K8S 底层网络所需要解决的两个问题
- 协助 k8s , 给每个 NODE上的 docker 容器都分配互相不冲突的 IP
- 在这些 IP 地址之间简历一个覆盖网络(overlay Network), 通过这个覆盖网络, 将数据包原封不动地传递到目标容器内.
Open vSwitch
Open vSwitch 可以建立多钟通信隧道, 例如Open vswitch with GRE/VXALN. 在K8S 场景下, 我们主要简历 L3 到 L3 的隧道. 网络架构如下
需要完成的步骤如下:
删除docker daemon 创建的网桥 docker0 已避免 docker0地址冲突.
手工创建一个linux网桥, 手动配置网桥的 IP
建立 Open vswitch 网桥 ovs-bridge, 使用 ovs-vsctl 给ovs-bridge 添加gre端口, 在添加端口是, 需要将目标 NODE 的 IP 地址设置为对端 IP 地址. 每个对端 IP 地址都需要这么操作.
将 ovs-bridge 作为网络接口, 加入docker 的网桥上(docker0 或自己手工创建的网桥)
重启 ovs-bridge 网桥 和 docker 的网桥, 并添加一个docker 的网段到docker 网桥的路由规则中
网络通信过程
当容器内的应用访问另一个容器地址时, 数据包会通过容器内的默认路由发送给docker0网桥, ovs的网桥是作为docker0 网桥的端口存在的, 它会将数据发送给ovs 网桥, ovs 通过gre隧道 送达对端的node.
配置步骤
在两个节点都安装ovs
安装ovs
yum install openvswitch
禁用selinux 并重启
#vi /etc/selinux/conifg
SELINUX=disabled
查看ovs状态
systemctl status openvswtich
创建网桥和 gre 隧道
在每个node上创建ovs 网桥 br0 然后在网桥上创建 gre 隧道
#创建ovs网桥
ovs-vsctl add-br br0
# 创建 GRE 隧道连接对端, remote_ip 为对端 eth0 的 IP, 注意在另一台机器上设置对端的时候,IP 要改为当前这台机器的 IP
ovs-vsctl add-port br0 gre1 -- set interface gre1 type gre option:remote_ip=192.168.18.128
# 添加br0 到本地 docker0 网桥, 使得容器流量通过 ovs 进入 tunnel
brctl addif docker0 br0
#启动br0 docker0 网桥
ip link set dev br0 up
ip link set dev docker0 up
由于128, 131 ip的两台机器docker0 网段分别是172.17.43.0/24, 172.17.42.0/24, 这两个网段的路由都需要经过本机docker0网桥.其中一个24网段通过ovs的gre 隧道到达对端. 因此需要在每个node上配置通过docker0 网桥的路由规则
ip route add 172.17.0.0/16 dev docker0
清空 docker 自带的iptables 规则及linux 的规则, 后者存在拒绝ICMP 保温通过防火墙的规则
iptables -t nat -F; iptalbes -F
直接路由
网络模型
在默认情况下docker0 的IP 在node 网络是没法感知到的, 通过手工设置路由, 可以让pod 在不同node 之间互通.
实现方式
通过部署multilayer switch (MLS) 来实现
假设 POD1 所在的 docker0 网桥的 IP 网段是 10.1.10.0 , NODE1 地址为 192. 168.1.128; 而 POD2 所在 docker0 ip 网段为 10.1.20.0 NODE2 地址为 192.168.1.129
1 在NODE 1 上添加一条到node2 上 docker0 的静态路由规则
route add -net 10.1.20.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 192.168.1.129
2 在 NODE 2 上添加一条到 NODE 1 上 docker0 的静态路由规则
route add -net 10.1.10.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 192.168.1.128
3 验证连通性, 在 NODE1 上 ping node2 上的 docker0 网络
ping 10.1.20.1
大规模集群下的实现方式, 手工建立 linux bridge 已避免 docker daemon 建立docker0 造成 IP 段冲突, 然后使用docker 的--bridge 命令来指定网桥.
