;
} else if (getUpgradeInbound() != null) {
return SocketState.UPGRADING_TOMCAT;
} else {
if (sendfileInProgress) {
return SocketState.SENDFILE;
} else {
if (openSocket) {
if (readComplete) {
return SocketState.OPEN;
} else {
return SocketState.LONG;
}
} else {
return SocketState.CLOSED;
}
}
}
}将对请求信息的处理过渡给 CoyoteAdapter 类
处理的细节是在 CoyoteAdapter 类的 service 方法中实现的。
首先会把 org.apache.coyote.Request 对象转换为 org.apache.catalina.connector.Request,org.apache.coyote.Response 转换为 org.apache.catalina.connector.Response 对象。
接着会根据请求的 URI(例如: /docs/setup.html),在 Mapper 中查找到后续需要的 Container ,然后设置到 org.apache.catalina.connector.Request 中(设置细节参见后文),便于后续的处理需要。
最后会调用 第一个 Container(StandardEngine[Catalina])进行处理。
CoyoteAdapter 类相当于进入基于 coyote-based servlet container 的入口,它的作用简单说来就是来处理底层的 Socket,并且把http 的请求、响应以及字节流层面的信息封装成对应的 request、response 对象,然后传入 Container。
关键调用点:
1. 调用第一个 Contaner(StandardEngine[Catalina])中的 PipeLine 的 第一个 Valve
CoyoteAdapter 类的 service 方法源码
/**
* Service method.
*/
@Override
public void service(org.apache.coyote.Request req,
org.apache.coyote.Response res)
throws Exception {
Request request = (Request) req.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);
Response response = (Response) res.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);
if (request == null) {
// Create objects
request = connector.createRequest();
System.out.println("CoyoteAdapter create request object");
request.setCoyoteRequest(req);
response = connector.createResponse();
System.out.println("CoyoteAdapter create response object");
response.setCoyoteResponse(res);
// Link objects
request.setResponse(response);
response.setRequest(request);
// Set as notes
req.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, request);
res.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, response);
// Set query string encoding
req.getParameters().setQueryStringEncoding
(connector.getURIEncoding());
}
if (connector.getXpoweredBy()) {
response.addHeader("X-Powered-By", POWERED_BY);
}
boolean comet = false;
boolean async = false;
boolean postParseSuccess = false;
try {
// Parse and set Catalina and configuration specific
// request parameters
req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(Thread.currentThread().getName());
postParseSuccess = postParseRequest(req, request, res, response);
if (postParseSuccess) {
//check valves if we support async
request.setAsyncSupported(connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
// Calling the container
Valve valve = connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst();
System.out.println(this + " CALL the container: " + valve);
valve.invoke(request, response);
System.out.println(this + " CALL the container: " + valve + " END");
if (request.isComet()) {
if (!response.isClosed() && !response.isError()) {
if (request.getAvailable() || (request.getContentLength() > 0 && (!request.isParametersParsed()))) {
// Invoke a read event right away if there are available bytes
if (event(req, res, SocketStatus.OPEN_READ)) {
comet = true;
res.action(ActionCode.COMET_BEGIN, null);
} else {
return;
}
} else {
comet = true;
res.action(ActionCode.COMET_BEGIN, null);
}
} else {
// Clear the filter chain, as otherwise it will not be reset elsewhere
// since this is a Comet request
request.setFilterChain(null);
}
}
}
if (request.isAsync()) {
async = true;
Throwable throwable =
(Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION);
// If an async request was started, is not going to end once
// this container thread finishes and an error occurred, trigger
// the async error process
if (!request.isAsyncCompleting() && throwable != null) {
request.getAsyncContextInternal().setErrorState(throwable, true);
}
} else if (!comet) {
try {
System.out.println(this + " request.finishRequest()");
request.finishRequest();
System.out.println(this + " request.finishRequest() END");
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + response + " finish");
response.finishResponse();
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + response + " finish END");
} finally {
if (postParseSuccess) {
// Log only if processing was invoked.
// If postParseRequest() failed, it has already logged it.
// If context is null this was the start of a comet request
// that failed and has already been logged.
