Android——Json和Gson分别是什么,以及Json 数据的解析方法
转载自:简书 用户hpp417 写的:Android——Json 数据全解析
前言
在现如今的 Android 开发中,尤其是互联网软件,客户端与服务器端的交互可谓是家常便饭,而在 Android 端,通过访问接口接收到服务器端返回的 Json 格式的数据的情形几乎百分之九十的开发者都会遇到,这篇文章就对一些基本的到复杂的 Json 数据的解析进行一个全面的分析,从实战出发,至少希望你看完,能知道怎么做。
一、Json 和 Gson
Json 是当前业内使用最为广泛的一种数据传输格式,大多数服务器端的 API 使用 JSON 作为数据的返回格式,也就是大家知道的,采用键值对的方式来记录数据。
Gson 是 Google 提供的用来在 Java 对象和 JSON 数据之间进行映射的 Java 类库。可以将一个 Json 字符转成一个 Java 对象,或者将一个 Java 转化为 Json 字符串。
其实一句话来说,json 是一种数据格式,便于数据传输、存储、交换,而 gson 是一种组件库,可以把 java 对象数据转换成 json 数据格式。
二、常规的 Json 数据解析
使用 Gson 对 Json 数据进行解析,其实只要根据 Json 数据设计好你的实体类,就没问题了,从实战出发,看 Json:
{ "resultcode":"200",
"reason":"successed!",
"result":{
"base":{
"temp":"24",
"wind_direction":"东北风",
"wind_strength":"2级",
"humidity":"28%",
"time":"17:38"
},
"today":{
"temperature":"15℃~26℃",
"weather":"多云转晴",
"wind":"东北风微风",
"week":"星期日",
},
},
"error_code":0
}
Json 数据的层次都很清晰,键值对的映射也一目了然,上面是一个查询天气的接口返回的数据,从外到内,你可以理解为有 resultcode,reason,result,error_code 四个类对象,而 reslut 里面还包含 base 和 today 两个类对象,以此类推。那么接下来就根据这个数据格式在你的工程中创建对应的实体类,当然你可以使用 Android Studio 的 GsonFormat 插件偷一偷懒:
安装此插件后,新建一个实体类,如新建一个 WeatherEntity 类,然后在类文件中调用菜单使用该插件:
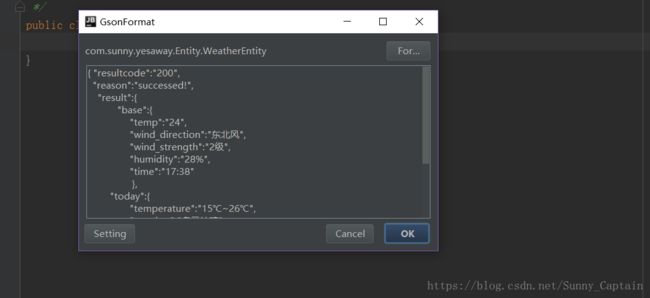
然后把你需要解析的 Json 数据复制粘贴到弹窗中,点 OK 就可以了,是不是很傻瓜式呢:
之后你的实体类就创建好了:
public class WeatherEntity {
/**
* resultcode : 200
* reason : successed!
* result : {"base":{"temp":"24","wind_direction":"东北风","wind_strength":"2级","humidity":"28%","time":"17:38"},"today":{"temperature":"15℃~26℃","weather":"多云转晴","wind":"东北风微风","week":"星期日"}}
* error_code : 0
*/
private String resultcode;
private String reason;
private ResultBean result;
private int error_code;
public String getResultcode() {
return resultcode;
}
public void setResultcode(String resultcode) {
this.resultcode = resultcode;
}
public String getReason() {
return reason;
}
public void setReason(String reason) {
this.reason = reason;
}
public ResultBean getResult() {
return result;
}
public void setResult(ResultBean result) {
this.result = result;
}
public int getError_code() {
return error_code;
}
public void setError_code(int error_code) {
this.error_code = error_code;
}
public static class ResultBean {
/**
* base: {"temp":"24","wind_direction":"东北风","wind_strength":"2级","humidity":"28%","time":"17:38"}
* today : {"temperature":"15℃~26℃","weather":"多云转晴","wind":"东北风微风","week":"星期日"}
*/
private BaseBean base;
private TodayBean today;
public BaseBean getBase() {
return base;
}
public void setBase(BaseBean base) {
this.base= base;
}
public TodayBean getToday() {
return today;
}
public void setToday(TodayBean today) {
this.today = today;
}
public static class BaseBean {
/**
* temp : 24
* wind_direction : 东北风
* wind_strength : 2级
* humidity : 28%
* time : 17:38
*/
private String temp;
private String wind_direction;
private String wind_strength;
private String humidity;
private String time;
public String getTemp() {
return temp;
}
public void setTemp(String temp) {
this.temp = temp;
}
public String getWind_direction() {
return wind_direction;
}
public void setWind_direction(String wind_direction) {
this.wind_direction = wind_direction;
}
public String getWind_strength() {
return wind_strength;
}
public void setWind_strength(String wind_strength) {
this.wind_strength = wind_strength;
}
public String getHumidity() {
return humidity;
}
public void setHumidity(String humidity) {
this.humidity = humidity;
}
public String getTime() {
return time;
}
public void setTime(String time) {
this.time = time;
}
}
public static class TodayBean {
/**
* temperature : 15℃~26℃
* weather : 多云转晴
* wind : 东北风微风
