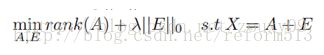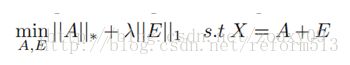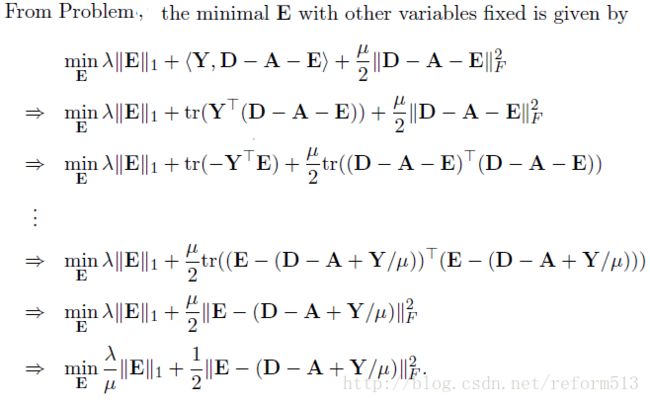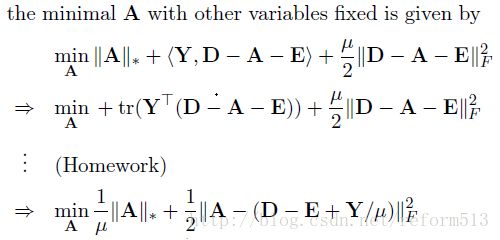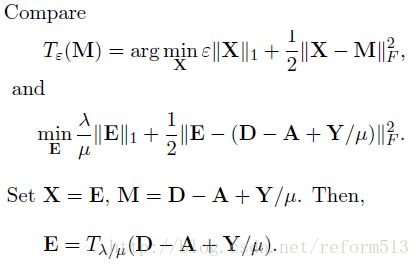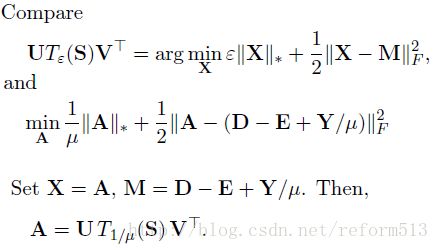拉格朗日乘子解Robust PCA以及Python实现
Robust PCA 将一个矩阵X分解成一个低阶矩阵A和一个稀疏矩阵E.
1. Problem Formulation
由于rank 和 L0 norm 都是non-convex and non-smooth, 所以我们通常把它们转化成求解下列松弛凸优化问题:
nuclear norm and L1 norm 都是 convex 的, 因此可以转化为经典的凸函数优化问题.
2. Solver
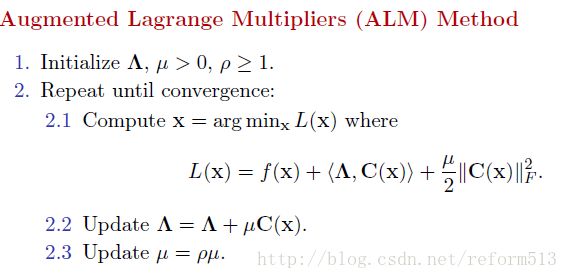
Solving Robust PCA using Augmented Lagrange Multiplier.