Context tem = (Context) request.getMappingData().context;
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + (Context) request.getMappingData().context);
tem.logAccess(
request, response,
System.currentTimeMillis() - req.getStartTime(),
false);
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + (Context) request.getMappingData().context + " END");
}
req.action(ActionCode.POST_REQUEST , null);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore
} finally {
AtomicBoolean error = new AtomicBoolean(false);
res.action(ActionCode.IS_ERROR, error);
if (request.isAsyncCompleting() && error.get()) {
// Connection will be forcibly closed which will prevent
// completion happening at the usual point. Need to trigger
// call to onComplete() here.
res.action(ActionCode.ASYNC_POST_PROCESS, null);
async = false;
}
req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(null);
// Recycle the wrapper request and response
if (!comet && !async) {
request.recycle();
response.recycle();
} else {
// Clear converters so that the minimum amount of memory
// is used by this processor
request.clearEncoders();
response.clearEncoders();
}
}
}Container之旅第一站:StandardEngine
在 Container 中真正执行逻辑的地方是在Container 包含的 PipeLine 中的 Valve,这里StandardEngine 的 StandardPipeLine 只包含一个 Valve:StandardEngineValve,所以执行逻辑在 StandardEngineValve 的 invoke 方法中。首先,通过传入的 request对象找到下一个 Container : host(例如:localHost) ,简单判断是否存在,是否支持异步,接着调用 host 的 pipeline 中的第一个 Valve:AccessLogValve[localhost]。
调用详细
1:调用 AccessLogValve[localhost] 的 invoke 方法
StandardEngineValve 的 invoke 方法源码
@Override
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Select the Host to be used for this Request
Host host = request.getHost();
if (host == null) {
response.sendError
(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST,
sm.getString("standardEngine.noHost",
request.getServerName()));
return;
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported()) {
request.setAsyncSupported(host.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
}
// Ask this Host to process this request
Valve valve = host.getPipeline().getFirst();
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + valve);
valve.invoke(request, response);
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + valve + " END");
}Container之旅第二站:StandardHost
StandardHost 的 PipeLine 包含的 Valve 有 3 个,AccessLogValve---》ErrorReportValve---》StandardHostValve。
StandardHost 的 PipeLine 中的 Valve 第一站:AccessLogValve
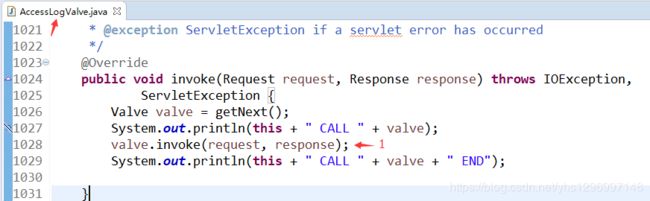
首先在 AccessLogValve 的 invoke 方法中执行
在 invoke 方法中,只是简单的做了透传的操作,把 request 对象传到 ErrorReportValve 。
调用详细:
1:调用 ErrorReportValve 中的 invoke 方法
AccessLogValve 中的 invoke 方法源码
@Override
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException,
ServletException {
Valve valve = getNext();
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + valve);
valve.invoke(request, response);
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + valve + " END");
}StandardHost 的 PipeLine 中的 Valve 第二站 :ErrorReportValve
执行 ErrorReportValve 中的 invoke 方法
在该 invoke 方法中,会首先调用当前 pipeline 中的下一个 Valve,这里是 StandardHostValve。然后根据返回的状态码进行判断,如果返回的状态码大于等于 400 ;或者在调用过程中出现了未捕获的异常,则会进行错误报告。
调用详细
1:调用 StandardHostValve 中的 invoke 方法
ErrorReportValve 中的 invoke 方法源码
@Override
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
// Perform the request
Valve valve = getNext();
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + valve);
valve.invoke(request, response);
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + valve + " END");
if (response.isCommitted()) {
if (response.setErrorReported()) {
// Error wasn't previously reported but we can't write an error
// page because the response has already been committed. Attempt
// to flush any data that is still to be written to the client.
try {
response.flushBuffer();
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
}
// Close immediately to signal to the client that something went
// wrong
response.getCoyoteResponse().action(ActionCode.CLOSE_NOW, null);
}
return;
}
Throwable throwable = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION);
// If an async request is in progress and is not going to end once this
// container thread finishes, do not process any error page here.
if (request.isAsync() && !request.isAsyncCompleting()) {
return;
}
if (throwable != null && !response.isError()) {
// Make sure that the necessary methods have been called on the
// response. (It is possible a component may just have set the
// Throwable. Tomcat won't do that but other components might.)
