Android 根证书管理与证书验证
PKI 体系依赖证书执行极为关键的身份验证,以此确认服务端的可信任性。证书验证在 SSL/TLS 握手过程中完成,验证过程通常包含三个步骤:
- 验证证书的合法性:这一步主要是验证证书是由合法有效的 CA 签发的。在客户端预先保存一个可靠的 CA 的根证书库,比如 FiexFox、Chrome、Android、Microsoft 等都有维护自己的根证书库,并据此验证服务端证书链的合法性。PKI 体系借助于可靠的中心化身份验证系统,即 CA,为服务端的身份合法性背书。根证书库的安全是 PKI 系统正常工作非常关键的部分。
- 验证证书域名的匹配性:服务端的证书都是为特定域名签发的,证书就像是网站的身份证一样。通过验证域名匹配性,可以有效的防止身份的仿冒,比如经营着 A 网站的经营者,拦截用户请求,并冒充 B 网站的身份,盗取信息。如果客户端不对域名的匹配性做检查,则将造成极大的攻击面,拿到任何一个域名的合法证书的人都将可以仿冒目标服务器。
- 证书钉扎验证:这是 PKI 体系中比较新的一种增强安全性的机制。目前的证书签发机构 CA 非常多,总数大概有几百个上千个,每个 CA 都可以为任何域名签发合法有效的证书,因而众多的 CA 就造成了非常大的攻击面。比如某个 CA 被攻破,或者犯了其它什么错误,为攻击者签发了 www.google.com 等域名的证书,则攻击者将可以仿冒这些网站。证书钉扎机制正是为了解决这一问题而产生——证书钉扎机制中,在客户端将特定域名的证书与特定的签发者绑定,即客户端只承认特定签发者签发的某个域名的证书,而不承认其它 CA 为该域名签发的证书。通过这种方式,来解除大量 CA 这个攻击面的威胁。
在 Android 系统的 Java 应用程序中,证书验证通常由不同层面的多个组件完成。第一步的证书合法性验证,主要由 Java 标准库的 javax.net.ssl.SSLSocket 在 startHandshake() 方法中完成,后面两个步骤由更上层的组件完成,比如 HTTPS 库 OkHttp 等。
本文主要讨论 Android 中根证书库的管理和证书的合法性验证。(本文分析说明主要依据 android-7.1.1/android-7.1.2 系统的行为,可以通过 Google 的 OpenGrok 服务器 阅读 Android 系统的源码。)
Android 的根证书管理
在 AOSP 源码库中,CA 根证书主要存放在 system/ca-certificates 目录下,而在 Android 系统中,则存放在 /system/etc/security/ 目录下,以 Android 7.1.1 系统的 Pixel 设备为例:
sailfish:/ # ls -l /system/etc/security/
total 40
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 2017-07-18 16:37 cacerts
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 2017-07-18 16:36 cacerts_google
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4995 2017-07-18 16:03 mac_permissions.xml
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1073 2017-07-18 16:59 otacerts.zip
其中 cacerts_google 目录下的根证书,主要用于 system/update_engine、external/libbrillo 和 system/core/crash_reporter 等模块,cacerts 目录下的根证书则用于所有的应用。cacerts 目录下的根证书,即 Android 系统的根证书库,像下面这样:
sailfish:/ # ls -l /system/etc/security/cacerts
total 2408
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4767 2017-07-18 16:37 00673b5b.0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 7195 2017-07-18 16:37 02756ea4.0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4919 2017-07-18 16:37 02b73561.0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 7142 2017-07-18 16:37 03f2b8cf.0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2877 2017-07-18 16:37 04f60c28.0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4836 2017-07-18 16:37 052e396b.0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5322 2017-07-18 16:37 08aef7bb.0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4922 2017-07-18 16:37 0d5a4e1c.0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2308 2017-07-18 16:37 0d69c7e1.0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4614 2017-07-18 16:37 10531352.0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4716 2017-07-18 16:37 111e6273.0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5375 2017-07-18 16:37 119afc2e.0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4927 2017-07-18 16:37 124bbd54.0
. . . . . .
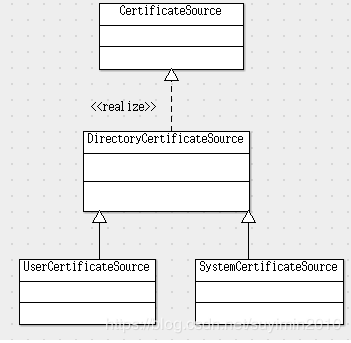
它们都是 PEM 格式的 X.509 证书。Android 系统通过 SystemCertificateSource、DirectoryCertificateSource 和 CertificateSource 等类管理系统根证书库。CertificateSource定义(位于frameworks/base/core/java/android/security/net/config/CertificateSource.java)了可以对根证书库执行的操作,主要是对根证书的获取和查找:
package android.security.net.config;
import java.security.cert.X509Certificate;
import java.util.Set;
/** @hide */
public interface CertificateSource {
Set getCertificates();
X509Certificate findBySubjectAndPublicKey(X509Certificate cert);
X509Certificate findByIssuerAndSignature(X509Certificate cert);
Set findAllByIssuerAndSignature(X509Certificate cert);
void handleTrustStorageUpdate();
}
DirectoryCertificateSource 类则基于文件系统上分开存放的根证书文件的形式保存的根证书库,提供证书的创建、获取和查找操作,这个类的定义(位于frameworks/base/core/java/android/security/net/config/DirectoryCertificateSource.java)如下:
package android.security.net.config;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.os.UserHandle;
import android.util.ArraySet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.util.Pair;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.security.cert.Certificate;
import java.security.cert.CertificateException;
import java.security.cert.CertificateFactory;
import java.security.cert.X509Certificate;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Set;
import libcore.io.IoUtils;
import com.android.org.conscrypt.Hex;
import com.android.org.conscrypt.NativeCrypto;
import javax.security.auth.x500.X500Principal;
/**
* {@link CertificateSource} based on a directory where certificates are stored as individual files
* named after a hash of their SubjectName for more efficient lookups.
* @hide
*/
abstract class DirectoryCertificateSource implements CertificateSource {
private static final String LOG_TAG = "DirectoryCertificateSrc";
private final File mDir;
private final Object mLock = new Object();
private final CertificateFactory mCertFactory;
private Set mCertificates;
protected DirectoryCertificateSource(File caDir) {
mDir = caDir;
try {
mCertFactory = CertificateFactory.getInstance("X.509");
} catch (CertificateException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to obtain X.509 CertificateFactory", e);
}
}
protected abstract boolean isCertMarkedAsRemoved(String caFile);
@Override
public Set getCertificates() {
// TODO: loading all of these is wasteful, we should instead use a keystore style API.
