Springboot集成Rabbitmq实现延时消费,并实现可靠的消息处理
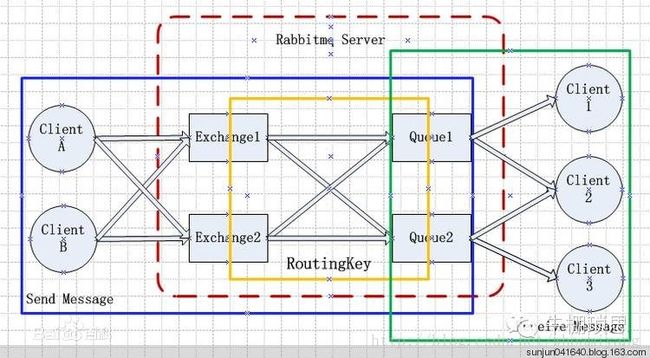
一、Rabbitmq简介
1.1 rabbitmq 架构
1.2 rabbitmq相关组件介绍
- exchange: 交换机,主要用来将生产者发送的消息路由给服务器中的队列。
- routing-key: 消息路由的key,生产者在将消息发到到exchange的时候,需要指定routing-key,这样exchange才知道将这条消息路由给哪些队列。
- message: 消息体,主要由消息头和消息body组成,消息头包括是否持久化,routing-key等。
- binding 将消息队列和exchange进行绑定,一个绑定就是基于路由键将交换机和消息队列连接起来。
- publisher: 消息生产者,可以理解为一个发送消息的客户端应用程序。
- consumer: 消息消费者,可以理解为一个从queue消费消息的应用程序。
- queue : 消息队列,用来保存消息直到发送给消费者,相当于一个容器,一个容器可以放N条消息等待被消费。
- channel : 通道,不管是发送消息还是订阅消息都是通过通道发送出去的,相当于复用TCP连接,因为每次都创建一个TCP连接时非常耗资源的。
1.3 rabbimq常用的3种exchange
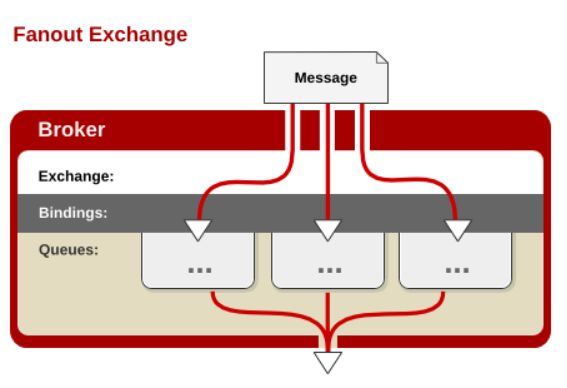
1.3.1 fanout exchange
不处理路由键,你只需要简单的将队列绑定到交换机上。一个发送到交换机的消息都会被转发到与该交换机绑定的所有队列上。
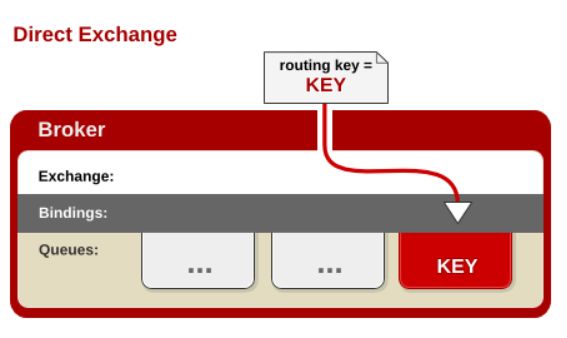
1.3.2 direct exchange
处理路由键。需要将一个队列绑定到交换机上,要求该消息与一个特定的路由键完全匹配。
1.4 rabbitmq消息的可靠传输
一般对于业务不允许由消息丢失的场景来说,消息需要保证被至少传输一次(消费端做幂等),在rabbitmq里面,可能存在几种情况,消息会出现丢失,
- 生产者弄丢了消息,即生产者在将消息发送到exchange的过程中,可能由于网络等原因半路就丢失了,这个时候可以采用rabbitmq的事务机制,也就是在消息发送之前,开启事务,如果没有发送到exchange,生产者收到报错后回滚事务,然会重新发送,如果消息正常到达,则提交事务。但是事务相当于同步操作,整体性能不高,所以一般在生产端建议开启Confirm机制。
- rabbitmq丢了消息,这个时候需要开启rabbitmq的持久化功能,首先是队列开启持久化,同时发送的消息的deliveryMode也设置为持久的,这样,消息就会持久化到磁盘了,即使rabbitmq挂了,重启后也能恢复数据,配合客户端的confirm机制,就算是在还没持久化到磁盘之前,rabbitmq挂了,生产者会重发,在重试次数范围内,只要持久化到磁盘了,就会返回ack。
- 消费者丢了消息,这个需要关闭rabbitmq的自动ack功能,因为自动ack的话,只要消费者收到了就会ack,并不关心消费者是否成功消费, 消费者ack需要由应用自己决定什么时候返回ack。
二、Demo演示
2.1 maven导入rabbitmq依赖包
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.0.2.RELEASE
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-amqp
org.projectlombok
lombok
provided
2.2 新建application
package com.yunsom.springboot.rabbitmq;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootMessageApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootMessageApplication.class, args);
}
}2.3 新建rabbitmq配置文件
在springboot里面,因为使用了其封装好的rabbitmq,在实际的开发中,根据不同的exchange模式,需要自己申明不同的exchange,下面以direct exchange模式为例子进行说明
package com.yunsom.springboot.rabbitmq.config;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Exchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.ExchangeBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.QueueBuilder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class RabbitMqConfig {
/**
* 死信队列 交换机标识符
*/
private static final String DEAD_LETTER_QUEUE_KEY = "x-dead-letter-exchange";
/**
* 死信队列交换机绑定键标识符
*/
private static final String DEAD_LETTER_ROUTING_KEY = "x-dead-letter-routing-key";
/**
* 死信队列里面消息的超时时间
*/
private static final String X_MESSAGE_TTL = "x-message-ttl";
/**
* 声明交换机,支持持久化.
* rabbitmq常用几种exchange,比如direct, fanout, topic,可根据具体业务需求配置
* 命名规范参考 scm3.services,scm3.services.retry,scm3.services.failed
* @return the exchange
*/
@Bean("scm3.materials")
public Exchange directExchange() {
//.durable(true) exchange的持久化
return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange("scm3.materials").durable(true).build();
}
@Bean("scm3.materials.retry")
public Exchange retryDirectExchange() {
