Linux安装包run、bin制作
制作run安装包
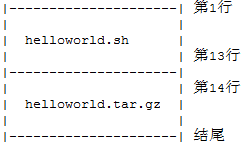
run程序安装包实质上是一个安装脚本加要安装的程序,如下图所示:
这样整个run安装包结构就一目了然了,实际上因为实际需要结构多少有点变动但这个无关紧要,只需要明白原理就行了。
安装脚本:helloworld.sh如下:
#!/bin/bash
lines=15
DEFAULT_DIR=/opt
read -p "Please enter the installation directory: " INSTALL_DIR
if [ ! -z "$INSTALL_DIR" ]; then
DEFAULT_DIR=$INSTALL_DIR
fi
if [ ! -d "$DEFAULT_DIR" ];then
mkdir -p $DEFAULT_DIR
fi
tail -n +$lines "$0" > /tmp/helloworld.tar.gz
tar -xzf /tmp/helloworld.tar.gz -C $DEFAULT_DIR
rm -rf /tmp/helloworld.tar.gz
exit 0
lines=15 #这个值是指这个脚本的行数加1,这个脚本共有14行
tail -n +$lines "$0" > /tmp/helloworld.tar.gz # $0表示脚本本身,这个命令用来把从$lines开始的内容写入一个/tmp目录的helloworld.tar.gz文件里
tar -xzf /tmp/helloworld.tar.gz -C $ DEFAULT_DIR #解压到指定目录
注意:第15行(空行)不能缺少,不然解压会有问题
安装程序压缩包:helloworld.tar.gz
进入程序helloworld父目录,执行以下命令:
tar -czf helloworld.tar.gz helloworld
压缩包名称:helloworld.tar.gz
程序文件夹:helloworld
然后使用cat命令连接安装脚本helloworld.sh和helloworld.tar.gz
cat helloworld.sh helloworld.tar.gz > helloworld.run
可以通过vi命令查看helloworld.run:
vi helloworld.run
前面14行是helloworld.sh,从第15行开始的乱码就是源程序
运行helloworld.run时,运行到第14行的exit 0脚本就退出了,所以不会去运行第14行以下的二进制数据(即 helloworld.tar.gz文件),而我们用了tail巧妙地把第14行以下的数据重新生成了一个helloworld.tar.gz文件。再执行安装。
run安装包制作较小的程序包是很好的选择,但是它也有缺点,做逻辑比较复杂的安装包,写的安装脚本将会很麻烦,因此此时还是用其他的安装包更好。
制作bin安装包
bin安装包结构和run包类似,是一个安装脚本加要安装的程序,如下图所示:
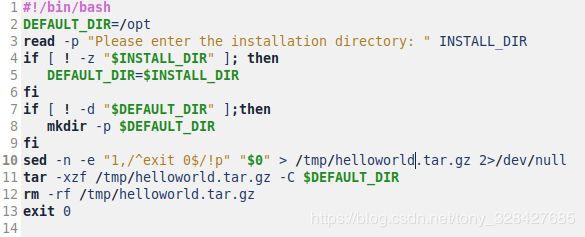
安装脚本:helloworld.sh如下:
#!/bin/bash
install_dir=/opt/helloworld
read -p "Please enter the installation directory:" install_dir
echo "The installation directory is:$install_dir"
mkdir -p $install_dir
sed -n -e "1,/^exit 0$/!p" "$0" > /tmp/helloworld.tar.gz 2>/dev/null
tar -xzf /tmp/helloworld.tar.gz -C ${install_dir}
rm -rf /tmp/helloworld.tar.gz
exit 0
最主要的是下面这句,是将二进制文件从.bin文件里分离出来
sed -n -e "1,/^exit 0$/!p" "$0" > /tmp/ helloworld.tar.gz 2>/dev/null #意思为打印除从第一行到所在exit 0的行的所有行到/tmp/helloworld.tar.gz,如果过程中有错误则输出到/dev/null
注意:第14行(空行)不能缺少,不然解压会有问题
安装程序压缩包:helloworld.tar.gz
进入程序helloworld父目录,执行以下命令:
tar -czf helloworld.tar.gz helloworld
压缩包名称:helloworld.tar.gz
程序文件夹:helloworld
然后使用cat命令连接安装脚本helloworld.sh和helloworld.tar.gz
cat helloworld.sh helloworld.tar.gz > helloworld.bin
可以通过vi命令查看helloworld.bin:
vi helloworld.bin
总结
上面两个例子,其实不管是bin也好run也好,其实Linux下一切皆文件,而且是不管什么文件,都是一样的看法。
所以这些后缀没有什么意义。上面两个不同的地方是分离,一个是用了tail命令,一个是用了sed来实现。
总之,这只是一种思路,不管用什么办法,只要能合起来然后又分开就行。