解密EVM实现机制
以下都是来自我的新作《解密EVM机制及合约安全漏洞》里的内容
电子版PDF下载:https://download.csdn.net/download/softgmx/10800947
研究环境:
| OS |
ubuntu 16.04 |
| VM及合约语言 |
EVM/ solidity |
| 合约调试器 |
https://remix.ethereum.org |
| Ethererum源码 |
go语言版本的 |
EVM机制原理
智能合约容易产生漏洞的主要原因:
- 开发人员对EVM的运行机制不了解
- stack、memory和storage是怎样存储数据的
- 合约间调用是怎样实现的,传参和返回值又是怎样在合约间传递的
- 用链上数据做随机数种子时,应注意伪随机的问题(链上数据是可见的,合约里定义的私有变量实际是公开可见的,且一些字段是可以被矿工操纵的)
- solidity封装好的区块访问方法实际上是读取区块链的哪部分数据
- 区块链中交易费用出价高者可以插队优先交易
- gas的消耗实现机制
- 开发人员对solidity编译器的一些内部处理不了解
- send、transfer和call底层转账方法的实现原理和区别
- fallback机制的实现原理
- storage变量的存储和索引原理
- 开发人员对solidity语言不熟悉
- 构造函数
- 鉴权方法
- 日志记录
- 算数溢出
这样我们分析问题可以抽象出的三个层次来研究,如下图:
图一 智能合约的层次
以太坊的智能合约机(EVM)构成及工作原理:
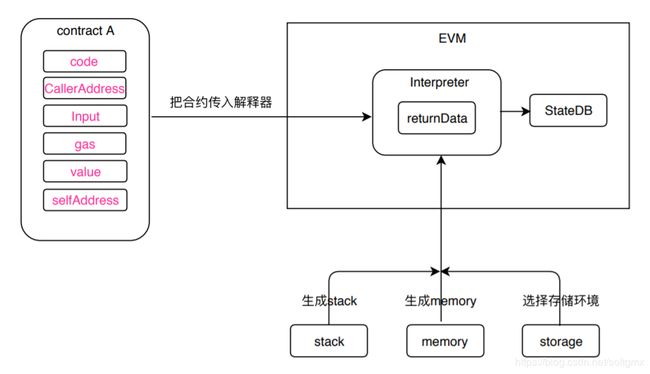
每次我们call一个合约方法时,在call的函数实现里,首先会创建一个contract 类对象,并填充对应的字段值(code,CallerAddress,Input,gas,value,selfAddress),然后把这个contract对象传入EVM的解释器Interpeter进行逐条指令的解释执行,但在开始解释之前,会生成一个新的stack和一个memory对象以用于后面程序的运行,并把结果写入合约地址对应的StateDB。
图二 EVM的工作原理
下面列出了EVM的几个关键类的定义:
图三 对应的类图
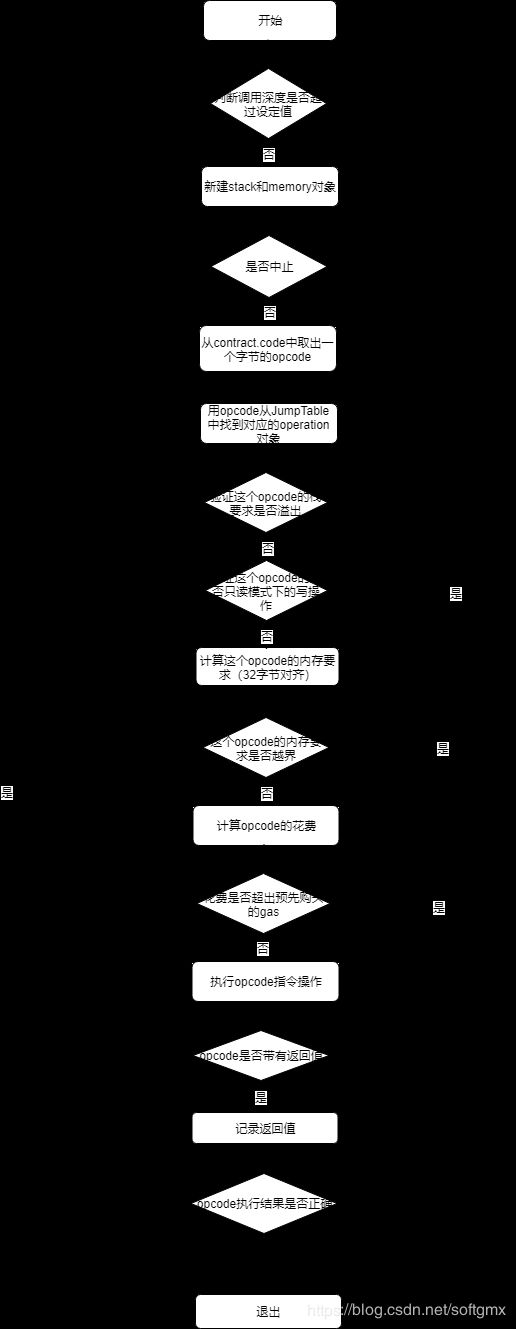
图四 EVM执行智能合约中function的过程
EVM三大核心部件:
- stack
- memory
- storage
Stack的实现:
type Stack struct {
data []*big.Int
}
- 最小单元32字节(最小对齐单位)
- 初始容量1024个元素
- 以动态数组方式实现,理论上可扩容(但实际上一个方法只有1024个元素可用)
- 主要指令push、pop、swap 、dup
- 数据不持久化
- 合约间调用,方法之间不共用栈(一个方法分配一个栈)
- 同一合约的方法调用不产生call, 直是简单的 jump
Memory的实现:
type Memory struct {
store []byte
lastGasCost uint64
}
- 最小单位有一个字节
- 以动态字节数组方式实现,可以扩容
- 类似x86架构里的堆,数据不具有持久性,合约执行完成,数据消失
- 主要指令mload、mstore
Storage的实现:
- 通过StateDB把数据存储在区块链上
- 主要指令sload、sstore
- 数据被持久化(写在链上了,并在所有矿机上同步)
- 容量是2的256次幂,storage[slot]=value, key和value都是32位对齐的
slot=[ 0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000,……
,0xffffffff ffffffff ffffffff ffffffff ffffffff ffffffff ffffffff ffffffff]
命令集分类:
- 算术、逻辑运算(add、sub、mul、div、mod、lt ,gt、 not、xor、or、and等)
- 栈操作、内存操作、存储操作(push、pop、mload、mstore、sload、sstore)
- 区块链操作(address、balance、gas、caller、callvalue、origin、blockhash、timestamp、difficulty、gaslimit、coinbase、log等)
- 执行流操作(jump、jumpi、call、callcode、delegatecall、 staticcall)
命令集具体说明:
| Instruction |
|
|
Explanation |
| stop |
- |
F |
stop execution, identical to return(0,0) |
| add(x, y) |
|
F |
x + y |
| sub(x, y) |
|
F |
x - y |
| mul(x, y) |
|
F |
x * y |
| div(x, y) |
|
F |
x / y |
| sdiv(x, y) |
|
F |
x / y, for signed numbers in two’s complement |
| mod(x, y) |
|
F |
x % y |
| smod(x, y) |
|
F |
x % y, for signed numbers in two’s complement |
| exp(x, y) |
|
F |
x to the power of y |
| not(x) |
|
F |
~x, every bit of x is negated |
| lt(x, y) |
|
F |
1 if x < y, 0 otherwise |
