MapReduce的Shuffle机制
1、MapReduce的shuffle机制
1.1、概述
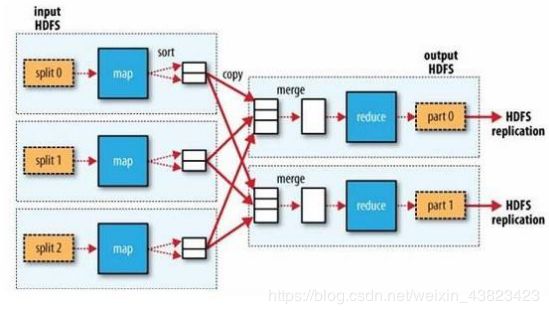
MapReduce中,mapper阶段处理的数据如何传递给reduce阶段,是MapReduce框架中最关键的一个流程,这个流程就叫shuffle.
Shuffle:数据混洗---------(核心机制:数据分区,排序,局部聚合,缓存,拉取,再合并排序)
具体来说,就是将MapTask输出的处理数据结果,按照Partitioner组件制定的规则分发ReduceTask,并在分发的过程中,对数据按key进行分区和排序
1.2、主要流程
Shuffle是MapReduce处理流程中的一个核心,它的每一个处理步骤是分散在各个Maptask和reducetask节点上完成的,整体来看,分为3个操作:
1、分区partition(如果reduceTask只有一个或者没有,那么partition将不起作用。设置没设置相当于没有)
2、Sort根据key排序(MapReduce编程中sort是一定会做的,并且只能按照key排序,当然如果没有reduce阶段,那么就不会对key排序)
3、Combiner进行局部value的合并(Combiner是可选的组件,作用是为了提高任务的执行效率)
1.3、详细流程
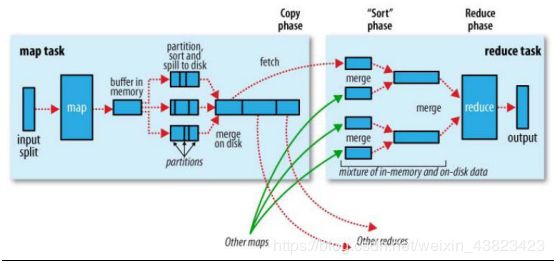
1、mapTask收集我们map()方法输出的kv对,放在内存缓冲区kvbuffer(环形缓冲区:内存中的一种首尾相连的数据结构,kvbuffer包含数据区和索引区)中,在存数据的时候,会调用partitioner进行分区编号的计算,并存入元数据中
2、当内存缓冲区的数据达到100*0.8时,就会开始溢写到本地磁盘文件file.out,可能会溢出多次,则会有多个文件,相应的缓冲区中的索引区数据溢出为磁盘索引文件file.out.index
3、在溢写前,会先根据分区编号排序,相同的分区的数据,排在一起,再根据map的key排序(快排)
4、多个溢写文件会被合并成大的溢出文件(归并排序)
5、在数据量大的时.候,可以对maptask结果启用压缩,将mapreduce.map.ouput.compress设为true,并使用
mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec设置使用的压缩算法,可以提高数据传输到reduce端的效率
6、reduceTask根据自己的分区号,去各个mapTask机器上取相应的结果分区数据
7、reduceTask会取到同一个分区的来自不同mapTask的结果文件,reduceTask会将这些文件再进行合并(归并排序)
8、合并成r大文件后,shuffle的过程也就结束了,后面进入reduceTask的逻辑运算过程(从文件中取出一个一个的键值对group,调用用户自定义的reduce()方法)
2、自定义Shuffle过程中的组件
1、自定义输入
默认输入类:TextInputFormat
自定义:
模仿 org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.LineRecordReader 和org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat
1、自定义类继承FileInputFormat
public class MyFileInputFormat extends FileInputFormat{
@Override
public RecordReader createRecordReader(InputSplit split, TaskAttemptContext context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//实例化一个
MyAllFileRecodReader reader = new MyAllFileRecodReader();
//split参数和context都是框架自动传入的,把这两个参数传给reader进行处理,以便获取相关信息
reader.initialize(split, context);
return reader;
}
/**
* 给定的文件名可拆分吗?返回false确保单个输入文件不会被分割。以便Mapper处理整个文件。
*/
@Override
protected boolean isSplitable(JobContext context, Path filename) {
return false;
}
}
2、自定义类实现RecordReader
public class MyFileRecodReader extends RecordReader{
//用于存储文件系统输入流
private FSDataInputStream open = null;
//保存文件长度
private int fileSplitLength = 0;
/**
* 当前的MyAllFileRecodReader读取到的一个key-value
*/
private Text key = new Text();
private LongWritable value = new LongWritable();
@Override
public void initialize(InputSplit split, TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//通过InputSplit对象获取文件路径
FileSplit fileSplit = (FileSplit)split;
Path path = fileSplit.getPath();
//获取文件长度
fileSplitLength = (int)fileSplit.getLength();
//通过context对象获取到配置文件信息,通过配置文件获取到一个当前文件系统
Configuration configuration = context.getConfiguration();
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(configuration);
//获取文件系统的一个输入流
open = fs.open(path);
}
/**
* 已读标记
* 如果为false,表示还没有进行读取
* 在需求中一个mapTask只处理一个小文件,一个mapTask最终只需要读取一次就完毕
* 如果一个文件读取完毕了,那么就把isRead这个变量标记为true
*/
private boolean isRead = false;
/**
* 实现读取规则:逐文件读取
*/
@Override
public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//如果没有读取过文件就进入
if(!isRead){
//准备一个字节数组长度为文件的长度
byte[] buffer = new byte[fileSplitLength];
//一次性把真个文件读入字节数组中
IOUtils.readFully(open, buffer);
//把读取到的文件传给key
key.set(buffer, 0, fileSplitLength);
//设置已读标记为true
isRead = true;
//返回读取一个文件成功标记
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
//获取key的方法
@Override
public Text getCurrentKey() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
return key;
}
//获取当前value值
@Override
public LongWritable getCurrentValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
return value;
}
/**
* 获取数据的处理进度的
*/
@Override
public float getProgress() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//已读为真返回1.0,没有读返回0
return isRead ? 1.0F : 0F;
}