// These are safe to call at this point as we know that the response
// has not been committed.
response.reset();
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
// One way or another, response.sendError() will have been called before
// execution reaches this point and suspended the response. Need to
// reverse that so this valve can write to the response.
response.setSuspended(false);
try {
report(request, response, throwable);
} catch (Throwable tt) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(tt);
}
}StandardHost 的 PipeLine 中的 Valve 第三站:StandardHostValve
执行 StandardHostValve 中的 invoke 方法
在该 invoke 方法中,首先从传入的 request 对象中找到下一个 Container:Context,如果没有找到合适的 context 则会返回合适的 http 错误。如果找到了合适的 context,则会调用 context 的 pipeline 的第一个 Valve,这里是 NonLoginAuthenticator。通过 NonLoginAuthenticator 可知,是要进行权限验证。
调用详细:
1:调用 NonLoginAuthenticator 中的 invoke 方法
StandardHostValve 的 invoke 方法源码
@Override
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Select the Context to be used for this Request
Context context = request.getContext();
if (context == null) {
response.sendError
(HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR,
sm.getString("standardHost.noContext"));
return;
}
// Bind the context CL to the current thread
if( context.getLoader() != null ) {
// Not started - it should check for availability first
// This should eventually move to Engine, it's generic.
if (Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
PrivilegedAction pa = new PrivilegedSetTccl(
context.getLoader().getClassLoader());
AccessController.doPrivileged(pa);
} else {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader
(context.getLoader().getClassLoader());
}
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported()) {
request.setAsyncSupported(context.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
}
boolean asyncAtStart = request.isAsync();
boolean asyncDispatching = request.isAsyncDispatching();
if (asyncAtStart || context.fireRequestInitEvent(request.getRequest())) {
// Ask this Context to process this request. Requests that are in
// async mode and are not being dispatched to this resource must be
// in error and have been routed here to check for application
// defined error pages.
try {
if (!asyncAtStart || asyncDispatching) {
Valve valve = context.getPipeline().getFirst();
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + valve);
valve.invoke(request, response);
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + valve + " END");
} else {
// Make sure this request/response is here because an error
// report is required.
if (!response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString("standardHost.asyncStateError"));
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
container.getLogger().error("Exception Processing " + request.getRequestURI(), t);
// If a new error occurred while trying to report a previous
// error allow the original error to be reported.
if (!response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION, t);
throwable(request, response, t);
}
}
// Now that the request/response pair is back under container
// control lift the suspension so that the error handling can
// complete and/or the container can flush any remaining data
response.setSuspended(false);
Throwable t = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION);
// Protect against NPEs if the context was destroyed during a
// long running request.
if (!context.getState().isAvailable()) {
return;
}
// Look for (and render if found) an application level error page
if (response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
if (t != null) {
throwable(request, response, t);
} else {
status(request, response);
}
}
if (!request.isAsync() && !asyncAtStart) {
context.fireRequestDestroyEvent(request.getRequest());
}
}
// Access a session (if present) to update last accessed time, based on a
// strict interpretation of the specification
if (ACCESS_SESSION) {
request.getSession(false);
}
// Restore the context classloader
if (Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
PrivilegedAction pa = new PrivilegedSetTccl(
StandardHostValve.class.getClassLoader());
AccessController.doPrivileged(pa);
} else {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader
(StandardHostValve.class.getClassLoader());
}
} Container之旅第三站:StandardContext
StandardContext 的 pipeline 中的 Valve 有 2 个,依次是:NonLoginAuthenticator---》StandardContextValve
StandardContext 的 pipeline 中的 Valve 第一站:NonLoginAuthenticator
执行 NonLoginAuthenticator 中的 invoke 方法
这里的 invoke 方法继承自父类 AuthenticatorBase。在该方法中首先获取在该容器中部署的 web application 的登录配置,然后进行检查。检查通过后,调用 StandardContextValve 的 invoke 方法,
调用详细
1: 调用 StandardContextValve 中的 invoke 方法。
NonLoginAuthenticator 中的 invoke 方法源码
@Override
public void invoke(Request request, Response response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Security checking request " +
request.getMethod() + " " + request.getRequestURI());
LoginConfig config = this.context.getLoginConfig();
// Have we got a cached authenticated Principal to record?