然后在每个节点运行quagga 路由学习软件.
calico
Calico 工作方式
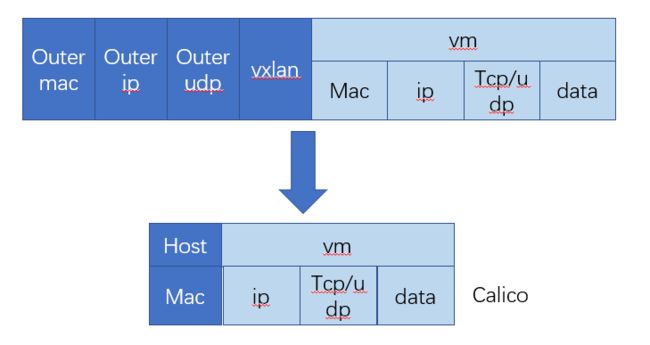
Calico可以创建并管理一个3层平面网络,为每个工作负载分配一个完全可路由的IP地址。 工作负载可以在没有IP封装或网络地址转换的情况下进行通信,以实现裸机性能,简化故障排除和提供更好的互操作性。 在需要使用overlay网络的环境中,Calico提供了IP-in-IP隧道技术,或者也可以与flannel等其他overlay网络配合使用。
Calico还提供网络安全规则的动态配置。 使用Calico的简单策略语言,就可以实现对容器、虚拟机工作负载和裸机主机各节点之间通信的细粒度控制。
Calico v3.4于2018.12.10号发布,可与Kubernetes、OpenShift和OpenStack良好地集成使用。
注意: 在Mesos, DC/OS和Docker orchestrators中使用Calico时,目前只支持到了 Calico v2.6.
Calico的IPIP与BGP模式
- IPIP是一种将各Node的路由之间做一个tunnel,再把两个网络连接起来的模式。启用IPIP模式时,Calico将在各Node上创建一个名为”tunl0″的虚拟网络接口。如下图所示。
- BGP模式则直接使用物理机作为虚拟路由路(vRouter),不再创建额外的tunnel
calico 在linux 内核中实现一个vRouter来负责数据转发, 通过 BGP 协议,将node 节点上的路由信息在整个calico 网络中广播, 并自动设置到达其他节点的路由转发规则.
Calico BGP模式在小规模集群中可以直接互联,在大规模集群中可以通过额外的BGP route reflector来完成。
Calico主要组件
Calico利用了Linux内核原生的路由和iptables防火墙功能。 进出各个容器、虚拟机和物理主机的所有流量都会在路由到目标之前遍历这些内核规则。
- Felix:主要的Calico代理agent,运行每台计算机上管理endpoints资源。
- calicoctl:允许从命令行界面配置实现高级策略和网络。
- orchestrator plugins:提供与各种流行的云计算编排工具的紧密集成和同步支持。
- key/value store:存储Calico的策略配置和网络状态信息,目前主要使用etcdv3或k8s api。
- calico/node:在每个主机上运行,从key/value存储中读取相关的策略和网络配置信息,并在Linux内核中实现它。
- Dikastes/Envoy:可选的Kubernetes sidecars,可以通过相互TLS身份验证保护工作负载到工作负载的通信,并增加应用层控制策略。
Felix
Felix是一个守护程序,它在每个提供endpoints资源的计算机上运行。在大多数情况下,这意味着它需要在托管容器或VM的宿主机节点上运行。 Felix 负责编制路由和ACL规则以及在该主机上所需的任何其他内容,以便为该主机上的endpoints资源正常运行提供所需的网络连接。
根据特定的编排环境,Felix负责以下任务:
- 管理网络接口,Felix将有关接口的一些信息编程到内核中,以使内核能够正确处理该endpoint发出的流量。 特别是,它将确保主机正确响应来自每个工作负载的ARP请求,并将为其管理的接口启用IP转发支持。它还监视网络接口的出现和消失,以便确保针对这些接口的编程得到了正确的应用。
- 编写路由,Felix负责将到其主机上endpoints的路由编写到Linux内核FIB(转发信息库)中。 这可以确保那些发往目标主机的endpoints的数据包被正确地转发。
- 编写ACLs,Felix还负责将ACLs编程到Linux内核中。 这些ACLs用于确保只能在endpoints之间发送有效的网络流量,并确保endpoints无法绕过Calico的安全措施。
- 报告状态,Felix负责提供有关网络健康状况的数据。 特别是,它将报告配置其主机时发生的错误和问题。 该数据会被写入etcd,以使其对网络中的其他组件和操作才可见。
Orchestrator Plugin
每个主要的云编排平台都有单独的Calico网络插件(例如OpenStack,Kubernetes)。 这些插件的目的是将Calico更紧密地绑定到编排工具中,允许用户管理Calico网络,就像他们管理编排工具中内置的网络工具一样。
一个好的Orchestrator插件示例是Calico Neutron ML2 驱动程序。 该插件与Neutron的ML2插件集成,允许用户通过Neutron API调用来配置Calico网络,实现了与Neutron的无缝集成。
Orchestrator插件负责以下任务:
- API Translation,每个云编排工具都不可避免地拥有自己的一套用于管理网络的API接口规范, Orchestrator插件的主要工作就是将这些API转换为Calico的数据模型,然后将其存储在Calico的数据存储区中。这种转换中的一些工作将非常简单,其他一部分可能更复杂,以便将单个复杂操作(例如,实时迁移)转换为Calico网络期望的一系列更简单的操作。
- Feedback,如有需要,orchestrator插件将从Calico网络向编排器提供管理命令的反馈信息。 包括提供有关Felix存活的信息,以及如果网络配置失败则将某些endpoints标记为失败。
etcd
etcd是一个分布式键值存储数据库,专注于实现数据存储一致性。 Calico使用etcd提供组件之间的数据通信,并作为可以保证一致性的数据存储,以确保Calico始终可以构建出一个准确的网络。
根据orchestrator插件的不同,etcd既可以是作为主数据存储使用,也可以是一个单独数据存储的轻量级镜像。例如,在OpenStack部署中,OpenStack数据库被认为是“真实配置信息的来源”,而etcd用于镜像其中有关网络配置的信息,并用于服务其他Calico组件。
