JavaScript笔记(四)
JavaScript笔记(四)
- 五、BOM(浏览器对象模型)
- 1. window对象
- 1.1. window对象属性
- window对象尺寸属性(window.innerHeight/outerHeight)
- window对象位置属性(pageXOffset/screen..)
- window对象导航属性(window.self/opener/parent/top)
- 1.2. window对象方法
- 1. 打开与关闭窗口
- 弹出窗体父子页面传值
- 父页面给子页面传值
- 子页面给父页面传值
- 2. 弹出框(alert(),confirm(),prompt())
- alert()
- confirm() 确认框:常用于确定删除
- prompt()提示框:提示对话框或者输入口令
- 3. 改变窗口位置、大小和内容滚动
- 6.定时器
- setInterval()和clearInterval()
- setTimeout()和clearTimeout():常用作提示信息
- setTimeout()示例:鼠标悬浮几秒之后出现提示信息
- 2. Screen对象
- 3. Location 对象
- 3.1. Location 对象属性
- 3.2. Location 对象方法(assign/reload/replace)
- 4. History对象
- 4.1. History 对象属性(history.length)
- 4.2. History 对象方法(back()/forward()/go())
- 5. Navigator对象(了解)
- 六、事件处理机制
- 1. 事件模型基本概念
- 1.1. 基本概念
- 1.2. 事件对象属性与方法
- 2. 绑定事件处理函数
- 2.1. 绑定HTML元素属性
- 2.2. 绑定JS对象属性
- 2.3. addEventListener与attachEvent(功能最强大)
- addEventListener(可以触发多个事件)
- 3. 事件处理函数的执行环境
- 3.1. 事件处理函数中的this关键字
- 3.2. 访问事件对象
- 3.3. 在代码中触发事件
- 3.4. 取消默认行为(event.preventDefault();)
- 3.5. 阻止事件传播(event.stopPropagation();)
五、BOM(浏览器对象模型)
1. window对象
例如:document、alert()
1.1. window对象属性
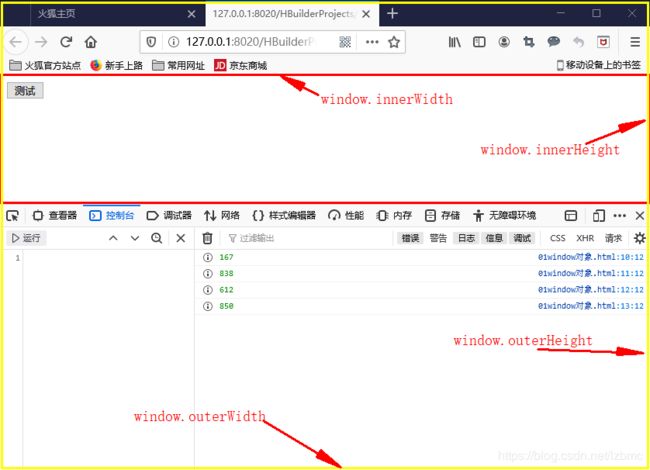
window对象尺寸属性(window.innerHeight/outerHeight)
<input type="button" value="测试" />
<script>
console.info(window.innerHeight); // 返回窗口的文档显示区的高度
console.info(window.innerWidth); // 窗口的文档显示区的宽度
console.info(window.outerHeight); // 整个浏览器的(包括导航栏和底部部分)
console.info(window.outerWidth);
</script>
window对象位置属性(pageXOffset/screen…)
window对象导航属性(window.self/opener/parent/top)
**window.self**返回对当前窗口的引用。等价于 Window 属性
**window.opener**返回对创建此窗口的窗口的引用
**window.parent**返回父窗口
**window.top**返回最顶层的先辈窗口
与下面的window.open方法一起学习。
1.2. window对象方法
1. 打开与关闭窗口
弹出窗体父子页面传值
父页面给子页面传值
要求:父页面不能输入,子页面输入之后,自动填写到父页面,且子页面关闭。
父页面不能输入:disabled;父页面input的值为子页面的input的值
父页面:
<!--disable把标签变成不可用-->
<input type="text" id="parUserName" disabled="disabled" />
<!--在此页面中打开dialog.htnl页面-->
<input type="button" value="弹出窗体" onclick="openDia()" />
<script>
function openDia() {
// 弹出窗体的宽和高,常用于系统的新增修改
// 弹出哪个页面,弹出页面的标题(一般是空字符串)
window.open("02dialog.html", "子窗口", "width=400, height=300;"); // window.open():打开子窗体
}
</script>
子页面:
<input type="text" id="sonUserName" />
<input type="button" value="确定" onclick="ok()" />
<script>
function ok(){
var userName = document.getElementById("sonUserName").value; // 获取input值,赋给父窗体
// document是属于window对象,可省略。写全应该是window.document.