synchronized (mLock) {
if (mCertificates != null) {
return mCertificates;
}
Set certs = new ArraySet();
if (mDir.isDirectory()) {
for (String caFile : mDir.list()) {
if (isCertMarkedAsRemoved(caFile)) {
continue;
}
X509Certificate cert = readCertificate(caFile);
if (cert != null) {
certs.add(cert);
}
}
}
mCertificates = certs;
return mCertificates;
}
}
@Override
public X509Certificate findBySubjectAndPublicKey(final X509Certificate cert) {
return findCert(cert.getSubjectX500Principal(), new CertSelector() {
@Override
public boolean match(X509Certificate ca) {
return ca.getPublicKey().equals(cert.getPublicKey());
}
});
}
@Override
public X509Certificate findByIssuerAndSignature(final X509Certificate cert) {
return findCert(cert.getIssuerX500Principal(), new CertSelector() {
@Override
public boolean match(X509Certificate ca) {
try {
cert.verify(ca.getPublicKey());
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
}
}
});
}
@Override
public Set findAllByIssuerAndSignature(final X509Certificate cert) {
return findCerts(cert.getIssuerX500Principal(), new CertSelector() {
@Override
public boolean match(X509Certificate ca) {
try {
cert.verify(ca.getPublicKey());
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
}
}
});
}
@Override
public void handleTrustStorageUpdate() {
synchronized (mLock) {
mCertificates = null;
}
}
private static interface CertSelector {
boolean match(X509Certificate cert);
}
private Set findCerts(X500Principal subj, CertSelector selector) {
String hash = getHash(subj);
Set certs = null;
for (int index = 0; index >= 0; index++) {
String fileName = hash + "." + index;
if (!new File(mDir, fileName).exists()) {
break;
}
if (isCertMarkedAsRemoved(fileName)) {
continue;
}
X509Certificate cert = readCertificate(fileName);
if (cert == null) {
continue;
}
if (!subj.equals(cert.getSubjectX500Principal())) {
continue;
}
if (selector.match(cert)) {
if (certs == null) {
certs = new ArraySet();
}
certs.add(cert);
}
}
return certs != null ? certs : Collections.emptySet();
}
private X509Certificate findCert(X500Principal subj, CertSelector selector) {
String hash = getHash(subj);
for (int index = 0; index >= 0; index++) {
String fileName = hash + "." + index;
if (!new File(mDir, fileName).exists()) {
break;
}
if (isCertMarkedAsRemoved(fileName)) {
continue;
}
X509Certificate cert = readCertificate(fileName);
if (cert == null) {
continue;
}
if (!subj.equals(cert.getSubjectX500Principal())) {
continue;
}
if (selector.match(cert)) {
return cert;
}
}
return null;
}
private String getHash(X500Principal name) {
int hash = NativeCrypto.X509_NAME_hash_old(name);
return Hex.intToHexString(hash, 8);
}
private X509Certificate readCertificate(String file) {
InputStream is = null;
try {
is = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File(mDir, file)));
return (X509Certificate) mCertFactory.generateCertificate(is);
} catch (CertificateException | IOException e) {
Log.e(LOG_TAG, "Failed to read certificate from " + file, e);
return null;
} finally {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(is);
}
}
}
获取根证书库的 getCertificates() 操作在第一次被调用时,遍历文件系统,并加载系统所有的根证书文件,并缓存起来,以备后面访问。根证书的查找操作,主要依据证书文件的文件名进行,证书文件被要求以 [SubjectName 的哈希值].[Index] 的形式命名。
SystemCertificateSource 类主要定义(位于frameworks/base/core/java/android/security/net/config/SystemCertificateSource.java)了系统根证书库的路径,以及无效一个根证书的机制:
package android.security.net.config;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.os.UserHandle;
import java.io.File;
/**
* {@link CertificateSource} based on the system trusted CA store.
* @hide
*/
public final class SystemCertificateSource extends DirectoryCertificateSource {
private static class NoPreloadHolder {
private static final SystemCertificateSource INSTANCE = new SystemCertificateSource();
}
private final File mUserRemovedCaDir;
private SystemCertificateSource() {
super(new File(System.getenv("ANDROID_ROOT") + "/etc/security/cacerts"));
File configDir = Environment.getUserConfigDirectory(UserHandle.myUserId());
mUserRemovedCaDir = new File(configDir, "cacerts-removed");
}
public static SystemCertificateSource getInstance() {
return NoPreloadHolder.INSTANCE;
}
@Override
protected boolean isCertMarkedAsRemoved(String caFile) {
return new File(mUserRemovedCaDir, caFile).exists();
}
}
Android 系统的根证书位于 /system/etc/security/cacerts/ 目录下。用户可以通过将特定根证书复制到用户配置目录的 cacerts-removed 目录下来无效一个根证书。
Android framework 还提供了另外一个用于加载并访问用户根证书库的组件 UserCertificateSource,这个类的定义(位于 frameworks/base/core/java/android/security/net/config/UserCertificateSource.java)如下:
package android.security.net.config;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.os.UserHandle;
import java.io.File;
/**
* {@link CertificateSource} based on the user-installed trusted CA store.
* @hide
*/
public final class UserCertificateSource extends DirectoryCertificateSource {
private static class NoPreloadHolder {
private static final UserCertificateSource INSTANCE = new UserCertificateSource();
}
private UserCertificateSource() {
super(new File(
Environment.getUserConfigDirectory(UserHandle.myUserId()), "cacerts-added"));
}
public static UserCertificateSource getInstance() {
return NoPreloadHolder.INSTANCE;
}
@Override
protected boolean isCertMarkedAsRemoved(String caFile) {
return false;
}
}
这个组件与 SystemCertificateSource 类似,只是它定义了用户根证书库的路径。
相关的几个组件结构如下图:
证书链合法性验证
有了根证书库之后,根证书库又是如何被用于 SSL/TLS 握手的证书验证过程的呢?
证书的合法性由 Java 标准库的 javax.net.ssl.SSLSocket 在 startHandshake() 方法中完成。对于 Android 系统而言,SSLSocket 基于 OpenSSL 库实现,这一实现由 external/conscrypt 模块提供,SSLSocket 的实现为 OpenSSLSocketImpl 类(位于external/conscrypt/src/main/java/org/conscrypt/OpenSSLSocketImpl.java)。
OpenSSLSocketImpl.startHandshake() 中的 SSL/TLS 握手是一个极为精巧的过程,我们略过详细的握手过程,主要关注证书验证的部分。
OpenSSLSocketImpl.startHandshake() 通过 NativeCrypto 类(位于external/conscrypt/src/main/java/org/conscrypt/NativeCrypto.java)中的静态本地层方法 SSL_do_handshake() 方法执行握手操作:
/**
* Returns the sslSessionNativePointer of the negotiated session. If this is
* a server negotiation, supplying the {@code alpnProtocols} will enable
* ALPN negotiation.
*/
public static native long SSL_do_handshake(long sslNativePointer,
FileDescriptor fd,
SSLHandshakeCallbacks shc,
int timeoutMillis,
boolean client_mode,
byte[] npnProtocols,
byte[] alpnProtocols)
throws SSLException, SocketTimeoutException, CertificateException;
NativeCrypto 类内部定义了一组将会在本地层由与 SSL 握手相关的 OpenSSL C/C++ 代码调用的回调 SSLHandshakeCallbacks,在上面的 SSL_do_handshake() 方法中,这组回调作为参数传入本地层。
SSLHandshakeCallbacks 定义如下:
/**
* A collection of callbacks from the native OpenSSL code that are
* related to the SSL handshake initiated by SSL_do_handshake.
*/
public interface SSLHandshakeCallbacks {
/**
* Verify that we trust the certificate chain is trusted.
*
* @param sslSessionNativePtr pointer to a reference of the SSL_SESSION
* @param certificateChainRefs chain of X.509 certificate references
* @param authMethod auth algorithm name
*
* @throws CertificateException if the certificate is untrusted
*/
public void verifyCertificateChain(long sslSessionNativePtr, long[] certificateChainRefs,
String authMethod) throws CertificateException;
/**
* Called on an SSL client when the server requests (or
* requires a certificate). The client can respond by using
* SSL_use_certificate and SSL_use_PrivateKey to set a
* certificate if has an appropriate one available, similar to
* how the server provides its certificate.
*
* @param keyTypes key types supported by the server,
* convertible to strings with #keyType
* @param asn1DerEncodedX500Principals CAs known to the server
*/
public void clientCertificateRequested(byte[] keyTypes,
byte[][] asn1DerEncodedX500Principals)
throws CertificateEncodingException, SSLException;
/**
* Gets the key to be used in client mode for this connection in Pre-Shared Key (PSK) key
* exchange.
*
* @param identityHint PSK identity hint provided by the server or {@code null} if no hint
* provided.
* @param identity buffer to be populated with PSK identity (NULL-terminated modified UTF-8)
* by this method. This identity will be provided to the server.
* @param key buffer to be populated with key material by this method.
*
* @return number of bytes this method stored in the {@code key} buffer or {@code 0} if an
* error occurred in which case the handshake will be aborted.