etcd组件穿插在整个部署中。它可以被分为两组主机节点:核心集群和代理。
对于小型部署,核心集群可以是一个节点的etcd集群(通常与orchestrator插件组件位于同一节点上)。这种部署模型很简单但没有为etcd提供冗余。在etcd失败的情况下,orchstrator插件必须重建数据库,例如OpenStack,它需要插件从OpenStack数据库重新同步状态到etcd。
在较大的部署中,核心群集可以根据etcd管理指南进行扩展。
此外,在运行Felix或orchstrator插件的每台计算机上,会运行一个etcd代理服务。这减少了etcd核心集群上的负载,并为主机节点屏蔽了etcd服务集群的细节。在etcd集群与orchstrator插件在同一台机器上都有成员的情况下,可以放弃在该机器上使用etcd代理。
etcd负责执行以下任务:
- Data Storage,etcd以分布式、一致和容错的方式存储Calico网络的数据(对于至少三个etcd节点的cluster大小)。 这确保Calico网络始终处于已知良好状态,同时允许运行etcd的个别机器节点失败或无法访问。Calico网络数据的这种分布式存储提高了Calico组件从数据库读取的能力。
- Communication,etcd也用作组件之间的通信服务。 我们通过让非etcd组件监视键值空间中的某些点来确保他们看到已经做出的任何更改,从而允许他们及时响应这些更改。 该功能允许将状态信息提交到数据库,然后触发基于该状态数据的进一步网络配置管理。
BGP Client (BIRD)
Calico在每个运行Felix服务的节点上都部署一个BGP客户端。 BGP客户端的作用是读取Felix程序编写到内核中并在数据中心内分发的路由信息。
BGP客户端负责执行以下任务:
- 路由信息分发,当Felix将路由插入Linux内核FIB时,BGP客户端将接收它们并将它们分发到集群中的其他工作节点。
BGP Route Reflector (BIRD)
对于较大规模的部署,简单的BGP可能成为限制因素,因为它要求每个BGP客户端连接到网状拓扑中的每一个其他BGP客户端。这需要越来越多的连接,迅速变得难以维护,甚至会让一些设备的路由表撑满。
因此,在较大规模的部署中,Calico建议部署BGP Route Reflector。通常是在Internet中使用这样的组件充当BGP客户端连接的中心点,从而防止它们需要与群集中的每个BGP客户端进行通信。为了实现冗余,也可以同时部署多个BGP Route Reflector服务。Route Reflector仅仅是协助管理BGP网络,并没有endpoint数据会通过它们。
在Calico中,此BGP组件也是使用的最常见的BIRD,配置为Route Reflector运行,而不是标准BGP客户端。
BGP Route Reflector负责以下任务:
- 集中式的路由信息分发,当Calico BGP客户端将路由从其FIB通告到Route Reflector时,Route Reflector会将这些路由通告给部署集群中的其他节点。
BIRD是什么
BIRD是布拉格查理大学数学与物理学院的一个学校项目,项目名是BIRD Internet Routing Daemon的缩写。 目前,它由CZ.NIC实验室开发和支持。
BIRD项目旨在开发一个功能齐全的动态IP路由守护进程,主要针对(但不限于)Linux,FreeBSD和其他类UNIX系统,并在GNU通用公共许可证下分发。详细信息参照官网https://bird.network.cz/。
作为一个开源的网络路由守护进程项目,BRID设计并支持了以下功能:
- both IPv4 and IPv6 protocols
- multiple routing tables
- the Border Gateway Protocol (BGPv4)
- the Routing Information Protocol (RIPv2, RIPng)
- the Open Shortest Path First protocol (OSPFv2, OSPFv3)
- the Babel Routing Protocol
- the Router Advertisements for IPv6 hosts
- a virtual protocol for exchange of routes between different routing tables on a single host
- a command-line interface allowing on-line control and inspection of status of the daemon
- soft reconfiguration (no need to use complex online commands to change the configuration, just edit the configuration file and notify BIRD to re-read it and it will smoothly switch itself to the new configuration, not disturbing routing protocols unless they are affected by the configuration changes)
- a powerful language for route filtering
K8S 中部署 calico
-
修改kube-api server 启动参数
--allow-priviledge=true (calico 需要特权模式) 修改kubelet 启动参数 --network-plugin=cni