// window.opener:打开者(父窗体)。先获取父页面的window对象,就可以对父页面操作,id赋值为刚刚输入的
window.opener.document. getElementById("parUserName").value = userName; // 子页面给父页面传值
window.close(); // 确定之后,关闭窗口
}
</script>
子页面给父页面传值
父页面输入框的内容在弹出子页面时,子页面也有。
在子页面获得父窗口的值,先要得到父页面
这里需要注意加载的先后顺序,需要定义全局变量,如果是局部变量,在加载子页面时,子页面的元素还没创建完。
父页面:
<input id="parUserName" type="text" />
<input type="button" value="弹出窗体" onclick="openDia()" />
<input type="button" value="关闭窗体" onclick="closeDia()" />
<script>
var v; // 全局变量,下面关闭窗体也需要使用
function openDia() {
v = document.open("03dialog.html", "", "width=400,height=300;"); // 获取子页面
// v.document.getElementById("sonUserName").value =
// document.getElementById("parUserName").value; // 这种写法03dialog.html中还没有读取到,为null
// 需要在子页面(03dialog.html)创建全局变量,js中全局变量都是window对象的
v.userName = document.getElementById("parUserName").value;
}
function closeDia(){
v.close();
}
</script>
子页面:
<input type="text" id="sonUserName"/>
<input type="button" value="确定" onclick="ok()" />
<script>
// js中所有的全局变量都是window对象的
var userName;
function ok(){
userName = document.getElementById("sonUserName").value; // 获取input值,赋给父窗体
// document是属于window对象,可省略。写全应该是window.document.
// 子页面给父页面传值
// window.opener:打开者(父窗体)。先获取父页面的window对象,就可以对父页面操作,id赋值为刚刚输入的
window.opener.document. getElementById("parUserName").value = userName;
window.close(); // 确定之后,关闭窗口
}
// 父页面给子页面传值
document.getElementById("sonUserName").value = userName;
</script>
2. 弹出框(alert(),confirm(),prompt())
alert()
confirm() 确认框:常用于确定删除
<input type="button" id="del" value="删除" onclick="disp_confirm()" />
<script>
// confirm() 确认框:常用于确定删除
function disp_confirm(){
var r = confirm("确认删除吗?");
if (r=true){
document.write("删除!");
}else{
document.write("取消!");
}
}
</script>
prompt()提示框:提示对话框或者输入口令
<input type="button" id="prompt" value="提示" onclick="disp_prompt()" />
<script>
// prompt()提示框:提示用户进行输入的对话框或者输入口令才可以继续进行
function disp_prompt(){
var name = prompt("请输入姓名");
if (name!=null && name!= ""){
document.write("嗨~" + name + "!");
}
}
</script>
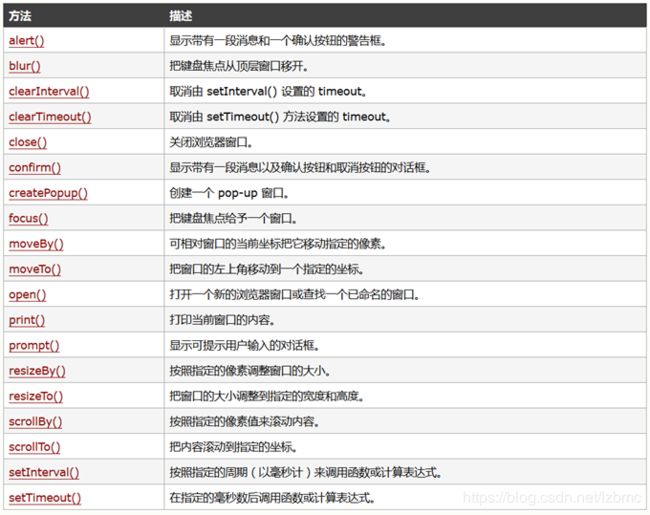
3. 改变窗口位置、大小和内容滚动
moveBy(): 相对窗口的当前坐标把它移动指定的像素;
moveTo():把窗口的左上角移动到一个指定的坐标;
resizeBy():按照指定的像素调整窗口的大小(增大或减小);
resizeTo():把窗口的大小调整到指定的宽度和高度;
scrollBy():按照指定的像素值来滚动内容;
scrollTo():把内容滚动到指定的坐标;
前面四个只对window.open打开的子页面起作用。需要用父页面打开此子页面
父窗口:
<input type="button" value="打开子窗体" onclick="openDia()" />
<script>
function openDia(){
window.open("位置大小滚动.html", "", "width=400, height=300;")
}
</script>
子窗口:
<body style="width: 2000px; height: 2000px; background: lavenderblush;">
<!--div不动-->
<div style="position: fixed;">
<!--前面四个只对window.open打开的子页面起作用。需要用父页面打开此子页面-->
<!--moveBy(): 相对窗口的当前坐标把它移动指定的像素-->