return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange("scm3.materials.retry").durable(true).build();
}
@Bean("scm3.materials.fail")
public Exchange failDirectExchange() {
return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange("scm3.materials.fail").durable(true).build();
}
/**
* ##########################################供需关系服务-声明queue#####################################################
*/
/**
* 声明一个队列 .{供需关系主队列} 队列名称参考 【服务名称】@订阅服务标识 如
* material@供需关系,material@供需关系@retry,material@供需关系@failed
* material@采购计划,material@采购计划@retry,@material@采购计划@failed
*
* @return the queue
*/
@Bean("material@supply")
public Queue directQueue() {
return QueueBuilder.durable("material@supply").build();
}
/**
* 供需关系 重试队列
*
* @return
*/
@Bean("material@supply@retry")
public Queue retryDirectQueue() {
Map args = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(3);
// 将消息重新投递到exchange中
args.put(DEAD_LETTER_QUEUE_KEY, "scm3.materials");
args.put(DEAD_LETTER_ROUTING_KEY, "material@supply");
//在队列中延迟30s后,消息重新投递到x-dead-letter-exchage对应的队列中,routingkey是自己配置的
args.put(X_MESSAGE_TTL, 30 * 1000);
return QueueBuilder.durable("material@supply@retry").withArguments(args).build();
}
/**
* 供需关系 失败队列
*
* @return
*/
@Bean("material@supply@failed")
public Queue failDirectQueue() {
return QueueBuilder.durable("material@supply@failed").build();
}
/**
* ###########################################供需关系结束###############################################
*/
/** ########################################用户服务开始############################################ */
/**
* @return the queue
*/
@Bean("material@user")
public Queue userDirectQueue() {
return QueueBuilder.durable("material@user").build();
}
/**
* 用户服务 重试队列
*
* @return
*/
@Bean("material@user@retry")
public Queue userRetryDirectQueue() {
Map args = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(3);
args.put(DEAD_LETTER_QUEUE_KEY, "scm3.materials");
args.put(DEAD_LETTER_ROUTING_KEY, "material@user");
args.put(X_MESSAGE_TTL, 30 * 1000);
return QueueBuilder.durable("material@user@retry").withArguments(args).build();
}
/**
* 供需关系 失败队列
*
* @return
*/
@Bean("material@user@failed")
public Queue userFailDirectQueue() {
return QueueBuilder.durable("material@user@failed").build();
}
/** #####################################用户服务结束################################################ */
/**
* 以下是消费者需要处理的 通过绑定键(rounting key) 将指定队列绑定到一个指定的交换机 .要求该消息与一个特定的路由键完全匹配
* @param queue the queue
* @param exchange the exchange
* @return the binding
*/
/**
* ######################################供需关系绑定###################################################
*/
@Bean
public Binding directBinding(@Qualifier("material@supply") Queue queue,
@Qualifier("scm3.materials") Exchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("direct_rounting_key").noargs();
}
@Bean
public Binding directQueueBinding(@Qualifier("material@supply") Queue queue,
@Qualifier("scm3.materials") Exchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("material@supply").noargs();
