mysql-connector-python数据库连接池使用
连接池介绍
官方网站介绍:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/connector-python/en/connector-python-api-mysqlconnectionpool.html
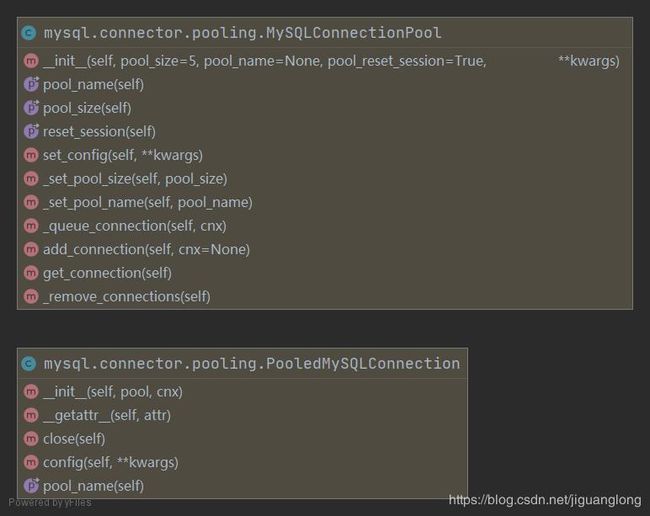
PooledMySQLConnection、MySQLConnectionPool、MySQLConnection三者的关系:
MySQLConnectionPool的 add_connection 方法会把连接(MySQLConnection的实例)会放入连接池中(MySQLConnectionPool的实例)。
MySQLConnectionPool的 get_connection 方法会把连接池中的连接池化,返回PooledMySQLConnection实例。
pcnx = PooledMySQLConnection(cnxpool, cnx)
# cnxpool: A MySQLConnectionPool instance.
# cnx: A MySQLConnection instance.所以,通过(MySQLConnectionPool 的) get_connection 方法得到的连接不是 MySQLConnection 的实例,而是 PooledMySQLConnection 实例。PooledMySQLConnection 的 close 方法也并不是关闭连接,而是调用了( MySQLConnectionPool 的 )add_connection方法把连接(MySQLConnection 的实例)放入了连接池中。
部分源码如下。大部分代码省略掉了,不影响理解。
class PooledMySQLConnection(object):
def __init__(self, pool, cnx):
if not isinstance(pool, MySQLConnectionPool):
raise AttributeError(
"pool should be a MySQLConnectionPool")
if not isinstance(cnx, MySQLConnection):
raise AttributeError(
"cnx should be a MySQLConnection")
self._cnx_pool = pool
self._cnx = cnx
def close(self):
try:
cnx = self._cnx
if self._cnx_pool.reset_session:
cnx.reset_session()
finally:
self._cnx_pool.add_connection(cnx)
self._cnx = None
class MySQLConnectionPool(object):
def __init__(self, pool_size=5, pool_name=None, pool_reset_session=True,
**kwargs):
** *省略 ** *
self._cnx_queue = queue.Queue(self._pool_size)
** *省略 ** *
if kwargs:
self.set_config(**kwargs)
cnt = 0
while cnt < self._pool_size:
self.add_connection()
cnt += 1
def _queue_connection(self, cnx):
** *省略 ** *
try:
self._cnx_queue.put(cnx, block=False)
except queue.Full:
raise errors.PoolError("Failed adding connection; queue is full")
def add_connection(self, cnx=None):
with CONNECTION_POOL_LOCK:
** *省略 ** *
self._queue_connection(cnx)
def get_connection(self):
with CONNECTION_POOL_LOCK:
** *省略 ** *
return PooledMySQLConnection(self, cnx)
报错信息解释
“Failed getting connection; pool exhausted”
如果连接池已经为空,继续调用 get_connection 方法获取连接的时候就会报错。在多线程获取连接时容易发生,特别是当线程数比连接池数还大的时候就更容易发生该错误。
连接池代码样例
import mysql.connector
import mysql.connector.pooling
from threading import Semaphore
from contextlib import contextmanager
mysql_config = {
'user': '***',
'password': '***',
'host': '***',
'port': '3306',
'database': '***'
}
class ReallyMySQLConnectionPool(mysql.connector.pooling.MySQLConnectionPool):
def __init__(self, **mysql_config):
pool_size = mysql_config.get('pool_size', 10)
self._semaphore = Semaphore(pool_size)
super().__init__(**mysql_config)
def get_connection(self):
self._semaphore.acquire()
return super().get_connection()
def put_connection(self, con):
con.close() # con是PooledMySQLConnection的实例
self._semaphore.release()
cnxpool = ReallyMySQLConnectionPool(**mysql_config, pool_name="mypool", pool_size=10,
connection_timeout=30)
@contextmanager
def get_cursor():
try:
con = cnxpool.get_connection()
cursor = con.cursor()
yield cursor
except mysql.connector.Error as err:
print('errno={}'.format(err))
finally:
cursor.close()
cnxpool.put_connection(con)
class PyMysql(object):
@staticmethod
def get_all(sql):
with get_cursor() as cursor:
cursor.execute(sql)
return cursor.fetchall()
if __name__ == '__main__':
import time
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
def t(n):
r1 = PyMysql.get_all("select * from TABLE")
print(str(n) + str(r1))
s = time.time()
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=15) as pool:
for i in range(20):
pool.submit(t, (i))
print(time.time() - s)
思路方式就是:
利用信号量来控制多线程获取的连接数,当一个线程获取连接后,信号量减一。当一个线程释放连接时,信号量加一。当信号量为0时,线程就会等待。