@Override
public void close() throws IOException {
//关闭输入流
IOUtils.closeQuietly(open);
} 2、自定义分区
需要: 1、继承 partitioner
2、重写getpartition()方法
3、在main方法中指定分区类 job.setPartitionclass()
package homework;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
public class Mypartition extends Partitioner {
@Override
public int getPartition(Student key, Text arg1, int arg2) {
if(key.getType().equals("math")){
return 0;
}
if(key.getType().equals("english")){
return 1;
}
if(key.getType().equals("computer")){
return 2;
}else{
return 3;
}
}
} 3、自定义排序
需要 : 1、实现writableComparable
2、重新write()、readFields()、compareTo()方法
package homework;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
public class Student implements WritableComparable {
private String type;
private String name;
private Double avg;
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(String type, String name, Double avg) {
super();
this.type = type;
this.name = name;
this.avg = avg;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Double getAvg() {
return avg;
}
public void setAvg(Double avg) {
this.avg = avg;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return type + "\t" + name + "\t" + avg ;
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.type=in.readUTF();
this.name=in.readUTF();
this.avg=in.readDouble();
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeUTF(type);
out.writeUTF(name);
out.writeDouble(avg);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
int temp=o.getType().compareTo(this.getType());
if(temp==0){
if(o.getAvg()>this.getAvg()){
return 1;
}else if(o.getAvg() 4、自定义分组
需要 : 1、继承writableComparable
2、重写compare()方法
3、指定分组类 job.setGroupingComparatorClass(MyGroup.class);
4、既有分区又有排序的时候,分组字段一定在排序字段中
package homework;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
public class MyGroup extends WritableComparator {
public MyGroup() {
super(Student.class,true);
}
@Override
public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
Student aa=(Student)a;
Student bb=(Student)b;
return aa.getType().compareTo(bb.getType());
}
}
5、自定义输出
1)模仿 org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat
public class MyMultipePathOutputFormat extends FileOutputFormat{
@Override
public RecordWriter getRecordWriter(TaskAttemptContext job) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获得当前的文件系统传给自定义的RecordWriter组件
Configuration configuration = job.getConfiguration();
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(configuration);
try {
//返回一个RecordWriter正在处理输出数据的组件
return new MyMutiplePathRecordWriter(fs);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
2)继承RecordWriter 并实现write()方法
public class MyMutiplePathRecordWriter extends RecordWriter{
//声明要输出的两个路径
private DataOutputStream out_jige;
private DataOutputStream out_bujige;
public MyMutiplePathRecordWriter(FileSystem fs) throws Exception {
//创建系统输出流
out_jige = fs.create(new Path("E:\\bigdata\\cs\\jige\\my_output_jige.txt"));
out_bujige = fs.create(new Path("E:\\bigdata\\cs\\bujige\\my_output_bujige.txt"));
}
/**
* 实现写出方法,根据需要写出的格式自定义
*/
@Override
public void write(Text key, NullWritable value) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//接受到的key格式为:course + "\t" + name + "\t" + avgScore
String keyStr = key.toString();
String[] split = keyStr.split("\t");
//获取到平均分字段
double score = Double.parseDouble(split[2]);
//没一行数据加入个换行符
byte[] bytes = (keyStr + "\n").getBytes();
//如果平均分大于60就用DataOutputStream写出到jige目录
if(score >= 60){
out_jige.write(bytes, 0, bytes.length);
}else{//小于60分的写道bujige目录
out_bujige.write(bytes, 0, bytes.length);
}
}
/**
* 在close方法中关闭输出流。
*/
@Override
public void close(TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
IOUtils.closeQuietly(out_jige);
IOUtils.closeQuietly(out_bujige);
}
}