if (cache) {
Principal principal = request.getUserPrincipal();
if (principal == null) {
Session session = request.getSessionInternal(false);
if (session != null) {
principal = session.getPrincipal();
if (principal != null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("We have cached auth type " +
session.getAuthType() +
" for principal " +
session.getPrincipal());
request.setAuthType(session.getAuthType());
request.setUserPrincipal(principal);
}
}
}
}
// Special handling for form-based logins to deal with the case
// where the login form (and therefore the "j_security_check" URI
// to which it submits) might be outside the secured area
String contextPath = this.context.getPath();
String requestURI = request.getDecodedRequestURI();
if (requestURI.startsWith(contextPath) &&
requestURI.endsWith(Constants.FORM_ACTION)) {
if (!authenticate(request, response, config)) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug(" Failed authenticate() test ??" + requestURI );
return;
}
}
// Special handling for form-based logins to deal with the case where
// a resource is protected for some HTTP methods but not protected for
// GET which is used after authentication when redirecting to the
// protected resource.
// TODO: This is similar to the FormAuthenticator.matchRequest() logic
// Is there a way to remove the duplication?
Session session = request.getSessionInternal(false);
if (session != null) {
SavedRequest savedRequest =
(SavedRequest) session.getNote(Constants.FORM_REQUEST_NOTE);
if (savedRequest != null) {
String decodedRequestURI = request.getDecodedRequestURI();
if (decodedRequestURI != null &&
decodedRequestURI.equals(
savedRequest.getDecodedRequestURI())) {
if (!authenticate(request, response)) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(" Failed authenticate() test");
}
/*
* ASSERT: Authenticator already set the appropriate
* HTTP status code, so we do not have to do anything
* special
*/
return;
}
}
}
}
Realm realm = this.context.getRealm();
// Is this request URI subject to a security constraint?
SecurityConstraint [] constraints
= realm.findSecurityConstraints(request, this.context);
if (constraints == null && !context.getPreemptiveAuthentication()) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug(" Not subject to any constraint");
Valve valve = getNext();
System.out.println(this + "(AuthenticatorBase) CALL " + valve);
valve.invoke(request, response);
System.out.println(this + "(AuthenticatorBase) CALL " + valve + " END");
return;
}
// Make sure that constrained resources are not cached by web proxies
// or browsers as caching can provide a security hole
if (constraints != null && disableProxyCaching &&
!"POST".equalsIgnoreCase(request.getMethod())) {
if (securePagesWithPragma) {
// Note: These can cause problems with downloading files with IE
response.setHeader("Pragma", "No-cache");
response.setHeader("Cache-Control", "no-cache");
} else {
response.setHeader("Cache-Control", "private");
}
response.setHeader("Expires", DATE_ONE);
}
int i;
if (constraints != null) {
// Enforce any user data constraint for this security constraint
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(" Calling hasUserDataPermission()");
}
if (!realm.hasUserDataPermission(request, response,
constraints)) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(" Failed hasUserDataPermission() test");
}
/*
* ASSERT: Authenticator already set the appropriate
* HTTP status code, so we do not have to do anything special
*/
return;
}
}
// Since authenticate modifies the response on failure,
// we have to check for allow-from-all first.