| gt(x, y) |
|
F |
1 if x > y, 0 otherwise |
| slt(x, y) |
|
F |
1 if x < y, 0 otherwise, for signed numbers in two’s complement |
| sgt(x, y) |
|
F |
1 if x > y, 0 otherwise, for signed numbers in two’s complement |
| eq(x, y) |
|
F |
1 if x == y, 0 otherwise |
| iszero(x) |
|
F |
1 if x == 0, 0 otherwise |
| and(x, y) |
|
F |
bitwise and of x and y |
| or(x, y) |
|
F |
bitwise or of x and y |
| xor(x, y) |
|
F |
bitwise xor of x and y |
| byte(n, x) |
|
F |
nth byte of x, where the most significant byte is the 0th byte |
| shl(x, y) |
|
C |
logical shift left y by x bits |
| shr(x, y) |
|
C |
logical shift right y by x bits |
| sar(x, y) |
|
C |
arithmetic shift right y by x bits |
| addmod(x, y, m) |
|
F |
(x + y) % m with arbitrary precision arithmetics |
| mulmod(x, y, m) |
|
F |
(x * y) % m with arbitrary precision arithmetics |
| signextend(i, x) |
|
F |
sign extend from (i*8+7)th bit counting from least significant |
| keccak256(p, n) |
|
F |
keccak(mem[p…(p+n))) |
| sha3(p, n) |
|
F |
keccak(mem[p…(p+n))) |
| jump(label) |
- |
F |
jump to label / code position |
| jumpi(label, cond) |
- |
F |
jump to label if cond is nonzero |
| pc |
|
F |
current position in code |
| pop(x) |
- |
F |
remove the element pushed by x |
| dup1 … dup16 |
|
F |
copy ith stack slot to the top (counting from top) |
| swap1 … swap16 |
* |
F |
swap topmost and ith stack slot below it |
| mload(p) |
|
F |
mem[p..(p+32)) |
| mstore(p, v) |
- |
F |
mem[p..(p+32)) := v |
| mstore8(p, v) |
- |
F |
mem[p] := v & 0xff (only modifies a single byte) |
| sload(p) |
|
F |
storage[p] |
| sstore(p, v) |
- |
F |
storage[p] := v |
| msize |
|
F |
size of memory, i.e. largest accessed memory index |
| gas |
|
F |
gas still available to execution |
| address |
|
F |
address of the current contract / execution context |
| balance(a) |
|
F |
wei balance at address a |
| caller |
|
F |
call sender (excluding delegatecall) |
| callvalue |
|
F |
wei sent together with the current call |
| calldataload(p) |
|
F |
call data starting from position p (32 bytes) |
| calldatasize |
|
F |
size of call data in bytes |
| calldatacopy(t, f, s) |
- |
F |
copy s bytes from calldata at position f to mem at position t |
| codesize |
|
F |
size of the code of the current contract / execution context |
| codecopy(t, f, s) |
- |
F |
copy s bytes from code at position f to mem at position t |
| extcodesize(a) |
|
F |
size of the code at address a |
| extcodecopy(a, t, f, s) |
- |
F |
like codecopy(t, f, s) but take code at address a |