}
@Bean
public Binding retryDirectBinding(@Qualifier("material@supply@retry") Queue queue,
@Qualifier("scm3.materials.retry") Exchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("material@supply").noargs();
}
@Bean
public Binding failDirectBinding(@Qualifier("material@supply@failed") Queue queue,
@Qualifier("scm3.materials.fail") Exchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("material@supply").noargs();
}
/**
* ######################################用户服务绑定###################################################
*/
@Bean
public Binding userDirectBinding(@Qualifier("material@user") Queue queue,
@Qualifier("scm3.materials") Exchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("direct_rounting_key").noargs();
}
@Bean
public Binding userDirectQueueBinding(@Qualifier("material@user") Queue queue,
@Qualifier("scm3.materials") Exchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("material@user").noargs();
}
@Bean
public Binding userRetryDirectBinding(@Qualifier("material@user@retry") Queue queue,
@Qualifier("scm3.materials.retry") Exchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("material@user").noargs();
}
@Bean
public Binding userFailDirectBinding(@Qualifier("material@user@failed") Queue queue,
@Qualifier("scm3.materials.fail") Exchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("material@user").noargs();
}
} 2.3 新建生产者
生产者只需要关注将某个消息发到某个exchange上,并指定routingkey即可。
package com.yunsom.springboot.rabbitmq.sender;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.UUID;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import org.springframework.amqp.AmqpException;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.MessageBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.support.CorrelationData;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MessageSender {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Value("${java.rabbitmq.send.service.exchange}")
private String sendExchange;
@Value("${java.rabbitmq.send.service.rountkey}")
private String rountKey;
/**
* demo级别,先本地缓存,真正实现可考虑用redis 如果是放到redis中,有可能exchange一直不给生产者反馈{比如rabbitmq挂了,这种只能重启rabbitmq}
* 如果是网络原因,恢复时间应该很快,下次重发的时候网络好了,进行正常的ack 在redis里面,不能设置消息的过期时间,可以用分布式定时任务,每隔一段时间
* 去查redis里面有没有被消息确认的消息,然后取出来重新发送(存的时候,就要存如当前消息被发送的时间)
*/
Map messageMap = new ConcurrentHashMap();
/**
* confirm机制,当生产者发送消息给exchange的时候,如果没有发到到exchange,会收不到ack,
* 如果送达到了exchange,会回调该方法,如果消息,队列,交换机都设置了持久化,那么消息 在持久化到磁盘后,才会ack给生产者,也就是说生产者收到了ack后,消息肯定是可靠的了,已经
* 到磁盘了
*/
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
/**
* 如果设置了spring.rabbitmq.publisher-confirms=true(默认是false),生产者会收到rabitmq-server返回的ack
* 这个回调方法里面没有原始消息,相当于只是一个通知作用
*/
rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback((correlationData, ack, cause) -> {
if (null != messageMap && !messageMap.isEmpty()) {
if (null != cause && !"".equals(cause)) {
System.out.println("失败原因:" + cause);
// 重发的时候到redis里面取,消费成功了,删除redis里面的msgId