boolean authRequired;
if (constraints == null) {
authRequired = false;
} else {
authRequired = true;
for(i=0; i < constraints.length && authRequired; i++) {
if(!constraints[i].getAuthConstraint()) {
authRequired = false;
} else if(!constraints[i].getAllRoles()) {
String [] roles = constraints[i].findAuthRoles();
if(roles == null || roles.length == 0) {
authRequired = false;
}
}
}
}
if (!authRequired && context.getPreemptiveAuthentication()) {
authRequired =
request.getCoyoteRequest().getMimeHeaders().getValue(
"authorization") != null;
}
if (!authRequired && context.getPreemptiveAuthentication() &&
HttpServletRequest.CLIENT_CERT_AUTH.equals(getAuthMethod())) {
X509Certificate[] certs = getRequestCertificates(request);
authRequired = certs != null && certs.length > 0;
}
if(authRequired) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(" Calling authenticate()");
}
if (!authenticate(request, response, config)) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(" Failed authenticate() test");
}
/*
* ASSERT: Authenticator already set the appropriate
* HTTP status code, so we do not have to do anything
* special
*/
return;
}
}
if (constraints != null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(" Calling accessControl()");
}
if (!realm.hasResourcePermission(request, response,
constraints,
this.context)) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(" Failed accessControl() test");
}
/*
* ASSERT: AccessControl method has already set the
* appropriate HTTP status code, so we do not have to do
* anything special
*/
return;
}
}
// Any and all specified constraints have been satisfied
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(" Successfully passed all security constraints");
}
getNext().invoke(request, response);
}StandardContext 的 pipeline 中的 Valve 第二站:StandardContextValve
执行 StandardContextValve 中的 invoke 方法
在该方法中,首先根据传入的 request 对象获取 requestPath,判断是否是直接获取 /META-INF/,/WEB-INF/ 目录下的资源 ,如果是则直接返回。接着从 request 对象中获取 wrapper。如果没有找到合适的 wrapper,则会返回合适的 http 错误;如果找到了则首先会 给 Http11AprProcessor 发送一个 ACK消息,接着调用 wrapper 中的 invoke 方法。
调用示意图
1:调用 StandardWrapperValve 中的 invoke 方法
StandardContextValve 中的 invoke 方法源码
@Override
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Disallow any direct access to resources under WEB-INF or META-INF
MessageBytes requestPathMB = request.getRequestPathMB();
if ((requestPathMB.startsWithIgnoreCase("/META-INF/", 0))
|| (requestPathMB.equalsIgnoreCase("/META-INF"))
|| (requestPathMB.startsWithIgnoreCase("/WEB-INF/", 0))
|| (requestPathMB.equalsIgnoreCase("/WEB-INF"))) {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND);
return;
}
// Select the Wrapper to be used for this Request
Wrapper wrapper = request.getWrapper();
if (wrapper == null || wrapper.isUnavailable()) {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND);
return;
}
// Acknowledge the request
try {
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + response);
response.sendAcknowledgement();
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + response + " END");
} catch (IOException ioe) {
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString(
"standardContextValve.acknowledgeException"), ioe);
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION, ioe);
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
return;
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported()) {
request.setAsyncSupported(wrapper.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
}
Valve valve = wrapper.getPipeline().getFirst();
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + valve);
valve.invoke(request, response);
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + valve + " END");
}Container之旅终点站:StandardWrapper
StandardWrapper 的 PipeLine 中的 Valve 只有一个:StandardWrapperValve。其实走到这里,也就意味着我们离目的地 servlet 不远了。换句话说,StandardWrapper 就是 servlet 的包装类
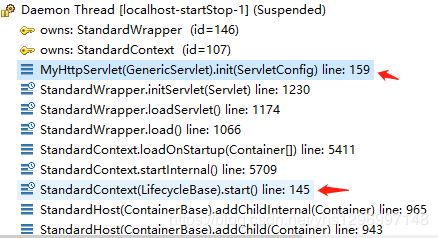
执行 StandardWrapperValve 中的 invoke 方法在该方法中,首先获取和 StandardWrapperValve 关联的 StandardWrapper(对应着一个 servlet),接着获取和 StandardWrapper 关联的 StandardContext(对应着一个应用程序 application ),然后检验 servlet 和 application 是否可用。接着,使用 StandardWrapper 分配一个 servlet 实例(这里的实例是在启动 tomcat 的时候就已经创建好的),到这里,我们知道了 servlet 是怎么一步步来的了。接着会创建一个过滤链(filterChain),紧接着就会调用 filterChain 中 doFilter 方法进行后续处理(在 doFilter 中会调用 servlet 的 service 方法)。
初始化 servlet 调用栈示意图
从图中可知,初始化操作是在启动Container: StandardContext 的过程中执行的
调用 doFilter 方法详情
1: 利用过滤链来处理request请求
StandardWrapperValve 中的 invoke 方法源码
@Override
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Initialize local variables we may need
boolean unavailable = false;
Throwable throwable = null;
// This should be a Request attribute...
