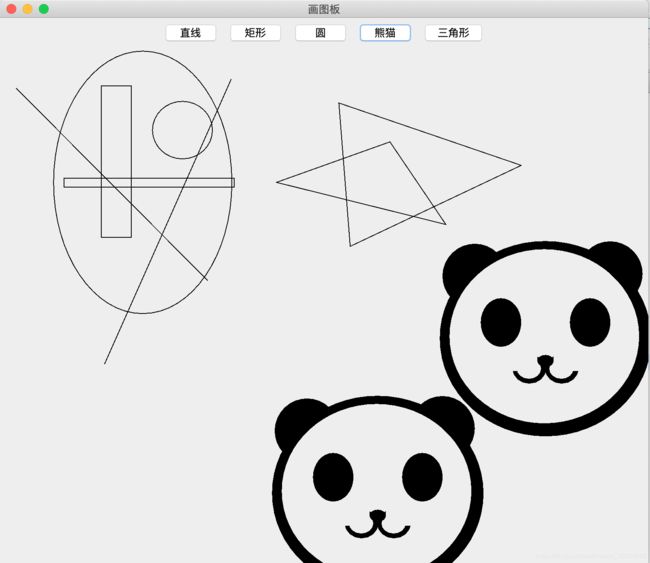
Java学习ing—— 接口的实现(画图板)
又来敲代码啦~
今天我们学习了监听器(接口)的使用,然后做了一个极其简单的画图板……
接口
接口是一个很神奇的东西,它不能直接实例化对象,不能定义变量,只能定义抽象方法(就是那种没有方法体【大括号】的)。然后用类来实现接口的时候,一定要在类里面把它的方法重载一遍,不然就会报错。
public class 类名 implements 接口名 {}
乍一看其实长得挺像继承的,接口还麻烦一些,那么我们为什么要用接口呢?
因为一个人可以有无数个叔叔!好吧,其实就是一个类可以接多个接口,但是继承只能有一个父类。
画图板的实现
思路
1.创建画图的界面
2.设定监听器的内容
3.把监听器加给按钮
今天我们要用两个接口,一个叫MouseListener(鼠标监听器),还有一个叫ActionListener(动作监听器),主要是因为鼠标的使用不能直接用ActionListener来实现,所以就用了两个。
pia
import javax.swing.JButton;//引入按钮
import javax.swing.JFrame;//引入界面
import java.awt.FlowLayout;//引入界面的布局方式
import java.awt.Graphics;//引入显示(有种显卡叫这个东西)
public class DrawPad {//画图板
public void show(){//定义显示方法
JFrame jf =new JFrame();//创建新界面
jf.setTitle("画图板");//界面标题
jf.setSize(800,700);//大小
jf.setLocationRelativeTo(null);//界面位置
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(3);//界面在点击完上面的关闭后,退出程序
FlowLayout layout = new FlowLayout();//创建新的流式布局(按顺序一个接一个,横着放不下了到下一行)
jf.setLayout(layout);//使用
//创建新按钮
JButton drawline=new JButton("直线");
JButton drawrec=new JButton("矩形");
JButton drawoval=new JButton("圆");
JButton panda=new JButton("熊猫");
JButton drawtri=new JButton("三角形");
//把按钮加到界面上
jf.add(drawline);
jf.add(drawrec);
jf.add(drawoval);
jf.add(panda);
jf.add(drawtri);
//创建新的监听器类,因为鼠标和动作监听器这个里面都有,只需要创建一个
DrawListener drawlistener=new DrawListener();
//把监听器加给按钮
drawline.addActionListener(drawlistener);
drawrec.addActionListener(drawlistener);
drawoval.addActionListener(drawlistener);
panda.addActionListener(drawlistener);
drawtri.addActionListener(drawlistener);
//界面添加鼠标监听器
jf.addMouseListener(drawlistener);
jf.setVisible(true);//一定要有可视化,而且要在显示前面(连个板都没有,你还显示什么东西啊)
Graphics gr=jf.getGraphics();//得到显示
drawlistener.g=gr;//把监听器的显示弄过来
}
public static void main(String[] args)//定义主方法
{
DrawPad dp=new DrawPad();
dp.show();
}
}
然后来搞我们的监听器
mport java.awt.event.ActionEvent;//引入动作
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;//引入动作监听器
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;//引入鼠标动作
import java.awt.event.MouseListener;//引入鼠标监听器
import java.awt.Graphics;//引入显示
import java.awt.Color;
public class DrawListener implements MouseListener, ActionListener {