Message message = messageMap.get(correlationData.getId());
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(sendExchange, rountKey, message, correlationData);
} else {
messageMap.remove(correlationData.getId());
System.out.println("消息唯一标识:" + correlationData + ";确认结果:" + ack);
}
}
});
// rabbitTemplate.setMandatory(true);如果设置了mandatory=true(默认为false)
// 这样设置的话,如果消息到达exchange后,没有queue与其绑定,会将消息返给生产者,生产者会
// 回调这个方法
rabbitTemplate
.setReturnCallback((message, replyCode, replyText, tmpExchange, tmpRoutingKey) -> {
System.out.println("send message failed: " + replyCode + " " + replyText);
});
}
/**
* 同步发送消息,效率低
*
* @param receiveMessage
*/
public void syncSend(String receiveMessage) {
Message message = MessageBuilder.withBody(receiveMessage.getBytes())
.setContentType("application/json").build();
// 同步等待的超时时间
rabbitTemplate.setReplyTimeout(3 * 1000);
Object receiveObject = rabbitTemplate.convertSendAndReceive(sendExchange, rountKey, message);
System.out.println("生产者收到消费者返回的消息:" + receiveObject);
}
/**
* 异步发送消息, 异步发送,性能更高,但是无法知道消息是否发送到了exchange,可以开启生产端的重试机制
* spring.rabbitmq.template.retry.enabled=true,默认是false,另外 重试机制默认是重试3次,每次间隔一定时间再次重试,
*
* @param receiveMessage
*/
public void asyncSend(String receiveMessage) {
String msgId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
CorrelationData correlationData = new CorrelationData(msgId);
// 默认消息就是持久化的 MessageDeliveryMode deliveryMode = MessageDeliveryMode.PERSISTENT;
Message message = MessageBuilder.withBody(receiveMessage.getBytes())
.setContentType("application/json").setCorrelationId(msgId).build();
messageMap.put(msgId, message);
// 第4个参数是关联发布确定的参数
try {
// rabbitTemplate.setMandatory(true);
// 如果不开启消息回调,可以不要第4个参数,因为在回调时,可以拿到这个correlationData
// 最后会调用到 void basicPublish(String exchange, String routingKey, boolean mandatory,
// BasicProperties props, byte[] body)
// throws IOException;
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(sendExchange, rountKey, message, correlationData);
log.info("生产者发送消息:" + receiveMessage + ",消息Id:" + msgId);
} catch (AmqpException e) {
log.info("生产者发送消息:" + receiveMessage + "发生了异常:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
} 2.4 新建消费者
2.4.1 用户服务消费者
package com.yunsom.springboot.rabbitmq.consumer;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.support.CorrelationData;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.yunsom.springboot.rabbitmq.service.MessageHandler;
import com.yunsom.springboot.rabbitmq.util.RabbitMqUtil;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
/**
* deliveryTag(唯一标识 ID):当一个消费者向 RabbitMQ 注册后,会建立起一个 Channel , RabbitMQ 会用 basic.deliver
* 方法向消费者推送消息,这个方法携带了一个 delivery tag, 它代表了 RabbitMQ 向该 Channel 投递的这条消息的唯一标识 ID,是一个单调递增的正整数,
* delivery tag 的范围仅限于 Channel
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class UserRabbitMqConsumer {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Resource
private MessageHandler messageHander;
@Value("${java.rabbitmq.consumer.service.retry.exchange}")