*/
public int clientPSKKeyRequested(String identityHint, byte[] identity, byte[] key);
/**
* Gets the key to be used in server mode for this connection in Pre-Shared Key (PSK) key
* exchange.
*
* @param identityHint PSK identity hint provided by this server to the client or
* {@code null} if no hint was provided.
* @param identity PSK identity provided by the client.
* @param key buffer to be populated with key material by this method.
*
* @return number of bytes this method stored in the {@code key} buffer or {@code 0} if an
* error occurred in which case the handshake will be aborted.
*/
public int serverPSKKeyRequested(String identityHint, String identity, byte[] key);
/**
* Called when SSL state changes. This could be handshake completion.
*/
public void onSSLStateChange(long sslSessionNativePtr, int type, int val);
}
其中 verifyCertificateChain() 回调用于服务端证书的验证。Android 系统通过这一回调,将根证书库的管理模块和底层 OpenSSL 的 SSL/TLS 握手及身份验证连接起来。
SSLHandshakeCallbacks 回调由 OpenSSLSocketImpl 实现,verifyCertificateChain() 的实现如下:
@SuppressWarnings("unused") // used by NativeCrypto.SSLHandshakeCallbacks
@Override
public void verifyCertificateChain(long sslSessionNativePtr, long[] certRefs, String authMethod)
throws CertificateException {
try {
X509TrustManager x509tm = sslParameters.getX509TrustManager();
if (x509tm == null) {
throw new CertificateException("No X.509 TrustManager");
}
if (certRefs == null || certRefs.length == 0) {
throw new SSLException("Peer sent no certificate");
}
OpenSSLX509Certificate[] peerCertChain = new OpenSSLX509Certificate[certRefs.length];
for (int i = 0; i < certRefs.length; i++) {
peerCertChain[i] = new OpenSSLX509Certificate(certRefs[i]);
}
// Used for verifyCertificateChain callback
handshakeSession = new OpenSSLSessionImpl(sslSessionNativePtr, null, peerCertChain,
getHostnameOrIP(), getPort(), null);
boolean client = sslParameters.getUseClientMode();
if (client) {
Platform.checkServerTrusted(x509tm, peerCertChain, authMethod, this);
if (sslParameters.isCTVerificationEnabled(getHostname())) {
byte[] tlsData = NativeCrypto.SSL_get_signed_cert_timestamp_list(
sslNativePointer);
byte[] ocspData = NativeCrypto.SSL_get_ocsp_response(sslNativePointer);
CTVerifier ctVerifier = sslParameters.getCTVerifier();
CTVerificationResult result =
ctVerifier.verifySignedCertificateTimestamps(peerCertChain, tlsData, ocspData);
if (result.getValidSCTs().size() == 0) {
throw new CertificateException("No valid SCT found");
}
}
} else {
String authType = peerCertChain[0].getPublicKey().getAlgorithm();
Platform.checkClientTrusted(x509tm, peerCertChain, authType, this);
}
} catch (CertificateException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CertificateException(e);
} finally {
// Clear this before notifying handshake completed listeners
handshakeSession = null;
}
}
OpenSSLSocketImpl 的 verifyCertificateChain() 从 sslParameters 获得 X509TrustManager,然后在 Platform.checkServerTrusted() (com.android.org.conscrypt.Platform,位于 external/conscrypt/src/compat/java/org/conscrypt/Platform.java)中执行服务端证书合法有效性的检查:
public static void checkServerTrusted(X509TrustManager tm, X509Certificate[] chain,
String authType, OpenSSLSocketImpl socket) throws CertificateException {
if (!checkTrusted("checkServerTrusted", tm, chain, authType, Socket.class, socket)
&& !checkTrusted("checkServerTrusted", tm, chain, authType, String.class,
socket.getHandshakeSession().getPeerHost())) {
tm.checkServerTrusted(chain, authType);
}
}
Platform.checkServerTrusted() 通过执行 X509TrustManager 的 checkServerTrusted() 方法执行证书有合法性检查。
X509TrustManager 来自于 OpenSSLSocketImpl 的 sslParameters,那 sslParameters 又来自于哪里呢?OpenSSLSocketImpl 的 sslParameters 由对象的创建者传入:
public class OpenSSLSocketImpl
extends javax.net.ssl.SSLSocket
implements NativeCrypto.SSLHandshakeCallbacks, SSLParametersImpl.AliasChooser,
SSLParametersImpl.PSKCallbacks {
. . . . . .
private final SSLParametersImpl sslParameters;
. . . . . .
protected OpenSSLSocketImpl(SSLParametersImpl sslParameters) throws IOException {
this.socket = this;
this.peerHostname = null;
this.peerPort = -1;
this.autoClose = false;
this.sslParameters = sslParameters;
}
protected OpenSSLSocketImpl(String hostname, int port, SSLParametersImpl sslParameters)
throws IOException {
super(hostname, port);
this.socket = this;
this.peerHostname = hostname;
this.peerPort = port;
this.autoClose = false;
this.sslParameters = sslParameters;
}
protected OpenSSLSocketImpl(InetAddress address, int port, SSLParametersImpl sslParameters)
throws IOException {
super(address, port);
this.socket = this;
this.peerHostname = null;
this.peerPort = -1;
this.autoClose = false;
this.sslParameters = sslParameters;
}
protected OpenSSLSocketImpl(String hostname, int port,
InetAddress clientAddress, int clientPort,
SSLParametersImpl sslParameters) throws IOException {
super(hostname, port, clientAddress, clientPort);
this.socket = this;
this.peerHostname = hostname;
this.peerPort = port;
this.autoClose = false;
this.sslParameters = sslParameters;
}
protected OpenSSLSocketImpl(InetAddress address, int port,
InetAddress clientAddress, int clientPort,
SSLParametersImpl sslParameters) throws IOException {
super(address, port, clientAddress, clientPort);
this.socket = this;
this.peerHostname = null;
this.peerPort = -1;
this.autoClose = false;
this.sslParameters = sslParameters;
}
/**
* Create an SSL socket that wraps another socket. Invoked by
* OpenSSLSocketImplWrapper constructor.
*/
protected OpenSSLSocketImpl(Socket socket, String hostname, int port,
boolean autoClose, SSLParametersImpl sslParameters) throws IOException {
this.socket = socket;
this.peerHostname = hostname;
this.peerPort = port;
this.autoClose = autoClose;
this.sslParameters = sslParameters;
// this.timeout is not set intentionally.