int x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4, x5, y5;//定义坐标
String btnstr;//定义一个字符串
Graphics g;//定义一个显示
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {//这个方法没什么别的用
btnstr = e.getActionCommand();// 得到按钮的内容
}
int count = 0;//用来搞三角形的
/*
*这里实现了一个循环,在第一次点击的时候得到第一个点的坐标,然后第二次得到第二个点的坐标,最后回来
*以实现点三个点构成三角形
*/
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e) {
if (btnstr.equals("三角形")) {
if (count == 0) {//第一个点
x3 = e.getX();
y3 = e.getY();
count++;//转到第二个点
}else if(count==1) {
x4 = e.getX();
y4 = e.getY();
g.drawLine(x3, y3, x4, y4);//画线
count++;//转到第三个点
}else if(count==2) {
x5 = e.getX();
y5 = e.getY();
g.drawLine(x5, y5, x4, y4);
g.drawLine(x5, y5, x3, y3);
count=0;//回到第一个点
}
}
}
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e) {
x1 = e.getX();//得到按压下去的点的坐标
y1 = e.getY();
}
public void mouseReleased(MouseEvent e) {
x2 = e.getX();
y2 = e.getY();
Color color = new Color(0, 0, 0);//创建颜色为黑色
g.setColor(color);//得到颜色
int a, b, c, d;//为了让我们的width和height为正数
if (x1 > x2) {
a = x1;
b = x2;
} else {
a = x2;
b = x1;
}
if (y1 > y2) {
c = y1;
d = y2;
} else {
c = y2;
d = y1;
}
if (btnstr.equals("直线")) {
g.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2);
} else if (btnstr.equals("矩形")) {
g.drawRect(b, d, a - b, c - d);
} else if (btnstr.equals("圆")) {
g.drawOval(b, d, a - b, c - d);
} else if (btnstr.equals("熊猫")) {
g.fillRoundRect(x1 + 120, y1 + 140, 20, 15, 150, 100);// 鼻子
g.fillArc(x1 + 3, y1 + 3, 80, 80, 44, 180);// 耳朵
g.fillArc(x1 + 170, y1, 80, 80, 315, 180);// 耳朵
g.fillOval(x1 + 50, y1 + 70, 50, 60);// 眼睛
g.fillOval(x1 + 160, y1 + 70, 50, 60);// 眼睛
for (int i = 1; i < 100; i++) {
g.drawOval(x1 + i / 9, y1 + i / 10, 260 - i / 4, 240 - i / 4);// 头
g.drawOval(x1 + 130 + i / 20, y1 + 140 + i / 20, 40 - i / 10, 35 - i / 10);
g.drawOval(x1 + 90 + i / 20, y1 + 140 + i / 20, 40 - i / 10, 35 - i / 10);// 嘴巴
}
g.setColor(new Color(238, 238, 238));//和背景板的颜色相同
g.fillRect(x1 + 89, y1 + 138, 31, 22);//把多的部分遮掉
g.setColor(new Color(238, 238, 238));
g.fillRect(x1 + 140, y1 + 138, 31, 22);
}
}
public void mouseEntered(MouseEvent e) {//这个暂时没有用,但是我们之前说了接口所有的抽象方法都要重载
}
public void mouseExited(MouseEvent e) {
}
}
好了,考完四级的我要去准备明年重考了