Python控制台运行结果输出到GUI(PyQt5)
一般情况下,程序运行结果在控制台输出,那如果不希望结果在控制台显示,而是输出到图形化用户界面呢?可以通过PyQt5,将运行结果输出定向到QTextEdit来完成。
环境:python3.7,pychram CE
1.准备工作
- Qt
- sip
- PyQt5
Qt 5可以在官网下载,选择免费的OpenSource系列,但速度较慢。推荐在清华镜像下载Qt-5.13.0,整个软件较大,大概3.2G。下载安装成功后把Qt5的bin目录加入到path。
brew安装sip, pyqt5
$brew install sip
$brew install pyqt5用brew安装时,brew updating会耗费一定时间。但install sip 和install pyqt都很快。
我在安装pyqt时发现安装依赖中有qt,而且下载速度比较慢,所以我中断了进程。单独安装qt:
$brew install qt这次qt的下载速度很快,安装完成后重新brew安装sip和pyqt5。
成功安装:sip-4.19.19_1,pyqt-5.10.1_2
2.在pycharm中配置QtDesigner和pyUIC
参考 Python - Mac下PyCharm&PyQt5环境搭建 完成pycharm中的环境搭建。
进行显示hello world安装成功测试。
3.一些简单的pyqt5例子
为熟悉pyqt5的使用方法,可以尝试一些小例子。
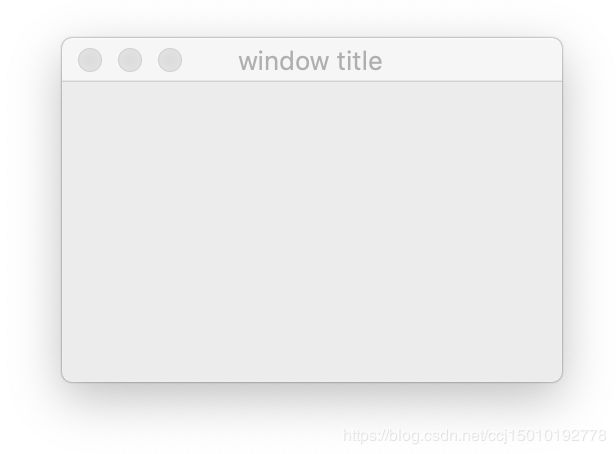
(1)创建一个空白窗口
import sys
from PyQt5.QtGui import *
from PyQt5.QtCore import *
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
'''
GUI—1:一个空白的窗口
构造窗体控件:w = QWidget()
'''
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
# 每一个GUI程序都有一个QApplication对象,创建时需要传参
# 因为PyQt可以识别一些自己到参数,比如-geometry和style
w = QWidget() # 构造窗体window
w.resize(250,150) # 设置宽高
w.move(300,300) # 移动到坐标(300,300)位置
w.setWindowTitle('window title') # 设置窗口标题
w.show() # 向QApplication事件列表中添加新的事件,以请求对特定窗口部件进行绘制
sys.exit(app.exec_())
# app.exec_()期待QApplication的事件循环
# sys.exit()是为了在窗口被关闭时,系统能得到通知运行结果:
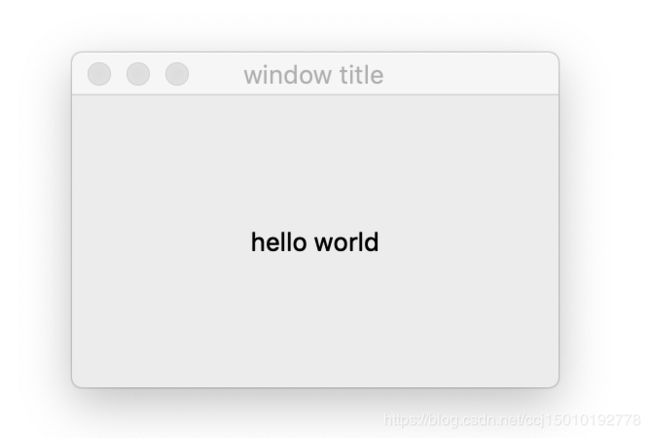
(2)创建一个带label显示helloworld的窗口
import sys
from PyQt5.QtGui import *
from PyQt5.QtCore import *
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
'''
GUI—2:一个显示hello world的窗口
构造标签控件:label=QLable()
'''
a = str([1,2,3])
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
lable = QLabel()
lable.setText(a)
lable.setAlignment(Qt.AlignCenter)
lable.resize(250, 150)
lable.move(300, 300)
# 设置窗口标题
lable.setWindowTitle('window title')
# 设置flags为闪屏模式可移除标题栏
lable.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
运行结果:
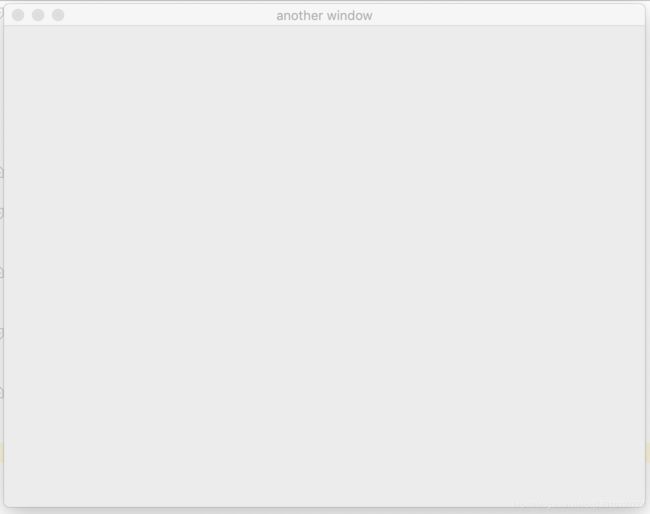
(3)通过另一种方式创建窗口
import sys
from PyQt5.QtGui import *
from PyQt5.QtCore import *
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
'''
GUI—3:创建窗口的另一种方式
定义class App(QWidget)
'''
class App(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.title = 'another window'
self.left = 10
self.top = 10
self.width = 640
self.height = 480
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.setWindowTitle(self.title)
self.setGeometry(self.left, self.top, self.width, self.height)
self.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = App()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
运行结果:
通过这些例子熟悉pyqt5的使用。大多情况下用第二种方法创建窗口,也就是例子(3)中定义class的方式。
4.运行结果输出到GUI
将python控制台输出打印到Qtextedit。
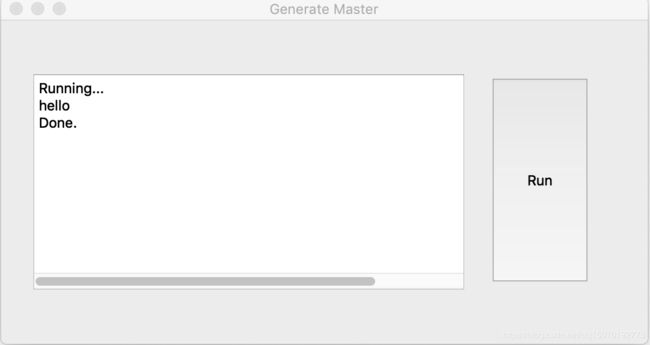
运行以下代码,弹出GUI,单击“run”按钮,显示'Running ...',然后执行函数printhello()输出hello,等待5秒,显示'Done'。