private String userServiceListenerRetryExchange;
@Value("${java.rabbitmq.consumer.service.fail.exchange}")
private String userServiceListenerFailExchange;
@Value("${java.rabbitmq.consumer.service.user.retry.routingkey}")
private String userSerivceRetryOrFailRoutingKey;
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
@RabbitListener(queues = {"material@user"})
public void consumerMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
try {
/**
* 消费者自己做幂等
*/
messageHander.HandlerMessage(message, "user");
/** 手动抛出异常,测试消息重试 */
int i = 5 / 0;
} catch (Exception e) {
long retryCount = RabbitMqUtil.getRetryCount(message.getMessageProperties());
CorrelationData correlationData =
new CorrelationData(message.getMessageProperties().getCorrelationId());
Message newMessage = null;
if (retryCount >= 3) {
/** 如果重试次数大于3,则将消息发送到失败队列等待人工处理 */
newMessage = RabbitMqUtil.buildMessage(message);
try {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(userServiceListenerFailExchange,
userSerivceRetryOrFailRoutingKey, newMessage, correlationData);
log.info("用户体系服务消费者消费消息在重试3次后依然失败,将消息发送到fail队列,发送消息:" + new String(newMessage.getBody()));
} catch (Exception e1) {
log.error("用户体系服务消息在发送到fail队列的时候报错:" + e1.getMessage() + ",原始消息:"
+ new String(newMessage.getBody()));
}
} else {
newMessage = RabbitMqUtil.buildMessage2(message);
try {
/** 如果当前消息被重试的次数小于3,则将消息发送到重试队列,等待重新被消费{延迟消费} */
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(userServiceListenerRetryExchange,
userSerivceRetryOrFailRoutingKey, newMessage, correlationData);
log.info("用户服务消费者消费失败,消息发送到重试队列;" + "原始消息:" + new String(newMessage.getBody()) + ";第"
+ (retryCount+1) + "次重试");
} catch (Exception e1) {
// 如果消息在重发的时候,出现了问题,可用nack,经过开发中的实际测试,当消息回滚到消息队列时,
// 这条消息不会回到队列尾部,而是仍是在队列头部,这时消费者会立马又接收到这条消息,进行处理,接着抛出异常,
// 进行回滚,如此反复进行。这种情况会导致消息队列处理出现阻塞,消息堆积,导致正常消息也无法运行
// channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false, true);
// 改为重新发送消息,经过多次重试后,如果重试次数大于3,就不会再走这,直接丢到了fail queue等待人工处理
log.error("消息发送到重试队列的时候,异常了:" + e1.getMessage() + ",重新发送消息");
}
}
} finally {
/**
* 关闭rabbitmq的自动ack,改为手动ack 1、因为自动ack的话,其实不管是否成功消费了,rmq都会在收到消息后立即返给生产者ack,但是很有可能 这条消息我并没有成功消费
* 2、无论消费成功还是消费失败,都要手动进行ack,因为即使消费失败了,也已经将消息重新投递到重试队列或者失败队列
* 如果不进行ack,生产者在超时后会进行消息重发,如果消费者依然不能处理,则会存在死循环
*/
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
}2.4.2 供需关系服务消费者
和用户服务消费者一样,每个消费者只关注本身的业务逻辑,消费异常的处理都是一样的。
2.5 application.properties配置
server.port=6006
spring.application.name=springboot_rabbitmq
#rabbitmq config
#spring.rabbitmq.addresses=单机,集群多个地址以,号隔开
spring.rabbitmq.host=localhost
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
spring.rabbitmq.username=tanjie
spring.rabbitmq.password=tanjie666
spring.rabbitmq.virtual-host=/
#开启rabbitmq的confirm机制,如果消息没有到达exchange,或者exchange在ack生产者的时候,生产者没有收到,那么生产者会进行重发
#如果设置为false,经过测试,不会进行回调
spring.rabbitmq.publisher-confirms=true
#开启rabbitmq的生产端{template}重试机制,默认是false,默认重试3次
spring.rabbitmq.template.retry.enabled=true