<input type="button" value="moveBy" onclick="window.moveBy(100,100)" />
<!--moveTo():把窗口的左上角移动到一个指定的坐标-->
<input type="button" value="moveTo" onclick="window.moveTo(100,100)" />
<!--resizeBy():按照指定的像素调整窗口的大小(增大或减小)-->
<input type="button" value="resizeBy" onclick="window.resizeBy(100,100)" />
<!--resizeTo():把窗口的大小调整到指定的宽度和高度-->
<input type="button" value="resizeTo" onclick="window.resizeTo(200,200)" />
<!--scrollBy():按照指定的像素值来滚动内容。-->
<input type="button" value="scrollBy" onclick="window.scrollBy(100,100)" />
<!--scrollTo():把内容滚动到指定的坐标-->
<input type="button" value="scrollTo" onclick="window.scrollTo(100,100)" />
</div>
</body>
6.定时器
setInterval()和clearInterval()
setInterval() 方法可按照指定的周期(以毫秒计)来调用函数或计算表达式。
setInterval() 方法会不停地调用函数,直到 clearInterval() 被调用或窗口被关闭。
由 setInterval() 返回的 ID 值可用作 clearInterval() 方法的参数。
var inter = setInterval(code,millisec[,"lang"]) # code 执行的函数或代码串;millisec:执行周期
clearInterval(inter);
<input type="text" id="clock" size="35" />
<script language=javascript>
// setInterval() 方法可按照指定的周期(以毫秒计)来调用函数或计算表达式。
// setInterval() 方法会“不停地”调用函数,直到 clearInterval() 被调用或窗口被关闭。
// 由 setInterval() 返回的 ID 值可用作 clearInterval() 方法的参数。
var inter = window.setInterval("clock()", 50); // 每隔50ms执行clock()函数
function clock() {
var t = new Date();
document.getElementById("clock").value = t;
}
</script>
<!--终止循环-->
<button onclick="window.clearInterval(inter)">Stop interval</button>
setTimeout()和clearTimeout():常用作提示信息
setTimeout() 方法用于在指定的毫秒数后调用函数或计算表达式。
语法
var clo = setTimeout(code,millisec);
clearTimeout(clo);
提示:setTimeout() 只执行 code 一次。如果要多次调用,请使用 setInterval() 或者让 code 自身再次调用 setTimeout()
<input type="text" id="clock2" size="50" />
<script>
// setTimeout() 和 clearTimeout()
// setTimeout() 方法用于在指定的毫秒数后调用函数或计算表达式。只执行一次。
var clo = null;
// 用setTimeout()方法实现setInterval()功能
function clock2() {
var t = new Date();
document.getElementById("clock2").value = t;
clo = setTimeout('clock2()', 50); // 每隔50ms执行clock2()方法,类似递归,反复调用
}
clock2(); // 手动调用
function closeClock() {
clearTimeout(clo);
}
</script>
<button onclick="closeClock()">Stop Timeout</button>
setTimeout()示例:鼠标悬浮几秒之后出现提示信息
<input type="text" id="clock" size="35" />
<script>
var clo = null;
var eventSource = null;
// 鼠标悬浮1000ms之后显示提示信息
function showinfo(arg) // this把当前按钮传过来了。arg就是按钮对象
{
eventSource = arg; // 把arg存到全局变量eventSource中
clo = window.setTimeout(showInfoReal,1000);
}
// 增加提示信息节点
function showInfoReal(){
var span = document.createElement("span");
span.appendChild(document.createTextNode("提示信息")); //就是 span.innerText = "提示信息";
eventSource.parentElement.appendChild(span); // 按钮的父元素添加span
// alert("提示信息");
}
// 鼠标离开,提示信息消除
function cancelShowInfo(arg){
if(arg.parentElement.getElementsByTagName("span").length > 0) // 按钮的父元素获取到的span长度大于0