long t1=System.currentTimeMillis();
requestCount.incrementAndGet();
StandardWrapper wrapper = (StandardWrapper) getContainer();
Servlet servlet = null;
Context context = (Context) wrapper.getParent();
// Check for the application being marked unavailable
if (!context.getState().isAvailable()) {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE,
sm.getString("standardContext.isUnavailable"));
unavailable = true;
}
// Check for the servlet being marked unavailable
if (!unavailable && wrapper.isUnavailable()) {
container.getLogger().info(sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable",
wrapper.getName()));
long available = wrapper.getAvailable();
if ((available > 0L) && (available < Long.MAX_VALUE)) {
response.setDateHeader("Retry-After", available);
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE,
sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable",
wrapper.getName()));
} else if (available == Long.MAX_VALUE) {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND,
sm.getString("standardWrapper.notFound",
wrapper.getName()));
}
unavailable = true;
}
// Allocate a servlet instance to process this request
try {
if (!unavailable) {
servlet = wrapper.allocate();
}
System.out.println(wrapper + " allocate a servlet instance: " + servlet);
} catch (UnavailableException e) {
container.getLogger().error(
sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocateException",
wrapper.getName()), e);
long available = wrapper.getAvailable();
if ((available > 0L) && (available < Long.MAX_VALUE)) {
response.setDateHeader("Retry-After", available);
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE,
sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable",
wrapper.getName()));
} else if (available == Long.MAX_VALUE) {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND,
sm.getString("standardWrapper.notFound",
wrapper.getName()));
}
} catch (ServletException e) {
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocateException",
wrapper.getName()), StandardWrapper.getRootCause(e));
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocateException",
wrapper.getName()), e);
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
servlet = null;
}
// Identify if the request is Comet related now that the servlet has been allocated
boolean comet = false;
if (servlet instanceof CometProcessor && Boolean.TRUE.equals(request.getAttribute(
Globals.COMET_SUPPORTED_ATTR))) {
comet = true;
request.setComet(true);
}
MessageBytes requestPathMB = request.getRequestPathMB();
DispatcherType dispatcherType = DispatcherType.REQUEST;
if (request.getDispatcherType()==DispatcherType.ASYNC) dispatcherType = DispatcherType.ASYNC;
request.setAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_TYPE_ATTR,dispatcherType);
request.setAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_REQUEST_PATH_ATTR,
requestPathMB);
// Create the filter chain for this request
ApplicationFilterFactory factory =
ApplicationFilterFactory.getInstance();
ApplicationFilterChain filterChain =
factory.createFilterChain(request, wrapper, servlet);
System.out.println("Create the filter["+ filterChain+"] chain for this request");
// Reset comet flag value after creating the filter chain
request.setComet(false);
// Call the filter chain for this request
// NOTE: This also calls the servlet's service() method
try {
if ((servlet != null) && (filterChain != null)) {
System.out.println(this + " CALL filterChain[" + filterChain + "]");
// Swallow output if needed
if (context.getSwallowOutput()) {
try {
SystemLogHandler.startCapture();
if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) {
request.getAsyncContextInternal().doInternalDispatch();
} else if (comet) {
filterChain.doFilterEvent(request.getEvent());
request.setComet(true);
} else {
filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(),
response.getResponse());
}
} finally {
String log = SystemLogHandler.stopCapture();
if (log != null && log.length() > 0) {
context.getLogger().info(log);
}
}
} else {
if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) {
request.getAsyncContextInternal().doInternalDispatch();
} else if (comet) {
request.setComet(true);
filterChain.doFilterEvent(request.getEvent());
} else {
filterChain.doFilter
(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
}
}
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + filterChain + " END");
}
} catch (ClientAbortException e) {
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
} catch (IOException e) {
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString(
"standardWrapper.serviceException", wrapper.getName(),
context.getName()), e);
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
} catch (UnavailableException e) {
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString(
"standardWrapper.serviceException", wrapper.getName(),
context.getName()), e);
// throwable = e;
// exception(request, response, e);
wrapper.unavailable(e);
long available = wrapper.getAvailable();
if ((available > 0L) && (available < Long.MAX_VALUE)) {
response.setDateHeader("Retry-After", available);
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE,
sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable",
wrapper.getName()));
} else if (available == Long.MAX_VALUE) {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND,
sm.getString("standardWrapper.notFound",
wrapper.getName()));
}
// Do not save exception in 'throwable', because we
// do not want to do exception(request, response, e) processing
} catch (ServletException e) {
Throwable rootCause = StandardWrapper.getRootCause(e);
if (!(rootCause instanceof ClientAbortException)) {
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString(
"standardWrapper.serviceExceptionRoot",
wrapper.getName(), context.getName(), e.getMessage()),
rootCause);
}
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString(
"standardWrapper.serviceException", wrapper.getName(),
context.getName()), e);
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
}
// Release the filter chain (if any) for this request
if (filterChain != null) {
if (request.isComet()) {
// If this is a Comet request, then the same chain will be used for the
// processing of all subsequent events.