#关闭消息的强制路由,当生产者将消息发到exchange,如果没有queue进行绑定, 禁止broker发送basic.return,表示当前消息无人消费
#因为我们配置了消息的持久性,就算没有消费者,消息也在磁盘,默认就是false
spring.rabbitmq.template.mandatory=false
#开启rabbitmq的消费者{listener}重试机制,该重试机制需要设置为自动ack,本次方案和PHP保持一致,如果消费者消费失败后,手动将消息放入死信队列等待消息被重新消费
# 默认该配置为false,设置为true的意思是,如果消费者消费失败了,rabbitmq server会自动重试3次
#spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.retry.enabled=true
#消费端采用手动应答
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.acknowledge-mode=manual
#默认缓存模式是channel,在springboot里面,比如在框架rabbitmqTemplate中使用的通道将会可靠地返回到缓存中
#spring.rabbitmq.cache.connection.mode=channel
#设置默认通道缓存的大小
#spring.rabbitmq.cache.channel.size=10
#配置生产者的配置,包括exchange,routingkey等
java.rabbitmq.send.service.exchange=scm3.materials
java.rabbitmq.send.service.rountkey=direct_rounting_key
#配置supply监听信息
java.rabbitmq.consumer.service.retry.exchange=scm3.materials.retry
java.rabbitmq.consumer.service.fail.exchange=scm3.materials.fail
java.rabbitmq.consumer.service.supply.retry.routingkey=material@supply
#配置user监听信息
java.rabbitmq.consumer.service.user.retry.routingkey=material@user2.6 工具类
package com.yunsom.springboot.rabbitmq.util;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.MessageProperties;
public final class RabbitMqUtil {
private RabbitMqUtil() {}
/**
* 获取消息被重试的次数
*
* @param messageProperties
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static long getRetryCount(MessageProperties messageProperties) {
Long retryCount = 0L;
if (null != messageProperties) {
Map headers = messageProperties.getHeaders();
if (null != headers && !headers.isEmpty()) {
if (headers.containsKey("x-death")) {
List> deaths = (List>) headers.get("x-death");
if (deaths.size() > 0) {
Map death = deaths.get(0);
retryCount = (Long) death.get("count");
}
}
}
}
return retryCount;
}
/**
* 获取原始的routingKey,这个key主要用来追踪一开始的routing-key
*
* @param properties AMQP消息属性
* @param defaultValue 默认值
* @return 原始的routing-key
*/
private static String getOrigRoutingKey(MessageProperties messageProperties,
String defaultValue) {
String routingKey = defaultValue;
if (null != messageProperties) {
Map headers = messageProperties.getHeaders();
if (null != headers && !headers.isEmpty()) {
if (headers.containsKey("x-orig-routing-key")) {
routingKey = headers.get("x-orig-routing-key").toString();
}
}
}
return routingKey;
}
private static MessageProperties createOverrideProperties(MessageProperties messageProperties,
Map headers) {
MessageProperties newMsgProperties = new MessageProperties();
newMsgProperties.setContentType(messageProperties.getContentType());
newMsgProperties.setContentEncoding(messageProperties.getContentEncoding());
// 从已有的properties中创建新的properties,使用提供的headers字段覆盖已有的headers
for (final Map.Entry mapHeaders : headers.entrySet()) {
newMsgProperties.setHeader(mapHeaders.getKey(), mapHeaders.getValue());
}
newMsgProperties.setDeliveryMode(messageProperties.getDeliveryMode());
newMsgProperties.setPriority(messageProperties.getPriority());