// OpenSSLSocketImplWrapper.getSoTimeout will delegate timeout
// to wrapped socket
}
也就是说,OpenSSLSocketImpl 的 sslParameters 来自于 javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory,即 OpenSSLSocketFactoryImpl。OpenSSLSocketFactoryImpl 定义(位于 external/conscrypt/src/main/java/org/conscrypt/OpenSSLSocketFactoryImpl.java)如下:
package org.conscrypt;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
import java.security.KeyManagementException;
public class OpenSSLSocketFactoryImpl extends javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory {
private final SSLParametersImpl sslParameters;
private final IOException instantiationException;
public OpenSSLSocketFactoryImpl() {
SSLParametersImpl sslParametersLocal = null;
IOException instantiationExceptionLocal = null;
try {
sslParametersLocal = SSLParametersImpl.getDefault();
} catch (KeyManagementException e) {
instantiationExceptionLocal = new IOException("Delayed instantiation exception:");
instantiationExceptionLocal.initCause(e);
}
this.sslParameters = sslParametersLocal;
this.instantiationException = instantiationExceptionLocal;
}
public OpenSSLSocketFactoryImpl(SSLParametersImpl sslParameters) {
this.sslParameters = sslParameters;
this.instantiationException = null;
}
@Override
public String[] getDefaultCipherSuites() {
return sslParameters.getEnabledCipherSuites();
}
@Override
public String[] getSupportedCipherSuites() {
return NativeCrypto.getSupportedCipherSuites();
}
@Override
public Socket createSocket() throws IOException {
if (instantiationException != null) {
throw instantiationException;
}
return new OpenSSLSocketImpl((SSLParametersImpl) sslParameters.clone());
}
@Override
public Socket createSocket(String hostname, int port) throws IOException, UnknownHostException {
return new OpenSSLSocketImpl(hostname, port, (SSLParametersImpl) sslParameters.clone());
}
@Override
public Socket createSocket(String hostname, int port, InetAddress localHost, int localPort)
throws IOException, UnknownHostException {
return new OpenSSLSocketImpl(hostname,
port,
localHost,
localPort,
(SSLParametersImpl) sslParameters.clone());
}
@Override
public Socket createSocket(InetAddress address, int port) throws IOException {
return new OpenSSLSocketImpl(address, port, (SSLParametersImpl) sslParameters.clone());
}
@Override
public Socket createSocket(InetAddress address,
int port,
InetAddress localAddress,
int localPort)
throws IOException {
return new OpenSSLSocketImpl(address,
port,
localAddress,
localPort,
(SSLParametersImpl) sslParameters.clone());
}
@Override
public Socket createSocket(Socket s, String hostname, int port, boolean autoClose)
throws IOException {
return new OpenSSLSocketImplWrapper(s,
hostname,
port,
autoClose,
(SSLParametersImpl) sslParameters.clone());
}
}
OpenSSLSocketImpl 最主要的职责,即是将 SSL/TLS 参数 SSLParametersImpl 与 SSLSocket 粘起来。主要来看默认情况下 SSLParametersImpl 的 X509TrustManager 是什么(位于external/conscrypt/src/main/java/org/conscrypt/SSLParametersImpl.java ):
/**
* Initializes the parameters. Naturally this constructor is used
* in SSLContextImpl.engineInit method which directly passes its
* parameters. In other words this constructor holds all
* the functionality provided by SSLContext.init method.
* See {@link javax.net.ssl.SSLContext#init(KeyManager[],TrustManager[],
* SecureRandom)} for more information
*/
protected SSLParametersImpl(KeyManager[] kms, TrustManager[] tms,
SecureRandom sr, ClientSessionContext clientSessionContext,
ServerSessionContext serverSessionContext, String[] protocols)
throws KeyManagementException {
this.serverSessionContext = serverSessionContext;
this.clientSessionContext = clientSessionContext;
// initialize key managers
if (kms == null) {
x509KeyManager = getDefaultX509KeyManager();
// There's no default PSK key manager
pskKeyManager = null;
} else {
x509KeyManager = findFirstX509KeyManager(kms);
pskKeyManager = findFirstPSKKeyManager(kms);
}
// initialize x509TrustManager
if (tms == null) {
x509TrustManager = getDefaultX509TrustManager();
} else {
x509TrustManager = findFirstX509TrustManager(tms);
}
// initialize secure random
// We simply use the SecureRandom passed in by the caller. If it's
// null, we don't replace it by a new instance. The native code below
// then directly accesses /dev/urandom. Not the most elegant solution,
// but faster than going through the SecureRandom object.
secureRandom = sr;
// initialize the list of cipher suites and protocols enabled by default
enabledProtocols = NativeCrypto.checkEnabledProtocols(
protocols == null ? NativeCrypto.DEFAULT_PROTOCOLS : protocols).clone();
boolean x509CipherSuitesNeeded = (x509KeyManager != null) || (x509TrustManager != null);
boolean pskCipherSuitesNeeded = pskKeyManager != null;
enabledCipherSuites = getDefaultCipherSuites(
x509CipherSuitesNeeded, pskCipherSuitesNeeded);
}
protected static SSLParametersImpl getDefault() throws KeyManagementException {
SSLParametersImpl result = defaultParameters;
if (result == null) {
// single-check idiom
defaultParameters = result = new SSLParametersImpl(null,
null,
null,
new ClientSessionContext(),
new ServerSessionContext(),
null);
}
return (SSLParametersImpl) result.clone();
}
. . . . . .
/**
* @return X.509 trust manager or {@code null} for none.
*/
protected X509TrustManager getX509TrustManager() {
return x509TrustManager;
}
. . . . . .
/**
* Gets the default X.509 trust manager.
*
* TODO: Move this to a published API under dalvik.system.
*/
public static X509TrustManager getDefaultX509TrustManager()
throws KeyManagementException {
X509TrustManager result = defaultX509TrustManager;
if (result == null) {
// single-check idiom
defaultX509TrustManager = result = createDefaultX509TrustManager();
}
return result;
}
private static X509TrustManager createDefaultX509TrustManager()
throws KeyManagementException {
try {
String algorithm = TrustManagerFactory.getDefaultAlgorithm();
TrustManagerFactory tmf = TrustManagerFactory.getInstance(algorithm);
tmf.init((KeyStore) null);
TrustManager[] tms = tmf.getTrustManagers();
X509TrustManager trustManager = findFirstX509TrustManager(tms);
if (trustManager == null) {
throw new KeyManagementException(
"No X509TrustManager in among default TrustManagers: "
+ Arrays.toString(tms));
}
return trustManager;
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new KeyManagementException(e);
} catch (KeyStoreException e) {
throw new KeyManagementException(e);
}
}
将 createDefaultX509TrustManager() 的代码复制到我们的应用程序中,就像下面这样:
private X509TrustManager systemDefaultTrustManager() {
try {
TrustManagerFactory trustManagerFactory = TrustManagerFactory.getInstance(
TrustManagerFactory.getDefaultAlgorithm());
trustManagerFactory.init((KeyStore) null);
TrustManager[] trustManagers = trustManagerFactory.getTrustManagers();
if (trustManagers.length != 1 || !(trustManagers[0] instanceof X509TrustManager)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected default trust managers:"
+ Arrays.toString(trustManagers));
}
return (X509TrustManager) trustManagers[0];
} catch (GeneralSecurityException e) {
throw new AssertionError(); // The system has no TLS. Just give up.
}
}
在应用程序执行时打断点,借助于 Android Studio 确认系统默认的 X509TrustManager 是什么,不难确认,它是 android.security.net.config.RootTrustManager。android.security.net.config.RootTrustManager 的 checkServerTrusted() 定义(位于 frameworks/base/core/java/android/security/net/config/RootTrustManager.java)如下:
@Override
public void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] certs, String authType, Socket socket)
throws CertificateException {
if (socket instanceof SSLSocket) {
SSLSocket sslSocket = (SSLSocket) socket;
SSLSession session = sslSocket.getHandshakeSession();
if (session == null) {
throw new CertificateException("Not in handshake; no session available");
}
String host = session.getPeerHost();
NetworkSecurityConfig config = mConfig.getConfigForHostname(host);
config.getTrustManager().checkServerTrusted(certs, authType, socket);
} else {
// Not an SSLSocket, use the hostname unaware checkServerTrusted.
checkServerTrusted(certs, authType);
}
}
@Override
public void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] certs, String authType, SSLEngine engine)
throws CertificateException {
SSLSession session = engine.getHandshakeSession();
if (session == null) {
throw new CertificateException("Not in handshake; no session available");
}
String host = session.getPeerHost();
NetworkSecurityConfig config = mConfig.getConfigForHostname(host);
config.getTrustManager().checkServerTrusted(certs, authType, engine);
}
@Override
public void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] certs, String authType)
throws CertificateException {
if (mConfig.hasPerDomainConfigs()) {
throw new CertificateException(
"Domain specific configurations require that hostname aware"
+ " checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[], String, String) is used");
}
NetworkSecurityConfig config = mConfig.getConfigForHostname("");
config.getTrustManager().checkServerTrusted(certs, authType);
}
/**
* Hostname aware version of {@link #checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[], String)}.
* This interface is used by conscrypt and android.net.http.X509TrustManagerExtensions do not
* modify without modifying those callers.
