哈夫曼树完成文件的压缩和解压
1、在这里只有工具类,依赖的树节点和树的类,见另一篇博客(https://blog.csdn.net/riapgypm/article/details/106103996)里的定义
2、压缩工作类的实现如下:
package com.cn.test.tree.zip;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
/**
* 压缩工具类
*/
public class ZipFileUtil {
public static Map huffCodes = new HashMap<>();
public static Map reverseHuffCodes = new HashMap<>();
private static byte[] readFile(String filePath){
byte[] content = null;
try {
FileInputStream fileReader = new FileInputStream(new File(filePath));
content = new byte[fileReader.available()];
fileReader.read(content);
fileReader.close();
return content;
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return content;
}
private static void writeToZipFile(byte[] bytes,String target){
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(target));
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
oos.writeObject(bytes);
oos.writeObject(huffCodes);
oos.close();
fos.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void unZipWriteToFile(byte[] bytes,String target){
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(target));
fos.write(bytes);
fos.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static byte[] readZipFile(String filePath){
byte[] content = null;
try {
FileInputStream fileReader = new FileInputStream(new File(filePath));
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fileReader);
byte[] zipContent = (byte[])ois.readObject();
huffCodes = (Map)ois.readObject();
ois.close();
fileReader.close();
return zipContent;
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return content;
}
/**
* 普通文件压缩
* @param sourcePath
* @return
*/
public static void zipFile(String sourcePath,String targetPath){
if(sourcePath==null){
return;
}
System.out.println("原始文件路径:"+sourcePath);
//构建哈夫曼树列表
byte[] bytes = readFile(sourcePath);
System.out.println("原始字节长度:"+ Arrays.toString(bytes));
//构建哈夫曼村
HuffTree huffTree = new HuffTree();
huffTree.buildTree(bytes);
huffTree.obtainHuffCodes(huffTree.getRoot(),"",huffCodes);
//生成压缩后的字符串二进制数
StringBuilder binaryBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (byte b:bytes){
binaryBuilder.append(huffCodes.get((int)b));
}
String strBinary= binaryBuilder.toString();
System.out.println("字符串二进制数:"+strBinary);
//把字符二进制数转换成真实的二进制数
int len = (strBinary.length()+7)/8;
byte[] result = new byte[len+1];
//byte[0]留出来,如果结尾补了位,把补位的数字放在这里
int index = 1;
for (int i = 0 ;i =strBinary.length()){
String last = strBinary.substring(i);
//补位,使其正好是8位
last += "00000000".substring(8-(i+8-strBinary.length()));
result[index++] = (byte)Integer.parseInt(last,2);
result[0] = (byte)(i+8-strBinary.length());
break;
}else{
result[index++] = (byte)Integer.parseInt(strBinary.substring(i,i+8),2);
i+=8;
}
}
writeToZipFile(result,targetPath);
}
/**
* 将二进制,转换成字符串二进制
* @param b
* @return
*/
public static String byte2Str(byte b){
String s = Integer.toBinaryString(b);
if(s.length()>8){
s = s.substring(s.length()-8);
}
if(s.length()<8){
s = String.format("%08d", Integer.parseInt(s));
}
return s;
}
/**
* 解压文件
* @param zipPath
* @param unZipPath
*/
public static void unZip(String zipPath,String unZipPath){
byte[] zipBytes = readZipFile(zipPath);
//解压之后的字符串
StringBuilder unZipBinaryBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 1 ;i0){
unZipBinary = unZipBinary.substring(0,unZipBinary.length()-buWei);
}
System.out.println("解压之后的字符串二进制数:"+unZipBinary);
for (Map.Entry entry:huffCodes.entrySet()){
reverseHuffCodes.put(entry.getValue(),entry.getKey());
}
List source = new ArrayList<>();
int j = 0;
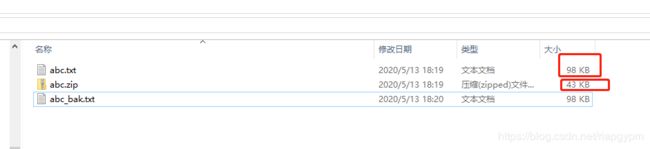
for (int i = 0 ; j 3、执行完之后,可以看文件的压缩情况
4、通过这个结果可以看到文件从98压缩到43,解压之后的文件还是98,也能够正常打开