import sys
import time
from PyQt5.QtCore import QObject, pyqtSignal, QEventLoop, QTimer
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QPushButton, QApplication, QTextEdit
from PyQt5.QtGui import QTextCursor
'''
控制台输出定向到Qtextedit中
'''
class Stream(QObject):
"""Redirects console output to text widget."""
newText = pyqtSignal(str)
def write(self, text):
self.newText.emit(str(text))
class GenMast(QMainWindow):
"""Main application window."""
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
# Custom output stream.
sys.stdout = Stream(newText=self.onUpdateText)
def onUpdateText(self, text):
"""Write console output to text widget."""
cursor = self.process.textCursor()
cursor.movePosition(QTextCursor.End)
cursor.insertText(text)
self.process.setTextCursor(cursor)
self.process.ensureCursorVisible()
def closeEvent(self, event):
"""Shuts down application on close."""
# Return stdout to defaults.
sys.stdout = sys.__stdout__
super().closeEvent(event)
def initUI(self):
"""Creates UI window on launch."""
# Button for generating the master list.
btnGenMast = QPushButton('Run', self)
btnGenMast.move(450, 50)
btnGenMast.resize(100, 200)
btnGenMast.clicked.connect(self.genMastClicked)
# Create the text output widget.
self.process = QTextEdit(self, readOnly=True)
self.process.ensureCursorVisible()
self.process.setLineWrapColumnOrWidth(500)
self.process.setLineWrapMode(QTextEdit.FixedPixelWidth)
self.process.setFixedWidth(400)
self.process.setFixedHeight(200)
self.process.move(30, 50)
# Set window size and title, then show the window.
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 600, 300)
self.setWindowTitle('Generate Master')
self.show()
def printhello(self):
print('hello')
def genMastClicked(self):
"""Runs the main function."""
print('Running...')
self.printhello()
loop = QEventLoop()
QTimer.singleShot(2000, loop.quit)
loop.exec_()
print('Done.')
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Run the application.
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
app.aboutToQuit.connect(app.deleteLater)
gui = GenMast()
sys.exit(app.exec_())运行结果:
简单解析:
def genMastClicked(self):
"""Runs the main function."""
print('Running...')
self.printhello()
loop = QEventLoop()
QTimer.singleShot(2000, loop.quit)
loop.exec_()
print('Done.')我们将要运行的函数放在genMastClicked(self)函数中执行。例如printhello()函数。
泛化使用时,只要像定义printhello()函数一样,定义其他函数,然后在genMastClicked(self)中执行即可。
主要参考资料:
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/ask/201670
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/35389494
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39626452/article/details/86700430