newMsgProperties.setCorrelationId(messageProperties.getCorrelationId());
newMsgProperties.setReplyTo(messageProperties.getReplyTo());
newMsgProperties.setExpiration(messageProperties.getExpiration());
newMsgProperties.setMessageId(messageProperties.getMessageId());
newMsgProperties.setTimestamp(messageProperties.getTimestamp());
newMsgProperties.setType(messageProperties.getType());
newMsgProperties.setClusterId(messageProperties.getClusterId());
newMsgProperties.setUserId(messageProperties.getUserId());
newMsgProperties.setAppId(messageProperties.getAppId());
newMsgProperties.setConsumerQueue(messageProperties.getConsumerQueue());
newMsgProperties.setConsumerTag(messageProperties.getConsumerTag());
return newMsgProperties;
}
public static Message buildMessage(Message message) {
Map headers = new HashMap<>();
return buildeLastMessage(message, headers);
}
public static Message buildMessage2(Message message) {
Map headers = message.getMessageProperties().getHeaders();
if (null == headers || headers.isEmpty()) {
headers = new ConcurrentHashMap();
}
return buildeLastMessage(message, headers);
}
private static Message buildeLastMessage(Message message, Map headers) {
headers.put("x-orig-routing-key", getOrigRoutingKey(message.getMessageProperties(),
message.getMessageProperties().getReceivedRoutingKey()));
MessageProperties messageProperties =
createOverrideProperties(message.getMessageProperties(), headers);
Message newMessage = new Message(message.getBody(), messageProperties);
return newMessage;
}
} 2.7 测试
启动springboot后,通过postman发送一个请求,其中模拟用户消费者消费失败,日志如下
2018-05-24 15:32:36.139 INFO 372672 --- [cTaskExecutor-1] c.y.s.r.consumer.UserRabbitMqConsumer : 用户服务消费者消费失败,消息发送到重试队列;原始消息:Hello rabbitmq;第0次重试
2018-05-24 15:32:36.185 DEBUG 372672 --- [nio-6006-exec-2] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name 'dispatcherServlet': assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling
2018-05-24 15:32:36.186 DEBUG 372672 --- [nio-6006-exec-2] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Successfully completed request
2018-05-24 15:33:06.187 INFO 372672 --- [cTaskExecutor-1] c.y.s.r.service.MessageHandlerImpl : 用户服务消费消息:Hello rabbitmq;该消息的id:5add0f1b-6d6f-48b7-90be-9fc3d0514e2b
2018-05-24 15:33:06.191 INFO 372672 --- [cTaskExecutor-1] c.y.s.r.consumer.UserRabbitMqConsumer : 用户服务消费者消费失败,消息发送到重试队列;原始消息:Hello rabbitmq;第1次重试
2018-05-24 15:33:36.269 INFO 372672 --- [cTaskExecutor-1] c.y.s.r.service.MessageHandlerImpl : 用户服务消费消息:Hello rabbitmq;该消息的id:5add0f1b-6d6f-48b7-90be-9fc3d0514e2b
2018-05-24 15:33:36.270 INFO 372672 --- [cTaskExecutor-1] c.y.s.r.consumer.UserRabbitMqConsumer : 用户服务消费者消费失败,消息发送到重试队列;原始消息:Hello rabbitmq;第2次重试
2018-05-24 15:34:06.303 INFO 372672 --- [cTaskExecutor-1] c.y.s.r.service.MessageHandlerImpl : 用户服务消费消息:Hello rabbitmq;该消息的id:5add0f1b-6d6f-48b7-90be-9fc3d0514e2b从日志可以看到,每隔30s重试消息被处理一次,查看rabbitmq的management,在失败队列里面存在消息如下,其中消息id和日志里面的消息id一样
三、补充说明
该方案的实现,对于MQ的消息的可靠传输保证,可能并不完美,后续该方案会持续维护更新。如需相关源码,请留言。