SpringBoot2.x系列教程38--整合JAX-RS之利用Jersey框架实现RESTful
SpringBoot2.x系列教程38--整合JAX-RS之利用Jersey框架实现RESTful
作者:一一哥
一. JAX-RS与Jersey简介
1. JAX-RS简介
在Java EE 6 中引入了对 JSR-311 的支持。JSR-311(也就是JAX-RS:Java API for RESTful Web Services)旨在定义一个统一的规范,它的核心概念是resource,也就是面向资源。JAX-RS使得 Java 程序员可以使用一套固定的接口来开发 REST 应用,避免了依赖于第三方框架。同时,JAX-RS 使用 POJO 编程模型和基于注解的配置,并集成了 JAXB,从而可以有效缩短 REST 应用的开发周期。
JAX-RS 定义的 API 位于 javax.ws.rs 包中,其中一些主要的接口、注解和抽象类如下图所示。
javax.ws.rs 包概况:
可以把 JAX-RS 理解为是一套开发协议,该协议具体的实现由第三方来完成,例如 Sun 的实现 Jersey框架、Apache 的 CXF框架 以及 JBoss 的 RESTEasy框架。
其中Jersey,RESTEasy这两个框架创建的应用,可以很方便地部署到Servlet 容器中,比如Tomcat,JBoss等。
2. Jersey框架简介
Jersey是对JAX-RS(JSR311)协议的实现,用于构建RESTful Web Service,可以进一步地简化 RESTful service 和 client 的开发。
也就是说Jersey是一个RESTful框架,与SpringMVC框架类似,但是使用上面和SpringMVC又有不同。此外Jersey还提供一些额外的API和扩展机制,所以我们可以按照自己的需要对Jersey进行扩展。
Jersey的一大特点就是,基于Jersey的REST应用,可以运行在Servlet环境下面,也可以脱离该环境。
3. Jersey常用注解
@Path
@Path注解的值是一个相对的URI路径。@Path的有没有/开头是一样的,同理,结尾有没有包含/也是一样的。
请求类注解
@GET, @PUT, @POST, @DELETE, … (HTTP Methods)
@GET, @PUT, @POST, @DELETE, @HEAD这些注解称为resource method designator,与HTTP规范中定义的方法一致。这些方法决定资源的行为。
@Produce
@Produce注解指定返回给客户端的MIME媒体类型。可以用于注解类或者注解方法。如果类中的方法没有指定,则默认使用类级别的@Produce值。@Produce注解可以指定多个值,同时可以指定quality factor:
@Produces({"application/xml; qs=0.9", "application/json"})
@Consumes
该注解用于指定可以接受的客户端请求的MIME媒体类型:
@POST
@Consumes("text/plain")
public void postClichedMessage(String message) {
// Store the message
参数注解(@*Param)
参数注解用于从请求中提取参数,例如上面的@PathParam用于提取路径中的参数。
@QueryParam
@QueryParam注解用于提取查询参数。
@MatrixParam
从url片段中提取参数,即url中冒号后面的参数。
@HeaderParam
从请求的头部提取Header。
@CookieParam
提取cookie。
@FormParam
用于提取请求中媒体类型为”application/x-www-form-urlencoded” 的参数,根据相应的表单类型提取其中的参数。
@BeanParam
该注解用于从请求的各部分中提取参数,并注入到对应的Bean中。
@Context的使用
Context注解一般用于获取request或者response相关的上下文,例如UriInfo。
三. Jersey框架实现RESTful
1. 创建web项目(略)
我们首先创建一个web项目,并将该项目改造成一个Spring boot项目,具体依赖包请参考之前的章节,此处略过! 

2. 引入jersey的依赖包
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-jersey
3. 创建service接口
3.1 创建IHelloService接口类:
package com.yyg.boot.service;
/**
* @Description Description
* @Author 一一哥Sun
* @Date Created in 2020/3/28
*/
public interface IHelloService {
void sayHi(String msg);
}
3.2 创建HelloServiceImpl实现类:
package com.yyg.boot.service.impl;
import com.yyg.boot.service.IHelloService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @Description Description
* @Author 一一哥Sun
* @Date Created in 2020/3/28
*/
@Slf4j
@Service
public class HelloService implements IHelloService {
@Override
public void sayHi(String msg) {
log.warn("展示信息:" + msg);
}
}
4. 创建Resource资源类
package com.yyg.boot.web;
import com.yyg.boot.service.IHelloService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.Produces;
import javax.ws.rs.QueryParam;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
import java.awt.*;
/**
* @Description Description
* @Author 一一哥Sun
* @Date Created in 2020/3/28
*/
@Component
@Path("hello")
public class HelloResource {
@Autowired
private IHelloService helloService;
/**
* @Produces(value =MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON):设置输出内容为json格式,且可以解决中文乱码问题;
* @Path("sayHi"):设置资源的请求路径;
* @GET:设置请求方式为get请求.
*/
@Produces(value =MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
@Path("sayHi")
@GET
public String sayHi(@QueryParam("msg") String msg) {
this.helloService.sayHi(msg);
return "success--->"+msg;
}
}
5. 对Jersey进行配置
Springboot中对Jersey的配置有三种方式:
- 第一种方式创建一个自定义的ResourceConfig;
- 第二种方式,返回一个ResourceConfig类型的@Bean;
- 第三种方式,配置一组ResourceConfigCustomizer对象。
我们这里以第一种配置方式来讲解如何实现配置。
package com.yyg.boot.config;
import com.yyg.boot.web.HelloResource;
import org.glassfish.jersey.server.ResourceConfig;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.ws.rs.ApplicationPath;
/**
* @Description Description
* @Author 一一哥Sun
* @Date Created in 2020/3/28
* @ApplicationPath("shop")资源根路径。
*/
@Configuration
@ApplicationPath("shop")
public class JerseyConfig extends ResourceConfig {
public JerseyConfig() {
register(HelloResource.class);
}
}
Springboot默认把Jersey的根路径映射在/*上;如果要更改默认的根路径设置,对于自定义的ResourceConfig方式来说,可以在类上面添加一个@ApplicationPath注解即可。
我们也可以在application.properties中添加配置来改变项目的根路径:
spring.jersey.application-path=shop
另外,Spring Boot建议在使用ResourceConfig添加资源类的时候,不要使用ResourceConfig类的packages方法去自动扫描,建议还是手动添加。
官方的解释为:
Jersey’s support for scanning executable archives is rather limited. For example, it cannot scan for endpoints in a package found in WEB-INF/classes when running an executable war file. To avoid this limitation, the packages method should not be used and endpoints should be registered individually using the register method
也就是使用Jersey的packages是比较有局限的,比如在应用运行在war包中的时候,就不能扫描到其中的包。所以建议单独的为每一个资源类独立使用register方法注册。
6. 创建入口类
package com.yyg.boot;
import com.yyg.boot.service.impl.HelloService;
import com.yyg.boot.web.HelloResource;
import org.glassfish.jersey.server.ResourceConfig;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
/**
* @Description Description
* @Author 一一哥Sun
* @Date Created in 2020/3/28
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class JerseyApplication {
/**
* 第二种方式,使用@Bean创建一个ResourceConfig类实例
*/
// @Bean
// public ResourceConfig resourceConfig() {
// ResourceConfig config = new ResourceConfig();
// config.register(HelloResource.class);
// return config;
// }
public static void main(String[] args){
SpringApplication.run(JerseyApplication.class,args);
}
}
7. 项目结构
8. 启动项目,测试接口
我们在浏览器中输入地址:
http://localhost:8080/shop/hello/sayHi?msg=%E4%B8%80%E4%B8%80%E5%93%A5
如果出现如下内容,说明我们的jersey与Spring Boot成功的实现了整合。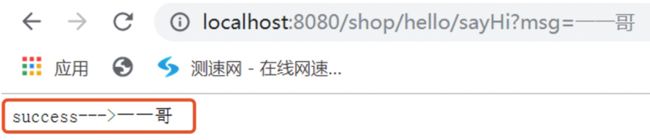 

9. 其他细节
9.1 Jersey注册方式
Jersey和Springboot的集成有两种方式,一种是使用Filter的方式注册,一种是使用Servlet的方式注册,默认使用的是Servlet的方式,也可以通过spring.jersey.type=filter或者通过spring.jersey.type=servlet来控制。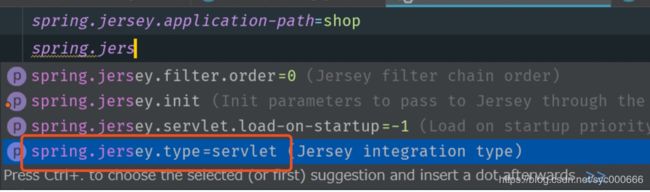
spring.jersey.type=servlet
9.2 更改延迟启动
如果使用Servlet的方式启动,默认是使用的延迟启动。
jerseyServletRegistration方法的代码就可以看出来:
registration.setName(getServletRegistrationName());
registration.setLoadOnStartup(this.jersey.getServlet().getLoadOnStartup());
return registration;
第二句代码setLoadOnStartup方法,调用的是this.jersey.getServlet().getLoadOnStartup(),而这个地方的jersey就是JerseyProperties对象:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.jersey")
public class JerseyProperties {...}
其中servlet的类代码为:
public static class Servlet {
/**
* Load on startup priority of the Jersey servlet.
*/
private int loadOnStartup = -1;
public int getLoadOnStartup() {
return this.loadOnStartup;
}
public void setLoadOnStartup(int loadOnStartup) {
this.loadOnStartup = loadOnStartup;
}
}
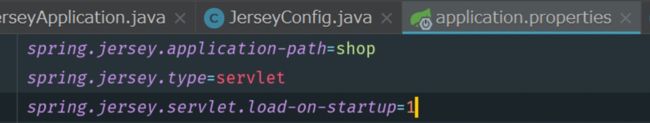
那么我们只需要在application.properties中配置spring.jersey.servlet.loadOnStartup=1即可立即让Jersey的Servlet实例化。
application.properties中配置spring.jersey.servlet.loadOnStartup=1