filterChain.reuse();
} else {
filterChain.release();
}
}
// Deallocate the allocated servlet instance
try {
if (servlet != null) {
wrapper.deallocate(servlet);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.deallocateException",
wrapper.getName()), e);
if (throwable == null) {
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
}
}
// If this servlet has been marked permanently unavailable,
// unload it and release this instance
try {
if ((servlet != null) &&
(wrapper.getAvailable() == Long.MAX_VALUE)) {
wrapper.unload();
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.unloadException",
wrapper.getName()), e);
if (throwable == null) {
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
}
}
long t2=System.currentTimeMillis();
long time=t2-t1;
processingTime += time;
if( time > maxTime) maxTime=time;
if( time < minTime) minTime=time;
}执行 filterChain 中的 doFilter 方法
在该方法中首先会执行一些安全检查(前提是安全检查系统打开了),然后利用 filterChain 中的每一个 filter 依次来处理 request 请求。当最后一个 filter 处理完成之后就会调用当前 servlet 的 service() 方法进行后续的逻辑处理。接着就会调用在 StandardWrapper 中分配的 servlet 实例中的 service 方法,这里是 MyHttpServlet 中的 service 方法,简单实现了 doGet、doPost 方法
至此,从获取到 socket 请求到最终的 servlet 的整个过程已经走完了。
调用servlet 的 service 方法详细
1:调用 MyHttpServlet 中的 service 方法
filterChain 中的 doFilter 方法源码
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if( Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
try {
java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new java.security.PrivilegedExceptionAction() {
@Override
public Void run()
throws ServletException, IOException {
internalDoFilter(req,res);
return null;
}
}
);
} catch( PrivilegedActionException pe) {
Exception e = pe.getException();
if (e instanceof ServletException)
throw (ServletException) e;
else if (e instanceof IOException)
throw (IOException) e;
else if (e instanceof RuntimeException)
throw (RuntimeException) e;
else
throw new ServletException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
} else {
internalDoFilter(request,response);
}
}
private void internalDoFilter(ServletRequest request,
ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Call the next filter if there is one
if (pos < n) {
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig = filters[pos++];
Filter filter = null;
try {
filter = filterConfig.getFilter();
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.BEFORE_FILTER_EVENT,
filter, request, response);
if (request.isAsyncSupported() && "false".equalsIgnoreCase(
filterConfig.getFilterDef().getAsyncSupported())) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.ASYNC_SUPPORTED_ATTR,
Boolean.FALSE);
}
if( Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
Principal principal =
((HttpServletRequest) req).getUserPrincipal();
Object[] args = new Object[]{req, res, this};
SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege
("doFilter", filter, classType, args, principal);
} else {
filter.doFilter(request, response, this);
}
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_FILTER_EVENT,
filter, request, response);
} catch (IOException e) {
if (filter != null)
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_FILTER_EVENT,
filter, request, response, e);
throw e;
} catch (ServletException e) {
if (filter != null)
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_FILTER_EVENT,
filter, request, response, e);
throw e;
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
if (filter != null)
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_FILTER_EVENT,
filter, request, response, e);
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
e = ExceptionUtils.unwrapInvocationTargetException(e);
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
if (filter != null)
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_FILTER_EVENT,
filter, request, response, e);
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("filterChain.filter"), e);