假设K8S 环境包含两个node节点 node1 (192,168.18.3) , node2 (192.168.18.4)
创建calico 服务, 主要包括calico-node 和 calico policy controller, 需要的K8S 资源对象如下
- configmap: calico-config 包含calico的配置参数
- secret: calico-etcd-secrets 用于TLS 连接etcd
- 在每个节点以daemonset的形式 部署calico/node 容器
- 在每个节点都安装calico cni 二进制文件和网络配置参数(由install-cni 容器完成)
- 部署一个名为calico/kube-policy-controller的deployment, 为K8S 集群中的POD 设置network policy
官方 calico k8s 安装 yaml 文件如下
calico-etcd.yaml
---
# Source: calico/templates/calico-etcd-secrets.yaml
# The following contains k8s Secrets for use with a TLS enabled etcd cluster.
# For information on populating Secrets, see http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/secrets/
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
type: Opaque
metadata:
name: calico-etcd-secrets
namespace: kube-system
data:
# Populate the following with etcd TLS configuration if desired, but leave blank if
# not using TLS for etcd.
# The keys below should be uncommented and the values populated with the base64
# encoded contents of each file that would be associated with the TLS data.
# Example command for encoding a file contents: cat | base64 -w 0
# etcd-key: null
# etcd-cert: null
# etcd-ca: null
---
# Source: calico/templates/calico-config.yaml
# This ConfigMap is used to configure a self-hosted Calico installation.
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: calico-config
namespace: kube-system
data:
# Configure this with the location of your etcd cluster.
#ETCD的服务地址
etcd_endpoints: "http://:"
# If you're using TLS enabled etcd uncomment the following.
# You must also populate the Secret below with these files.
etcd_ca: "" # "/calico-secrets/etcd-ca"
etcd_cert: "" # "/calico-secrets/etcd-cert"
etcd_key: "" # "/calico-secrets/etcd-key"
# Typha is disabled.
typha_service_name: "none"
# Configure the backend to use.
calico_backend: "bird"
# Configure the MTU to use
veth_mtu: "1440"
# The CNI network configuration to install on each node. The special
# values in this config will be automatically populated.
cni_network_config: |-
{
"name": "k8s-pod-network",
"cniVersion": "0.3.1",
"plugins": [
{
"type": "calico",
"log_level": "info",
"etcd_endpoints": "__ETCD_ENDPOINTS__",
"etcd_key_file": "__ETCD_KEY_FILE__",
"etcd_cert_file": "__ETCD_CERT_FILE__",
"etcd_ca_cert_file": "__ETCD_CA_CERT_FILE__",
"mtu": __CNI_MTU__,
"ipam": {
"type": "calico-ipam"
},
"policy": {
"type": "k8s"
},
"kubernetes": {
"kubeconfig": "__KUBECONFIG_FILEPATH__"
}
},
{
"type": "portmap",
"snat": true,
"capabilities": {"portMappings": true}
}
]