| returndatasize |
|
B |
size of the last returndata |
| returndatacopy(t, f, s) |
- |
B |
copy s bytes from returndata at position f to mem at position t |
| create(v, p, s) |
|
F |
create new contract with code mem[p..(p+s)) and send v wei and return the new address |
| create2(v, n, p, s) |
|
C |
create new contract with code mem[p..(p+s)) at address keccak256( . n . keccak256(mem[p..(p+s))) and send v wei and return the new address |
| call(g, a, v, in, insize, out, outsize) |
|
F |
call contract at address a with input mem[in..(in+insize)) providing g gas and v wei and output area mem[out..(out+outsize)) returning 0 on error (eg. out of gas) and 1 on success |
| callcode(g, a, v, in, insize, out, outsize) |
|
F |
identical to call but only use the code from a and stay in the context of the current contract otherwise |
| delegatecall(g, a, in, insize, out, outsize) |
|
H |
identical to callcode but also keep caller and callvalue |
| staticcall(g, a, in, insize, out, outsize) |
|
B |
identical to call(g, a, 0, in, insize, out, outsize) but do not allow state modifications |
| return(p, s) |
- |
F |
end execution, return data mem[p..(p+s)) |
| revert(p, s) |
- |
B |
end execution, revert state changes, return data mem[p..(p+s)) |
| selfdestruct(a) |
- |
F |
end execution, destroy current contract and send funds to a |
| invalid |
- |
F |
end execution with invalid instruction |
| log0(p, s) |
- |
F |
log without topics and data mem[p..(p+s)) |
| log1(p, s, t1) |
- |
F |
log with topic t1 and data mem[p..(p+s)) |
| log2(p, s, t1, t2) |
- |
F |
log with topics t1, t2 and data mem[p..(p+s)) |
| log3(p, s, t1, t2, t3) |
- |
F |
log with topics t1, t2, t3 and data mem[p..(p+s)) |
| log4(p, s, t1, t2, t3, t4) |
- |
F |
log with topics t1, t2, t3, t4 and data mem[p..(p+s)) |
| origin |
|
F |
transaction sender |
| gasprice |
|
F |
gas price of the transaction |
| blockhash(b) |
|
F |
hash of block nr b - only for last 256 blocks excluding current |
| coinbase |
|
F |
current mining beneficiary |
| timestamp |
|
F |
timestamp of the current block in seconds since the epoch |
| number |
|
F |
current block number |
| difficulty |
|
F |
difficulty of the current block |
| gaslimit |
|
F |
block gas limit of the current block |
storage、memory和stack操作的gas花费对比:
| 指令 |
对应宏定义 |
消耗gas数量 |
| 创建合约 |
TxGasContractCreation |
53000 |
| 创建新账户(对方地址不存在) |
CallNewAccountGas |
25000 |
| SSTORE |
SstoreSetGas |
20000 |
| MSTORE |
MemoryGas |
3*N(N为有多少个32字节) |
| PUSH(1…N) |
GasFastestStep |
3 |