arg.parentElement.removeChild(arg.parentElement.getElementsByTagName("span")[0]); // 移除第一个span
clearTimeout(clo); // 一定别忘了清除timeout,不清每悬浮一次显示一次且不消除
}
</script>
<div><button onmouseover="showinfo(this)" onmouseout="cancelShowInfo(this)">鼠标提留</button></div>
<div><button onmouseover="showinfo(this)" onmouseout="cancelShowInfo(this)">鼠标提留</button></div>
<div><button onmouseover="showinfo(this)" onmouseout="cancelShowInfo(this)">鼠标提留</button></div>
<div><button onmouseover="showinfo(this)" onmouseout="cancelShowInfo(this)">鼠标提留</button></div>
<div><button onmouseover="showinfo(this)" onmouseout="cancelShowInfo(this)">鼠标提留</button></div>
<div><button onmouseover="showinfo(this)" onmouseout="cancelShowInfo(this)">鼠标提留</button></div>
<div><button onmouseover="showinfo(this)" onmouseout="cancelShowInfo(this)">鼠标提留</button></div>
<div><button onmouseover="showinfo(this)" onmouseout="cancelShowInfo(this)">鼠标提留</button></div>
<div><button onmouseover="showinfo(this)" onmouseout="cancelShowInfo(this)">鼠标提留</button></div>
2. Screen对象
3. Location 对象
3.1. Location 对象属性
<script>
// Location就是获取url的信息
console.info("location.hash:" + location.hash); // 跳转锚点的位置 #后部分
console.info("location.host:" + location.host); // ip地址+端口号
console.info("location.hostname:" + location.hostname); // 主机名(ip地址)
console.info("location.href:" + location.href); // 完整的url
console.info("location.pathname:" + location.pathname); // 端口号后面的页面路径
console.info("location.port:" + location.port); // 端口
console.info("location.protocol:" + location.protocol); // 协议
console.info("location.search:" + location.search); // ?部分(参数)
</script>
3.2. Location 对象方法(assign/reload/replace)
window.location.replace():最重要,例如支付、下单等,不能回退场景
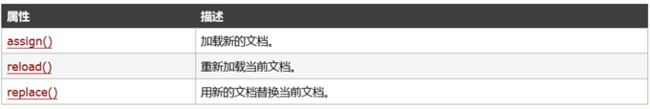
<!--通过js跳转页面:window.location.assign('.html')和window.location.href='.html',更常使用后者-->
<input type="button" value="assign" onclick="window.location.assign('02位置大小滚动.html')" />
<!--reload:和刷新按钮效果一样。可以选择从服务器下载页面(true)或者缓存中下载页面(默认false)-->
<input type="button" value="reload" onclick="window.location.reload('02位置大小滚动.html')" />
<!--replace:页面无法回退。常用于支付功能、下单等-->
<input type="button" value="replace" onclick="window.location.replace('02位置大小滚动.html')" />
4. History对象
就是历史记录
4.1. History 对象属性(history.length)
- history.length:当前窗口(不是浏览器所有的)的历史记录的URL条数
跳转新页面才会增加,回退到之前页面不变
可以理解为当前窗口可以回退的次数+1,不是浏览器所有记录条数。
4.2. History 对象方法(back()/forward()/go())

history.back():后退一级
history.go(-2):后退两级
history.forward():前进一级
5. Navigator对象(了解)
六、事件处理机制
1. 事件模型基本概念
1.1. 基本概念
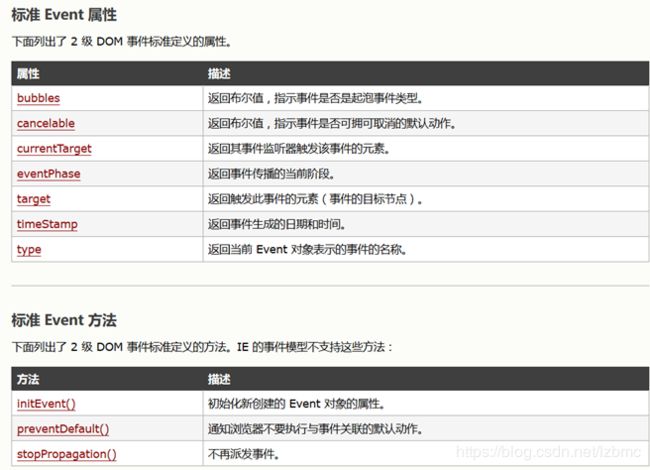
JS事件模型中的概念:
-
事件类型(event type):就是一个用于说明类型的普通字符串,比如“click”代表点击事件、“mouseover”代表鼠标进入某个元素的事件。