*/
public List checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] certs, String authType,
String hostname) throws CertificateException {
if (hostname == null && mConfig.hasPerDomainConfigs()) {
throw new CertificateException(
"Domain specific configurations require that the hostname be provided");
}
NetworkSecurityConfig config = mConfig.getConfigForHostname(hostname);
return config.getTrustManager().checkServerTrusted(certs, authType, hostname);
}
NetworkSecurityConfig 的 getTrustManager() 定义(位于 frameworks/base/core/java/android/security/net/config/NetworkSecurityConfig.java)如下:
public NetworkSecurityTrustManager getTrustManager() {
synchronized(mTrustManagerLock) {
if (mTrustManager == null) {
mTrustManager = new NetworkSecurityTrustManager(this);
}
return mTrustManager;
}
}
NetworkSecurityConfig 将管根证书库的组件 SystemCertificateSource 、 UserCertificateSource 和执行证书合法性验证的 NetworkSecurityTrustManager 粘起来:
public static final Builder getDefaultBuilder(int targetSdkVersion) {
Builder builder = new Builder()
.setCleartextTrafficPermitted(DEFAULT_CLEARTEXT_TRAFFIC_PERMITTED)
.setHstsEnforced(DEFAULT_HSTS_ENFORCED)
// System certificate store, does not bypass static pins.
.addCertificatesEntryRef(
new CertificatesEntryRef(SystemCertificateSource.getInstance(), false));
// Applications targeting N and above must opt in into trusting the user added certificate
// store.
if (targetSdkVersion <= Build.VERSION_CODES.M) {
// User certificate store, does not bypass static pins.
builder.addCertificatesEntryRef(
new CertificatesEntryRef(UserCertificateSource.getInstance(), false));
}
return builder;
}
同时 NetworkSecurityConfig 还提供了一些根据特定条件查找根证书的操作:
public Set getTrustAnchors() {
synchronized (mAnchorsLock) {
if (mAnchors != null) {
return mAnchors;
}
// Merge trust anchors based on the X509Certificate.
// If we see the same certificate in two TrustAnchors, one with overridesPins and one
// without, the one with overridesPins wins.
// Because mCertificatesEntryRefs is sorted with all overridesPins anchors coming first
// this can be simplified to just using the first occurrence of a certificate.
Map anchorMap = new ArrayMap<>();
for (CertificatesEntryRef ref : mCertificatesEntryRefs) {
Set anchors = ref.getTrustAnchors();
for (TrustAnchor anchor : anchors) {
X509Certificate cert = anchor.certificate;
if (!anchorMap.containsKey(cert)) {
anchorMap.put(cert, anchor);
}
}
}
ArraySet anchors = new ArraySet(anchorMap.size());
anchors.addAll(anchorMap.values());
mAnchors = anchors;
return mAnchors;
}
}
. . . . . .
public NetworkSecurityTrustManager getTrustManager() {
synchronized(mTrustManagerLock) {
if (mTrustManager == null) {
mTrustManager = new NetworkSecurityTrustManager(this);
}
return mTrustManager;
}
}
/** @hide */
public TrustAnchor findTrustAnchorBySubjectAndPublicKey(X509Certificate cert) {
for (CertificatesEntryRef ref : mCertificatesEntryRefs) {
TrustAnchor anchor = ref.findBySubjectAndPublicKey(cert);
if (anchor != null) {
return anchor;
}
}
return null;
}
/** @hide */
public TrustAnchor findTrustAnchorByIssuerAndSignature(X509Certificate cert) {
for (CertificatesEntryRef ref : mCertificatesEntryRefs) {
TrustAnchor anchor = ref.findByIssuerAndSignature(cert);
if (anchor != null) {
return anchor;
}
}
return null;
}
/** @hide */
public Set findAllCertificatesByIssuerAndSignature(X509Certificate cert) {
Set certs = new ArraySet();
for (CertificatesEntryRef ref : mCertificatesEntryRefs) {
certs.addAll(ref.findAllCertificatesByIssuerAndSignature(cert));
}
return certs;
}
真正执行证书合法性验证的还不是 NetworkSecurityTrustManager,而是 TrustManagerImpl(位于 external/conscrypt/src/platform/java/org/conscrypt/TrustManagerImpl.java),由 NetworkSecurityTrustManager 的定义(位于frameworks/base/core/java/android/security/net/config/NetworkSecurityTrustManager.java)不难看出这一点:
public NetworkSecurityTrustManager(NetworkSecurityConfig config) {
if (config == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("config must not be null");
}
mNetworkSecurityConfig = config;
try {
TrustedCertificateStoreAdapter certStore = new TrustedCertificateStoreAdapter(config);
// Provide an empty KeyStore since TrustManagerImpl doesn't support null KeyStores.
// TrustManagerImpl will use certStore to lookup certificates.
KeyStore store = KeyStore.getInstance(KeyStore.getDefaultType());
store.load(null);
mDelegate = new TrustManagerImpl(store, null, certStore);
} catch (GeneralSecurityException | IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
. . . . . .
@Override
public void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] certs, String authType)
throws CertificateException {
checkServerTrusted(certs, authType, (String) null);
}
@Override
public void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] certs, String authType, Socket socket)
throws CertificateException {
List trustedChain =
mDelegate.getTrustedChainForServer(certs, authType, socket);
checkPins(trustedChain);
}
@Override
public void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] certs, String authType, SSLEngine engine)
throws CertificateException {
List trustedChain =
mDelegate.getTrustedChainForServer(certs, authType, engine);
checkPins(trustedChain);
}
/**
* Hostname aware version of {@link #checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[], String)}.
* This interface is used by conscrypt and android.net.http.X509TrustManagerExtensions do not
* modify without modifying those callers.
*/
public List checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] certs, String authType,
String host) throws CertificateException {
List trustedChain = mDelegate.checkServerTrusted(certs, authType, host);
checkPins(trustedChain);
return trustedChain;
}
private void checkPins(List chain) throws CertificateException {
PinSet pinSet = mNetworkSecurityConfig.getPins();
if (pinSet.pins.isEmpty()
|| System.currentTimeMillis() > pinSet.expirationTime
|| !isPinningEnforced(chain)) {
return;
}
Set pinAlgorithms = pinSet.getPinAlgorithms();
Map digestMap = new ArrayMap(
pinAlgorithms.size());
for (int i = chain.size() - 1; i >= 0 ; i--) {
X509Certificate cert = chain.get(i);
byte[] encodedSPKI = cert.getPublicKey().getEncoded();
for (String algorithm : pinAlgorithms) {
MessageDigest md = digestMap.get(algorithm);
if (md == null) {
try {
md = MessageDigest.getInstance(algorithm);
} catch (GeneralSecurityException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
digestMap.put(algorithm, md);
}
if (pinSet.pins.contains(new Pin(algorithm, md.digest(encodedSPKI)))) {
return;
}
}
}
// TODO: Throw a subclass of CertificateException which indicates a pinning failure.
throw new CertificateException("Pin verification failed");
}
TrustedCertificateStoreAdapter 为根证书库提供了 TrustedCertificateStore 接口的查找操作,以方便 TrustManagerImpl 使用(位于frameworks/base/core/java/android/security/net/config/TrustedCertificateStoreAdapter.java):
public class TrustedCertificateStoreAdapter extends TrustedCertificateStore {
private final NetworkSecurityConfig mConfig;
public TrustedCertificateStoreAdapter(NetworkSecurityConfig config) {
mConfig = config;
}
@Override
public X509Certificate findIssuer(X509Certificate cert) {
TrustAnchor anchor = mConfig.findTrustAnchorByIssuerAndSignature(cert);
if (anchor == null) {
return null;
}
return anchor.certificate;
}
@Override
public Set findAllIssuers(X509Certificate cert) {
return mConfig.findAllCertificatesByIssuerAndSignature(cert);
}
@Override
public X509Certificate getTrustAnchor(X509Certificate cert) {
TrustAnchor anchor = mConfig.findTrustAnchorBySubjectAndPublicKey(cert);
if (anchor == null) {
return null;
}
return anchor.certificate;
}
@Override
public boolean isUserAddedCertificate(X509Certificate cert) {
// isUserAddedCertificate is used only for pinning overrides, so use overridesPins here.
