【ICE】 ICE通信框架 - hello world
1、安装库:ice安装
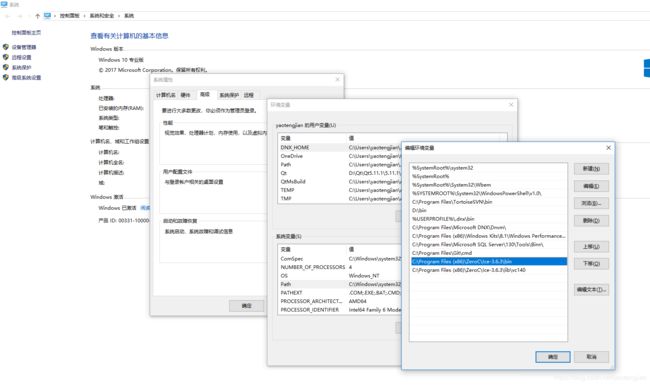
2、环境配置:如图所示:
示例代码及运行结果,部分注释已经在代码中给出:
//.ice
module Demo
{
interface Printer
{
void printString(string s);
};
};
//
//// ICE_client.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
// ICE.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
//#include
//#include
#include"Printer.h"
#include
//#include
using namespace std;
using namespace Demo;
//客户端只需要一个main函数:
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int status = 0;
Ice::CommunicatorPtr ic;
try {
//初始化ice运行时
ic = Ice::initialize(argc, argv);
//使用一个字符串来生成一个对象代理,对象代理包含有服务端的服务对象的方法定义,并且和服务端的对象进行通信
//字符串中指定了对象代理对应的服务器端的对象的名称,以及服务器对象监听的协议和端口,这些信息要与服务端的一致
//objectprx在客户端代理服务器端
Ice::ObjectPrx base = ic->stringToProxy("SimplePrinter:default -p 10000");
//checkedCast会与服务端进行通信,以判断该对象是否成功为printer对象代理,如果转换失败,将返回空对象代理
PrinterPrx printer = PrinterPrx::checkedCast(base);
if (!printer)
throw "Invalid proxy";
//调用printer对象代理的printstring方法,调用将会通过对象代理被发送到服务端
printer->printString("hello minivision!");
}
catch (const Ice::Exception& ex)
{
cerr << ex << endl;
status = 1;
}
catch (const char* msg)
{
cerr << msg << endl;
status = 1;
}
if (ic)
ic->destroy();
return status;
}
//
// ICE_server.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include
//#include
#include"Printer.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace Demo;
//从printer抽象类派生
class PrinterI : public Printer
{
public:
virtual void printString(const string& s, const Ice::Current &);
};
//RFC接口的实现代码
void PrinterI::printString(const string& s, const Ice::Current &)
{
cout << s << endl;
}
//服务端从main函数开始运行
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int status = 0;//退出状态
//ic是一个指向ice的智能指针,通过ic获取运行时的各种资源
Ice::CommunicatorPtr ic;
try
{
ic = Ice::initialize(argc, argv);//初始化一个ICE运行时
//adapter监听tcp/ip的10000端口
Ice::ObjectAdapterPtr adapter = ic->createObjectAdapterWithEndpoints("SimplePrinterAdapter", "default -p 10000");
//实例化一个PrinterI对象,该对象将为接口printer提供服务
Ice::ObjectPtr object = new PrinterI;
adapter->add(object, ic->stringToIdentity("SimplePrinter"));
//启动objectAdapter,此后,objectAdptr开始处理实际的调用
adapter->activate();
//阻塞主线程,知道服务端的运行时被关闭
ic->waitForShutdown();
}
catch (const Ice::Exception& e)
{
cerr << e << endl;
status = 1;
}
catch (const char* msg) {
cerr << msg << endl;
status = 1;
}
//程序结束时,需要销毁ice运行时资源,如果在程序退出时没有对ice运行时进行销毁,可能引起未知错误。
if (ic)
{
try
{
ic->destroy();
}
catch (const Ice::Exception& e) {
cerr << e << endl;
status = 1;
}
}
return status;
}
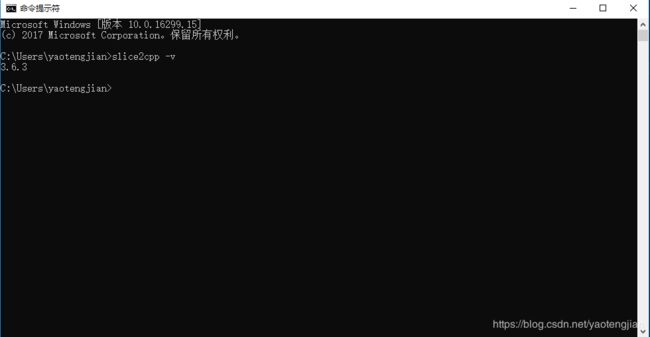
注意:编译.ice文件是很重要的一步,在cmd命令行中输入:slice2cpp xxx.ice,如有不懂的请参照:
https://blog.csdn.net/oXiaoErBuYu123456/article/details/51866007
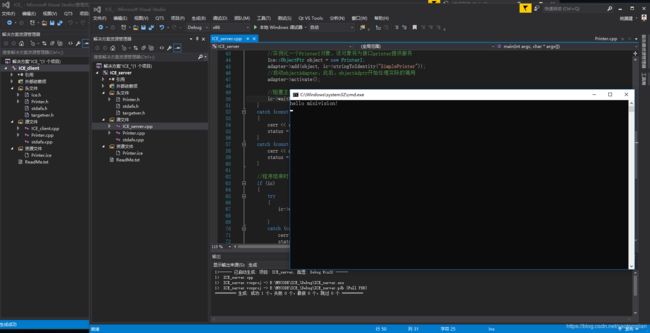
最后,运行结果如图所示: