Java反射机制
文章目录
- 1. 反射机制概述
- 1.1 反射机制提供的功能
- 1.2 反射相关API
- 1.3 反射的应用举例
- 2. Class类
- 2.1 Class类概述
- 2.2 Class类的常用方法
- 2.3 获取Class类的实例(四种方法)
- 代码演示:
- 2.4 哪些类型可以有Class对象
- 3.类的加载 和 ClassLoader
- 3.1 类的加载过程
- 3.3.1 概述
- 3.3.2 ClassLoader相关方法
- 3.3.3 ClassLoader 相关方法具体代码演示
- 4.创建运行时类的对象
- 4.1 newInstance方法
- 4.2 体会反射的动态性
- 5. 获取运行时类的完整结构
- 5.1 方法概述
- 5.2 获取属性结构
- 5.3 获取运行时类的方法结构
- 5.4 获取构造器结构
- 5.5 获取运行时类的父类 & 泛型 相关
- 5.5.1 获取运行时类的父类
- 5.5.2 获取运行时类的带泛型的父类
- 5.5.3 获取运行时类的带泛型的父类的泛型
- 5.6 获取运行时类声明的注解
- 5.7 获取运行时类所在的包
- 5.8 获取运行时类实现的接口相关&父类实现的接口
- 6. 调用运行时类中指定的结构:属性、方法、构造器
- 6.1 如何操作运行时类中的指定的方法
- 6.2 如何操作运行时类中的指定的属性
- 6.3 调用运行时类中的指定的构造器 (使用较少,大部分用 .newInstance调用空参构造器)
1. 反射机制概述
1.1 反射机制提供的功能
1.2 反射相关API
1.3 反射的应用举例
public class ReflectionTest {
//反射之前,对于Person类的操作
@Test
public void test1(){
//1.创建Person类的对象
Person p1 = new Person("tom",12);
//2.通过对象,调用其内部的属性和方法
p1.age = 10;
System.out.println(p1);
p1.show();
//在Person类外部,不可以通过Person类的对象调用其内部私有结构
//比如:name、showNation()以及私有的构造器
}
//反射之后,对于Person类的操作
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
Class clazz = Person.class;
//1.通过反射,创建Person类的对象
Constructor cons = clazz.getConstructor(String.class, int.class);
Object obj = cons.newInstance("tom", 12);
Person p = (Person)obj;
System.out.println(obj.toString());
//2.通过反射,调用对象指定的属性和指定的方法
//调用属性
Field age = clazz.getDeclaredField("age");
age.set(p,10);
System.out.println(p.toString());
//调用方法
Method show = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("show");
show.invoke(p);
System.out.println("********************");
//通过反射,可以调用Person类的私有结构的。比如:私有的构造器、方法、属性
//调用私有的构造器
Constructor cons1 = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
cons1.setAccessible(true);
Object jerry = cons1.newInstance("jerry");
Person p1 = (Person)jerry;
System.out.println(p1);
//调用私有的属性
Field name = clazz.getDeclaredField("name");
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(p1,"hanmeimei");
System.out.println(p1);
//调用私有的方法
Method showNation = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("showNation", String.class);
showNation.setAccessible(true);
String nation = (String)showNation.invoke(p1, "中国");//相当于String nation = p1.showNation("中国);
System.out.println(nation);
}
//疑问:通过直接new的方式或反射的方式都可以调用公共的结构,开发中用哪个?
//建议:直接new的方式。
//什么时候会用:反射的方式。 反射的特征:动态性
//疑问:反射机制与面线对象中的封装性是不是矛盾的?如何看待这两个技术?
//不矛盾。
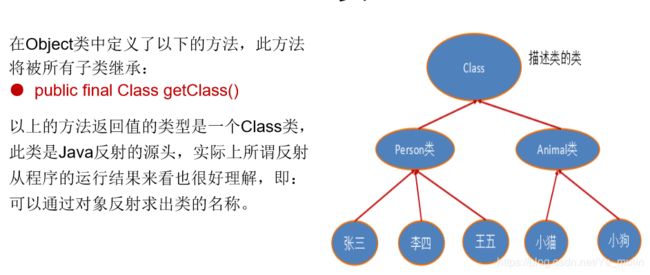
2. Class类
2.1 Class类概述
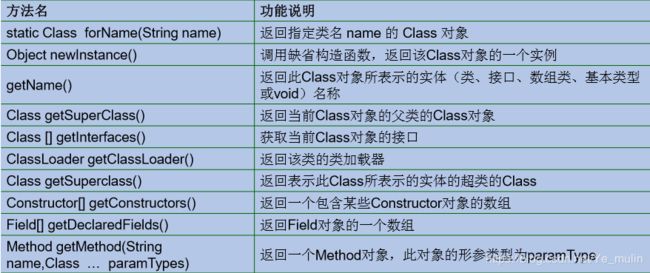
2.2 Class类的常用方法
2.3 获取Class类的实例(四种方法)
代码演示:
/*
关于java.lang.Class类的理解
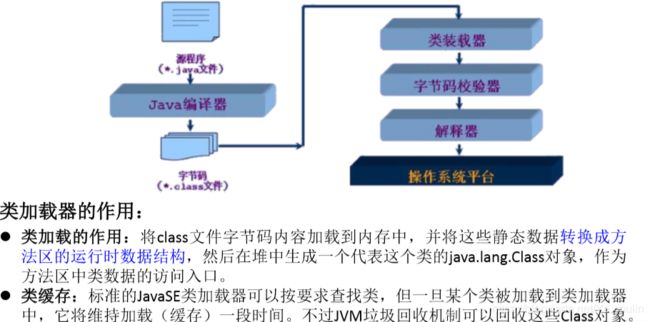
1.类的加载过程:
程序经过javac.exe命令以后,会生成一个或多个字节码文件(.class结尾)。
接着我们使用java.exe命令对某个字节码文件进行解释运行。相当于将某个字节码文件
加载到内存中。此过程就称为类的加载。加载到内存中的类,我们就称为运行时类,此
运行时类,就作为Class的一个实例。
2.换句话说,Class的实例就对应着一个运行时类。
3.加载到内存中的运行时类,会缓存一定的时间。在此时间之内,我们可以通过不同的方式
来获取此运行时类。
*/
//获取Class的实例的方式(前三种方式需要掌握)
@Test
public void test3() throws ClassNotFoundException {
//方式一:调用运行时类的属性:.class
Class clazz1 = Person.class;
System.out.println(clazz1);
//方式二:通过运行时类的对象,调用getClass()
Person p1 = new Person();
Class clazz2 = p1.getClass();
System.out.println(clazz2);
//方式三:调用Class的静态方法:forName(String classPath)
Class clazz3 = Class.forName("studyjava.day11_reflect.java.Person");
// clazz3 = Class.forName("java.lang.String");
System.out.println(clazz3);
System.out.println(clazz1 == clazz2);
System.out.println(clazz1 == clazz3);
//方式四:使用类的加载器:Classloader(了解)
ClassLoader classLoader = ReflectionTest.class.getClassLoader();
Class clazz4 = classLoader.loadClass("studyjava.day11_reflect.java.Person");
System.out.println(clazz1 == clazz4);
}
//万事万物皆对象?对象.xxx,File,URL,反射,前端、数据库操作
}
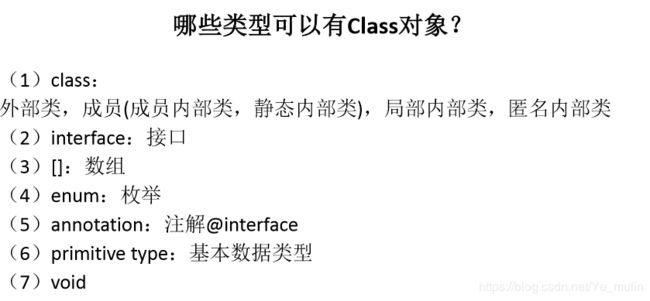
2.4 哪些类型可以有Class对象
//Class实例可以是哪些结构的说明:
@Test
public void test4(){
Class c1 = Object.class;
Class c2 = Comparable.class;
Class c3 = String[].class;
Class c4 = int[][].class;
Class c5 = ElementType.class;
Class c6 = Override.class;
Class c7 = int.class;
Class c8 = void.class;
Class c9 = Class.class;
int[] a = new int[10];
int[] b = new int[100];
Class c10 = a.getClass();
Class c11 = b.getClass();
// 只要数组的元素类型与维度一样,就是同一个Class
System.out.println(c10 == c11);
}
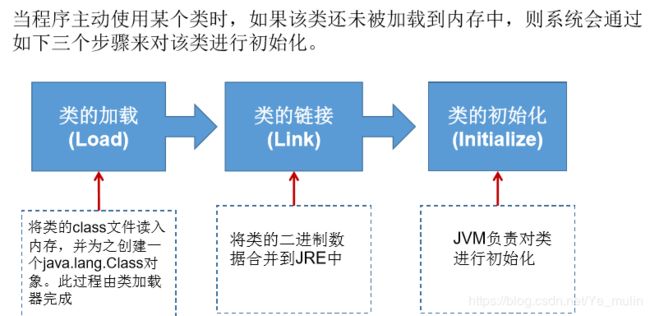
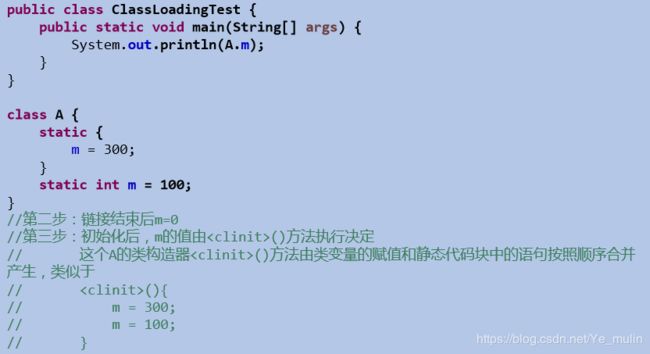
3.类的加载 和 ClassLoader
3.1 类的加载过程
## 3.2 类的初始化
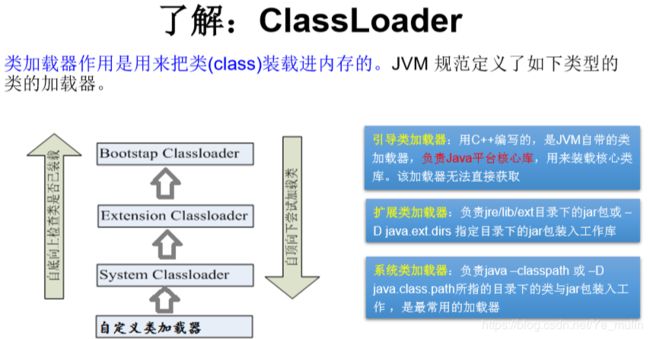
## 3.3 类加载器 ClassLoader
3.3.1 概述
3.3.2 ClassLoader相关方法
3.3.3 ClassLoader 相关方法具体代码演示
public class ClassLoaderTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
//对于自定义类,使用系统类加载器进行加载
ClassLoader classLoader = ClassLoaderTest.class.getClassLoader();
System.out.println(classLoader);//sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
//调用系统类加载器的getParent():获取扩展类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader1 = classLoader.getParent();
System.out.println(classLoader1);//sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader@8efb846
//调用扩展类加载器的getParent():无法获取引导类加载器
//引导类加载器主要负责加载java的核心类库,无法加载自定义类的。
ClassLoader classLoader2 = classLoader1.getParent();
System.out.println(classLoader2); //null
ClassLoader classLoader3 = String.class.getClassLoader();
System.out.println(classLoader3); //null
}
/*
Properties:用来读取配置文件
*/
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
Properties pros = new Properties();
//此时的文件默认在当前的module下
//读取配置文件方式一:
// FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties");
// pros.load(fis);
//读取配置文件的方式二:使用ClassLoader
//配置文件默认识别为:当前module的src下
ClassLoader classLoader = ClassLoaderTest.class.getClassLoader();
InputStream is = classLoader.getResourceAsStream("jdbc1.properties");
pros.load(is);
String user = pros.getProperty("user");
String password = pros.getProperty("password");
System.out.println("user = " + user + ",password = " + password);
}
}
4.创建运行时类的对象
4.1 newInstance方法
@Test
public void test1() throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
Class clazz = Person.class;
/*
newInstance():调用此方法,创建对应的运行时类的对象。内部调用了运行时类的空参的构造器。
要想此方法正常的创建运行时类的对象,要求:
1.运行时类必须提供空参的构造器
2.空参的构造器的访问权限得够。通常,设置为public。
在javabean中要求提供一个public的空参构造器。原因:
1.便于通过反射,创建运行时类的对象
2.便于子类继承此运行时类时,默认调用super()时,保证父类有此构造器
*/
Person obj = (Person) clazz.newInstance();
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
4.2 体会反射的动态性
//体会反射的动态性
@Test
public void test2() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
int num = new Random().nextInt(3);//0,1,2
String classPath = "";
switch (num) {
case 0:
classPath = "java.util.Date";
break;
case 1:
classPath = "java.lang.Object";
break;
case 2:
classPath = "studyjava.day11_reflect.java.Person";
break;
}
try {
Object obj = getInstance(classPath);
System.out.println(obj);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/*
创建一个指定类的对象。
classPath:指定类的全类名
*/
public Object getInstance(String classPath) throws Exception {
Class clazz = Class.forName(classPath);
return clazz.newInstance();
}
}
5. 获取运行时类的完整结构
5.1 方法概述
5.2 获取属性结构
public class FieldTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
//获取属性结构
//getFields():获取当前运行时类及其父类中声明为public访问权限的属性
Field[] fields = clazz.getFields();
for (Field f : fields){
System.out.println(f);
}
System.out.println();
//getDeclaredFields():获取当前运行时类中声明的所有属性。(不包含父类中声明的属性)
Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field f : declaredFields){
System.out.println(f);
}
}
//权限修饰符 数据类型 变量名
@Test
public void test2(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field f : declaredFields){
//1.权限修饰符
int modifiers = f.getModifiers();
// System.out.println(modifiers);//2 0 1
System.out.print(Modifier.toString(modifiers) + "\t");//private public
//2.数据类型
Class type = f.getType();
System.out.print(type.getTypeName() + "\t");
//3.变量名
String fName = f.getName();
System.out.print(fName + "\t");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
5.3 获取运行时类的方法结构
/**
*
* 获取运行时类的方法结构
*
* @ClassName : MethodTest
* @Description :
* @Author : Yemulin
* @Date : 2020/03/28 02:08
* @Version : 1.0
*/
public class MethodTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
//getMethods():获取当前运行时类及其所有父类中声明为public权限的方法
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for (Method m : methods){
System.out.println(m);
}
System.out.println();
//getDeclaredMethods():获取当前运行时类中声明的所有方法。(不包含父类中声明的方法)
Method[] declaredMethods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method m : declaredMethods){
System.out.println(m);
}
}
/*
@Xxxx
权限修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数类型1 形参名1,...) throws XxxException{}
*/
@Test
public void test2() {
Class clazz = Person.class;
Method[] declaredMethods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method m : declaredMethods) {
//1.获取方法声明的注解
Annotation[] annos = m.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation a : annos) {
System.out.println(a);
}
//2.权限修饰符
System.out.print(Modifier.toString(m.getModifiers()) + "\t");
//3.返回值类型
System.out.print(m.getReturnType().getTypeName() + "\t");
//4.方法名
System.out.print(m.getName());
System.out.print("(");
//5.形参列表
Class[] parameterTypes = m.getParameterTypes();
if (!(parameterTypes == null && parameterTypes.length == 0)){
for (int i = 0; i < parameterTypes.length; i++ ){
if (i == parameterTypes.length - 1){
System.out.print(parameterTypes[i].getTypeName() + " args_" + i);
break;
}
System.out.print(parameterTypes[i].getTypeName() + " args_" + i + ",");
}
}
System.out.print(")");
//6.抛出的异常
Class[] exceptionTypes = m.getExceptionTypes();
if (!(exceptionTypes == null || exceptionTypes.length == 0)){
System.out.print("throws ");
for (int i = 0; i < exceptionTypes.length; i++){
if (i == exceptionTypes.length - 1){
System.out.print(exceptionTypes[i].getTypeName());
break;
}
System.out.print(exceptionTypes[i].getTypeName() + ",");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
5.4 获取构造器结构
/*
获取构造器结构
*/
@Test
public void test1() {
Class clazz = Person.class;
//getConstructors():获取当前运行时类中声明为public的构造器
Constructor[] constructors = clazz.getConstructors();
for (Constructor c : constructors) {
System.out.println(c);
}
System.out.println();
//getDeclaredConstructors():获取当前运行时类中声明的所有的构造器
Constructor[] declaredConstructors = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor c : declaredConstructors) {
System.out.println(c);
}
}
5.5 获取运行时类的父类 & 泛型 相关
5.5.1 获取运行时类的父类
/*
获取运行时类的父类
*/
@Test
public void test2() {
Class clazz = Person.class;
Class superclass = clazz.getSuperclass();
System.out.println(superclass);
}
5.5.2 获取运行时类的带泛型的父类
/*
获取运行时类的带泛型的父类
*/
@Test
public void test3() {
Class clazz = Person.class;
Type genericSuperclass = clazz.getGenericSuperclass();
System.out.println(genericSuperclass);
}
5.5.3 获取运行时类的带泛型的父类的泛型
/*
获取运行时类的带泛型的父类的泛型
代码:逻辑性代码 vs 功能性代码
*/
@Test
public void test4() {
Class clazz = Person.class;
Type genericSuperclass = clazz.getGenericSuperclass();
ParameterizedType paramType = (ParameterizedType) genericSuperclass;
//获取泛型类型
Type[] actualTypeArguments = paramType.getActualTypeArguments();
// System.out.println(actualTypeArguments[0].getTypeName());
System.out.println(((Class)actualTypeArguments[0]).getName());
}
}
5.6 获取运行时类声明的注解
/*
获取运行时类声明的注解
*/
@Test
public void test7(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
Annotation[] annotations = clazz.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annos : annotations){
System.out.println(annos);
}
}
5.7 获取运行时类所在的包
/*
获取运行时类所在的包
*/
@Test
public void test6(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
Package pack = clazz.getPackage();
System.out.println(pack);
}
5.8 获取运行时类实现的接口相关&父类实现的接口
/*
获取运行时类实现的接口
*/
@Test
public void test5(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
Class[] interfaces = clazz.getInterfaces();
for (Class c : interfaces){
System.out.println(c);
}
System.out.println();
//获取运行时类的父类实现的接口
Class[] interfaces1 = clazz.getSuperclass().getInterfaces();
for (Class c : interfaces1){
System.out.println(c);
}
}
}
6. 调用运行时类中指定的结构:属性、方法、构造器
6.1 如何操作运行时类中的指定的方法
/*
如何操作运行时类中的指定的方法 -- 需要掌握
*/
@Test
public void testMethod() throws Exception {
Class clazz = Person.class;
//创建运行时类的对象
Person p = (Person) clazz.newInstance();
/*
1.获取指定的某个方法
getDeclaredMethod():参数1 :指明获取的方法的名称 参数2:指明获取的方法的形参列表
*/
Method show = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("show", String.class);
//2.保证当前方法是可访问的
show.setAccessible(true);
/*
3. 调用方法的invoke():参数1:方法的调用者 参数2:给方法形参赋值的实参
invoke()的返回值即为对应类中调用的方法的返回值。
*/
Object returnValue = show.invoke(p, "CHN"); //相当于之前的String nation = p.show("CHN");
System.out.println(returnValue);
System.out.println("*****************************");
// private static void showDesc()
Method showDesc = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("showDesc");
showDesc.setAccessible(true);
//如果调用的运行时类中的方法没有返回值,则此invoke()返回null
// Object returnVal = showDesc.invoke(null);
Object returnVal = showDesc.invoke(Person.class);
System.out.println(returnVal); //null
}
6.2 如何操作运行时类中的指定的属性
/*
如何操作运行时类中的指定的属性 -- 需要掌握
*/
@Test
public void testField1() throws Exception {
Class clazz = Person.class;
//创建运行时类的对象
Person p = (Person) clazz.newInstance();
//1.getDeclaredField(String fieldName):获取运行时类中指定变量名的属性
Field name = clazz.getDeclaredField("name");
//2.保证当前属性是可访问的
name.setAccessible(true);
//3.获取、设置指定对象的此属性值
name.set(p,"tom");
System.out.println(name.getName());
}
6.3 调用运行时类中的指定的构造器 (使用较少,大部分用 .newInstance调用空参构造器)
/*
如何调用运行时类中的指定的构造器 (使用较少,大部分用clazz.newInstance调用空参构造器)
*/
@Test
public void testConstructor() throws Exception {
Class clazz = Person.class;
//private Person(String name)
/*
1.获取指定的构造器
getDeclaredConstructor():参数:指明构造器的参数列表
*/
Constructor constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
//2.保证此构造器是可访问的
constructor.setAccessible(true);
//3.调用此构造器创建运行时类的对象
Person per = (Person) constructor.newInstance("tom");
System.out.println(per);
}