【java】单元测试Mockito中的Mock和Spy
项目中,有些函数需要处理某个服务的返回结果,而在对函数单元测试的时候,又不能启动那些服务,这里就可以利用Mockito工具。Mockito中的Mock和Spy都可用于拦截那些尚未实现或不期望被真实调用的对象和方法,并为其设置自定义行为。二者的区别在于:
1、Mock声明的对象,对函数的调用均执行mock(即虚假函数),不执行真正部分。
2、Spy声明的对象,对函数的调用均执行真正部分。
例:
public class Main {
public void fun(String s) {
System.out.println(s + " : fun");
fun1(s);
fun2(s);
}
public void fun1(String s) {
System.out.println(s + " : fun1");
}
private void fun2(String s) {
System.out.println(s + " : fun2");
}
public int getVal(){
return 5;
}
}Mock使用实例
1、使用doCallRealMethod().when()调用函数真正部分。
2、使用when().thenReturn自定义函数返回值。
import static org.mockito.ArgumentMatchers.anyString;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.doCallRealMethod;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.when;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.mockito.Mock;
import org.mockito.MockitoAnnotations;
public class MainTest {
@Mock
Main mockMain;
@Before
public void init() {
MockitoAnnotations.initMocks(this);
}
@Test
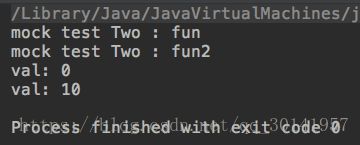
public void testFun() {
// 执行mock,而不是真正部分,所以没有打印任何信息
mockMain.fun("mock test One");
// doCallRealMethod声明后,执行真正部分
// 但是Mock只能对public(fun1)和protected函数进行mock
// 对private函数(fun2)仍执行真正部分
// 所以输出fun和fun2
doCallRealMethod().when(mockMain).fun(anyString());
mockMain.fun("mock test Two");
// 执行mock,输出int的默认值0,而不是5
System.out.println("val: " + mockMain.getVal());
// when声明后,既不走真正部分,也不走mock,直接返回thenReturn()中定义的值
// 注意:该值的类型需要和when中函数返回值类型一致
when(mockMain.getVal()).thenReturn(10);
System.out.println("val: " + mockMain.getVal());
}
}Spy使用实例
1、使用when().thenReturn自定义函数返回值。
import static org.mockito.Mockito.when;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.mockito.MockitoAnnotations;
import org.mockito.Spy;
public class MainTest {
@Spy
Main spyMain;
@Before
public void init() {
MockitoAnnotations.initMocks(this);
}
@Test
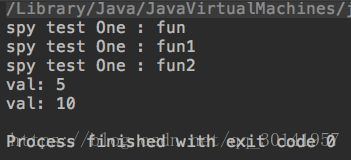
public void testFun() {
// 执行真正部分
spyMain.fun("mock test One");
// 执行真正部分
System.out.println("val: " + spyMain.getVal());
// 自定义返回值
when(spyMain.getVal()).thenReturn(10);
System.out.println("val: " + spyMain.getVal());
}
}
注意事项
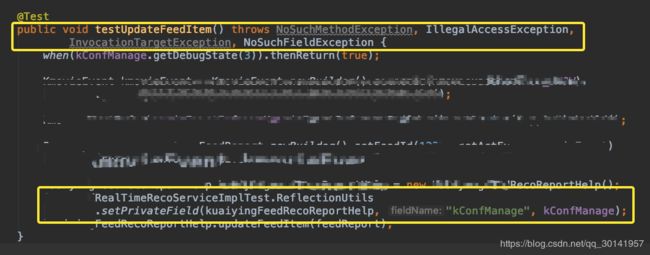
在代码中,xxxService经常声明为private。所以在单元测试中需要使用java的反射机制去设置xxxService的值。下面贴上代码
private static class ReflectionUtils {
/**
* 使用java反射机制
* 获取私有成员变量的值
*/
public static Object getPrivateField(Object instance, String filedName)
throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
Field field = instance.getClass().getDeclaredField(filedName);
field.setAccessible(true);
return field.get(instance);
}
/**
* 设置私有成员的值
*/
public static void setPrivateField(Object instance, String fieldName, Object value)
throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
Field field = instance.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(instance, value);
}
/**
* 访问私有方法
*/
public static Object invokePrivateMethod(Object instance, String methodName,
Class[] classes, long objects)
throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
Method method = instance.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(methodName, classes);
method.setAccessible(true);
return method.invoke(instance, objects);
}
}上面给出的是一个封装好的工具类,调用方法如下:
一定要在方法后面加上下面的代码,否则会出现NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException错误:
throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException,
InvocationTargetException, NoSuchFieldException
参考文章:
1、mockito中实现部分mock两种方式
2、@mock和@spy在mock私有方法的区别,使用@spy模拟私有方法进行测试时sonar统计是有覆盖率的
3、Mockito的参数匹配