}
---
# Source: calico/templates/rbac.yaml
# Include a clusterrole for the kube-controllers component,
# and bind it to the calico-kube-controllers serviceaccount.
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: calico-kube-controllers
rules:
# Pods are monitored for changing labels.
# The node controller monitors Kubernetes nodes.
# Namespace and serviceaccount labels are used for policy.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources:
- pods
- nodes
- namespaces
- serviceaccounts
verbs:
- watch
- list
# Watch for changes to Kubernetes NetworkPolicies.
- apiGroups: ["networking.k8s.io"]
resources:
- networkpolicies
verbs:
- watch
- list
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: calico-kube-controllers
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: calico-kube-controllers
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: calico-kube-controllers
namespace: kube-system
---
# Include a clusterrole for the calico-node DaemonSet,
# and bind it to the calico-node serviceaccount.
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: calico-node
rules:
# The CNI plugin needs to get pods, nodes, and namespaces.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources:
- pods
- nodes
- namespaces
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups: [""]
resources:
- endpoints
- services
verbs:
# Used to discover service IPs for advertisement.
- watch
- list
- apiGroups: [""]
resources:
- nodes/status
verbs:
# Needed for clearing NodeNetworkUnavailable flag.
- patch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: calico-node
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: calico-node
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: calico-node
namespace: kube-system
---
# Source: calico/templates/calico-node.yaml
# This manifest installs the calico-node container, as well
# as the CNI plugins and network config on
# each master and worker node in a Kubernetes cluster.
kind: DaemonSet
apiVersion: apps/v1
metadata:
name: calico-node
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: calico-node
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: calico-node
updateStrategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxUnavailable: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: calico-node
annotations:
# This, along with the CriticalAddonsOnly toleration below,
# marks the pod as a critical add-on, ensuring it gets
# priority scheduling and that its resources are reserved
# if it ever gets evicted.
scheduler.alpha.kubernetes.io/critical-pod: ''
spec:
nodeSelector:
beta.kubernetes.io/os: linux
hostNetwork: true
tolerations:
# Make sure calico-node gets scheduled on all nodes.
- effect: NoSchedule
operator: Exists
# Mark the pod as a critical add-on for rescheduling.
- key: CriticalAddonsOnly
operator: Exists
- effect: NoExecute
operator: Exists
serviceAccountName: calico-node
# Minimize downtime during a rolling upgrade or deletion; tell Kubernetes to do a "force
# deletion": https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod/#termination-of-pods.
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
priorityClassName: system-node-critical
initContainers:
# This container installs the CNI binaries
# and CNI network config file on each node.
- name: install-cni
image: calico/cni:v3.8.0
command: ["/install-cni.sh"]
env:
# Name of the CNI config file to create.
- name: CNI_CONF_NAME
value: "10-calico.conflist"
# The CNI network config to install on each node.
- name: CNI_NETWORK_CONFIG
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: calico-config
key: cni_network_config
# The location of the etcd cluster.
- name: ETCD_ENDPOINTS
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: calico-config
key: etcd_endpoints
# CNI MTU Config variable
- name: CNI_MTU
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: calico-config
key: veth_mtu
# Prevents the container from sleeping forever.
- name: SLEEP
value: "false"
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /host/opt/cni/bin
name: cni-bin-dir
- mountPath: /host/etc/cni/net.d
name: cni-net-dir
- mountPath: /calico-secrets
name: etcd-certs
# Adds a Flex Volume Driver that creates a per-pod Unix Domain Socket to allow Dikastes
# to communicate with Felix over the Policy Sync API.
- name: flexvol-driver
image: calico/pod2daemon-flexvol:v3.8.0
volumeMounts:
- name: flexvol-driver-host
mountPath: /host/driver
containers:
# Runs calico-node container on each Kubernetes node. This
# container programs network policy and routes on each
# host.
- name: calico-node
image: calico/node:v3.8.0
env:
# The location of the etcd cluster.
- name: ETCD_ENDPOINTS
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: calico-config
key: etcd_endpoints
# Location of the CA certificate for etcd.
- name: ETCD_CA_CERT_FILE
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: calico-config
key: etcd_ca
# Location of the client key for etcd.
- name: ETCD_KEY_FILE
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: calico-config
key: etcd_key
# Location of the client certificate for etcd.
- name: ETCD_CERT_FILE
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: calico-config
key: etcd_cert
# Set noderef for node controller.
- name: CALICO_K8S_NODE_REF
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.nodeName
# Choose the backend to use.
- name: CALICO_NETWORKING_BACKEND
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: calico-config
key: calico_backend
# Cluster type to identify the deployment type
- name: CLUSTER_TYPE
value: "k8s,bgp"
# Auto-detect the BGP IP address.
- name: IP
value: "autodetect"
# Enable IPIP
- name: CALICO_IPV4POOL_IPIP
value: "Always"
# Set MTU for tunnel device used if ipip is enabled
- name: FELIX_IPINIPMTU
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: calico-config
key: veth_mtu
# The default IPv4 pool to create on startup if none exists. Pod IPs will be
# chosen from this range. Changing this value after installation will have
# no effect. This should fall within `--cluster-cidr`.
- name: CALICO_IPV4POOL_CIDR
value: "192.168.0.0/16"
# Disable file logging so `kubectl logs` works.
- name: CALICO_DISABLE_FILE_LOGGING
value: "true"
# Set Felix endpoint to host default action to ACCEPT.
- name: FELIX_DEFAULTENDPOINTTOHOSTACTION
value: "ACCEPT"
# Disable IPv6 on Kubernetes.
- name: FELIX_IPV6SUPPORT
value: "false"
# Set Felix logging to "info"
- name: FELIX_LOGSEVERITYSCREEN
value: "info"
- name: FELIX_HEALTHENABLED
value: "true"
securityContext:
privileged: true
resources:
requests:
cpu: 250m
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /liveness
port: 9099
host: localhost
periodSeconds: 10
initialDelaySeconds: 10
failureThreshold: 6
readinessProbe:
exec:
command:
- /bin/calico-node
- -bird-ready
- -felix-ready
periodSeconds: 10
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /lib/modules
name: lib-modules
readOnly: true
- mountPath: /run/xtables.lock
name: xtables-lock
readOnly: false
- mountPath: /var/run/calico
name: var-run-calico
readOnly: false
- mountPath: /var/lib/calico
name: var-lib-calico
readOnly: false
- mountPath: /calico-secrets
name: etcd-certs
- name: policysync
mountPath: /var/run/nodeagent
volumes:
# Used by calico-node.
- name: lib-modules
hostPath:
path: /lib/modules
- name: var-run-calico
hostPath:
path: /var/run/calico
- name: var-lib-calico
hostPath:
path: /var/lib/calico
- name: xtables-lock
hostPath:
path: /run/xtables.lock
type: FileOrCreate
# Used to install CNI.
- name: cni-bin-dir
hostPath:
path: /opt/cni/bin
- name: cni-net-dir
hostPath:
path: /etc/cni/net.d
# Mount in the etcd TLS secrets with mode 400.
# See https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/secret/
- name: etcd-certs
secret:
secretName: calico-etcd-secrets
defaultMode: 0400
# Used to create per-pod Unix Domain Sockets
- name: policysync
hostPath:
type: DirectoryOrCreate
path: /var/run/nodeagent
# Used to install Flex Volume Driver
- name: flexvol-driver-host
hostPath:
type: DirectoryOrCreate
path: /usr/libexec/kubernetes/kubelet-plugins/volume/exec/nodeagent~uds
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: calico-node
namespace: kube-system
---
# Source: calico/templates/calico-kube-controllers.yaml
# See https://github.com/projectcalico/kube-controllers
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: calico-kube-controllers
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: calico-kube-controllers
spec:
# The controllers can only have a single active instance.
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: calico-kube-controllers
strategy:
type: Recreate
template:
metadata:
name: calico-kube-controllers
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: calico-kube-controllers
annotations:
scheduler.alpha.kubernetes.io/critical-pod: ''
spec:
nodeSelector:
beta.kubernetes.io/os: linux
tolerations:
# Mark the pod as a critical add-on for rescheduling.
- key: CriticalAddonsOnly
operator: Exists
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
effect: NoSchedule
serviceAccountName: calico-kube-controllers
priorityClassName: system-cluster-critical
# The controllers must run in the host network namespace so that
# it isn't governed by policy that would prevent it from working.
hostNetwork: true
containers:
- name: calico-kube-controllers
image: calico/kube-controllers:v3.8.0
env:
# The location of the etcd cluster.
- name: ETCD_ENDPOINTS
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: calico-config
key: etcd_endpoints
# Location of the CA certificate for etcd.
- name: ETCD_CA_CERT_FILE
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: calico-config
key: etcd_ca
# Location of the client key for etcd.
- name: ETCD_KEY_FILE
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: calico-config
key: etcd_key
# Location of the client certificate for etcd.
- name: ETCD_CERT_FILE
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: calico-config
key: etcd_cert
# Choose which controllers to run.
- name: ENABLED_CONTROLLERS
value: policy,namespace,serviceaccount,workloadendpoint,node
volumeMounts:
# Mount in the etcd TLS secrets.
- mountPath: /calico-secrets
name: etcd-certs
readinessProbe:
exec:
command:
- /usr/bin/check-status
- -r
volumes:
# Mount in the etcd TLS secrets with mode 400.
# See https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/secret/
- name: etcd-certs
secret:
secretName: calico-etcd-secrets
defaultMode: 0400
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: calico-kube-controllers
namespace: kube-system
---
# Source: calico/templates/calico-typha.yaml
---
# Source: calico/templates/configure-canal.yaml
---
# Source: calico/templates/kdd-crds.yaml
kubectl apply -f calico-etcd.yaml
注意修改参数
更多calico设置
coredns
启用 coredns 需要在kubelet 上添加两个参数
--cluster-dns=169.169.0.100 IP 为DNS服务的cluster ip
--cluster-domain=cluster.local 为dns服务设置的域名
需要部署的coredns yaml文件
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: coredns
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
kubernetes.io/bootstrapping: rbac-defaults
name: system:coredns
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- endpoints
- services
- pods
- namespaces
verbs:
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- nodes
verbs:
- get
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
annotations:
rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: "true"
labels:
kubernetes.io/bootstrapping: rbac-defaults
name: system:coredns
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: system:coredns
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: coredns
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: coredns
namespace: kube-system
data:
Corefile: |
.:53 {
errors
health
ready
kubernetes CLUSTER_DOMAIN REVERSE_CIDRS {
pods insecure
fallthrough in-addr.arpa ip6.arpa
}FEDERATIONS
prometheus :9153
forward . UPSTREAMNAMESERVER
cache 30
loop
reload
loadbalance
}STUBDOMAINS
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: coredns
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: kube-dns
kubernetes.io/name: "CoreDNS"
spec:
replicas: 2
strategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxUnavailable: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: kube-dns
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kube-dns
spec:
priorityClassName: system-cluster-critical
serviceAccountName: coredns
tolerations:
- key: "CriticalAddonsOnly"
operator: "Exists"
nodeSelector:
beta.kubernetes.io/os: linux
containers:
- name: coredns
image: coredns/coredns:1.5.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
limits:
memory: 170Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 70Mi
args: [ "-conf", "/etc/coredns/Corefile" ]
volumeMounts:
- name: config-volume
mountPath: /etc/coredns
readOnly: true
ports:
- containerPort: 53
name: dns
protocol: UDP
- containerPort: 53
name: dns-tcp
protocol: TCP
- containerPort: 9153
name: metrics
protocol: TCP
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
add:
- NET_BIND_SERVICE
drop:
- all
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /health
port: 8080
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 60
timeoutSeconds: 5
successThreshold: 1
failureThreshold: 5
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /ready
port: 8181
scheme: HTTP
dnsPolicy: Default
volumes:
- name: config-volume
configMap:
name: coredns
items:
- key: Corefile
path: Corefile
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: kube-dns
namespace: kube-system
annotations:
prometheus.io/port: "9153"
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
labels:
k8s-app: kube-dns
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: "true"
kubernetes.io/name: "CoreDNS"
spec:
selector:
k8s-app: kube-dns
#这里要和kubelet 参数对应上
clusterIP: 169.169.0.100
ports:
- name: dns
port: 53
protocol: UDP
- name: dns-tcp
port: 53
protocol: TCP
- name: metrics
port: 9153
protocol: TCP
如果想知道现有集群中使用的配置项可以使用如下命令进行查看
kubectl -n kube-system get configmap coredns -o yaml
如果文章对您有帮助,请点一下下面的 "喜欢"