}
return;
}
// We fell off the end of the chain -- call the servlet instance
try {
if (ApplicationDispatcher.WRAP_SAME_OBJECT) {
lastServicedRequest.set(request);
lastServicedResponse.set(response);
}
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.BEFORE_SERVICE_EVENT,
servlet, request, response);
if (request.isAsyncSupported()
&& !support.getWrapper().isAsyncSupported()) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.ASYNC_SUPPORTED_ATTR,
Boolean.FALSE);
}
// Use potentially wrapped request from this point
if ((request instanceof HttpServletRequest) &&
(response instanceof HttpServletResponse)) {
if( Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
Principal principal =
((HttpServletRequest) req).getUserPrincipal();
Object[] args = new Object[]{req, res};
SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege("service",
servlet,
classTypeUsedInService,
args,
principal);
} else {
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + servlet);
servlet.service(request, response);
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + servlet + " END");
}
} else {
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + servlet);
servlet.service(request, response);
System.out.println(this + " CALL " + servlet + "END");
}
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_SERVICE_EVENT,
servlet, request, response);
} catch (IOException e) {
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_SERVICE_EVENT,
servlet, request, response, e);
throw e;
} catch (ServletException e) {
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_SERVICE_EVENT,
servlet, request, response, e);
throw e;
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_SERVICE_EVENT,
servlet, request, response, e);
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_SERVICE_EVENT,
servlet, request, response, e);
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("filterChain.servlet"), e);
} finally {
if (ApplicationDispatcher.WRAP_SAME_OBJECT) {
lastServicedRequest.set(null);
lastServicedResponse.set(null);
}
} 执行 MyHttpServlet 中的 service 方法
MyHttpServlet 继承自 HttpServlet,到这里大家应该比较熟悉了。MyHttpServlet 里面包含了 doGet、doPost 等方法就是继承自 HttpServlet。然后如果想要访问到我们自定义 MyHttpServlet,还需要在 web.xml 中做如下操作:
定义 MyHttpServlet,同时定义访问的映射
MyHttpServlet
org.apache.catalina.servlets.MyHttpServlet
MyHttpServlet
/MyHttpServletPath
例如 tomcat 其它配置默认,且在本地启动 tomcat。这时想要访问 MyHttpServlet,可以通过 http://127.0.0.1:8080/MyHttpServletPath 来实现
MyHttpServlet.java 源码
package org.apache.catalina.servlets;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
*
* @author hsyang
*
*/
public class MyHttpServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("my get request");
OutputStream os = resp.getOutputStream();
os.write("MyHttpServlet response ".getBytes());
os.flush();
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("my post request");
}
}
一些细节
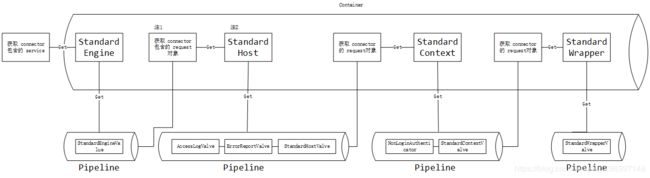
Container中request请求流动图
注1:Connector 中的 request 来至于 org.apache.coyote.Request 。 org.apache.coyote.Request 中包含了host,context,wrapper等 Container,当 request 通过了 host 的重重验证之后,会获取 context 对象,然后跳转到 context 进一步处理,以此类推。这样每一个请求都会按照 host---》context---》wrapper(servlet),这样的顺序到达最终的 servlet,然后执行 servlet 中相关的业务逻辑。
注2:每一个Container都包含一个 PipeLine,PipeLine 中包含了一个或者多个 Valve,每一个 Valve 都各司其职,只有通过了当前 valve 的验证,才能到达下一个 valve。一个 request 请求想要到达最终的目的地 servlet,必须要通过每一个 Container 中 pipeline 设置的各个 valve的检测,只要有一个 valve 验证不通过就会返回合适的 http 返回码。从前面的描述可知这里使用了责任链模式,首先,把每个 Container 通过 request 串联起来,然后每个 Container 内部又包含一个 Pipeline ,可以在 Pipeline 中增加任意多个处理逻辑,程序灵活性显著提高了。这里的 request 可以比作一个信使,他知道他的下一个驿站在哪里(对应各个Container),然后在每一个驿站内还需要经过驿站首领(PipeLine)重重关卡(Valve)的考验,只有通过了才能到达下一个驿站,一直到目的地(servlet)
请求路径映射器 mapper
这里有一篇博文写的比较好:https://blog.csdn.net/wangyangzhizhou/article/details/51933668
Tomcat连接器:Coyote框架
https://blog.csdn.net/wangchengsi/article/details/2973012