TrustAnchor anchor = mConfig.findTrustAnchorBySubjectAndPublicKey(cert);
if (anchor == null) {
return false;
}
return anchor.overridesPins;
}
不难看出 Android 中 Java 层证书验证的过程如下图所示:
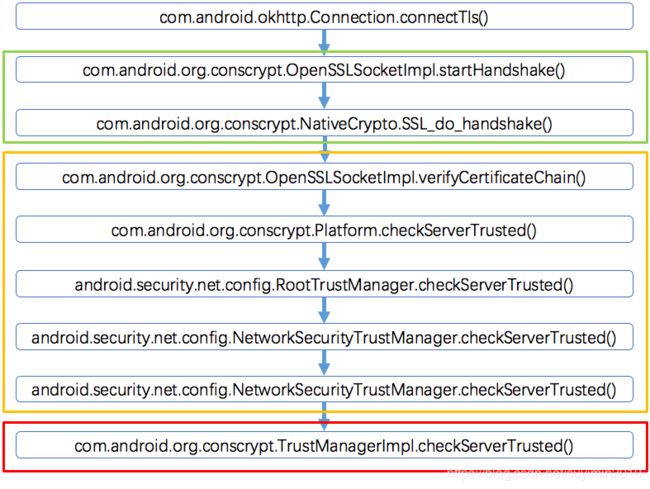
OpenSSLSocketImpl.startHandshake() 和 NativeCrypto.SSL_do_handshake() 执行完整的 SSL/TLS 握手过程。证书合法性验证作为 SSL/TLS 握手的一个重要步骤,通过本地层调用的 Java 层的回调方法 SSLHandshakeCallbacks.verifyCertificateChain() 完成,OpenSSLSocketImpl 实现这一回调。OpenSSLSocketImpl.verifyCertificateChain()、Platform.checkServerTrusted()、RootTrustManager.checkServerTrusted() 和NetworkSecurityTrustManager.checkServerTrusted() 用于将真正的根据系统根证书库执行证书合法性验证的 TrustManagerImpl 和 SSL/TLS 握手过程粘起来。OpenSSLSocketFactoryImpl 将 OpenSSLSocketImpl 和 SSLParametersImpl 粘起来。SSLParametersImpl 将 OpenSSLSocketImpl 和 RootTrustManager 粘起来。
NetworkSecurityConfig 将 RootTrustManager 和 NetworkSecurityTrustManager 粘起来。NetworkSecurityConfig、NetworkSecurityTrustManager 和 TrustedCertificateStoreAdapter 将 TrustManagerImpl 和管理系统根证书库的 SystemCertificateSource 粘起来。
TrustManagerImpl 是证书合法性验证的核心,它会查找系统根证书库,并对服务端证书的合法性做验证。
这个过程的调用栈如下:
com.android.org.conscrypt.TrustManagerImpl.checkServerTrusted()
android.security.net.config.NetworkSecurityTrustManager.checkServerTrusted()
android.security.net.config.NetworkSecurityTrustManager.checkServerTrusted()
android.security.net.config.RootTrustManager.checkServerTrusted()
com.android.org.conscrypt.Platform.checkServerTrusted()
com.android.org.conscrypt.OpenSSLSocketImpl.verifyCertificateChain()
com.android.org.conscrypt.NativeCrypto.SSL_do_handshake()
com.android.org.conscrypt.OpenSSLSocketImpl.startHandshake()
com.android.okhttp.Connection.connectTls()
还有两个问题,一是 SSLParametersImpl 是如何找到的 RootTrustManager;二是如何定制或者影响证书合法性的验证过程。
TrustManager 的查找
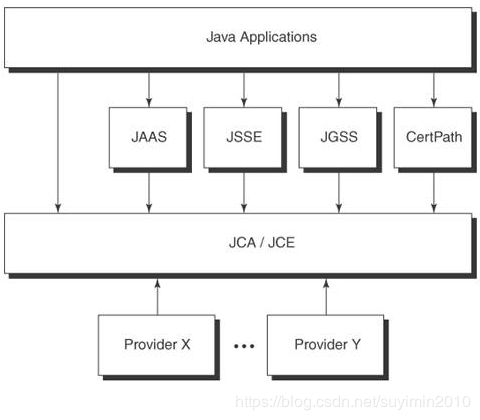
Java 加密体系架构(JCA)是一个非常灵活的架构,它的整体结构如下图:
Java 应用程序通过接口层访问加密服务,接口层的组成包括 JAAS(Java Authentication Authorization Service,Java验证和授权API)、JSSE(Java Secure Socket Extension,Java 安全 套接字扩展)、JGSS(Java Generic Security Service )和 CertPath等。具体的组件如我们前面看到的 CertificateFactory、TrustManagerFactory 和 SSLSocketFactory 等。
JCA 还定义了一组加密服务 Provider 接口,如 javax.net.ssl.SSLContextSpi 和 javax.net.ssl.TrustManagerFactorySpi 等。加密服务的实现者实现这些接口,并通过 java.security.Security 提供的接口注册进 JCA 框架。
对于 Android 系统来说,TrustManagerFactory 加密服务的注册是在 ActivityThread 的 handleBindApplication() 中做的,相关代码(位于 frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java)如下:
// Install the Network Security Config Provider. This must happen before the application
// code is loaded to prevent issues with instances of TLS objects being created before
// the provider is installed.
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "NetworkSecurityConfigProvider.install");
NetworkSecurityConfigProvider.install(appContext);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
NetworkSecurityConfigProvider 类的定义(位于 frameworks/base/core/java/android/security/net/config/NetworkSecurityConfigProvider.java)如下:
package android.security.net.config;
import android.content.Context;
import java.security.Security;
import java.security.Provider;
/** @hide */
public final class NetworkSecurityConfigProvider extends Provider {
private static final String PREFIX =
NetworkSecurityConfigProvider.class.getPackage().getName() + ".";
public NetworkSecurityConfigProvider() {
// TODO: More clever name than this
super("AndroidNSSP", 1.0, "Android Network Security Policy Provider");
put("TrustManagerFactory.PKIX", PREFIX + "RootTrustManagerFactorySpi");
put("Alg.Alias.TrustManagerFactory.X509", "PKIX");
}
public static void install(Context context) {
ApplicationConfig config = new ApplicationConfig(new ManifestConfigSource(context));
ApplicationConfig.setDefaultInstance(config);
int pos = Security.insertProviderAt(new NetworkSecurityConfigProvider(), 1);
if (pos != 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to install provider as highest priority provider."
