【C++手写Vector模板类】构造与模板初试
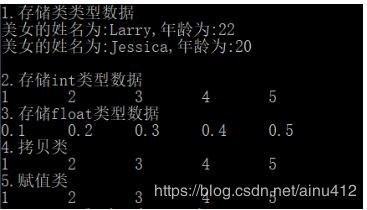
一.输出效果
测试文件:
main.cpp
#include "Vector.hpp"
#include btV(2);btV[0] = la;拷贝全部耗费空间太大;Vector类内会根据Beauty大小
//仅分配了Beauty*的内存,故指针还要另外分配对象内存
//Beauty la(22, "Larry");
//Beauty je(20, "Jessica");
btV[0] = new Beauty(22, "Larry");//可同时初始化,避免创造新la和je浪费内存
//btV[0] = &la;//*btv[0]=la;×放地址就行
btV[1] = new Beauty(20, "Jessica");
//btV[1] = &je;
for (int i = 0; i < btV.getCnt(); i++) {
cout << *btV[i];
}cout << endl;
delete btV[0];
delete btV[1];
cout << "2.存储int类型数据" << endl;
//对默认构造函数存储元素赋值为1-5
Vector<int> intV(5);//integar vector
for (int i = 0; i < intV.getCnt(); i++) {
intV[i] = i + 1;
}
//打印数组元素
cout << intV;
cout << "3.存储float类型数据" << endl;
Vector<float> floatV(5);//integar vector
for (int i = 0; i < floatV.getCnt(); i++) {
floatV[i] = (i + 1) * 0.1f;
}
cout << floatV;
//拷贝类
cout << "4.拷贝类" << endl;
Vector<int> intV1(intV);
cout << intV1;
//赋值类
cout << "5.赋值类" << endl;
Vector<int> intV2(2);
intV2 = intV;
cout << intV2;
return 0;
}
二.设计思路
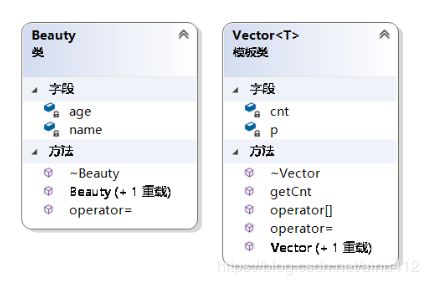
设计类图:
设计思路: 数组模板类( Vector ),完成对int、char、float、double 以及任意的自定义类等类型元素进行管理.cnt标识元素个数, p标识元素首地址. 具以下方法:
a.默认+带参构造函数, 确定存储元素个数
b.拷贝构造函数, 针对动态分配元素, delete与new
c.<<重载: 直接打印数组全部元素 cout << myVector
d.[]重载: 直接访问存储元素 myVector[i] = m_base[i] = *(m_base+i) = 存储及打印元素值
e.赋值构造函数, 整个对象各元素依次赋值
f.获取存有对象存储元素个数 cnt
#pragma once
#include 模板类实现文件, 因具有头文件的多文件适用性, 又具cpp文件的实现函数功能, 故命名为hpp文件, 因h在前, 故编译时要include包含.h文件
Vector.hpp
#include "Vector.h"
template<typename T>
inline Vector<T>::Vector(int cnt) {
this->cnt = cnt > 0 ? cnt : 128;
p = new T[this->cnt];
}
template<typename T>
inline Vector<T>::~Vector()
{
delete[] p;
p = nullptr;
}
template<typename T>
inline T& Vector<T>::operator[](int i)
{
if (i >= 0) {
return p[i];
}
else {
cout << "数组长度有误!" << endl;
exit(1);
}
}
template<typename T>
inline unsigned Vector<T>::getCnt()
{
return cnt;
}
template<typename T>
inline Vector<T>::Vector(Vector& src)
{
p = new T[src.cnt];
cnt = src.cnt;
for (int i = 0; i < src.cnt; i++) {
p[i] = src[i];//this[i]好像不行??
}
}
template<typename T>
inline Vector<T>& Vector<T>::operator=(Vector& src)
{
if (p) {
delete[] p;
}
p = new T[src.cnt];
cnt = src.cnt;
for (int i = 0; i < src.cnt; i++) {
(*this)[i] = src[i];
}
return *this;
}
template<typename T>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Vector<T>& object)
{
for (int i = 0; i < object.cnt; i++) {
os << object.p[i] << "\t";//若存储值,可直接打印;若存储对象,无法直接打印->可直接创建os<
}os << endl;
return os;
}
辅助测试的类文件:
Beauty.h
#pragma once
#include Beauty.cpp
#include "Beauty.h"
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Beauty& beauty)
{
os << "美女的姓名为:" << beauty.name
<< ",年龄为:" << beauty.age << endl;
return os;
}
Beauty::Beauty(int age, const char* name) :age(age)
{//指针的浅拷贝和深拷贝才有差别->浅拷贝指向同一块内存,深拷贝指向不同内存
//此次数据成员若不含指针,故无需再手动定义深拷贝
/*int len = name.length() + 1;
this->name = new char[len];
strcpy_s(this->name, len, name.c_str());*/
int len = strlen(name) + 1;
this->name = new char[len];
strcpy_s(this->name, len, name);
}
Beauty::~Beauty()
{
if (name) {
delete[] name;
}
}
Beauty::Beauty(const Beauty& src)
{
int len = strlen(src.name) + 1;
this->name = new char[len];
strcpy_s(this->name, len, src.name);
age = src.age;
}
Beauty& Beauty::operator=(const Beauty& src)
{
if (name) {
delete[] name;
}
int len = strlen(src.name) + 1;
this->name = new char[len];
strcpy_s(this->name, len, src.name);
age = src.age;
return *this;
}