* week : 星期日
*/
private String temperature;
private String weather;
private String wind;
private String week;
public String getTemperature() {
return temperature;
}
public void setTemperature(String temperature) {
this.temperature = temperature;
}
public String getWeather() {
return weather;
}
public void setWeather(String weather) {
this.weather = weather;
}
public String getWind() {
return wind;
}
public void setWind(String wind) {
this.wind = wind;
}
public String getWeek() {
return week;
}
public void setWeek(String week) {
this.week = week;
}
}
}
}
需要提醒各位的是,实体类的类名你可以按自己心情定,但是对象名一定要与 Json 数据中的 key 一一对应,如上面的 “private ResultBean result” 里的 "result",就不能随意取名。
然后在网络请求中直接使用如下语句就可以将 Json 数据转化到你的实体类对象了:
Gson gson = new Gson();
WeatherEntity weatherEntity = gson.fromJson(result, WeatherEntity .class);//result就是服务器返回的Json字符串
三、解析 key 为动态未知字段的 Json 数据
上面是一个很简单很标准的 Json 数据,每一个 key 指向一个 value,key 不会发生变化,不同的只是其中的 value,但是如果该 Json 数据加上以下的内容,你还会不会正常的解析出来呢:
{ "resultcode":"200",
"reason":"successed!",
"result":{
"base":{
"temp":"24",
"wind_direction":"东北风",
"wind_strength":"2级",
"humidity":"28%",
"time":"17:38"
},
"today":{
"temperature":"15℃~26℃",
"weather":"多云转晴",
"wind":"东北风微风",
"week":"星期日",
},
"future":{
"day_20181011":{"temperature":"15℃~26℃","weather":"多云转晴"},
"day_20181012":{"temperature":"16℃~27℃","weather":"晴转多云"},
"day_20181013":{"temperature":"16℃~26℃","weather":"多云转晴"},
}
},
"error_code":0
}
如上述 Json 数据,在天气数据中增加了未来几天的天气,如果你依然按照之前的方法,对该数据进行类实体化,那么可想而知你的 Future 类里会出现以下三个类:day_20181011 类,day_20181011 类和 day_20181011 类,因为 Gson 是高度封装的,你的 key 是什么,他就会根据你的 key 生成对应的类,用这种传统的方法无法对这种 key 是动态的,未知的情况进行处理,像天气这种数据,每一天的日期都不同,采用这种动态值作为 key 的时候,我们该如何解析呢?
答案是,在 Gson 中,我们可以用 Map 的形式来对这种动态 key 的 Json 数据进行解析,例如上面的 Future 类,里面的 key 是动态可变的日期,值是一个固定的天气类数据(温度和天气类型),那么我们可以如下表示该字段:
private Map future;//String就对应着动态变化的day_20181011、day_20181012...
public static class FutureWeather{
private String temperature;
private String weather;
.........//get set 方法...
}
明白了吗,当然对应的该 Map 对象的属性名一定要为 "future",与 Json 数据中的字段对应,这一点一定要注意,所以上述 Json 完整的实体类应为(此处略去 set/get 方法):
public class WeatherEntity {
/**
* resultcode : 200
* reason : successed!
* result : {"base":{"temp":"24","wind_direction":"东北风","wind_strength":"2级","humidity":"28%","time":"17:38"},"today":{"temperature":"15℃~26℃","weather":"多云转晴","wind":"东北风微风","week":"星期日"}}
* error_code : 0
*/
private String resultcode;
private String reason;
private ResultBean result;
private int error_code;
public static class ResultBean {
/**
* base: {"temp":"24","wind_direction":"东北风","wind_strength":"2级","humidity":"28%","time":"17:38"}
* today : {"temperature":"15℃~26℃","weather":"多云转晴","wind":"东北风微风","week":"星期日"}
*/
private BaseBean base;
private TodayBean today;
private Map future;
public static class FutureWeather{
private String temperature;
private String weather;
}
public static class BaseBean {
/**
* temp : 24
* wind_direction : 东北风
* wind_strength : 2级
* humidity : 28%
* time : 17:38
*/
private String temp;
private String wind_direction;
private String wind_strength;
private String humidity;
private String time;
}
public static class TodayBean {
/**
* temperature : 15℃~26℃
* weather : 多云转晴
* wind : 东北风微风
* week : 星期日
*/
private String temperature;
private String weather;
private String wind;
private String week;
}
}
}
接下来你就可以使用同样的方法把 Json 数据转化为实体类了。
使用 Gson 解析 Json 数据的方法今天暂且写这么多,大家可能已经遇到了更为复杂的数据,但是万变不离其宗,也欢迎大家留言讨论~
祝大家敲的刺激,敲的愉快(滑稽)~
作者:hpp417
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/0a748ea5135d
来源:简书
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。