springboot全局异常处理
一.混乱的异常处理
在做web项目时,对于controller,service,dao的三层架构,异常到底在哪一层抛出或者捕获,或者是捕获后包装后再返回还是直接返回,一直是个令人头疼的问题。有时候我们需要重复写很多throws Exception,或者 try catch 块,代码冗余度很高,可读性较差,无法集中于具体业务处理。
下面代码的做法是每一层的异常都直接抛出,在顶层的controller里进行try catch,有异常则封装错误返回。
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public ResultObj delete(@PathVariable int id) {
try {
appTempletService.delete(id);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("delete record error, record id <{}>, error <{}>", id, e.getMessage());
return errorReturn(ErrorCode.SERVER_ERROR, e.getMessage());
}
return successReturn();
}
controller里的方法一多,这种写法就带来大量的冗余代码了。
二.全局异常处理
通过@ControllerAdvance注解,我们可以实现全局的异常控制。
首先看看这个注解的java doc.
/** * Specialization of {@link Component @Component} for classes that declare * {@link ExceptionHandler @ExceptionHandler}, {@link InitBinder @InitBinder}, or * {@link ModelAttribute @ModelAttribute} methods to be shared across * multiple {@code @Controller} classes. * *Classes with {@code @ControllerAdvice} can be declared explicitly as Spring * beans or auto-detected via classpath scanning. All such beans are sorted via * {@link org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationAwareOrderComparator * AnnotationAwareOrderComparator}, i.e. based on * {@link org.springframework.core.annotation.Order @Order} and * {@link org.springframework.core.Ordered Ordered}, and applied in that order * at runtime. For handling exceptions, an {@code @ExceptionHandler} will be * picked on the first advice with a matching exception handler method. For * model attributes and {@code InitBinder} initialization, {@code @ModelAttribute} * and {@code @InitBinder} methods will also follow {@code @ControllerAdvice} order. * *
Note: For {@code @ExceptionHandler} methods, a root exception match will be * preferred to just matching a cause of the current exception, among the handler * methods of a particular advice bean. However, a cause match on a higher-priority * advice will still be preferred to a any match (whether root or cause level) * on a lower-priority advice bean. As a consequence, please declare your primary * root exception mappings on a prioritized advice bean with a corresponding order! * *
By default the methods in an {@code @ControllerAdvice} apply globally to * all Controllers. Use selectors {@link #annotations()}, * {@link #basePackageClasses()}, and {@link #basePackages()} (or its alias * {@link #value()}) to define a more narrow subset of targeted Controllers. * If multiple selectors are declared, OR logic is applied, meaning selected * Controllers should match at least one selector. Note that selector checks * are performed at runtime and so adding many selectors may negatively impact * performance and add complexity. * * @author Rossen Stoyanchev * @author Brian Clozel * @author Sam Brannen * @since 3.2 */
提炼下关键因素:
- 该注解专门用于在那些使用@ExceptionHandler,@InitBinder,@ModelAttribute这三个注解来声明方法的类,以便提供一种全局的(对于多个controller)的能力。翻译成人能听懂的话就是,假如某个类你用了@ExceptionHandler这些注解来修饰方法,你在这个类上再用@ControllerAdvance注解,那么所有的controller都可以使用你@ExceptionHandler标注的方法所提供的特性。
- 该注解带有@Component,使用该注解的类能被spring扫到作为容器里的bean(也会按照@Order注解的顺序来被扫描)。
- 该注解修饰的类中的所有方法,默认会在所有的controller中生效,或者是在该注解的basepackage中配置的controller中生效。
在spring中,我们可以在某个controller中使用@ExceptionHandler注解修饰某个方法,来处理这个controller中出现的异常,但是这个注解的作用域只有当前的controller。
示例如下:
public class TestController{
//...
@ExceptionHandler(value = xxxException.class)
public void handleException(Throwable e) {
//
}
}
那么配合着ControllerAdvance,我们就可以提供一种全局的异常处理能力了,即在所有controller里出现或者该controller调用service方法出现的异常,我们都能捕获的到。
三.代码验证
1.自定义异常
因为@ExceptionHandler注解的value,可以指定异常的类型,我们这里模拟一种自定义Exception和一种通用Exception,观察效果。
public class AccessDenyException extends RuntimeException {
public AccessDenyException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public AccessDenyException() {
super();
}
}
2.编写全局异常处理类
我们这里的处理异常的方式是把异常错误码和错误信息用json串的方式返回到调用方,所以需要在类上加@ResponseBody注解。把返回的对象转成json串再返回。
@ControllerAdvice
@ResponseBody
public class GlobleExceptionHandler {
/**
* 通用异常处理,当该类没有明确具体异常类型的异常或者error,都在该方法进行处理
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(Throwable.class)
public ResultObj exception(Throwable e) {
return handleError(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, e);
}
/**
* 处理自定义的权限错误异常
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(AccessDenyException.class)
public ResultObj accessDeny(AccessDenyException e) {
return handleError(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN, e);
}
public ResultObj handleError(HttpStatus httpStatus, Throwable e) {
return new ResultObj(httpStatus, e.getMessage());
}
}
-
模拟两种异常
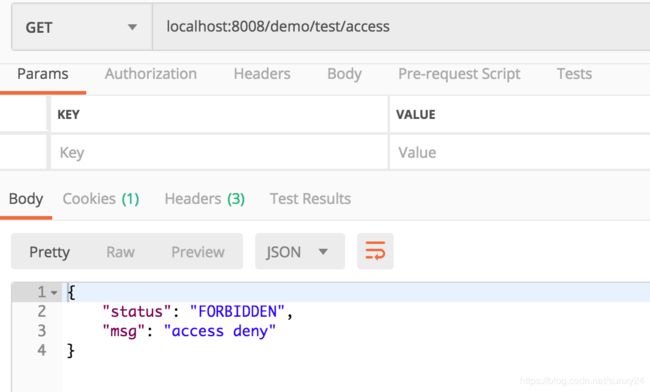
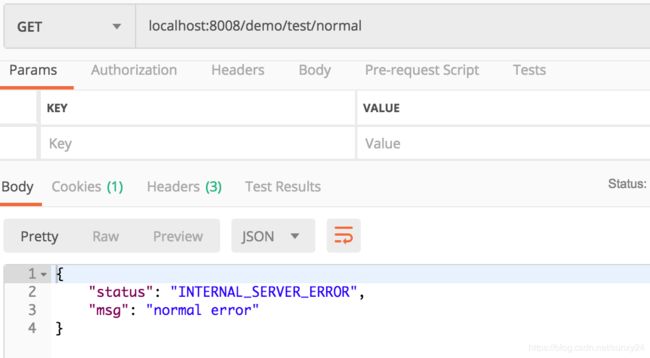
@RestController @RequestMapping("/test") public class TestController { @GetMapping("/access") public ResultObj accessDenyException() { throw new AccessDenyException("access deny"); } @GetMapping("/normal") public ResultObj normalException() { throw new RuntimeException("normal error"); } }
4.运行效果
当为自定义的AccessDeny异常的时候,被全局异常处理类的accessDeny()方法捕获处理。
当为普通的运行时异常的时候,被全局异常处理类的exception()方法捕获处理。