+ " Provider was installed at position " + pos);
}
libcore.net.NetworkSecurityPolicy.setInstance(new ConfigNetworkSecurityPolicy(config));
}
}
在 NetworkSecurityConfigProvider.install() 方法中,通过 Security.insertProviderAt() 将 NetworkSecurityConfigProvider 注册进 JCA 框架中。从 NetworkSecurityConfigProvider 的构造函数可以看到,它将 android.security.net.config.RootTrustManagerFactorySpi 带进 JCA 框架。
android.security.net.config.RootTrustManagerFactorySpi 的定义(位于 frameworks/base/core/java/android/security/net/config/RootTrustManagerFactorySpi.java)如下:
package android.security.net.config;
import android.util.Pair;
import java.security.InvalidAlgorithmParameterException;
import java.security.InvalidParameterException;
import java.security.KeyStore;
import java.security.KeyStoreException;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.security.Provider;
import java.security.Security;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.net.ssl.ManagerFactoryParameters;
import javax.net.ssl.TrustManager;
import javax.net.ssl.TrustManagerFactory;
import javax.net.ssl.TrustManagerFactorySpi;
import com.android.internal.annotations.VisibleForTesting;
/** @hide */
public class RootTrustManagerFactorySpi extends TrustManagerFactorySpi {
private ApplicationConfig mApplicationConfig;
private NetworkSecurityConfig mConfig;
@Override
public void engineInit(ManagerFactoryParameters spec)
throws InvalidAlgorithmParameterException {
if (!(spec instanceof ApplicationConfigParameters)) {
throw new InvalidAlgorithmParameterException("Unsupported spec: " + spec + ". Only "
+ ApplicationConfigParameters.class.getName() + " supported");
}
mApplicationConfig = ((ApplicationConfigParameters) spec).config;
}
@Override
public void engineInit(KeyStore ks) throws KeyStoreException {
if (ks != null) {
mApplicationConfig = new ApplicationConfig(new KeyStoreConfigSource(ks));
} else {
mApplicationConfig = ApplicationConfig.getDefaultInstance();
}
}
@Override
public TrustManager[] engineGetTrustManagers() {
if (mApplicationConfig == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("TrustManagerFactory not initialized");
}
return new TrustManager[] { mApplicationConfig.getTrustManager() };
}
@VisibleForTesting
public static final class ApplicationConfigParameters implements ManagerFactoryParameters {
public final ApplicationConfig config;
public ApplicationConfigParameters(ApplicationConfig config) {
this.config = config;
}
}
}
RootTrustManagerFactorySpi 的 TrustManager 来自于 ApplicationConfig,ApplicationConfig 中 TrustManager 相关的代码(位于 frameworks/base/core/java/android/security/net/config/ApplicationConfig.java)如下:
public final class ApplicationConfig {
private static ApplicationConfig sInstance;
private static Object sLock = new Object();
private Set> mConfigs;
private NetworkSecurityConfig mDefaultConfig;
private X509TrustManager mTrustManager;
. . . . . .
/**
* Returns the {@link X509TrustManager} that implements the checking of trust anchors and
* certificate pinning based on this configuration.
*/
public X509TrustManager getTrustManager() {
ensureInitialized();
return mTrustManager;
}
. . . . . .
private void ensureInitialized() {
synchronized(mLock) {
if (mInitialized) {
return;
}
mConfigs = mConfigSource.getPerDomainConfigs();
mDefaultConfig = mConfigSource.getDefaultConfig();
mConfigSource = null;
mTrustManager = new RootTrustManager(this);
mInitialized = true;
}
}
ApplicationConfig 的 TrustManager 是 RootTrustManager。
再来看 JCA 接口层的 javax.net.ssl.TrustManagerFactory 的定义:
public class TrustManagerFactory {
// The provider
private Provider provider;
// The provider implementation (delegate)
private TrustManagerFactorySpi factorySpi;
// The name of the trust management algorithm.
private String algorithm;
. . . . . .
public final static String getDefaultAlgorithm() {
String type;
type = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction() {
public String run() {
return Security.getProperty(
"ssl.TrustManagerFactory.algorithm");
}
});
if (type == null) {
type = "SunX509";
}
return type;
}
. . . . . .
/**
* Creates a TrustManagerFactory object.
*
* @param factorySpi the delegate
* @param provider the provider
* @param algorithm the algorithm
*/
protected TrustManagerFactory(TrustManagerFactorySpi factorySpi,
Provider provider, String algorithm) {
this.factorySpi = factorySpi;
this.provider = provider;
this.algorithm = algorithm;
}
. . . . . .
public static final TrustManagerFactory getInstance(String algorithm)
throws NoSuchAlgorithmException {
GetInstance.Instance instance = GetInstance.getInstance
("TrustManagerFactory", TrustManagerFactorySpi.class,
algorithm);
return new TrustManagerFactory((TrustManagerFactorySpi)instance.impl,
instance.provider, algorithm);
}
. . . . . .
public final void init(KeyStore ks) throws KeyStoreException {
factorySpi.engineInit(ks);
}
/**
* Initializes this factory with a source of provider-specific
* trust material.
*
* In some cases, initialization parameters other than a keystore
* may be needed by a provider. Users of that particular provider
* are expected to pass an implementation of the appropriate
* ManagerFactoryParameters as defined by the
* provider. The provider can then call the specified methods in
* the ManagerFactoryParameters implementation to obtain the
* needed information.
*
* @param spec an implementation of a provider-specific parameter
* specification
* @throws InvalidAlgorithmParameterException if an error is
* encountered
*/
public final void init(ManagerFactoryParameters spec) throws
InvalidAlgorithmParameterException {
factorySpi.engineInit(spec);
}
/**
* Returns one trust manager for each type of trust material.
*
* @throws IllegalStateException if the factory is not initialized.
*
* @return the trust managers
*/
public final TrustManager[] getTrustManagers() {
return factorySpi.engineGetTrustManagers();
}
TrustManagerFactory 通过 JCA 框架提供的 sun.security.jca.GetInstance 找到注册的 javax.net.ssl.TrustManagerFactorySpi。应用程序通过 javax.net.ssl.TrustManagerFactory -> android.security.net.config.RootTrustManagerFactorySpi -> android.security.net.config.ApplicationConfig 得到 android.security.net.config.RootTrustManager,即 X509TrustManager。
私有 CA 签名证书的应用
自签名证书是无需别的证书为其签名来证明其合法性的证书,根证书都是自签名证书。私有 CA 签名证书则是指,为域名证书签名的 CA,其合法有效性没有得到广泛的认可,该 CA 的根证书没有被内置到系统中。
在实际的开发过程中,有时为了节省昂贵的购买证书的费用,而想要自己给自己的服务器的域名签发域名证书,这即是私有 CA 签名的证书。为了能够使用这种证书,需要在客户端预埋根证书,并对客户端证书合法性验证的过程进行干预,通过我们预埋的根证书为服务端的证书做合法性验证,而不依赖系统的根证书库。
自定义 javax.net.ssl.SSLSocket 的代价太高,通常不会通过自定义 javax.net.ssl.SSLSocket 来修改服务端证书的合法性验证过程。以此为基础,从上面的分析中不难看出,要想定制 OpenSSLSocketImpl 的证书验证过程,则必然要改变 SSLParametersImpl,要改变 OpenSSLSocketImpl 的 SSLParametersImpl,则必然需要修改 SSLSocketFactory。修改 SSLSocketFactory 常常是一个不错的方法。
在 Java 中,SSLContext 正是被设计用于这一目的。创建定制了 SSLParametersImpl,即定制了 TrustManager 的 SSLSocketFactory 的方法如下:
TrustManager[] trustManagers = new TrustManager[] { new HelloX509TrustManager() };;
SSLContext context = null;
try {
context = SSLContext.getInstance("TLS");
context.init(null, trustManagers, new SecureRandom());
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
Log.i(TAG,"NoSuchAlgorithmException INFO:"+e.getMessage());
} catch (KeyManagementException e) {
Log.i(TAG, "KeyManagementException INFO:" + e.getMessage());
}
HttpsURLConnection.setDefaultSSLSocketFactory(context.getSocketFactory());
SSLContext 的相关方法实现(位于libcore/ojluni/src/main/java/javax/net/ssl/SSLContext.java)如下:
private final SSLContextSpi contextSpi;
. . . . . .
public static SSLContext getInstance(String protocol)
throws NoSuchAlgorithmException {
GetInstance.Instance instance = GetInstance.getInstance
("SSLContext", SSLContextSpi.class, protocol);
return new SSLContext((SSLContextSpi)instance.impl, instance.provider,
protocol);
}
. . . . . .
public final void init(KeyManager[] km, TrustManager[] tm,
SecureRandom random)
throws KeyManagementException {
contextSpi.engineInit(km, tm, random);
} /**
* Returns a SocketFactory object for this
* context.
*
* @return the SocketFactory object
* @throws IllegalStateException if the SSLContextImpl requires
* initialization and the init() has not been called
*/
public final SSLSocketFactory getSocketFactory() {
return contextSpi.engineGetSocketFactory();
}
其中 SSLContextSpi 为 OpenSSLContextImpl,该类的实现(位于external/conscrypt/src/main/java/org/conscrypt/OpenSSLContextImpl.java)如下:
package org.conscrypt;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.security.GeneralSecurityException;
import java.security.KeyManagementException;
import java.security.SecureRandom;
import javax.net.ssl.KeyManager;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLContextSpi;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLEngine;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLServerSocketFactory;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;
import javax.net.ssl.TrustManager;
/**
* OpenSSL-backed SSLContext service provider interface.