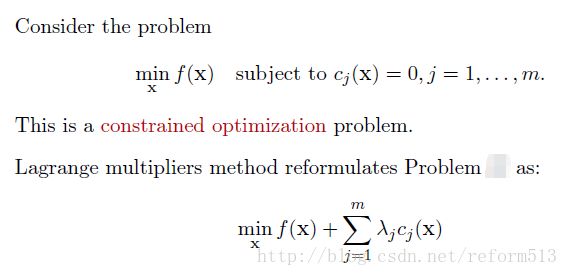
1). General Problem
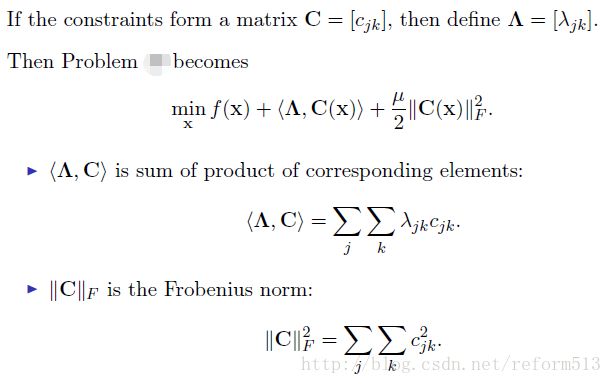
2) Target Problem
3) Minimization
接下来的事情就是找到使cost 最小的A, E 和 Y 了。 我们使用coordinate descent 方法, 即在每一个迭代周期内, 先沿着一个坐标轴方向(e.g., A) 求极值而固定其它所有的坐标轴(e.g., E and Y), 依次循环。
至于Y, the derivative of cost function w.r.t Y is D-A-E, 设置一个步长u, 分别更新A 和 E 后, 再更新Y为 :
Y = Y + u*(D - A - E)
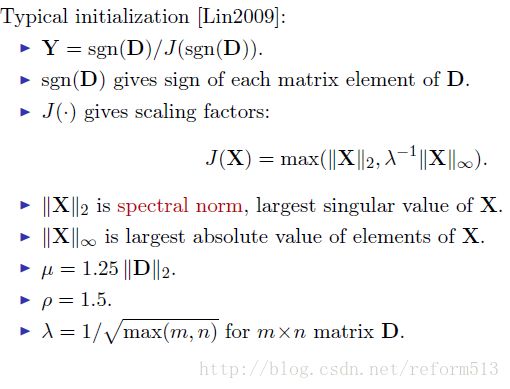
4) Summary
3. Implementation of Python
import numpy as np
from numpy.linalg import norm, svd
def inexact_augmented_lagrange_multiplier(X, lmbda=.01, tol=1e-3,
maxiter=100, verbose=True):
"""
Inexact Augmented Lagrange Multiplier
"""
Y = X
norm_two = norm(Y.ravel(), 2)
norm_inf = norm(Y.ravel(), np.inf) / lmbda
dual_norm = np.max([norm_two, norm_inf])
Y = Y / dual_norm
A = np.zeros(Y.shape)
E = np.zeros(Y.shape)
dnorm = norm(X, 'fro')
mu = 1.25 / norm_two
rho = 1.5
sv = 10.
n = Y.shape[0]
itr = 0
while True:
Eraw = X - A + (1 / mu) * Y
Eupdate = np.maximum(Eraw - lmbda / mu, 0) + np.minimum(Eraw + lmbda / mu, 0)
U, S, V = svd(X - Eupdate + (1 / mu) * Y, full_matrices=False)
svp = (S > 1 / mu).shape[0]
if svp < sv:
sv = np.min([svp + 1, n])
else:
sv = np.min([svp + round(.05 * n), n])
Aupdate = np.dot(np.dot(U[:, :svp], np.diag(S[:svp] - 1 / mu)), V[:svp, :])
A = Aupdate
E = Eupdate
Z = X - A - E
Y = Y + mu * Z
mu = np.min([mu * rho, mu * 1e7])
itr += 1
if ((norm(Z, 'fro') / dnorm) < tol) or (itr >= maxiter):
break
if verbose:
print("Finished at iteration %d" % (itr))
return A, Enum, d1, d2 = 500, 180, 320
dt = np.load('test\\image_data.npz')['data']
data = np.empty((num, d1, d2), dtype=np.uint8)
for i in range(num):
data[i] = cv2.resize(dt[i], dsize=(d2, d1))
X = data.reshape(num, -1).T / 255.0
print(X.shape)
A, E = inexact_augmented_lagrange_multiplier(X)
A = (A.T.reshape(num, d1, d2) * 255).astype('uint8')
E = (E.T.reshape(num, d1, d2) * 255).astype('uint8')
for i in range(data.shape[0]):
cv2.imshow('Original', cv2.resize(data[i], dsize=(d2, d1)))
cv2.imshow('LowRank', cv2.resize(A[i], dsize=(d2, d1)))
cv2.imshow('Sparse', cv2.resize(E[i], dsize=(d2, d1)))
cv2.waitKey(0)