-
事件目标(event target):事件模型中的事件源(例如点击按钮,按钮就是事件源),也就是引发事件的对象,比如窗口、document、HTML元素等。Javascript 之所以采用“事件目标”这种说法,是因为DOM事件模型中的事件对象可以通过target属性来访问事件源(事件目标)。
-
事件(event):当浏览器、窗口、document、HTML元素上发生某些事情时,Web浏览器负责生成的对象,该对象封装了所发生事件的详细信息。通常来说,事件至少包括两个属性,即type和target,其中type代表事件类型,target代表事件目标。对于标准的DOM事件模型而言,Web浏览器生成事件对象之后,该事件对象会以参数形式传给事件处理函数,因此定义事件处理时通常会定义一个参数,用于接收事件对象。
-
事件处理器(event handler)或事件监听器(event listener):都是代表用于处理或相应事件的JS函数,因此事件处理器也被称为事件处理函数。在其他GUI事件模型中,事件处理器和事件监听器可能都有一定的差异,但是JS事件模型中,事件处理器和事件监听器是一个东西。当浏览器、窗口、 document、HTML元素上发生某些事情时,Web浏览器就会生成event对象,注册在浏览器、窗口、document、HTML元素上的事件处理器(函数)就会自动执行,这个过程被称为触发。
1.2. 事件对象属性与方法
2. 绑定事件处理函数
2.1. 绑定HTML元素属性
最常用的绑定事件处理器的方法是直接绑定到HTML元素的属性。
比如:
<input type="button" value="按钮" onclick="alert('提示信息')"/>
// 或
<input type="button" value="按钮" onclick="func()"/>
事件属性名称由事件类型前加一个“on”前缀构成,例如onclick、ondbclick等。这些属性的值也被称为事件处理器。
这种事件绑定方式简单易用,但绑定事件处理器时需要直接修改HTML页面代码。
- 两个坏处:
直接修改HTML元素属性,增加了页面逻辑的复杂度。
开发人员需要直接修改HTML页面,不利于团队协作开发。
无法为HTML元素进行批量指定事件处理函数。
2.2. 绑定JS对象属性
开发者无需修改HTML元素的代码,而是将事件处理函数放在Javascript脚本中绑定。
必须先在代码中获得需要绑定事件处理函数的HTML元素对象的Javascript对象,该Javascript对象就是触发事件的事件源,然后给该Javascript对象的onclick等属性赋值,其合法的属性值是一个JS函数的引用。
注意,该属性值不要在函数后添加括号,添加了括号就成了调用该函数了。
function func(){}
document.getElementById("btn").onclick=func; //对 √
document.getElementById("btn").onclick=func(); //错 ×
<input type="button" value="绑定事件方法一" onclick="bindEvent()" />
<input id="btn" type="button" value="绑定事件方法二" />
<script>
// 方法一
function bindEvent(){
alert("点击了我");
}
// 方法二:函数的名称,不能加括号。直接用名称相当于变量
// 加括号是调用函数,立马调用,点击不会触发事件。
// 可以不用去修改html元素
document.getElementById("btn").onclick = bindEvent;
</script>
2.3. addEventListener与attachEvent(功能最强大)
addEventListener(可以触发多个事件)
objectTarget.addEventListener("eventType",handler,captureFlag)
- 第一个参数时事件类型字符串(将前面事件属性去掉前缀”on”,例如click、mousedown、keypress等)
- 第二个参数是事件处理函数
- 第三个参数用于指定监听事件传播的哪个阶段(true表示监听捕获阶段,false表示监听冒泡阶段)。
补充:捕获(capture)和冒泡(bubble)
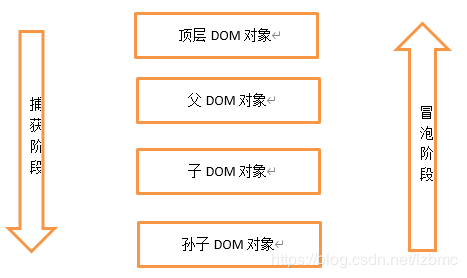
removeEventListener()
该方法与addEventListener()方法相对应,用于删除事件处理器。语法如下:
objectTarget.removeEventListener(“eventType”,handler,captureFlag)
绑定HTML元素属性和js对象属性的事件处理函数的方式:冒泡阶段。
3. 事件处理函数的执行环境
3.1. 事件处理函数中的this关键字
函数属于谁,this就是指谁
<!--!!!函数属于谁,this就是指谁!!!-->
<script>
window.name = "测试窗口";
var showThisName = function() {
alert(this.name); // 函数中this是当前的window对象
}
</script>
<!--1. 直接给HTML元素的事件设置事件处理函数。this与事件源HTML元素没有关系。-->
<input type="button" value="按钮" name="bn" onclick="showThisName();" />
<!--2. 在JS脚本中为JS对象指定一个函数作为事件处理函数。this引用的是JavaScript对象本身。-->
<input id="btn" type="button" value="按钮2" name="bn" />
<script>
document.getElementById("btn").onclick = showThisName; // this是input
</script>
<!--3. 当程序使用的是addEventListener()方法注册事件处理函数,