*/
public class OpenSSLContextImpl extends SSLContextSpi {
/**
* The default SSLContextImpl for use with
* SSLContext.getInstance("Default"). Protected by the
* DefaultSSLContextImpl.class monitor.
*/
private static DefaultSSLContextImpl DEFAULT_SSL_CONTEXT_IMPL;
/** TLS algorithm to initialize all sockets. */
private final String[] algorithms;
/** Client session cache. */
private final ClientSessionContext clientSessionContext;
/** Server session cache. */
private final ServerSessionContext serverSessionContext;
protected SSLParametersImpl sslParameters;
/** Allows outside callers to get the preferred SSLContext. */
public static OpenSSLContextImpl getPreferred() {
return new TLSv12();
}
protected OpenSSLContextImpl(String[] algorithms) {
this.algorithms = algorithms;
clientSessionContext = new ClientSessionContext();
serverSessionContext = new ServerSessionContext();
}
/**
* Constuctor for the DefaultSSLContextImpl.
*
* @param dummy is null, used to distinguish this case from the public
* OpenSSLContextImpl() constructor.
*/
protected OpenSSLContextImpl() throws GeneralSecurityException, IOException {
synchronized (DefaultSSLContextImpl.class) {
this.algorithms = null;
if (DEFAULT_SSL_CONTEXT_IMPL == null) {
clientSessionContext = new ClientSessionContext();
serverSessionContext = new ServerSessionContext();
DEFAULT_SSL_CONTEXT_IMPL = (DefaultSSLContextImpl) this;
} else {
clientSessionContext = DEFAULT_SSL_CONTEXT_IMPL.engineGetClientSessionContext();
serverSessionContext = DEFAULT_SSL_CONTEXT_IMPL.engineGetServerSessionContext();
}
sslParameters = new SSLParametersImpl(DEFAULT_SSL_CONTEXT_IMPL.getKeyManagers(),
DEFAULT_SSL_CONTEXT_IMPL.getTrustManagers(), null, clientSessionContext,
serverSessionContext, algorithms);
}
}
/**
* Initializes this {@code SSLContext} instance. All of the arguments are
* optional, and the security providers will be searched for the required
* implementations of the needed algorithms.
*
* @param kms the key sources or {@code null}
* @param tms the trust decision sources or {@code null}
* @param sr the randomness source or {@code null}
* @throws KeyManagementException if initializing this instance fails
*/
@Override
public void engineInit(KeyManager[] kms, TrustManager[] tms, SecureRandom sr)
throws KeyManagementException {
sslParameters = new SSLParametersImpl(kms, tms, sr, clientSessionContext,
serverSessionContext, algorithms);
}
@Override
public SSLSocketFactory engineGetSocketFactory() {
if (sslParameters == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("SSLContext is not initialized.");
}
return Platform.wrapSocketFactoryIfNeeded(new OpenSSLSocketFactoryImpl(sslParameters));
}
如我们前面讨论,验证服务端证书合法性是 PKI 体系中,保障系统安全极为关键的环节。如果不验证服务端证书的合法性,则即使部署了 HTTPS,HTTPS 也将形同虚设,毫无价值。因而在我们自己实现的 X509TrustManager 中,加载预埋的根证书,并据此验证服务端证书的合法性必不可少,这一检查在 checkServerTrusted() 中完成。然而为了使我们实现的 X509TrustManager 功能更完备,在根据我们预埋的根证书验证失败后,我们再使用系统默认的 X509TrustManager 做验证,像下面这样:
private final class HelloX509TrustManager implements X509TrustManager {
private X509TrustManager mSystemDefaultTrustManager;
private X509Certificate mCertificate;
private HelloX509TrustManager() {
mCertificate = loadRootCertificate();
mSystemDefaultTrustManager = systemDefaultTrustManager();
}
private X509Certificate loadRootCertificate() {
String certName = "netease.crt";
X509Certificate certificate = null;
InputStream certInput = null;
try {
certInput = new BufferedInputStream(MainActivity.this.getAssets().open(certName));
CertificateFactory certificateFactory = CertificateFactory.getInstance("X.509");
certificate = (X509Certificate) certificateFactory.generateCertPath(certInput).getCertificates().get(0);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (CertificateException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (certInput != null) {
try {
certInput.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
return certificate;
}
private X509TrustManager systemDefaultTrustManager() {
try {
TrustManagerFactory trustManagerFactory = TrustManagerFactory.getInstance(
TrustManagerFactory.getDefaultAlgorithm());
trustManagerFactory.init((KeyStore) null);
TrustManager[] trustManagers = trustManagerFactory.getTrustManagers();
if (trustManagers.length != 1 || !(trustManagers[0] instanceof X509TrustManager)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected default trust managers:"
+ Arrays.toString(trustManagers));
}
return (X509TrustManager) trustManagers[0];
} catch (GeneralSecurityException e) {
throw new AssertionError(); // The system has no TLS. Just give up.
}
}
@Override
public void checkClientTrusted(X509Certificate[] chain, String authType) throws CertificateException {
mSystemDefaultTrustManager.checkClientTrusted(chain, authType);
}
@Override
public void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] chain, String authType) throws CertificateException {
for (X509Certificate certificate : chain) {
try {
certificate.verify(mCertificate.getPublicKey());
return;
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvalidKeyException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchProviderException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SignatureException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
mSystemDefaultTrustManager.checkServerTrusted(chain, authType);
}
@Override
public X509Certificate[] getAcceptedIssuers() {
return mSystemDefaultTrustManager.getAcceptedIssuers();
}
}
此外,也可以不自己实现 X509TrustManager,而仅仅修改 X509TrustManager 所用的根证书库,就像下面这样:
private TrustManager[] createX509TrustManager() {
CertificateFactory cf = null;
InputStream in = null;
TrustManager[] trustManagers = null
try {
cf = CertificateFactory.getInstance("X.509");
in = getAssets().open("ca.crt");
Certificate ca = cf.generateCertificate(in);
KeyStore keystore = KeyStore.getInstance(KeyStore.getDefaultType());
keystore.load(null, null);
keystore.setCertificateEntry("ca", ca);
String tmfAlgorithm = TrustManagerFactory.getDefaultAlgorithm();
TrustManagerFactory tmf = TrustManagerFactory.getInstance(tmfAlgorithm);
tmf.init(keystore);
trustManagers = tmf.getTrustManagers();
} catch (CertificateException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (KeyStoreException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return trustManagers;
}
自己实现 X509TrustManager 接口和通过 TrustManagerFactory,仅定制 KeyStore 这两种创建 X509TrustManager 对象的方式,当然是后一种方式更好一些了。如我们前面看到的,系统的 X509TrustManager 实现 RootTrustManager 集成自 X509ExtendedTrustManager,而不是直接实现的 X509TrustManager 接口 。JCA 的接口层也在随着新的安全协议和 SSL 库的发展在不断扩展,在具体的 Java 加密服务实现中,可能会实现并依赖这些扩展的功能,如上面看到的 X509TrustManager,而且加密服务的实现中常常通过反射,来动态依赖一些扩展的接口。因而,自己实现 X509TrustManager 接口时,以及其它加密相关的接口时,如 SSLSocket 等,可能会破坏一些功能。
很多时候可以看到,为了使用私有 CA 签名的证书,而定制域名匹配验证的逻辑,即自己实现 HostnameVerifier。不过通常情况下,网络库都会按照规范对域名与证书的匹配性做严格的检查,因而不是那么地有必要,除非域名证书有什么不那么规范的地方。
关于证书钉扎,在使用私有 CA 签名的证书时,通常似乎也没有那么必要。