SpringBoot2.1.X 日志集成
一、 日志介绍
1、常用处理java的日志组件 slf4j,log4j,logback,common-logging 等
2、logback介绍:基于Log4j基础上大量改良,不能单独使用,推荐配合日志框架SLF4J来使用
logback当前分成三个模块:logback-core,logback-classic和logback-access;
logback-core是其它两个模块的基础模块
3、Logback的核心对象:
Logger:日志记录器
Appender:指定日志输出的目的地,目的地可以是控制台,文件
Layout:日志布局 格式化日志信息的输出
4、日志级别:DEBUG < INFO < WARN < ERROR
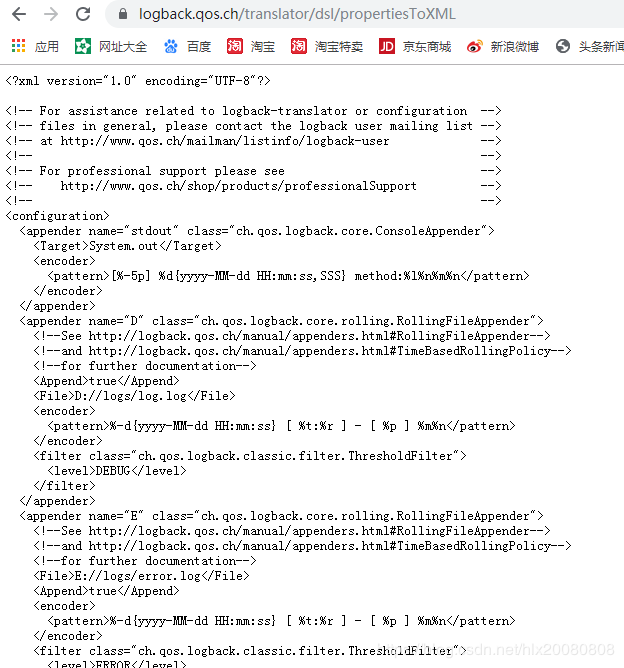
5、Log4j日志转换为logback在线工具(支持log4j.properties转换为logback.xml,不支持 log4j.xml转换为logback.xml)
https://logback.qos.ch/translator/
二、实战操作
使用starters启动器,Spring Boot将使用Logback作为默认日志框架;
spring-boot-starter启动器包含spring-boot-starter-logging启动器并集成了slf4j日志抽象及Logback日志框架。
1、官网介绍:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.1.8.BUILD-SNAPSHOT/reference/htmlsingle/#boot-features-logging
各个组件案例:https://logback.qos.ch/manual/index.html
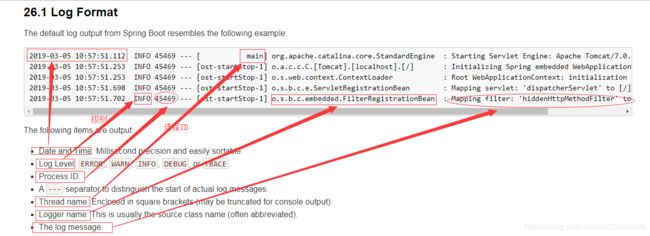
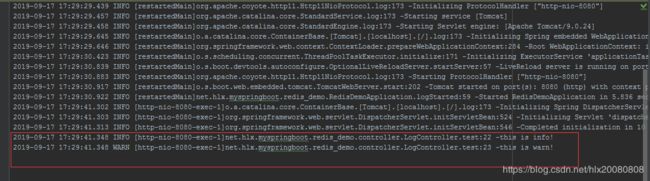
2、分析SpringBoot启动日志
1)默认情况下,Spring Boot将日志输出到控制台
3、整合Logback实战
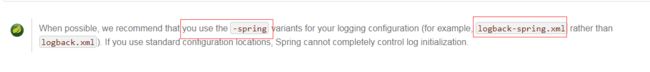
1)创建 日志文件logback-spring.xml,官方推荐 -spring.xml结尾
默认加载加载配置顺序 logback-spring.xml, logback-spring.groovy, logback.xml, or logback.groovy
在resources目录下创建logback-spring.xml文件
%date{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} %-5level[%thread]%logger{56}.%method:%L -%msg%n
ERROR
DENY
ACCEPT
%date{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} %-5level[%thread]%logger{56}.%method:%L -%msg%n
app_log/log/app.info.%d.log
ERROR
%date{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} %-5level[%thread]%logger{56}.%method:%L -%msg%n
app_log/log/app.err.%d.log
1
控制器类
import net.hlx.myspringboot.redis_demo.entity.JsonData;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/log/my")
public class LogController {
//日志对象
private Logger logger= LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@GetMapping("test")
public Object test(){
logger.debug("this is debug!");
logger.info("this is info!");
logger.warn("this is warn!");
logger.error("this is error!");
return JsonData.buildSuccess();
}
}
工程结构图: 启动后
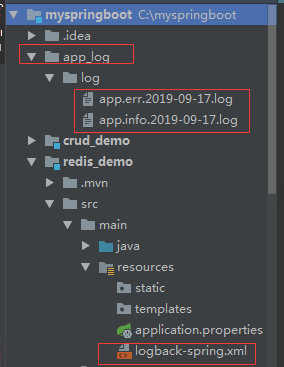
启动:
分别打开日志文件:
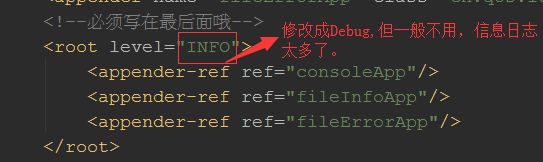
可以修改logback-spring.xml文件,但一般不用Debug哦!要么使用INFO,WARN哦!