事件处理函数执行时,this指的同样是事件目标。-->
<input id="btn3" type="button" value="按钮3" name="bn" />
<script>
document.getElementById("btn3").addEventListener("click", showThisName, true); // this是input
</script>
3.2. 访问事件对象
<input type="button" id="btn" value="按钮" name="bn" />
<input type="button" id="btn2" value="按钮2" name="bn" />
<script>
// 访问事件对象:给函数加一个参数
var clickbtn = function(e) { // e就是事件对象
alert(e.target.name); //
//alert(e.currentTarget.name);
//alert(e.target.outerHTML);
}
// 1.使用js对象属性绑定事件
document.getElementById("btn").onclick = clickbtn;
// 2.使用addEventListener
document.getElementById("btn").addEventListener("click", clickbtn, true);
</script>
<!-- 3.HTML元素属性:这种方式没办法使用事件对象,报错:undefined or null-->
<input type="button" id="btn3" value="按钮3" name="bn" onclick="clickbtn()" />
3.3. 在代码中触发事件
<input type="button" id="btn" value="按钮" />
<script>
var clickbtn = function(event) {
event = event || window.event;
if(event.target) {
//对于DOM事件模型,访问事件目标用target属性
alert(event.target.outerHTML);
} else {
//对于IE8及更早版本的IE浏览器,访问事件目标用srcElement属性
alert(event.srcElement.innerHTML);
}
}
// 通过代码点击按钮
document.getElementById("btn").onclick = clickbtn; // 绑定事件
document.getElementById("btn").click(); // 点击按钮
</script>
3.4. 取消默认行为(event.preventDefault();)
注意:
如果要阻止form表单的提交。需要在表单form 的onsubmit事件上return false才可以。按钮上不起作用。
<!--取消默认行为:例如点击超链接不让其跳转页面,或者弹出提示;阻止表单提交-->
<!--方法一:使用返回值取消事件默认行为(禁止跳转)-->
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" onclick="return false)">跳转百度方法一</a>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" onclick="return confirm('确定跳转?')">是否跳转到百度</a>
<br />
<!--方法二:DOM方式取消事件默认行为-->
<a id="mylink" href="http://www.baidu.com">跳转百度方法二</a>
<script>
var killClicks = function(event) {
// 阻止默认行为
event.preventDefault(); //标准方式
alert("超链接被点击");
// //针对IE8及更早版本浏览器的代码
// event = event || window.event;
// if(event.preventDefault)
// event.preventDefault(); //标准方式
// if(event.returnValue)
// event.returnValue = false; //IE8及更早版本的IE浏览器
// alert("超链接被点击");
}
//为按钮绑定事件处理函数(捕获阶段)
document.getElementById("mylink").addEventListener("click", killClicks, true);
3.5. 阻止事件传播(event.stopPropagation();)
外面容器也有此事件,不想它触发时,要阻止事件冒泡传播
<!--不让超链接跳转,并且阻止事传播(捕获或者冒泡)-->
<a id="mylink" href="http://www.baidu.com">跳转到百度(冒泡)</a>
<div id="show"></div>
<script>
//事件冒泡阶段的处理函数
var killClick = function(event) {
//取消事件的默认行为(非常关键)
event.preventDefault();
//阻止事件传播
event.stopPropagation();
document.getElementById("show").innerHTML += '事件冒泡阶段' + event.currentTarget + "
";
}
//在事件冒泡阶段,分别为超链接对象、document对象绑定事件处理函数
document.addEventListener("click", killClick, false);
document.getElementById("mylink").addEventListener("click", killClick, false);
</script>